Impact of Native Form Oat β-Glucan on the Physical and Starch Digestive Properties of Whole Oat Bread
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Determination of Dough Properties
2.2.1. Dough Production
2.2.2. Extension Test of the Dough
2.2.3. Expansion Volume of the Dough
2.3. Determination of Bread Quality
2.3.1. Bread Making
2.3.2. Specific Volume of the Bread
2.3.3. Texture Analysis of the Bread
2.3.4. Moisture Content of the Bread
2.3.5. Color Analysis of the Bread
2.4. Evaluation of Low GI efficacy
2.4.1. Estimated Glycemic Index In Vitro
2.4.2. In Vitro Starch Digestion Characteristics
2.4.3. α-Amylase Inhibition Rate
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
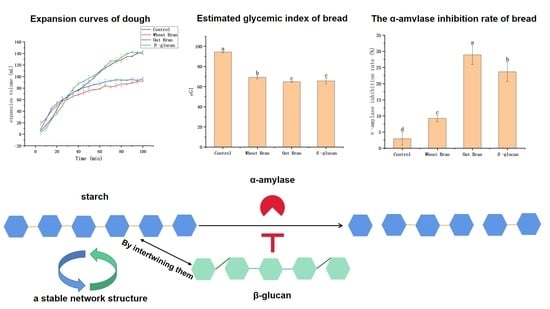
3.1. Effects of Different Additives on the Extensibility and Expansion Volume of Dough
3.2. Effects of Different Additives on Bread Quality
3.2.1. Specific Volume and Texture Properties of Bread
3.2.2. The Moisture Content and Color of Bread Crust and Crumb
3.3. Effects of Different Additives on Bread GI
3.3.1. eGI In Vitro
3.3.2. In Vitro Digestion Properties of Starch
3.3.3. α-Amylase Inhibition Rate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| eGI | estimated glycemic index |
| GI | glycemic index |
| RDS | rapidly digestible starch |
| RS | resistant starch |
| SDS | slowly digestible starch |
References
- Sachan, R.; Kundu, A.; Dey, P.; Son, J.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, D.E.; Kim, H.R.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.-H.; et al. Dendropanax morbifera protects against renal fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF diabetes atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045 diabetesss. Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 183, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithran, N.; Kumar, H.; Menon, A.S.; Pillai, G.K.; Sundaram, K.R.; Ojo, O. South indian cuisine with low glycemic index ingredients reduces cardiovascular risk factors in subjects with type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Environ. Health 2020, 17, 6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, E.S.; Tosh, S.M.; Batterham, M.J.; Tapsell, L.C.; Huang, X.F. Oat beta-glucan increases postprandial cholecystokinin levels, decreases insulin response and extends subjective satiety in overweight subjects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummer, Y.; Duss, R.; Wolever, T.M.S.; Tosh, S.M. Glycemic response to extruded oat bran cereals processed to vary in molecular weight. Cereal Chem. 2012, 89, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, Y.J.; Song, Z.B.; Ai, L.Z. Interaction between barley β-glucan and corn starch and its effects on the in vitro digestion of starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Veronesi, M.; Strocchi, E.; Grandi, E.; Rizzoli, E.; Poli, A.; Marangoni, F.; Borghi, C. A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial to evaluate the medium-term effects of oat fibers on human health: The beta-glucan effects on lipid profile, glycemia and in Testinal Health (BELT) study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ellis, P.R. Oat beta-glucan: Physico-chemical characteristics in relation to its blood-glucose and cholesterol-lowering properties. Brit. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, S4–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.J.; Yang, J.; Du, L.; Li, K.; Zhou, Y. Association of whole grain, refined grain, and cereal consumption with gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Chatli, M.K.; Mehta, N.; Malav, O.; Verma, A.K.; Kumar, D. Quality attributes and storage stability of chicken meat biscuits incorporated with wheat and oat bran. J. Food Qual. 2016, 39, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.N.; Rajan, A. Fibres as an additive for oil reduction in deep fat fried poori. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdošová, A.; Petruláková, Z.; Havrlentová, M.; Červená, V.; Hozová, B.; Šturdík, E.; Kogan, G. The content of water-soluble and water-insoluble β-glucan in selected oats and barley varieties. Carbohyd. Polym. 2007, 70, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.Y.; Xu, D.; Ma, Y.S.; Jin, Y.M.; Wu, F.F.; Xu, X.M. Effect of egg yolk on the properties of wheat dough and bread. Food Biosci. 2020, 37, 100689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmutlu, O.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. Effects of different formulations on the quality of microwave baked breads. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001, 213, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilufer, D.; Boyacioglu, D.; Vodovotz, Y. Functionality of soymilk powder and its components in fresh soy bread. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousif, A.; Nhepera, D.; Johnson, S. Influence of sorghum flour addition on flat bread in vitro starch digestibility, antioxidant capacity and consumer acceptability. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.Q.; Zhou, W.Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.Z.; Lin, D.X.; He, Z.D.; Wu, X.L. Acteoside and acyl-migrated acteoside, compounds in chinese kudingcha tea, inhibit alpha-amylase in vitro. J. Med. Food. 2017, 20, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Liu, R.; Wu, T.; Sui, W.; Zhang, M. Influence of konjac glucomannan and frozen storage on rheological and tensile properties of frozen dough. Polymers. 2019, 11, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.F.; Liu, C.Y.; Bai, J.; Liang, J.F. Mixing, tensile and pasting properties of wheat flour mixed with raw and enzyme treated rice bran. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3014–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Guan, E.Q.; Zhang, L.L.; Pang, J.Y.; Li, M.M.; Bian, K. Effects of vacuum degree, mixing speed, and water amount on the moisture distribution and rheological properties of wheat flour dough. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 2421–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, M.; Fujita, K.; Ma, L.; Gao, M.N.; Dong, C.X.; Wang, J.M.; Luan, G.Z. The effects of extruded black rice flour on rheological and structural properties of wheat-based dough and bread quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Xiao, S.S.; Gong, A.Q.; Liu, X.R.; Wu, Y.; Du, J.; Ding, W.P.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.D. Effect of lactosucrose on the evaluation of visual appearance, texture, water mobility, microstructure and inhibition of staling in wheat bread. Iny. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 3862–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Li, L.M.; Hao, C.M.; Zheng, X.L.; Bian, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.X. Effects of different milling processes on whole wheat flour quality and performance in steamed bread making. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarini, L.S.; Bustos, M.C.; Vignola, M.B. A study on fibre addition to gluten free bread: Its effects on bread quality and in vitro digestibility. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.M.; Cui, X.B.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhou, T.; Gao, R.; Li, Y.X.; Ding, X.X. Effect of beta-endoxylanase and alpha-arabinofuranosidase enzymatic hydrolysis on nutritional and technological properties of wheat brans. Food Chem. 2020, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Brennan, M.; Serventi, L.; Brennan, C. Effect of wheat bran on dough rheology and final quality of chinese steamed bread. Cereal Chem. 2017, 94, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzetti, S.; Theunissen, M.; Horrevorts, K. A systematic comparison of the intrinsic properties of wheat and oat bran fractions and their effects on dough and bread properties: Elucidation of chemical mechanisms, water binding, and steric hindrance. Foods. 2021, 10, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemdane, S.; Langenaeken, N.A.; Jacobs, P.J.; Verspreet, J.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. Study of the role of bran water binding and the steric hindrance by bran in straight dough bread making. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.C.; Zhang, B.J.; Niu, M.; Zhao, S.M. Protein polymerization and water mobility in whole-wheat dough influenced by bran particle size distribution. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Puig, E.; Monedero, V.; Haros, M. Bread with whole quinoa flour and bifidobacterial phytases increases dietary mineral intake and bioavailability. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamberts, L.; Brijs, K.; Mohamed, R.; Verhelst, N.; Delcour, J.A. Impact of browning reactions and bran pigments on color of parboiled rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9924–9929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; White, P.J. In vitro digestion rate and estimated glycemic index of oat flours from typical and high β-Glucan oat lines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5237–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.; Urooj, A. In vitro hypoglycemic effects and starch digestibility characteristics of wheat based composite functional flour for diabetics. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4530–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCleary, B.V. An integrated procedure for the measurement of total dietary fibre (including resistant starch), non-digestible oligosaccharides and available carbohydrates. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, A.H.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, M.Y.; Zhu, B.; Wang, S.M.; Zhang, J.F. The chemical and digestive properties of a soluble glucan from Agrobacterium sp.ZX09. Carbohyd. Polym. 2010, 82, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Hu, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.L.; Du, X.F. In vitro digestibility of kudzu starch by using alpha-amylase and glucoamylase. Starke-Starch. 2016, 68, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdath, D.D.; Liu, Q.; Donner, E.; Hawke, A.; Kalinga, D.; Winberga, J.; Woleverb, T.M.S. Investigating the relationship between lentil carbohydrate fractions and in vivo postprandial blood glucose response by use of the natural variation in starch fractions among 20 lentil varieties. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3783–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, N.; Yamaguchi, Y. 3D structural insights into beta-glucans and their binding proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, Y.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Deka, S.C. Bread fortified with dietary fibre extracted from culinary banana bract: Its quality attributes and in vitro starch digestibility. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2359–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoozani, A.A.; Kebede, B.; Birch, J.; Bekhit, A.E.A. The effect of bread fortification with whole green banana flour on its physicochemical, nutritional and in vitro digestibility. Foods 2020, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Kim, E.; Kwak, H.S.; Jeong, Y. The ingredients in Saengshik, a formulated health food, inhibited the activity of α-amylase and α-glucosidase as anti-diabetic function. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2014, 8, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Ingredients | Control (g) | Wheat Bran (g) | Oat Bran (g) | β-Glucan (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat flour | 500 (100%) | 500 (100%) | 500 (100%) | 500 (100%) |
| Water | 300 (60%) | 330 (66%) | 330 (66%) | 300 (60%) |
| Sugar | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Dry yeast | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| NaCl | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Wheat bran | - | 50 (10%) | - | - |
| Oat bran | - | - | 50 (10%) | - |
| β-Glucan | - | - | - | 4.29 (0.858%) |
| Group | Specific Volume (cm3/g) | Hardness (N) | Resilience | Chewiness | Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3.62 ± 0.01 b | 3.05 ± 0.03 b | 0.69 ± 0.01 b | 1.37 ± 0.06 b | 0.29 ± 0.00 b |
| Wheat bran | 3.02 ± 0.08 d | 4.93 ± 0.35 a | 0.67 ± 0.01 c | 1.83 ± 0.24 a | 0.27 ± 0.00 c |
| Oat bran | 3.23 ± 0.02 c | 5.16 ± 0.37 a | 0.66 ± 0.01 c | 1.98 ± 0.12 a | 0.27 ± 0.01 c |
| β-Glucan | 3.82 ± 0.04 a | 2.85 ± 0.25 b | 0.71 ± 0.01 a | 1.12 ± 0.09 c | 0.32 ± 0.00 a |
| Group | Crust | Crumb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content (%) | L* | a* | b* | Moisture Content (%) | L* | a* | b* | |
| Control | 23.45 ± 0.32 c | 45.16 ± 2.04 a | 18.80 ± 0.84 a | 33.31 ± 1.54 a | 42.57 ± 0.18 b | 65.11 ± 0.22 a | 0.33 ± 0.08 c | 10.60 ± 0.48 c |
| Wheat bran | 28.03 ± 1.00 a | 44.36 ± 0.96 a | 19.42 ± 0.59 a | 33.34 ± 0.71 a | 45.90 ± 0.54 a | 63.10 ± 0.72 ab | 1.73 ± 0.16 b | 13.51 ± 0.79 b |
| Oat bran | 26.14 ± 0.38 b | 40.72 ± 0.24 b | 19.18 ± 0.17 a | 29.30 ± 1.39 b | 45.65 ± 0.26 a | 62.93 ± 1.65 ab | 2.60 ± 0.16 a | 15.40 ± 0.65 a |
| β-Glucan | 27.48 ± 0.89 ab | 45.07 ± 1.07 a | 19.00 ± 0.68 a | 33.99 ± 0.59 a | 45.62 ± 0.50 a | 61.56 ± 1.47 b | 0.43 ± 0.24 c | 10.95 ± 0.69 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, H.; Lin, H.; Xiao, L.; Guo, M.; Yan, X.; Su, X.; Liu, L.; Sang, S. Impact of Native Form Oat β-Glucan on the Physical and Starch Digestive Properties of Whole Oat Bread. Foods 2022, 11, 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172622
Hu H, Lin H, Xiao L, Guo M, Yan X, Su X, Liu L, Sang S. Impact of Native Form Oat β-Glucan on the Physical and Starch Digestive Properties of Whole Oat Bread. Foods. 2022; 11(17):2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172622
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Han, Huihui Lin, Lei Xiao, Minqi Guo, Xi Yan, Xueqian Su, Lianliang Liu, and Shangyuan Sang. 2022. "Impact of Native Form Oat β-Glucan on the Physical and Starch Digestive Properties of Whole Oat Bread" Foods 11, no. 17: 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172622
APA StyleHu, H., Lin, H., Xiao, L., Guo, M., Yan, X., Su, X., Liu, L., & Sang, S. (2022). Impact of Native Form Oat β-Glucan on the Physical and Starch Digestive Properties of Whole Oat Bread. Foods, 11(17), 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172622