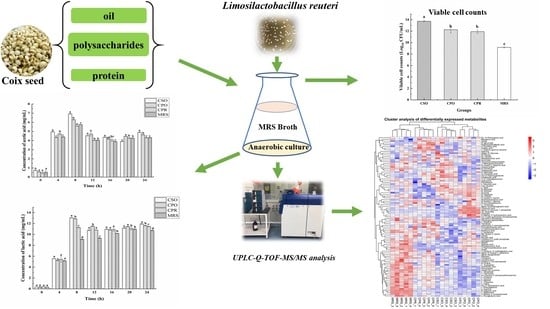
Effect of Coix Seed Extracts on Growth and Metabolism of Limosilactobacillus reuteri
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Chemical Reagents
2.2. Strains and Culture Conditions
2.3. Preparation of Coix Seed Extracts
2.4. Inoculation and Fermentation
2.5. Determination of pH and Total Reducing Sugar (TRS)
2.6. Viable Cell Counts
2.7. Analysis of Organic Acids by HPLC
2.8. Measurement of LDH Activity
2.9. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS Analysis
2.10. Data Processing
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in pH and TRS during the Growth of L. reuteri
3.2. Effect of CSE on the Growth of L. reuteri
3.3. Effects of CSE on Organic Acids
3.4. Effect of CSE on LDH Activity during the Growth of L. reuteri
3.5. Results of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (OPLS-DA) of Cultured Samples from Different Extracts
3.6. KEGG Annotation and Metabolic Pathway Analysis
3.7. Identification of Different Metabolites
3.7.1. Carbohydrate Metabolism
3.7.2. Amino Acid and Peptide Metabolism
3.7.3. Nucleotide Metabolism
3.7.4. Other Metabolism Pathways
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamada, N.; Seo, S.; Chen, G.Y.; Núñez, G. Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, Å.; Palmgren, A.; Nord, C.E. Effect of Lactobacillus paracasei on Intestinal Colonisation of Lactobacilli, Bifidobacteria andClostridium difficile in Elderly Persons. Anaerobe 2001, 7, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, J. A novel cell modification method used in biotransformation of glycerol to 3-HPA by Lactobacillus reuteri. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 4325–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, T.; Asasaka, T.; Sato, E.; Mori, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Ohori, H. Inhibition of binding of Helicobacter pylori to the glycolipid receptors by probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 32, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, B.; Hoang, T.K.; Wang, T.; Ferris, M.; Taylor, C.M.; Tian, X.; Luo, M.; Tran, D.Q.; Zhou, J.; Tatevian, N.; et al. Resetting microbiota by Lactobacillus reuteri inhibits T reg deficiency–induced autoimmunity via adenosine A2A receptors. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallin, A.; Agback, P.; Jonsson, H.; Roos, S. Evaluation of growth, metabolism and production of potentially bioactive components during fermentation of barley with Lactobacillus reuteri. Food Microbiol. 2016, 57, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, B.; Campaniello, D.; Monacis, N.; Bevilacqua, A.; Sinigaglia, M.; Corbo, M.R. Functional cream cheese supplemented with Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis DSM 10140 and Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 20016 and prebiotics. Food Microbiol. 2018, 72, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastmalchi, F.; Razavi, S.H.; Faraji, M.; Labbafi, M. Effect of Lactobacillus casei- casei and Lactobacillus reuteri on acrylamide formation in flat bread and Bread roll. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.; Prabhu, P.N.; Benefiel, A.C.; Miller, M.J.; Chow, J.; Davis, S.R.; Gaskins, H.R. Galacto-oligosaccharides may directly enhance intestinal barrier function through the modulation of goblet cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczynska, R.; Slizewska, K.; Litwin, M.; Szalecki, M.; Zarski, A.; Kapusniak, J. The effect of dietary fibre preparations from potato starch on the growth and activity of bacterial strains belonging to the phyla Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, S.; Rezessy-Szabó, J.M.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Hoschke, Á. Changes of microbial population and some components in carrot juice during fermentation with selected Bifidobacterium strains. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Hong, R.; Zhang, R.; Dong, L.; Bai, Y.; Liu, L.; Jia, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M. Dynamic variation in biochemical properties and prebiotic activities of polysaccharides from longan pulp during fermentation process. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.P.A.; Lauretti, L.B.C.; Alvarenga, V.O.; Paulino, B.N.; Angolini, C.F.F.; Neri-Numa, I.A.; Orlando, E.A.; Pallone, J.A.L.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Pastore, G.M. Evaluation of fruta-do-lobo (Solanum lycocarpum St. Hill) starch on the growth of probiotic strains. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, N.; Hamedi, H.; Kargozari, M.; Shotorbani, P.M. Investigation of potential prebiotic activity of rye sprout extract. Food Biosci. 2017, 19, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.M.; Pandiella, S.S.; Wang, R.H.; Webb, C. Influence of malt, wheat, and barley extracts on the bile tolerance of selected strains of lactobacilli. Food Microbiol. 2004, 21, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Mao, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. The impact of heat-moisture treatment on the molecular structure and physicochemical properties of Coix seed starches. Starch-Stärke 2016, 68, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Rong, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. Rapid Determination of Fat, Protein and Amino Acid Content in Coix Seed Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Technique. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Coix: Chemical composition and health effects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Charles, A.; Huang, T. Determination of the contents of the main biochemical compounds of Adlay (Coxi lachrymal-jobi). Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, J. Antioxidant activity of methanolic extracts from some grains consumed in Korea. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wu, C.; Shih, C.; Liu, C.; Shih, P.; Shieh, T.; Lin, C.; Chiang, W.; Hsia, S. Application of the solvent extraction technique to investigation of the anti-inflammatory activity of adlay bran. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsia, S.M.; Chiang, W.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wang, P.S. Downregulation of progesterone biosynthesis in rat granulosa cells by adlay (Coix lachryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf.) bran extracts. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2006, 18, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, J.; Yang, T.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, Y. Kanglaite Injection Combined with Chemotherapy versus Chemotherapy Alone for the Improvement of Clinical Efficacy and Immune Function in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Fan, Z.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Wen, D.C.; Zhang, S.Y. Effect of polysaccharides from adlay seed on anti-diabetic and gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4372–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraj, R.D.; Jeepipalli, S.P.K.; Xu, B.J. Phytochemistry and health promoting effects of Job’s tears (Coix lacryma-jobi)—A critical review. Food Biosci. 2020, 34, 100537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Min, W.; Bi, P.; Zhou, H.; Huang, F. Stimulatory effects of Coix lacryma-jobi oil on the mycelial growth and metabolites biosynthesis by the submerged culture of Ganoderma lucidum. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 76, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, B.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Fan, Z. Preparation, characterization and anti-diabetic activity of polysaccharides from adlay seed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zamani, S.; Liang, L.; Chen, L. Extraction methods significantly impact pea protein composition, structure and gelling properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.; Salmerón, I.; Pandiella, S.S. Production of potentially probiotic beverages using single and mixed cereal substrates fermented with lactic acid bacteria cultures. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iraporda, C.; Rubel, I.A.; Manrique, G.D.; Abraham, A.G. Influence of inulin rich carbohydrates from Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) tubers on probiotic properties of Lactobacillus strains. LWT 2019, 101, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hati, S.; Patel, N.; Mandal, S. Comparative Growth Behaviour and Biofunctionality of Lactic Acid Bacteria during Fermentation of Soy Milk and Bovine Milk. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.L.F.; Feitosa, W.S.C.; Abreu, V.K.G.; Lemos, T.D.O.; Gomes, W.F.; Narain, N.; Rodrigues, S. Impact of fermentation conditions on the quality and sensory properties of a probiotic cupuassu (Theobroma grandiflorum) beverage. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottokandler, K.S.R.K. Lactobacillus reuteri sp. nov., a new species of heterofermentative lactobacilli. Zent. Für Bakteriol. I. Abt. Orig. C Allg. Angew. Und Okol. Mikrobiol. 1980, 1, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerez, C.L.; Cuezzo, S.; Rollán, G.; Font De Valdez, G. Lactobacillus reuteri CRL 1100 as starter culture for wheat dough fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Dobruchowska, J.M.; van der Kaaij, R.M.; Gerwig, G.J.; Dijkhuizen, L. Structural basis for the roles of starch and sucrose in homo-exopolysaccharide formation by Lactobacillus reuteri 35-5. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 151, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Jang, W.J.; Lee, E.; Kong, I. β-glucooligosaccharides derived from barley β-glucan promote growth of lactic acid bacteria and enhance nisin Z secretion by Lactococcus lactis. LWT 2020, 122, 109014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsogning, S.D.; Fischer, S.; Becker, T. Investigating on the fermentation behavior of six lactic acid bacteria strains in barley malt wort reveals limitation in key amino acids and buffer capacity. Food Microbiol. 2018, 73, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, M.; Gat, Y.; Harmalkar, M.; Waghmare, R. Development of non-dairy fermented probiotic drink based on germinated and ungerminated cereals and legume. LWT 2018, 91, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankaanpää, P.E.; Salminen, S.J.; Isolauri, E.; Lee, Y.K. The in£uence of polyunsaturated fatty acids on probiotic growth and adhesion. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, H.; Gu, Z.; Tian, F.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Chen, Y.Q.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H. Synthesis of conjugated linoleic acid by the linoleate isomerase complex in food-derived lactobacilli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, T.; Sarwar, A.; Ud Din, J.; Al Dalali, S.; Khan, A.A.; Din, Z.U.; Yang, Z. Biotransformation of linoleic acid into different metabolites by food derived Lactobacillus plantarum 12-3 and in silico characterization of relevant reactions. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apirattananusorn, S.; Tongta, S.; Cui, S.W.; Wang, Q. Chemical, Molecular, and Structural Characterization of Alkali Extractable Nonstarch Polysaccharides from Job’s Tears. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8549–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo-Morales, M.; Robles-Olvera, V.; García, H.S. Lactobacillus reuteri β-galactosidase activity and low milk acidification ability. Can. J. Microbiol. 2005, 51, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gänzle, M.G. Genetic and phenotypic analysis of carbohydrate metabolism and transport in Lactobacillus reuteri. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 272, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongmo, N.S.; Procopio, S.; Sacher, B.; Becker, T. Flavor of lactic acid fermented malt based beverages: Current status and perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmerón, I.; Thomas, K.; Pandiella, S.S. Effect of potentially probiotic lactic acid bacteria on the physicochemical composition and acceptance of fermented cereal beverages. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 15, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Mancini, L.; Fox, P.F. Pros and cons for using non-starter lactic acid bacteria (NSLAB) as secondary/adjunct starters for cheese ripening. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, Z.; Tian, H. Influence of 4 lactic acid bacteria on the flavor profile of fermented apple juice. Food Biosci. 2019, 27, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedele, A.; Gross, S.; Rigling, M.; Zhang, Y. Reduction of green off-flavor compounds: Comparison of key odorants during fermentation of soy drink with Lycoperdon pyriforme. Food Chem. 2021, 334, 127591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalán, Z.; Hudáček, J.; Štětina, J.; Chumchalová, J.; Halász, A. Production of organic acids by Lactobacillus strains in three different media. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 230, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman-Salit, A.; Hering, S.; Messiha, H.L.; Veith, N.; Cojocaru, V.; Sieg, A.; Westerhoff, H.V.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Wade, R.C.; Fiedler, T. Regulation of the Activity of Lactate Dehydrogenases from Four Lactic Acid Bacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21295–21306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, Y.; Gammon, S.T.; Sutton, M.N.; Zacharias, N.M.; Bhattacharya, P.; Piwnica-Worms, D. Excess exogenous pyruvate inhibits lactate dehydrogenase activity in live cells in an MCT1-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busto, F.L.; De Arriaga, D.; Soler, J. ATP, ADP and AMP on the regulation of lactate dehydrogenase activity of Phycomyces blakesleeanus. Int. J. Biochem. 1983, 15, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yu, J.; Miao, W.; Shuang, Q. A UPLC-Q-TOF-MS-based metabolomics approach for the evaluation of fermented mare’s milk to koumiss. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudigl, P.; Haltrich, D.; Peterbauer, C.K. l-Arabinose Isomerase and d-Xylose Isomerase from Lactobacillus reuteri: Characterization, Co-expression in the Food Grade Host Lactobacillus plantarum, and Application in the Conversion of d-Galactose and d-Glucose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Qu, X. Genetic mechanisms of prebiotic carbohydrate metabolism in lactic acid bacteria: Emphasis on Lacticaseibacillus casei and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei as flexible, diverse and outstanding prebiotic carbohydrate starters. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 115, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.K.F.; Santos, B.N.; Fonteles, T.V.; Rodrigues, S. Cashew apple juice containing gluco-oligosaccharides, dextran, and tagatose promotes probiotic microbial growth. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsiridetchai, C.; Jonjaroen, V.; Sawangwan, T.; Charoenrat, T.; Chantorn, S. Evaluation of prebiotic mannooligosaccharides obtained from spent coffee grounds for nutraceutical application. LWT 2021, 148, 111717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savijoki, K.; Ingmer, H.; Varmanen, P. Proteolytic systems of lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, R.; Motamedzadegan, A.; Ovissipour, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Gildberg, A.; Rasco, B. Use of Hydrolysates from Yellowfin Tuna (Thunnus albacares) Heads as a Complex Nitrogen Source for Lactic Acid Bacteria. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mis Solval, K.; Chouljenko, A.; Chotiko, A.; Sathivel, S. Growth kinetics and lactic acid production of Lactobacillus plantarum NRRL B-4496, L. acidophilus NRRL B-4495, and L. reuteri B-14171 in media containing egg white hydrolysates. LWT 2019, 105, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redon, E.; Loubiere, P.; Cocaign-Bousquet, M. Transcriptome Analysis of the Progressive Adaptation of Lactococcus lactis to Carbon Starvation. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3589–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rollan, G.; Lorca, G.L.; de Valdez, G.F. Arginine catabolism and acid tolerance response in Lactobacillus reuteri isolated from sourdough. Food Microbiol. 2003, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Du, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y. Enhanced production of l-methionine in engineered Escherichia coli with efficient supply of one carbon unit. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Fan, F.; Wu, D.; Yu, C.; Wang, Z.; Du, M. Antioxidant and ACE Inhibitory Activity of Enzymatic Hydrolysates from Ruditapes philippinarum. Molecules 2018, 23, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azevedo, R.A.; Lancien, M.; Lea, P.J. The aspartic acid metabolic pathway, an exciting and essential pathway in plants. Amino Acids 2006, 30, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yang, H.; Coldea, T.E.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, H. Metabonomic analysis reveals enhanced growth and ethanol production of brewer’s yeast by wheat gluten hydrolysates and potassium supplementation. LWT 2021, 145, 111387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Hwang, H.; Lee, J. Effect of lactic acid bacteria on phenyllactic acid production in kimchi. Food Control 2019, 106, 106701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axel, C.; Brosnan, B.; Zannini, E.; Peyer, L.C.; Furey, A.; Coffey, A.; Arendt, E.K. Antifungal activities of three different Lactobacillus species and their production of antifungal carboxylic acids in wheat sourdough. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Lynch, K.M.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K. Fundamental study on the improvement of the antifungal activity of Lactobacillus reuteri R29 through increased production of phenyllactic acid and reuterin. Food Control 2018, 88, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, N.; Gánzle, M.G.; Vogel, R.F. Influence of Peptide Supply and Cosubstrates on Phenylalanine Metabolism of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis DSM20451T and Lactobacillus plantarum TMW1.468. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3832–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markkinen, N.; Pariyani, R.; Jokioja, J.; Kortesniemi, M.; Laaksonen, O.; Yang, B. NMR-based metabolomics approach on optimization of malolactic fermentation of sea buckthorn juice with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zheng, Y.; Kwok, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, T. Metabolic footprinting revealed key biochemical changes in a brown fermented milk product using Streptococcus thermophilus. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilstrup, M.; Hammer, K.; Ruhdaljensen, P.; Martinussen, J. Nucleotide metabolism and its control in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 555–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Rodriguez, A.J.; Romling, U. Nucleotide Second Messenger Signaling as a Target for the Control of Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1928–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Mendonca, M.L.; Mccarry, B.E.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Surette, M.G. Metabolic and transcriptomic profiling of Streptococcus intermedius during aerobic and anaerobic growth. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elli, M.; Zink, R.; Reniero, R.; Morelli, L. Growth requirements of Lactobacillus johnsonii in skim and UHT milk. Int. Dairy J. 1999, 9, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Shah, N.; Prajapati, J.B. Biosynthesis of vitamins and enzymes in fermented foods by lactic acid bacteria and related genera—A promising approach. Croat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa, M.; Snell, E.E. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Homologs of Pyridoxal and Pyridoxamine. J. Acad. Chem. Soc. 1954, 70, 637–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliarda, A.; Robert, H.; Jebbar, M.; Blanco, C.; Deschamps, A.; Le Marrec, C. Potential osmoprotectants for the lactic acid bacteria Pediococcus pentosaceus and Tetragenococcus halophila. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 84, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kets, E.P.W.; Groot, M.N.; Galinski, E.A.; De Bont, J.A.M. Choline and acetylcholine: Novel cationic osmolytes in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 48, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishmayana, S.; Kennedy, U.J.; Learmonth, R.P. Preliminary Evidence of Inositol Supplementation Effect on Cell Growth, Viability and Plasma Membrane Fluidity of the Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Procedia Chem. 2015, 17, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasser, A.; Hussein, A.; Chamba, C.; Yonazi, M.; Mushi, R.; Schuh, A.; Luzzatto, L. Molecular response to imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in Tanzania. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Wen, A.; Qin, L.; Zhu, Y. Effect of Coix Seed Extracts on Growth and Metabolism of Limosilactobacillus reuteri. Foods 2022, 11, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020187
Yang Z, Wen A, Qin L, Zhu Y. Effect of Coix Seed Extracts on Growth and Metabolism of Limosilactobacillus reuteri. Foods. 2022; 11(2):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020187
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhoujie, Anyan Wen, Likang Qin, and Yi Zhu. 2022. "Effect of Coix Seed Extracts on Growth and Metabolism of Limosilactobacillus reuteri" Foods 11, no. 2: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020187
APA StyleYang, Z., Wen, A., Qin, L., & Zhu, Y. (2022). Effect of Coix Seed Extracts on Growth and Metabolism of Limosilactobacillus reuteri. Foods, 11(2), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020187