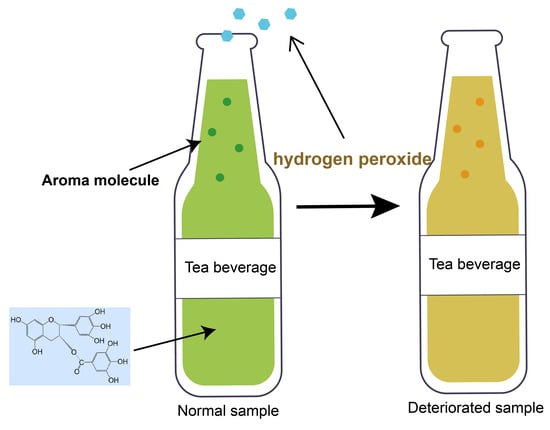
Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide Produced by Catechins on the Aroma of Tea Beverages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Tea Samples
2.2.1. Preparation of the Monomer Reaction System
2.2.2. Preparation of the Tea Infusion Reaction System
2.3. Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide
2.4. Determination of Aroma Compounds
2.5. Determination of Catechin Content
2.6. Antioxidant Activity Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Hydrogen Peroxide Formation from Catechins under Various Reaction Conditions
3.2. Effect of Key Aroma Component Linalool on Hydrogen Peroxide Production by EGCG
3.3. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on the Key Aroma Component Linalool
3.4. Analysis of the Formation of Hydrogen Peroxide in Tea Infusions
3.5. Mechanism of Hydrogen Peroxide Production in Tea Beverages
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GC–MS | gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| ABTS | 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) |
References
- Aoshima, H.; Ayabe, S. Prevention of the deterioration of polyphenol-rich beverages. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsugu, A.; Tomoko, S.; Kyozo, S. Production of hydrogen peroxide by polyphenols and polyphenol-rich beverages under quasi-physiological conditions. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 2632–2640. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.F.; Kim, D.M.; Lee, C.Y. Effects of heat processing and storage on flavanols and sensory qualities of green tea beverage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4227–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Baldermann, S.; Watanabe, N. Recent studies of the volatile compounds in tea. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Liu, P.; Chen, G.S.; Chen, J.X.; Yuan, H.B.; Yin, J.F. Effect of tea polyphenols concentration on the stability of green tea infusion. J. Tea Sci. 2011, 31, 525–531. [Google Scholar]
- Franks, M.; Lawrence, P.; Abbaspourrad, A.; Dando, R. The Influence of Water Composition on Flavor and Nutrient Extraction in Green and Black Tea. Nutrients 2019, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murugesh, C.S.; Manoj, J.B.; Haware, D.J.; Ravi, R.; Subramanian, R. Influence of water quality on nutritional and sensory characteristics of green tea infusion. J. Food Process. Eng. 2017, 40, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Chen, G.S.; Wang, Q.S.; Yuan, H.B.; Feng, C.H.; Yin, J.F. Irreversible sediment formation in green tea infusions. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C298–C302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.B.; Deng, Y.L.; Chen, G.S.; Xu, Y.Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, P.; Zhong, X.; Yin, J.F. Effect of raw material processing by different fixation technology on the stability with quality of tea beverage. J. Tea Sci. 2012, 32, 236–246. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.B.; Hua, J.J.; Deng, Y.L.; Li, J.; Dong, C.W.; Yang, Y.Q. Effect of different drying technologies during raw tea processing on the quality of green tea beverage. J. Tea Sci. 2017, 37, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, H.L.; Li, C.M.; Hao, J.F.; Hu, W.F. Study on the change of the main biochemical compounts, representative aromatic compounds as well as their correlation of green tea beverages during storage. J. Tea Sci. 2008, 3, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Veal, E.A.; Day, A.M.; Morgan, B.A. Hydrogen peroxide sensing and signaling. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, M.; Cheng, N.; Xue, X.; Wu, L.; Cao, W. A modified FOX-1 method for Micro-determination of hydrogen peroxide in honey samples. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, U.; Sauer, T.; Weigel, I.; Pichner, R.; Pischetsrieder, M. Identification of H2O2 as a major antimicrobial component in coffee. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayabe, S.; Aoshima, H. Aqueous extract of citrus peel reduces production of hydrogen peroxide in catechin-enriched green tea. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1594–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.H.; Lan, A.N.B.; Hsuan, F.T.Y.; Halliwell, B. Generation of hydrogen peroxide by “antioxidant” beverages and the effect of milk addition. Is cocoa the best beverage? Free Radic. Res. 1999, 31, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Enoki, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Hydrogen peroxide formation during catechin oxidation is inhibited by superoxide dismutase. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 1995, 1, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, L.H.; Clement, M.V.; Halliwell, B. Artifacts in cell culture: Rapid generation of hydrogen peroxide on addition of (-)-epigallocatechin, (−)-epigallocatechin gallate, (+)-catechin, and quercetin to commonly used cell culture media. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.Q.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, F.; Xu, Y.Q. Effect of baking on the flavor stability of green tea beverages. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-Q.; Fu, Y.-Q.; Chen, J.-X.; Wang, F.; Feng, Z.-H.; Yin, J.-F.; Zeng, L.; Xu, Y.-Q. Effects of baking treatment on the sensory quality and physicochemical properties of green tea with different processing methods. Food Chem. 2022, 380, 132217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, F.; Chen, G.S.; Yin, J.F.; Xu, Y.Q. Effect of ferrous ion on heat-induced aroma deterioration of green tea infusion. Molecules 2021, 26, 4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Li, X.; Luo, H.; Ding, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Bai, W. Comparative study on the stability and antioxidant activity of six pyranoanthocyanins based on malvidin-3-glucoside. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2783–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Lewis, J.; Wataha, J.; Dickinson, D.; Singh, B.; Bollag, W.B.; Ueta, E.; Osaki, T.; Athar, M.; Schuster, G.; et al. Roles of catalase and hydrogen peroxide in green tea polyphenol-induced chemopreventive effects. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Ichiba, M.; Kuwabara, M.; Kajiya, K.; Kumazawa, S. Mechanisms and structural specificity of hydrogen peroxide formation during oxidation of catechins. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2002, 8, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grzesik, M.; Bartosz, G.; Stefaniuk, I.; Pichla, M.; Namiesnik, J.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. Dietary antioxidants as a source of hydrogen peroxide. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhang, M.; Wu, G.Q.; Hu, X.J.; Long, D. Change of physical and chemical components and sensory qualities in sugar-free oolong tea beverage during storage. Beverage Ind. 2021, 24, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, C.H.; Zheng, B.; Ning, H.M.; Guo, R.Y.; Chen, G.M.; Chen, Z.X. Effects of single-factor inorganic metal ions on tea soup. Xiamen Sci. Technol. 2018, 3, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Podmore, I.D. Vitamin C exhibits pro-oxidant properties. Nature 1998, 392, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boatright, W.L. Oxygen dependency of one-electron reactions generating ascorbate radicals and hydrogen peroxide from ascorbic acid. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, D.; Li, P.; Ma, F. Anthocyanin contributes more to hydrogen peroxide scavenging than other phenolics in apple peel. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, P.C.; Long, L.H.; Halliwell, B. Contribution of hydrogen peroxide to the cytotoxicity of green tea and red wines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbling, L.; Weiss, R.M.; Teufelhofer, O.; Uhl, M.; Knasmueller, S.; Schulte-Hermann, R.; Mickshe, M. Green tea extract and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, the major tea catechin, exert oxidant but lack antioxidant activities. Faseb J. 2005, 19, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Biological production, detection and fate of hydrogen peroxide. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bopitiya, D.; Christensen, D.; Martin, M.; Zhang, J.; Bennett, L.E. Production of hydrogen peroxide in formulated beverages is associated with the presence of ascorbic acid combined with selected redox-active functional ingredients. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Chasteen, N.D. Oxidation of Good’s buffers by hydrogen peroxide. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 349, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Types of Catechins * | Production of Hydrogen Peroxide (Μm) |
|---|---|
| GA | 1.417 ± 0.167 d |
| EC | 6.167 ± 0.694 c,d |
| ECG | 8.417 ± 1.316 c |
| EGC | 51.500 ± 6.501 b |
| EGCG | 127.000 ± 6.633 a |
| Concentration of Tea Polyphenols (mg/L) | Concentration of H2O2 (μM) | DPPH (M Trolox Equivalents) | ABTS (M Trolox Equivalents) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 75.111 ± 0.476 a | 92.196 ± 3.674 b | 60.091 ± 5.233 d |
| 500 | 58.603 ± 0.825 b | 94.801 ± 5.952 b | 95.323 ± 6.370 c |
| 750 | 50.825 ± 2.651 c | 101.415 ± 0.000 b | 133.290 ± 4.550 b |
| 1000 | 40.508 ± 0.727 d | 112.238 ± 1.701 a | 167.234 ± 2.048 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.-Q.; Gao, Y.; Long, D.; Yin, J.-F.; Zeng, L.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Xu, Y.-Q. Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide Produced by Catechins on the Aroma of Tea Beverages. Foods 2022, 11, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091273
Wang J-Q, Gao Y, Long D, Yin J-F, Zeng L, Xu Y-Q, Xu Y-Q. Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide Produced by Catechins on the Aroma of Tea Beverages. Foods. 2022; 11(9):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091273
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jie-Qiong, Ying Gao, Dan Long, Jun-Feng Yin, Liang Zeng, Yan-Qun Xu, and Yong-Quan Xu. 2022. "Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide Produced by Catechins on the Aroma of Tea Beverages" Foods 11, no. 9: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091273
APA StyleWang, J. -Q., Gao, Y., Long, D., Yin, J. -F., Zeng, L., Xu, Y. -Q., & Xu, Y. -Q. (2022). Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide Produced by Catechins on the Aroma of Tea Beverages. Foods, 11(9), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091273