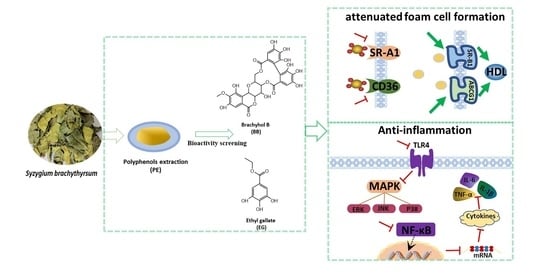
Polyphenolics from Syzygium brachythyrsum Inhibits Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Macrophage-Derived Foam Cell Formation and Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extractions and Isolations
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Oil Red O Staining
2.5. Dil-ox-LDL Uptake Determination
2.6. Cholesterol Efflux Assay
2.7. RT-qPCR
2.8. Western Blot Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of PE and Isolated Compounds on ox-LDL-Induced Foam Cell Formation
3.2. The Effect of PE and Isolated Compounds on ox-LDL Uptake
3.3. The Effect of PE and Its Two Components BB and EG on Cholesterol Efflux
3.4. BB and EG Regulated Cholesterol Homeostasis
3.5. BB and EG Regulated P65 NF-κB, TLR4 and JNK, ERK1/2, P38 MAPK Activity in ox-LDL-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
3.6. BB and EG Inhibited LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Björkegren, J.L.M.; Lusis, A.J. Atherosclerosis: Recent developments. Cell 2022, 185, 1630–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Buring, J.E.; Badimon, L.; Hansson, G.K.; Deanfield, J.; Bittencourt, M.S. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.H.; Fu, Y.C.; Zhang, D.W.; Yin, K.; Tang, C.K. Foam cells in atherosclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 424, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.; Yu, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Shen, P. Apigenin, a modulator of PPARγ, attenuates HFD-induced NAFLD by regulating hepatocyte lipid metabolism and oxidative stress via Nrf2 activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 136, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geovanini, G.R.; Libby, P. Atherosclerosis and inflammation: Overview and updates. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Mardani, F.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochain, C.; Zernecke, A. Macrophages in vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Pflügers Arch. -Eur. J. Physiol. 2017, 469, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijsse, B.; Weikert, C.; Drogan, D.; Bergmann, M.; Boeing, H. Chocolate consumption in relation to blood pressure and risk of cardiovascular disease in German adults. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.; Mukhtar, H. Tea Polyphenols in Promotion of Human Health. Nutrients 2018, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, F. Polyphenols can Potentially Prevent Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease by Modulating Macrophage Cholesterol Metabolism. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Cao, H.; Shen, D.; Li, S.; Yan, L.; Chen, C.; Xing, S.; Dou, F. Quercetin protects against atherosclerosis by regulating the expression of PCSK9, CD36, PPARγ, LXRα and ABCA1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Editorial Committee of the Flora of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019; Volume 53. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, H.-S.; Qiu, J.-Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, S.-H.; Huang, Z.-H.; Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Han, B. Rapid discovery of new derivatives of short-sequence bushy-leaved albicans based on UHPLC-Q-Exactive-MS technique. J. Anal. Test. 2022, 41, 988–997. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Li, X. Extraction of pigments from short-sequence bushy peach fruit and its stability. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2014, 53, 647–650. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Chen, X.; Liang, P.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Gong, M.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W. Integrating approach to discover novel bergenin derivatives and phenolics with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities from bio-active fraction of Syzygium brachythyrsum. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Kang, S.; Fan, Y.; Hao, Z. Bergenin Monohydrate Attenuates Inflammatory Response via MAPK and NF-κB Pathways Against Klebsiella pneumonia Infection. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 651664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo Puga, C.; Cuchillo-Hilario, M.; Navarro Ocaña, A.; Medina-Campos, O.N.; Nieto Camacho, A.; Ramírez Apan, T.; Gerardo, L.-T.Z.; Margarita, D.M.; Alejandra, Á.M.; Rosalina, C.M.Y.; et al. Phenolic Compounds in Organic and Aqueous Extracts from Acacia farnesiana Pods Analyzed by ULPS-ESI-Q-oa/TOF-MS. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity and Anti-Inflammatory Response in CD-1 Mice. Molecules 2018, 23, 2386. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.F.; Hsu, J.T.; Wu, K.C.; Hsiao, C.F.; Lin, J.A.; Cheng, Y.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Lee, D.-Y.; Chang, H.-H.; Cho, D.-Y.; et al. A systematic identification of anti-inflammatory active components derived from Mu Dan Pi and their applications in inflammatory bowel disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.Y.; Lin, J.J.; Jiang, J.G.; Wang, T.X.; Zhu, W. Potential roles of dietary flavonoids from Citrus aurantium L. var. amara Engl. in atherosclerosis development. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.L.; Chen, X.L.; Gong, M.J.; Xu, Y.; Tu, H.S.; Zhang, L.; Liao, B.S.; Qiu, X.H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.H.; et al. Guang Chen Pi (the pericarp of Citrus reticulata Blanco’s cultivars ‘Chachi’) inhibits macrophage-derived foam cell formation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293, 115328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, S.; Mao, L.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; He, H.; Yu, C.; et al. The P2RY12 receptor promotes VSMC-derived foam cell formation by inhibiting autophagy in advanced atherosclerosis. Autophagy 2021, 17, 980–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.-L.; Liang, Q.-W.; He, P.-W.; Chen, X.-L.; Xu, Y.; Tu, H.-S.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, X.-H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.-H.; et al. Three polymethoxyflavones from the peel of Citrus reticulata “Chachi” inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced macrophage-derived foam cell formation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 924551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzawa-Ishimoto, Y.; Hwang, S.; Cadwell, K. Autophagy and Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 73–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, J.; Shen, J.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, H. ATG5-mediated autophagy suppresses NF-κB signaling to limit epithelial inflammatory response to kidney injury. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Xia, B.; Yu, W. The role of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in periodontitis-induced liver inflammation of rats. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, J. Effects of the TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway on NLRP3 Inflammasome in Coronary Microembolization-Induced Myocardial Injury. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Lv, X.; Sun, Y.; Ye, Z.; Kong, B.; Qin, Z. Role of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in coronary microembolization-induced myocardial injury prevented and treated with nicorandil. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dong, M.; Chu, L.; Feng, L.; Sun, X. MicroRNA-451 relieves inflammation in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via the Toll-like receptor 4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 3043–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, J.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, C.; Qi, M.P.; Liu, R.N.; Zhu, X.F.; Zhou, Q.G.; Chen, Y.Y.; Guo, A.Z.; Hu, C.M. Indirubin Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation via TLR4 Abrogation Mediated by the NF-kB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Inflammation 2017, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Wardill, H.R.; Bowen, J.M. Role of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated interleukin-6 (IL-6) production in chemotherapy-induced mucositis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Su, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, S.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Y. Resveratrol suppresses oxidised low-density lipoprotein-induced macrophage apoptosis through inhibition of intracellular reactive oxygen species generation, LOX-1, and the p38 MAPK pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.A.; Murao, K.; Imachi, H.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Wong, N.C.; Ishida, T. Human scavenger receptor class B type 1 is regulated by activators of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-gamma in hepatocytes. Endocrine 2009, 35, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.M.; Xiao, L.; Kang, C.M.; Ding, L.; Guo, F.X.; Li, P.; Lu, Z.F.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.J.; Bai, H.L.; et al. LncRNA AC096664.3/PPAR-γ/ABCG1-dependent signal transduction pathway contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 13775–13782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Anwaier, G.; Cao, Y.; Lian, G.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Tuerdi, N.; Qi, R. Atheroprotective Mechanisms of Tilianin by Inhibiting Inflammation Through Down-Regulating NF-κB Pathway and Foam Cells Formation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adam, G.O.; Kim, G.B.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, S.J. Red Ginseng Reduces Inflammatory Response via Suppression MAPK/P38 Signaling and p65 Nuclear Proteins Translocation in Rats and Raw 264.7 Macrophage. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 1589–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.U.; Lee, J.H.; Shehzad, A.; Ahn, E.M.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, Y.S. Decursinol Angelate Inhibits LPS-Induced Macrophage Polarization through Modulation of the NFκB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2018, 23, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plotkin, J.D.; Elias, M.G.; Dellinger, A.L.; Kepley, C.L. NF-κB inhibitors that prevent foam cell formation and atherosclerotic plaque accumulation. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, S.; Martel, G. Gain-of-Function Mutations in the Toll-Like Receptor Pathway: TPL2-Mediated ERK1/ERK2 MAPK Activation, a Path to Tumorigenesis in Lymphoid Neoplasms? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Yang, X.; Geng, M.; Huang, M. Targeting ERK, an Achilles’ Heel of the MAPK pathway, in cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Twardowski, L.; Fehr, S.; Aner, C.; Schaeffeler, E.; Joos, T.; Knorpp, T.; Dorweiler, B.; Laufer, S.; Schwab, M.; et al. Selective p38α MAP kinase/MAPK14 inhibition in enzymatically modified LDL-stimulated human monocytes: Implications for atherosclerosis. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Hu, T.; Gu, Y.; Li, J. Trimethylamine N-oxide promotes atherosclerosis via CD36-dependent MAPK/JNK pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.P.; Prashanth, K.V.H.; Venkatesh, Y.P. Structural analyses and immunomodulatory properties of fructo-oligosaccharides from onion (Allium cepa). Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saji, N.; Francis, N.; Schwarz, L.J.; Blanchard, C.L.; Santhakumar, A.B. The Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Rice Bran Phenolic Extracts. Foods 2020, 9, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Genes | Forward Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | GGTTGTCTCCTGCGACTTCA | TGGTCCAGGGTTTCTTACTCC |
| SR-A1 | GACACTGATAGCTGCTCCGAATCTG | AAACACGAGGAGGTAAAGGGCAATC |
| CD36 | GTCTATCTACGCTGTGTTCGGATCTG | TGTCTGGATTCTGGAGGGGTGATG |
| ABCG1 | CTGCTGCCTCACCTCACTGTTC | TCTCGTCTGCCTTCATCCTTCTCC |
| SR-B1 | AGCATTCCTTGTTCCTAGACATCCATC | AACCACAGCAACGGCAGAACTAC |
| TNF-α | CGCTCTTCTGTCTACTGAACTTCGG | GTGGTTTGTGAGTGTGAGGGTCTG |
| IL-6 | CTTCTTGGGACTGATGCTGGTGAC | AGTGGTATCCTCTGTGAAGTCTCCTC |
| IL-1β | CACTACAGGCTCCGAGATGAACAAC | TGTCGTTGCTTGGTTCTCCTTGTAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.-L.; Liang, P.-L.; Gong, M.-J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, X.-H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.-H.; Xu, W. Polyphenolics from Syzygium brachythyrsum Inhibits Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Macrophage-Derived Foam Cell Formation and Inflammation. Foods 2022, 11, 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213543
Chen X-L, Liang P-L, Gong M-J, Xu Y, Zhang L, Qiu X-H, Zhang J, Huang Z-H, Xu W. Polyphenolics from Syzygium brachythyrsum Inhibits Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Macrophage-Derived Foam Cell Formation and Inflammation. Foods. 2022; 11(21):3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213543
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xue-Lian, Pu-Lin Liang, Ming-Jiong Gong, Ya Xu, Liang Zhang, Xiao-Hui Qiu, Jing Zhang, Zhi-Hai Huang, and Wen Xu. 2022. "Polyphenolics from Syzygium brachythyrsum Inhibits Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Macrophage-Derived Foam Cell Formation and Inflammation" Foods 11, no. 21: 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213543
APA StyleChen, X.-L., Liang, P.-L., Gong, M.-J., Xu, Y., Zhang, L., Qiu, X.-H., Zhang, J., Huang, Z.-H., & Xu, W. (2022). Polyphenolics from Syzygium brachythyrsum Inhibits Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Macrophage-Derived Foam Cell Formation and Inflammation. Foods, 11(21), 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213543