Physicochemical, Structural, and Digestive Properties of Banana Starch Modified by Ultrasound and Resveratrol Treatments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Extraction of Banana Starch
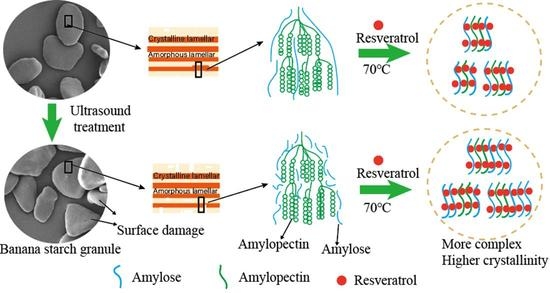
2.3. Ultrasonic Treatment
2.4. Preparation of Green-Banana-Starch–Resveratrol Complexes
2.5. Complex Index
2.6. Physicochemical Properties
2.6.1. Solubility and Swelling Power
2.6.2. Oil-Absorption Capacity
2.6.3. Freeze-Thaw Stability
2.6.4. Analysis of Thermal Properties
2.7. Rheological Properties
2.7.1. Steady Shear Analysis
2.7.2. Dynamic Oscillatory Analysis
2.8. Determination of In Vitro Digestibility
2.9. Structural Characterization
2.9.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.9.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Relative Crystallinity (RC)
2.9.3. Morphological Analysis
2.10. In Vitro Resveratrol Release from Starch–Resveratrol Complex
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on CI
3.2. Characterization of Physicochemical Properties
3.2.1. S and SP
3.2.2. Oil-Absorption Capacity
3.2.3. Freeze-Thaw Stability
3.2.4. Thermal Characteristics
3.3. Steady Shear Analysis
3.4. Dynamic Oscillatory
3.5. In Vitro Digestibility
3.6. Structural Characterization of Starch–Resveratrol Complexes
3.6.1. Short-Range Ordered Structure
3.6.2. Long-Range Ordered Structure
3.6.3. Morphological Changes
3.7. In Vitro Release Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- You, H.; Liang, C.; Zhang, O.; Xu, H.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, X. Variation of resistant starch content in different processing types and their starch granules properties in rice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, M.; Rai, A.K.; Mishra, B.B.; Singh, S.P. Novel insight into valorization of potato peel biomass into type III resistant starch and maltooligosaccharide molecules. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Shen, H.; Su, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Li, W. The improving effects of cold plasma on multi-scale structure, physicochemical and digestive properties of dry heated red adzuki bean starch. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.-Y.; Lu, X.-X.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Luo, Z.-G.; Xiao, Z.-G. Fine structure, crystalline and physicochemical properties of waxy corn starch treated by ultrasound irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 51, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Li, H. Modification of quinoa flour functionality using ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 52, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Li, C.; Liu, P.-H.; Lei, C.-Y.; Li, J.-B. Retrogradation, gel texture properties, intrinsic viscosity and degradation mechanism of potato starch paste under ultrasonic irradiation. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Li, L.; Fu, X. Ultrasound Effects on the Structure and Chemical Reactivity of Cornstarch Granules. Starch–Stärke 2007, 59, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cao, S.; Yu, Y.; Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Chen, W. Modification in physicochemical, structural and digestive properties of pea starch during heat-moisture process assisted by pre- and post-treatment of ultrasound. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Jia, C.; Cao, D.; Muhoza, B.; Zhang, X. Formation, characterization and properties of resveratrol-dietary fiber composites: Release behavior, bioaccessibility and long-term storage stability. LWT 2020, 129, 109556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Samdani, K.J.; Yoo, D.H.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, N.H.; Yoo, I.-S.; Lee, J.H. Resveratrol cross-linked chitosan loaded with phospholipid for controlled release and antioxidant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andishmand, H.; Tabibiazar, M.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Hamishehkar, H. Pectin-zinc-chitosan-polyethylene glycol colloidal nano-suspension as a food grade carrier for colon targeted delivery of resveratrol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-P.; Le, Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.-F. Resveratrol nanodispersion with high stability and dissolution rate. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Z. Digestibility and supramolecular structural changes of maize starch by non-covalent interactions with gallic acid. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, M.; Wang, M. Rheological, thermal and in vitro digestibility properties on complex of plasma modified Tartary buckwheat starches with quercetin. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yao, F.; Zhang, M.; Khalifa, I.; Li, K.; Li, C. Effect of persimmon tannin on the physicochemical properties of maize starch with different amylose/amylopectin ratios. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, F.; Awika, J.M.; Rooney, L.W. Interaction of Tannins and Other Sorghum Phenolic Compounds with Starch and Effects on in Vitro Starch Digestibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11609–11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Sheng, Z. Ability of resveratrol to inhibit advanced glycation end product formation and carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzyme activity, and to conjugate methylglyoxal. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.L.; Chen, G.Y.; Hou, Y.J.; Chen, Y. Improved solubility of banana starch by dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, K.; Takato, S.; Sasaki, T.; Kajiwara, K. Complex formation, thermal properties, and in-vitro digestibility of gelatinized potato starch–fatty acid mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zeng, S.; Lu, X.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, B. Structural and physicochemical properties of lotus seed starch treated with ultra-high pressure. Food Chem. 2015, 186, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z.; Bao, Q.; Zhou, B.; Li, T.; Li, S. Preparation and characterization of highly lipophilic modified potato starch by ultrasound and freeze-thaw treatments. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 64, 105054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Tian, J.; Kong, X.; Yang, W.; Yin, X.; Xu, E.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Ye, X. Physicochemical and digestibility characterisation of maize starch–caffeic acid complexes. LWT 2020, 121, 108857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Wu, J.; Hu, X.; McClements, D.J. A simulated gastrointestinal tract study of texturized rice grains: Impact of texturization on starch digestibility. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 89, 102800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goñi, I.; Garcia-Alonso, A.; Saura-Calixto, F. A starch hydrolysis procedure to estimate glycemic index. Nutr. Res. 1997, 17, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Choi, S.J.; Park, C.-S.; Moon, T.W. Kinetic studies of in vitro digestion of amylosucrase-modified waxy corn starches based on branch chain length distributions. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 65, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, H.N.; Kingman, S.M.; Cummings, J.H. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46 (Suppl. S2), S33–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadian, M.; Salami, M.; Momen, S.; Alavi, F.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Fabrication of curcumin-loaded whey protein microgels: Structural properties, antioxidant activity, and in vitro release behavior. LWT 2019, 103, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Xie, F.; Li, L.; Bai, G. Modulating the in vitro digestibility and predicted glycemic index of rice starch gels by complexation with gallic acid. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Wang, R.; Kang, X.; Cui, B.; Yu, B. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on amylose-lipid complex formation and properties of sweet potato starch-based films. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 44, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Lu, J.; Zheng, J.; Sun, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Q. Ultrasonically aided enzymatical effects on the properties and structure of mung bean starch. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 20, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, Y.; Rivero, S.; García, M.A. Microstructural and techno-functional properties of cassava starch modified by ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 42, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.-J.; Liu, Q.; Hoover, R. Impact of annealing and heat-moisture treatment on rapidly digestible, slowly digestible and resistant starch levels in native and gelatinized corn, pea and lentil starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Liu, Y.; Jing, L.; Zhao, K.; Wu, H.; Zhang, G.; Yang, S.O.; Li, W. The Changes in Structural, Physicochemical, and Digestive Properties of Red Adzuki Bean Starch after Repeated and Continuous Annealing Treatments. Starch–Stärke 2018, 70, 1700322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Kong, X.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Fang, H.; Tian, J.; Ye, X. Controlled ultrasound treatments modify the morphology and physical properties of rice starch rather than the fine structure. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 59, 104709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Luo, F.; Lin, Q. Modulating the in vitro digestibility of chemically modified starch ingredient by a non-thermal processing technology of ultrasonic treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 70, 105350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonkwo, V.C.; Kwofie, E.M.; Mba, O.I.; Ngadi, M.O. Impact of thermo-sonication on quality indices of starch-based sauces. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumdas, R.; Trimukhe, A.; Deshmukh, R.R.; Annapure, U.S. Functional and rheological properties of cold plasma treated rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Zheng, M.; Guo, J.; Qi, J.; Chen, Y.; Miao, S.; Zheng, B. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound irradiation on the stability and structural features of coconut-grain milk composite systems utilizing maize kernels and starch with different amylose contents. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 55, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneya, T.; Ishibashi, K.; Hironaka, K.; Yamamoto, K. Influence of cross-linked potato starch treated with POCl3 on DSC, rheological properties and granule size. Carbohydr. Polym. 2003, 53, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Niu, M.; Xu, H. Pasting behaviors, gel rheological properties, and freeze-thaw stability of rice flour and starch modified by green tea polyphenols. LWT 2020, 118, 108796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Zhu, F. Effect of ultrasound on structural and physicochemical properties of sweetpotato and wheat flours. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 66, 105118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wan, N.; Wang, X.; Yang, M. Extraction of high-amylose starch from Radix Puerariae using high-intensity low-frequency ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 59, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F.; Cao, J.; Fan, R.; Zhang, X.; et al. The effects of dielectric barrier discharge plasma on physicochemical and digestion properties of starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Tan, C.; Gao, Y.; Feng, Y. Four phenolic acids from purple sweet potato and their effects on physicochemical, digestive and structural characteristics of starch. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 1896–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonto, A.P.; Tiozon, R.N.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Camacho, D.H. Impact of ultrasonic treatment on rice starch and grain functional properties: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 71, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Interactions between starch and phenolic compound. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Fu, X.; He, X.; Luo, F.; Gao, Q.; Yu, S. Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on the Physicochemical Properties of Maize Starches Differing in Amylose Content. Starch–Stärke 2008, 60, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwasra, B.L.; Kaur, M.; Gill, B.S. Impact of ultrasonication on functional and structural properties of Indian wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivar starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabana, S.; Prasansha, R.; Kalinina, I.; Potoroko, I.; Bagale, U.; Shirish, S.H. Ultrasound assisted acid hydrolyzed structure modification and loading of antioxidants on potato starch nanoparticles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 51, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Mishra, S.; Pradhan, R.C. Ultrasound-assisted hydration of finger millet (Eleusine Coracana) and its effects on starch isolates and antinutrients. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, B.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Zheng, B. Insight into the characterization and digestion of lotus seed starch-tea polyphenol complexes prepared under high hydrostatic pressure. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, K.; Ma, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. Impact of ultrasonication on the aggregation structure and physicochemical characteristics of sweet potato starch. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Qi, H.; Wang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zou, J.; Xu, B.; Ren, X.; Ma, H. The ex-situ and in-situ ultrasonic assisted oxidation of corn starch: A comparative study. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 61, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastromatteo, M.; Lecce, L.; De Vietro, N.; Favia, P.; Del Nobile, M.A. Plasma deposition processes from acrylic/methane on natural fibres to control the kinetic release of lysozyme from PVOH monolayer film. J. Food Eng. 2011, 104, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Samples | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS | 64.10 ± 0.26 d | 71.14 ± 0.19 d | 73.92 ± 0.20 d | 1.73 ± 0.14 d |
| U60S | 64.82 ± 0.13 c | 71.72 ± 0.16 c | 74.30 ± 0.22 c | 2.36 ± 0.07 b |
| Res-NS | 68.17 ± 0.23 b | 74.74 ± 0.13 a | 77.17 ± 0.19 a | 2.12 ± 0.11 c |
| Res-U60S | 70.77 ± 0.16 a | 73.99 ± 0.21 b | 75.83 ± 0.15 b | 2.92 ± 0.10 a |
| Samples | K (Pa·sn) | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NS | 7.211 ± 0.080 c | 0.572 ±0.003 a | 0.993 |
| U60S | 7.582 ± 0.015 b | 0.566 ± 0.008 a | 0.985 |
| Res-NS | 7.545 ± 0.073 b | 0.568 ± 0.005 a | 0.977 |
| Res-U60S | 9.446 ± 0.088 a | 0.372 ± 0.008 b | 0.960 |
| Samples | k (×10−2/min) | C∞ (%) | RDS (%) | SDS (%) | RS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS | 1.57 ± 0.30 b | 44.12 ± 0.65 a | 32.29 ± 0.29 b | 11.40 ± 0.16 a | 56.31 ± 0.13 c |
| U60S | 1.16 ± 0.19 b | 42.82 ± 0.19 b | 32.88 ± 0.32 ab | 9.93 ± 0.13 b | 57.19 ± 0.19 b |
| Res-NS | 1.42 ± 0.24 b | 43.51 ± 0.10 b | 33.69 ± 0.44 a | 9.83 ± 0.52 b | 56.48 ± 0.10 c |
| Res-U60S | 2.69 ± 0.76 a | 40.25 ± 0.16 c | 33.74 ± 0.28 a | 7.60 ± 0.44 c | 58.75 ± 0.16 a |
| Samples | Models | Fitting Equations | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Res-NS | Zero-order | Qt = 0.0052 × t | 0.1145 |
| First-order | Ln(1 − Qt) = 0.0418 × t − 0.5227 | 0.9951 | |
| Higuchi | Qt = 0.0536 × t1/2 | 0.8453 | |
| Ritger–Peppas | LnQt = 9.8287 × Lnt − 0.3517 | 0.9063 | |
| Res-U60S | Zero-order | Qt = 0.0039 × t | 0.4442 |
| First-order | Ln(1 − Qt) = 0.0293 × t − 0.4179 | 0.9902 | |
| Higuchi | Qt = 0.0394 × t1/2 | 0.9324 | |
| Ritger–Peppas | LnQt = 18.5753 × Lnt − 0.4282 | 0.9402 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ai, B.; Sheng, Z. Physicochemical, Structural, and Digestive Properties of Banana Starch Modified by Ultrasound and Resveratrol Treatments. Foods 2022, 11, 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223741
Sun Y, Yang Y, Zheng L, Zheng X, Xiao D, Wang S, Zhang Z, Ai B, Sheng Z. Physicochemical, Structural, and Digestive Properties of Banana Starch Modified by Ultrasound and Resveratrol Treatments. Foods. 2022; 11(22):3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223741
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Ying, Yang Yang, Lili Zheng, Xiaoyan Zheng, Dao Xiao, Shenwan Wang, Zhengke Zhang, Binling Ai, and Zhanwu Sheng. 2022. "Physicochemical, Structural, and Digestive Properties of Banana Starch Modified by Ultrasound and Resveratrol Treatments" Foods 11, no. 22: 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223741
APA StyleSun, Y., Yang, Y., Zheng, L., Zheng, X., Xiao, D., Wang, S., Zhang, Z., Ai, B., & Sheng, Z. (2022). Physicochemical, Structural, and Digestive Properties of Banana Starch Modified by Ultrasound and Resveratrol Treatments. Foods, 11(22), 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223741