Evaluation of Virulence Factors, Antibiotic Resistance, and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Milk and Dairy Products in Isfahan, Iran
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
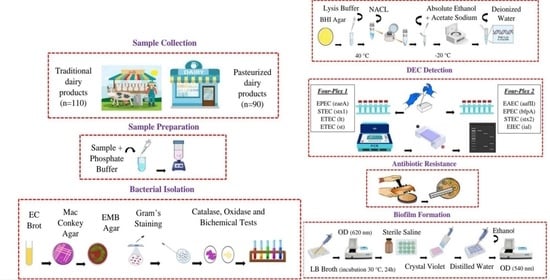
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Culture, Screening, and Biochemical Tests of E. coli
2.3. Extraction of Genomic DNA and Molecular Identification of E. coli
2.4. Antibiotic Resistance Testing
2.5. Biofilm Formation Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of E. coli Isolates
3.2. Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of E. coli
3.3. Biofilm Formation of E. coli
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bedasa, S.; Shiferaw, D.; Abraha, A.; Moges, T. Occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility profile of Escherichia coli O157: H7 from food of animal origin in Bishoftu town, Central Ethiopia. Int. J. Food Contam. 2018, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abebe, E.; Gugsa, G.; Ahmed, M. Review on major food-borne zoonotic bacterial pathogens. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 2020, 4674235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Estimates of Foodborne Illness in the United States: CDC 2011 Estimates. 2011. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/foodborneburden/2011-foodborne-estimates.html (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Farrokh, C.; Jordan, K.; Auvray, F.; Glass, K.; Oppegaard, H.; Raynaud, S.; Thevenot, D.; Condron, R.; De Reu, K.; Govaris, A. Review of Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and their significance in dairy production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 162, 190–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canizalez-Roman, A.; Gonzalez-Nuñez, E.; Vidal, J.E.; Flores-Villaseñor, H.; León-Sicairos, N. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance profiles of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from food items in northwestern Mexico. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 164, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, J.N.; Gorman, S.P.; Gilmore, B.F. Clinical relevance of the ESKAPE pathogens. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo-Ariyama, H.A.; García-Heredia, A.; Heredia, N.; García, S.; León, J.; Jaykus, L.; Solís-Soto, L. Phylogroups, pathotypes, biofilm formation and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolates in farms and packing facilities of tomato, jalapeño pepper and cantaloupe from Northern Mexico. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 290, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.C.; Martínez, N.; Del Rio, B.; Ladero, V.; Fernández, M.; Alvarez, M.A. A novel real-time polymerase chain reaction-based method for the detection and quantification of lactose-fermenting Enterobacteriaceae in the dairy and other food industries. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Saucedo, C.; Cerna, J.F.; Villegas-Sepulveda, N.; Thompson, R.; Velazquez, F.R.; Torres, J.; Tarr, P.I.; Estrada-García, T. Single multiplex polymerase chain reaction to detect diverse loci associated with diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, F.; Svennerholm, A.M.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Sack, R.B. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in developing countries: Epidemiology, microbiology, clinical features, treatment, and prevention. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lai, Z.; Zhu, X. Prevalence, genetic diversity, and antibiotic resistance of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in retail ready-to-eat foods in China. Food Control 2016, 68, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqua, M.; Michelacci, V.; Di Martino, M.L.; Tozzoli, R.; Grossi, M.; Colonna, B.; Morabito, S.; Prosseda, G. The intriguing evolutionary journey of enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC) toward pathogenicity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nataro, J.P. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2005, 21, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García-Heredia, A.; García, S.; Merino-Mascorro, J.Á.; Feng, P.; Heredia, N. Natural plant products inhibits growth and alters the swarming motility, biofilm formation, and expression of virulence genes in enteroaggregative and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Food Microbiol. 2016, 59, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.K.; Taneja, N.K.; Shivaprasad, D.P.; Chakotiya, A.; Patel, P.; Taneja, P.; Sachdev, D.; Gupta, S.; Sanal, M.G. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of biofilm forming, antimicrobial resistant, pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from Indian dairy and meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 336, 108899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei, S.; Zahedi, M.; Abtahi, M.; Doustmohammadian, A.; Dadkhah, M.; Zoghi, T.; Hajigholam Saryazdi, M. Consumption of milk and dairy products in Iranian population; barriers and facilitators. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2021, 38, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzpour, Z.; Sami, M.; Falahati, H.; Mohammadi, R. Bacterial and mold contamination of milk and dairy products distributed by traditional or commercial producers in Isfahan, Iran, in 2015. J. Isfahan Med. Sch. 2016, 34, 712–717. [Google Scholar]
- Chaleshtori, F.S.; Arani, N.M.; Aghadavod, E.; Naseri, A.; Chaleshtori, R.S. Molecular characterization of Escherichia coli recovered from traditional milk products in Kashan, Iran. Vet. World 2017, 10, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collignon, P.C.; Conly, J.M.; Andremont, A.; McEwen, S.A.; Aidara-Kane, A. World Health Organization Ranking of Antimicrobials According to Their Importance in Human Medicine:A Critical Step for Developing Risk Management Strategies to Control Antimicrobial Resistance From Food Animal Production. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alizade, H. Escherichia coli in Iran: An overview of antibiotic resistance: A review article. Iran J. Public Health 2018, 47, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Olowe, O.A.; Adefioye, O.J.; Ajayeoba, T.A.; Schiebel, J.; Weinreich, J.; Ali, A.; Burdukiewicz, M.; Rödiger, S.; Schierack, P. Phylogenetic grouping and biofilm formation of multidrug resistant Escherichia coli isolates from humans, animals and food products in South-West Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2019, 6, e00158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Amer, A.E.; Shobrak, M.Y.; Altalhi, A.D. Isolation and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from farm chickens in Taif, Saudi Arabia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Tay, M.Y.F.; Aung, K.T.; Seow, K.L.G.; Ng, L.C.; Purbojati, R.W.; Drautz-Moses, D.I.; Schuster, S.C.; Schlundt, J. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of antimicrobial resistant Escherichia coli isolated from ready-to-eat food in Singapore using disk diffusion, broth microdilution and whole genome sequencing methods. Food Control 2019, 99, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Alvseike, O.; Omer, M.K.; Heir, E.; Axelsson, L.; Holck, A.; Prieto, M. Heterogeneity in resistance to food-related stresses and biofilm formation ability among verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 161, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadekuzzaman, M.; Yang, S.; Mizan, M.F.R.; Ha, S.D. Current and recent advanced strategies for combating biofilms. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srey, S.; Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S.D. Biofilm formation in food industries: A food safety concern. Food Control 2013, 31, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, T.V.; da Silva Fernandes, M.; Perdoncini, M.R.F.G.; dos Anjos, M.M.; de Abreu Filho, B.A. Capacity of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus to produce biofilm on stainless steel surfaces in the presence of food residues. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombarak, R.A.; Hinenoya, A.; Awasthi, S.P.; Iguchi, A.; Shima, A.; Elbagory, A.-R.M.; Yamasaki, S. Prevalence and pathogenic potential of Escherichia coli isolates from raw milk and raw milk cheese in Egypt. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 221, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.P.; Kuo, T.T. A simple and rapid method for the preparation of gram-negative bacterial genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.Y.; Jang, H.I.; Hwang, I.G.; Rhee, M.S. Prevalence and classification of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from fresh beef, poultry, and pork in Korea. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 134, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro Júnior, J.C.; Silva, F.F.; Lima, J.B.A.; Ossugui, E.H.; Teider Junior, P.I.; Campos, A.; Navarro, A.; Tamanini, R.; Ribeiro, J.; Alfieri, A.A. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance of pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from raw milk and Minas Frescal cheeses in Brazil. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 37, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, M.P.; Lewis, J.S.; Bobenchik, A.M.; Campeau, S.; Cullen, S.K.; Galas, M.F.; Gold, H.; Humphries, R.M.; Kirn, T.J.; Limbago, B.; et al. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; CLSI Document M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Luo, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; Ji, H. Antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from retail foods in northern Xinjiang, China. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2035–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naves, P.; Del Prado, G.; Huelves, L.; Gracia, M.; Ruiz, V.; Blanco, J.; Rodríguez-Cerrato, V.; Ponte, M.C.; Soriano, F. Measurement of biofilm formation by clinical isolates of Escherichia coli is method-dependent. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, R.; Dehkordi, F.S.; Shahreza, M.H.S.; Rahimi, E. Prevalence, identification of virulence factors, O-serogroups and antibiotic resistance properties of Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from raw milk and traditional dairy products. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disassa, N.; Sibhat, B.; Mengistu, S.; Muktar, Y.; Belina, D. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of E. coli O157: H7 isolated from traditionally marketed raw cow milk in and around Asosa town, western Ethiopia. Vet. Med. Int. 2017, 2017, 7581531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehkordi, F.S.; Yazdani, F.; Mozafari, J.; Valizadeh, Y. Virulence factors, serogroups and antimicrobial resistance properties of Escherichia coli strains in fermented dairy products. BMC Res. 2014, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos, A.C.L.P.; Puno-Sarmiento, J.J.; Medeiros, L.P.; Gazal, L.E.S.; Maluta, R.P.; Navarro, A.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Fagan, E.P.; Nakazato, G. Virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli from cheese made from unpasteurized milk in Brazil. Foodborne Path. Dis. 2018, 15, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, N.; Ghaemi, M.; Ghazvini, K.; Rad, M.; Jamshidi, A. Occurrence, pathotypes, and antimicrobial resistance profiles of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains in animal source food products from public markets in Mashhad, Iran. Food Control 2021, 121, 107640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, A.I.; Castro, V.S.; Santos, L.F.; Lisboa, R.C.; Vallim, D.C.; Silva, M.C.; Figueiredo, E.E.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Costa, M.P. Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli isolated from pasteurized dairy products from Bahia, Brazil. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 6535–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, P.; Abiri, R. Isolation of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) from raw milk in Kermanshah by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Jundishapur. J. Microbiol. 2013, 6, 5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, Z.N.; da Cunha, A.S.; Lins, M.C.; Carneiro, L.d.A.M.; Almeida, A.C.d.F.; Queiroz, M.L.P. Isolation and serological identification of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pasteurized milk in Brazil. Rev. Saude Publica 2001, 35, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trabulsi, L.R.; Keller, R.; Gomes, T.A.T. Typical and Atypical Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Orco, F.; Gusmara, C.; Loiacono, M.; Gugliotta, T.; Albonico, F.; Mortarino, M.; Zecconi, A. Evaluation of virulence factors profiles and antimicrobials resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from bulk tank milk and raw milk filters. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 123, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abri, R.; Javadi, A.; Asghari, R.; Razavilar, V.; Salehi, T.Z.; Safaeeyan, F.; Rezaee, M.D. Surveillance for enterotoxigenic & enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from animal source foods in Northwest Iran. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 150, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aijuka, M.; Santiago, A.E.; Girón, J.A.; Nataro, J.P.; Buys, E.M. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli is the predominant diarrheagenic E. coli pathotype among irrigation water and food sources in South Africa. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 278, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hegde, A.; Ballal, M.; Shenoy, S. Detection of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli by multiplex PCR. Indian. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 30, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, G.; Franconieri, I.; Basanisi, M.G.; La Bella, G.; Tozzoli, R.; Caprioli, A.; La Salandra, G. Isolation of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in raw milk and mozzarella cheese in southern Italy. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7877–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooman, N.; Mansour-Ghanaei, R.; Yaghoubi, M.; Nakhaie, S. The prevalence of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in patients with gastroenteritis and sources of infections in Iran: A systematic review study protocol. J. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 4, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, R.; Schumacher, S.; Corti, S.; Krause, G.; Danuser, J.; Beutin, L. Prevalence and characteristics of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in Swiss raw milk cheeses collected at producer level. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 2561–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elafify, M.; Khalifa, H.O.; Al-Ashmawy, M.; Elsherbini, M.; El Latif, A.A.; Okanda, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Koseki, S.; Abdelkhalek, A. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in milk and dairy products in Egypt. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2020, 55, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Foodborne antimicrobial resistance as a biological hazard, Scientific opinion of the panel on biological hazards. ERA J. 2008, 6, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarddon, M.; Miranda, J.M.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Vázquez, B.I.; Cepeda, A.; Franco, C.M. Real-time polymerase chain reaction for the quantitative detection of tetA and tetB bacterial tetracycline resistance genes in food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 146, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtaz, H.; Dehkordi, F.S.; Rahimi, E.; Ezadi, H.; Arab, R. Incidence of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli serogroups in ruminant’s meat. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzeniewska, E.; Korzeniewska, A.; Harnisz, M. Antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli in hospital and municipal sewage and their emission to the environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 91, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmonir, W.; Shalaan, S.; Tahoun, A.; Mahmoud, S.F.; Remela, E.M.A.; Eissa, R.; El-Sharkawy, H.; Shukry, M.; Zahran, R.N. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and genotyping of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in foods of cattle origin, diarrheic cattle, and diarrheic humans in Egypt. Gut Pathog. 2021, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, M.M.; Stringer, A.P. Prevalence, molecular characterization, and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella enterica, and Escherichia coli O157: H7 on dairy cattle farms in Jordan. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 8710–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, G.N.; Mikcha, J.M.G.; Bando, E.; Siqueira, V.L.D.; Machinski, M., Jr. Occurrence and antibiotic resistance of coliform bacteria and antimicrobial residues in pasteurized cow’s milk from Brazil. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 1684–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonyadian, M.; Moshtaghi, H.; Akhavan Taheri, M. Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of enterotoxigenic and entero-aggregative Escherichia coli isolated from raw milk and unpasteurized cheeses. Vet. Res. Forum 2014, 5, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, M.O.; Ribeiro, A.R.; dos Santos, L.R.; Pilotto, F.; de Moraes, H.L.S.; Salle, C.T.P.; da Silveira Rocha, S.L.; do Nascimento, V.P. Antibiotic resistance in Salmonella Enteritidis isolated from broiler carcasses. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2006, 37, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, A.M.; Shimamoto, T. Molecular analysis of multidrug resistance in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157: H7 isolated from meat and dairy products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 193, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messele, Y.E.; Abdi, R.D.; Tegegne, D.T.; Bora, S.K.; Babura, M.D.; Emeru, B.A.; Werid, G.M. Analysis of milk-derived isolates of E. coli indicating drug resistance in central Ethiopia. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bag, M.A.S.; Khan, M.S.R.; Sami, M.D.H.; Begum, F.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, M.T.; Hassan, J. Virulence determinants and antimicrobial resistance of E. coli isolated from bovine clinical mastitis in some selected dairy farms of Bangladesh. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6317–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holko, I.; Tančin, V.; Vršková, M.; Tvarožková, K. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of udder pathogens isolated from dairy cows in Slovakia. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhum, A.A.; Khudor, M.H. Phenotypic and molecular characteristics of biofilm and other virulence genes in E. coli and K. pneumoniae isolates from healthy dairy cow, human and environmental sources. Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2021, 15, 2453. [Google Scholar]
- Marti, R.; Schmid, M.; Kulli, S.; Schneeberger, K.; Naskova, J.; Knøchel, S.; Ahrens, C.H.; Hummerjohann, J. Biofilm formation potential of heat-resistant Escherichia coli dairy isolates and the complete genome of multidrug-resistant, heat-resistant strain FAM21845. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00628-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Bumunang, E.W.; Stanford, K.; Bie, X.; Niu, Y.D.; McAllister, T.A. Biofilm formation by shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli on stainless steel coupons as affected by temperature and incubation time. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendonça, R.C.S.; Morelli, A.M.F.; Pereira, J.A.M.; de Carvalho, M.M.; de Souza, N.L. Prediction of Escherichia coli O157: H7 adhesion and potential to form biofilm under experimental conditions. Food Control 2012, 23, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corcoran, M.; Morris, D.; De Lappe, N.; O’connor, J.; Lalor, P.; Dockery, P.; Cormican, M. Commonly used disinfectants fail to eradicate Salmonella enterica biofilms from food contact surface materials. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Sample Source | No. (%) of E. coli Positive | No. (%) Virulence Factor Positive | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | boiled | 1 (10) | 1 (10) |
| pasteurized | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | |
| raw | 18 (90) | 9 (45) | |
| Cheese | traditional | 5 (50) | 4 (40) |
| pasteurized | ND *** | ND *** | |
| Butter | traditional | 5 (50) | 3 (30) |
| pasteurized | 2 (20) | 1 (10) | |
| Yogurt | traditional | 3 (30) | 2 (20) |
| pasteurized | ND *** | ND *** | |
| Kashk * | traditional | 2 (20) | 2 (20) |
| pasteurized | ND *** | ND *** | |
| Cream | traditional | 4 (40) | 4 (40) |
| pasteurized | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | |
| Doogh ** | traditional | 3 (30) | 3 (30) |
| pasteurized | ND *** | ND *** | |
| Ice cream | traditional | 3 (30) | 2 (20) |
| pasteurized | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | |
| Pizza cheese | traditional | 4 (40) | 3 (30) |
| pasteurized | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | |
| Total | 54 (27) | 38 (19) | |
| Sample Source | EPEC (bfpA+ eaeA) * | EPEC (eaeA) | ETEC (lt) | ETEC (st) | EIEC (ial) | STEC (stx2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | boiled | ND ** | 1 (10) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| pasteurized | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 (10) | ND | |
| raw | 1 (5) | 5 (25) | ND | 1 (5) | ND | 2 (10) | |
| Cheese | traditional | ND | 1 (10) | ND | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | 1 (10) |
| Butter | traditional | 1 (10) | 2 (20) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| pasteurized | ND | 1 (10) | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Yogurt | traditional | ND | ND | ND | 2 (20) | ND | ND |
| Kashk | traditional | ND | ND | 1 (10) | ND | 1 (10) | ND |
| Cream | traditional | 1 (10) | 2 (20) | ND | ND | 1 (10) | ND |
| pasteurized | ND | ND | ND | 1 (10) | ND | ND | |
| Doogh | traditional | 1 (10) | ND | ND | ND | 1 (10) | 1 (10) |
| Ice cream | traditional | ND | ND | ND | ND | 2 (20) | ND |
| pasteurized | 1 (10) | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Pizza cheese | traditional | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | ND | ND | ND |
| pasteurized | ND | 1 (10) | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Total | 6 (11.1) | 14 (25.9) | 2 (3.7) | 5 (9.2) | 7 (13) | 4 (7.4) | |
| Antibiotic Resistance in Different Degrees of Biofilm Formation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | No. (%) of Strong Biofilm Formation (n = 11) | No. (%) of Moderate Biofilm Formation (n = 4) | No. (%) of Weak Biofilm Formation (n = 11) | No. (%) of Non-Biofilm Former (n = 12) |
| AM | 2 (18.2) | 1 (25) | 4 (36.4) | 4 (33.3) |
| AN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AMC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (16.7) |
| FOX | 0 | 0 | 1 (9.1) | 2 (16.7) |
| CTX | 1 (9.1) | 0 | 2 (18.2) | 1 (8.3) |
| CRO | 1 (9.1) | 0 | 2 (18.2) | 1 (8.3) |
| C | 1 (9.1) | 0 | 1 (9.1) | 3 (25) |
| CP | 0 | 1 (25) | 2 (18.2) | 0 (0) |
| SXT | 3 (27.3) | 2 (50) | 8 (72.7) | 3 (25) |
| GM | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (8.3) |
| K | 3 (27.3) | 0 | 2 (18.2) | 1 (8.3) |
| NA | 0 | 0 | 1 (9.1) | 0 |
| TE | 5 (45.5) | 2 (50) | 9 (81.8) | 3 (25) |
| S | 7 (63.6) | 1 (25) | 8 (72.7) | 6 (50) |
| Total | 23 | 7 | 40 | 27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madani, A.; Esfandiari, Z.; Shoaei, P.; Ataei, B. Evaluation of Virulence Factors, Antibiotic Resistance, and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Milk and Dairy Products in Isfahan, Iran. Foods 2022, 11, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11070960
Madani A, Esfandiari Z, Shoaei P, Ataei B. Evaluation of Virulence Factors, Antibiotic Resistance, and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Milk and Dairy Products in Isfahan, Iran. Foods. 2022; 11(7):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11070960
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadani, Arghavan, Zahra Esfandiari, Parisa Shoaei, and Behrooz Ataei. 2022. "Evaluation of Virulence Factors, Antibiotic Resistance, and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Milk and Dairy Products in Isfahan, Iran" Foods 11, no. 7: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11070960
APA StyleMadani, A., Esfandiari, Z., Shoaei, P., & Ataei, B. (2022). Evaluation of Virulence Factors, Antibiotic Resistance, and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Milk and Dairy Products in Isfahan, Iran. Foods, 11(7), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11070960