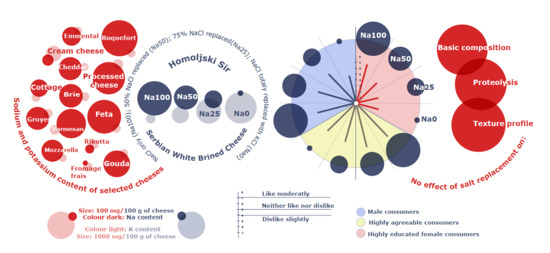
Sodium Reduction by Partial and Total Replacement of NaCl with KCl in Serbian White Brined Cheese
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cheese Manufacture and Sampling
2.2. Basic Cheese Composition
2.3. Macroelements
2.4. Proteolysis Assessment
2.5. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.6. Consumer Testing for Sensory Acceptance of Cheeses
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Composition
3.2. Macroelements
3.3. Proteolysis Assessment
3.4. Textural Properties of Cheese
3.5. Consumer Testing for Sensory Acceptance of Cheeses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guinee, T.P. Salting and the role of salt in cheese. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2004, 57, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahnaky, A.; Mousavi, S.H.; Nasiri, M. Role of salt in Iranian ultrafiltered Feta cheese: Some textural and physicochemical changes during ripening. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2013, 66, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkye, N.Y.; Guinee, T.P. Low-Fat and Low-Sodium Cheeses. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics & Microbiology; McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Cotter, P.D., Everett, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press & Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 699–711. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, A.G.; Faria, J.A.F.; Pollonio, M.A.R.; Bolini, H.M.A.; Celeghini, R.M.S.; Granato, D.; Shah, N.P. Cheeses with reduced sodium content: Effects on functionality, public health benefits and sensory properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases in the WHO European Region; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lacey, C.; Clark, B.; Frewer, L.; Kuznesof, S. “Reaching its limits”: Industry perspectives on salt reduction. Br. Food J. 2016, 118, 1610–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Strategic Plan for Salt Intake Reduction in Croatia; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Miloradovic, Z.; Blazic, M.; Barukcic, I.; Font i Furnols, M.; Smigic, N.; Tomasevic, I.; Miocinovic, J. Serbian, Croatian and Spanish consumers’ beliefs towards artisan cheese. Br. Food J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alichanidis, E.; Polychroniadou, A. Characteristics of major traditional regional cheese varieties of East-Mediterranean countries: A review. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2008, 88, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miocinovic, J.; Miloradovic, Z. Production and characteristics of different types of Serbian cheeses. In Cheeses around the World; Guinee, R.d.P.F., Correia, P.M.d.R., Ferrao, A.C., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 183–203. [Google Scholar]
- Miloradovic, Z.; Smigic, N.; Djekic, I.; Tomasevic, I.; Kljajevic, N.; Nedeljkovic, A.; Miocinovic, J. The influence of NaCl concentration of brine and different packaging on goat white brined cheese characteristics. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 79, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobowski, N.; Rendahl, A.; Vickers, Z. A longitudinal comparison of two salt reduction strategies: Acceptability of a low sodium food depends on the consumer. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 40, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.; Fernando, A.L.; Alvarenga, N.; Martins, A.P.L. Substitution of sodium chloride by potassium chloride in São João cheese of Pico Island. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2016, 96, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsiari, M.C.; Voutsinas, L.P.; Alichanidis, E.; Roussis, I.G. Reduction of sodium content in Feta cheese by partial substitution of NaCl by KCl. Int. Dairy J. 1997, 7, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.M.; Shah, N.P. The effect of substituting NaCl with KCl on Nabulsi cheese: Chemical composition, total viable count, and texture profile. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akan, E.; Kinik, O. Effect of mineral salt replacement on properties of Turkish White cheese. Mljekarstvo 2018, 68, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, I.; Park, J.-H.; Choi, H.-Y.; Jung, H.-K. Emerging Innovations to Reduce the Salt Content in Cheese; Effects of Salt on Flavor, Texture, and Shelf Life of Cheese; and Current Salt Usage: A Review. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2017, 37, 793–798. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, V.; Mishra, S.K. Reduced-sodium cheeses: Implications of reducing sodium chloride on cheese quality and safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 19, 733–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Güven, M.; Karaca, O.B. Proteolysis levels of white cheeses salted and ripened in brines prepared from various salts. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2001, 54, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagözlü, C.; Kinik, Ö.; Akbulut, N. Effects of fully and partial substitution of NaCl by KCl on physico-chemical and sensory properties of white pickled cheese. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 59, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafi, R.; Bari, M.R.; Khosroshahi, A.; Alizadeh, M. Minimization of sodium in Iranian white brined cheese. Asian J. Chem. 2009, 21, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar]
- Miloradovic, Z.; Kljajevic, N.; Miocinovic, J.; Tomic, N.; Smiljanic, J.; Macej, O. High heat treatment of goat cheese milk. The effect on yield, composition, proteolysis, texture and sensory quality of cheese during ripening. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 68, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation, S. Amendment on Sebian Regulation 2010 “Quality of Dairy Products and Strarter Cultures”. 33/10. 2014. Available online: http://extwprlegs1.fao.org/docs/pdf/srb141808.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- O’Brien, N.M.; O’Connor, T.P. Nutritional Aspects of Cheese. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics & Microbiology; McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Cotter, P.D., Everett, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press & Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 603–611. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry: A Food Labeling Guide. Appendix A: Definitions of Nutrient Content Claims; FDA: Silver Spring, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vandevijvere, S.; Van Oyen, H. Sodium intake in the Belgian population: Research limitations and policy implications. Arch. Public Healthy 2008, 66, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Guinee, T.P.; O’Kennedy, B.T. Mechanisms of taste perception and physiological controls. In Reducing Salt in Foods: Practical Strategies; Guinee, T.P., O’Kennedy, B.T., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Boca Raton LA, USA, 2007; pp. 246–287. [Google Scholar]
- Czarnacka-Szymani, J.; Jezewska-Zychowicz, M. Impact of nutritional information on consumers’ acceptance of cheese with reduced sodium chloride content. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 40, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Time Lapse | Manufacturing Procedures | |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-processing of milk | Standardization of fat to 3.5–3.6%, pasteurization (72 °C/20 s) and cooling (32 ± 1 °C) | |
| 0 min | Addition of starter culture a until the acidity reaches 7.4–7.6° SH | |
| 30 min | Addition of CaCl2 and rennet b (0,16 g/10 L) | |
| 1 h 20 min | Cutting of the gel into 5 cm cubes and resting | |
| 1 h 25 min | Transfer of curd to rectangular press | |
| 1 h 30 min | Draining | |
| 2 h 30 min | Pressing | |
| 6 h | Cutting the curd into blocks 10 × 10 cm (250 g), and dry salting at surface, with 4 different salt mixtures and packing into plastic containers | Salt mixtures: |
| Na100 (100% NaCl) | ||
| Na50 (50% NaCl and 50% KCl) | ||
| Na25 (25% NaCl and 75% KCl) | ||
| Na0 (100% KCl) | ||
| 6 h 30 min | Storing at room temperature | |
| 30 h 30 min | Ripening in 4 different brine solutions (12%) for 60 days at 16–18 °C | Brine solutions: |
| Na100 (100% NaCl) | ||
| Na50 (50% NaCl and 50% KCl) | ||
| Na25 (25% NaCl and 75% KCl) | ||
| Na0 (100% KCl) | ||
| Parameter Days | Cheese Variants | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sig * | Na100 | Na50 | Na25 | Na0 | |||
| pH | |||||||
| 1 | c | 5.36 ± 0.06 | 5.35 ± 0.06 | 5.33 ± 0.12 | 5.38 ± 0.16 | ||
| 30 | b | 4.69 ± 0.02 | 4.57 ± 0.04 | 4.59 ± 0.02 | 4.53 ± 0.10 | ||
| 60 | a | 4.32 ± 0.02 | 4.29 ± 0.02 | 4.36 ± 0.08 | 4.29 ± 0.02 | ||
| DM (%) | |||||||
| 1 | a | 39.27 ± 1.11 | 38.93 ± 0.22 | 38.63 ± 0.34 | 38.61 ± 0.40 | ||
| 30 | b | 47.24 ± 2.67 | 46.95 ± 0.74 | 47.85 ± 2.73 | 48.14 ± 1.34 | ||
| 60 | b | 46.95 ± 0.34 | 47.32 ± 0.14 | 48.64 ± 2.35 | 46.21 ± 1.38 | ||
| MF (%) | |||||||
| 1 | a | 20.00 ± 0.00 | 21.50 ± 0.00 | 20.50 ± 0.58 | 20.00 ± 0.00 | ||
| 30 | b | 27.25 ± 0.87 | 27.50 ± 1.73 | 30.50 ± 2.89 | 33.50 ± 7.50 | ||
| 60 | b | 28.50 ± 0.58 | 28.50 ± 0.58 | 28.50 ± 0.58 | 28.50 ± 0.57 | ||
| TP (%) | |||||||
| 1 | a | 13.10 ± 1.06 | 13.73 ± 0.49 | 13.71 ± 0.92 | 13.05 ± 0.76 | ||
| 30 | b | 16.31 ± 1.32 | 16.10 ± 0.68 | 16.29 ± 2.21 | 16.67 ± 1.04 | ||
| 60 | b | 17.31 ± 0.77 | 15.88 ± 0.81 | 17.22 ± 0.99 | 16.44 ± 1.27 | ||
| 60 | Cl− (%) | 2.05 ± 0,44 | 1.87 ± 0.20 | 1.84 ± 0.14 | 1.59 ± 0.17 | ||
| Macroelements: | |||||||
| 60 | Na (mg/100 g) | 1542.0 ± 146.0 a | 750.5 ± 75.6 b | 408.5 ± 17.7 c | 39.3 ± 3.54 d | ||
| 60 | K (mg/100 g) | 113.0 ± 11.3 a | 365.5 ± 74.2 b | 768.5 ± 36.1 c | 1266.0 ± 219.2 d | ||
| 60 | Ca (mg/100 g) | 297.0 ± 52.74 | 236.0 ± 2.84 | 270.0 ± 13.6 | 292.0 ± 24.8 | ||
| 60 | Mg (mg/100 g) | 10.43 ± 2.79 | 10.10 ± 2.84 | 13.35 ± 0.92 | 10.28 ± 2.58 | ||
| Parameter Days | Cheese Variants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sig * | Na100 | Na50 | Na25 | Na0 | |
| αs1-index | |||||
| 4 | a | 0.50 ± 0.02 | 0.53 ± 0.04 | 0.55 ± 0.05 | 0.52 ± 0.04 |
| 30 | a | 0.50 ± 0.01 | 0.51 ± 0.02 | 0.54 ± 0.03 | 0.53 ± 0.03 |
| 60 | b | 0.61 ± 0.04 | 0.61 ± 0.03 | 0.60 ± 0.03 | 0.58 ± 0.06 |
| β-CN index | |||||
| 4 | a | 0.76 ± 0.17 | 0.74 ± 0.13 | 0.76 ± 0.13 | 0.75 ± 0.10 |
| 30 | a | 0.73 ± 0.17 | 0.73 ± 0.13 | 0.73 ± 0.10 | 0.72 ± 0.09 |
| 60 | a | 0.78 ± 0.16 | 0.87 ± 0.05 | 0.79 ± 0.01 | 0.76 ± 0.13 |
| RI | |||||
| 1 | a | 8.15 ± 1.10 | 7.76 ± 0.77 | 6.61 ± 1.98 | 8.07 ± 0.87 |
| 30 | a | 9.68 ± 1.19 | 8.09 ± 1.48 | 9.33 ± 0.65 | 7.77 ± 1.89 |
| 60 | b | 10.58 ± 2.10 | 10.69 ± 1.44 | 11.43 ± 0.78 | 11.77 ± 0.50 |
| PTA/TN | |||||
| 60 | 0.81 ± 0.07 | 0.78 ± 0.19 | 0.81 ± 0.03 | 1.24 ± 0.31 | |
| Parameter Days | Cheese Variants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sig * | Na100 | Na50 | Na25 | Na0 | |
| Hardness (g) | |||||
| 1 | a | 344.5 ± 24.2 | 339.4 ± 28.1 | 307.9 ± 16.4 | 273.3 ± 28.9 |
| 30 | c | 1543.2 ± 35.0 | 1528.9 ± 82.8 | 1640.8 ± 123.5 | 1667.3 ± 269.3 |
| 60 | b | 1065.5 ± 202.0 | 1206.1 ± 114.5 | 996.6 ± 17.9 | 1085.4 ± 102.4 |
| Adhesiveness (g s) | |||||
| 1 | c | 22.2 ± 0.4 | 22.8 ± 0.8 | 20.6 ± 2.4 | 20.9 ± 1.4 |
| 30 | b | 10.6 ± 2.1 | 10.6 ± 2.8 | 8.9 ± 1.1 | 8.1 ± 2.3 |
| 60 | a | 4.1 ± 1.3 | 3.6 ± 1.7 | 3.9 ± 2.3 | 4.1 ± 1.8 |
| Springiness (mm) | |||||
| 1 | b | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 0.97 ± 0.03 | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 0.97 ± 0.03 |
| 30 | a | 0.79 ± 0.05 | 0.80 ± 0.05 | 0.87 ± 0.08 | 0.76 ± 0.05 |
| 60 | b | 0.97 ± 0.04 | 0.93 ± 0.07 | 0.93 ± 0.08 | 0.91 ± 0.03 |
| Cohesiveness | |||||
| 1 | b | 0.83 ± 0.02 | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 0.83 ± 0.03 |
| 30 | a | 0.46 ± 0.05 | 0.47 ± 0.11 | 0.52 ± 0.10 | 0.54 ± 0.10 |
| 60 | a | 0.50 ± 0.06 | 0.44 ± 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.03 | 0.46 ± 0.02 |
| Chewiness | |||||
| 1 | a | 265.0 ± 15.4 | 262.4 ± 23.7 | 216.5 ± 14.0 | 214.8 ± 21.3 |
| 30 | c | 496.5 ± 19.0 | 480.1 ± 13.1 | 502.4 ± 61.1 | 492.2 ± 59.3 |
| 60 | b | 266.6 ± 19.3 | 242.3 ± 29.3 | 289.6 ± 47.9 | 278.3 ± 48.4 |
| Resilience | |||||
| 1 | b | 0.46 ± 0.02 | 0.46 ± 0.01 | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 0.45 ± 0.02 |
| 30 | a | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.05 |
| 60 | a | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.03 |
| Overall (100%) | Cluster 1 (47.8%) | Cluster 2 (30.4%) | Cluster 3 (21.8%) | ||
| Gender (%) | Female | 41.3 | 22.7 | 50.0 | 70.0 |
| Male | 58.7 | 77.3 | 50.0 | 30.0 | |
| Age (%) | 21–40 | 52.2 | 45.5 | 57.1 | 60.0 |
| 41–60 | 47.8 | 54.5 | 42.9 | 40.0 | |
| Education (%) | Elementary/High school | 63.1 | 63.6 | 85.7 | 30.0 |
| University: BSc, MSc, PhD | 36.9 | 36.4 | 14.3 | 70.0 | |
| Hedonic Attributes | Consumers (N = 46) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 (47.8%) | Cluster 2 (30.4%) | Cluster 3 (21.8%) | ||
| Na100 | OVERALL | 7.45 ± 1,26 | 7.50 ± 1.56 | 7.10 ± 2.02 |
| ODOR | 7.05 ± 1.86 | 6.71 ± 2.46 | 7.40 ± 1.78 | |
| TASTE | 7.59 ± 1.65 | 6.93 ± 2.73 | 6.70 ± 1.83 | |
| TEXTURE | 7.64 ± 1.18 | 7.64 ± 1.22 | 7.00 ± 2.11 | |
| Na50 | OVERALL | 7.32 ± 1.52 b | 7.14 ± 1.66 ab | 5.40 ± 2.32 a |
| ODOR | 7.32 ± 1.70 b | 7.71 ± 1.27 b | 5.10 ± 1.97 a | |
| TASTE | 7.68 ± 1.49 b | 7.07 ± 1.77 ab | 4.60 ± 2.99 a | |
| TEXTURE | 7.45 ± 1.65 b | 7.71 ± 1.27 b | 5.00 ± 2.00 a | |
| Na25 | OVERALL | 7.36 ± 1.18 b | 8.07 ± 0.73 b | 3.50 ± 2.01 a |
| ODOR | 7.09 ± 1.72 b | 7.79 ± 1.05 b | 4.60 ± 1.90 a | |
| TASTE | 7.00 ± 1.72 b | 7.93 ± 1.59 b | 3.60 ± 1.84 a | |
| TEXTURE | 7.23 ± 1.60 b | 8.00 ± 1.24 b | 3.90 ± 2.02 a | |
| Na0 | OVERALL | 4.86 ± 1.91 a | 7.07 ± 1.49 b | 3.60 ± 2.50 a |
| ODOR | 4.82 ± 1.65 a | 7.50 ± 1.09 b | 3.30 ± 2.00 a | |
| TASTE | 3.50 ± 2.09 a | 7.29 ± 1.38 b | 2.80 ± 2.04 a | |
| TEXTURE | 5.45 ± 1.65 a | 7.79 ± 0.89 b | 4.10 ± 0.99 a | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miocinovic, J.; Miloradovic, Z.; Radovanovic, M.; Sredovic Ignjatovic, I.; Radulovic, A.; Nastaj, M.; Sołowiej, B.G.; Tomasevic, I. Sodium Reduction by Partial and Total Replacement of NaCl with KCl in Serbian White Brined Cheese. Foods 2022, 11, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030374
Miocinovic J, Miloradovic Z, Radovanovic M, Sredovic Ignjatovic I, Radulovic A, Nastaj M, Sołowiej BG, Tomasevic I. Sodium Reduction by Partial and Total Replacement of NaCl with KCl in Serbian White Brined Cheese. Foods. 2022; 11(3):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030374
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiocinovic, Jelena, Zorana Miloradovic, Mira Radovanovic, Ivana Sredovic Ignjatovic, Ana Radulovic, Maciej Nastaj, Bartosz G. Sołowiej, and Igor Tomasevic. 2022. "Sodium Reduction by Partial and Total Replacement of NaCl with KCl in Serbian White Brined Cheese" Foods 11, no. 3: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030374
APA StyleMiocinovic, J., Miloradovic, Z., Radovanovic, M., Sredovic Ignjatovic, I., Radulovic, A., Nastaj, M., Sołowiej, B. G., & Tomasevic, I. (2022). Sodium Reduction by Partial and Total Replacement of NaCl with KCl in Serbian White Brined Cheese. Foods, 11(3), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030374