Low Allergenicity in Processed Wheat Flour Products Using Tannins from Agri-Food Wastes
Abstract
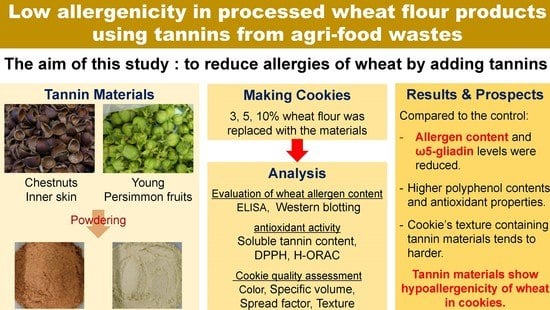
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cookie Ingredients
2.2. Cookie Production Method
2.3. Evaluation of Wheat Allergen Content
2.3.1. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.3.2. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Soluble Tannin Content (STC) and Antioxidant Activity Assay
2.5. Cookie Quality Assessment
2.5.1. Appearance and Color
2.5.2. Specific Volume
2.5.3. Spread Factor
2.5.4. Textural Properties
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wheat Protein Contents Evaluated Using ELISA
3.2. SDS-PAGE Analysis and ω5-Gliadin Detection Using Immunoblotting
3.3. STC and Antioxidant Activity
3.4. Cookie Quality
3.4.1. Color and Appearance
3.4.2. Specific Volume and Spread Factor
3.4.3. Textural Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ebisawa, M.; Ito, K.; Fujisawa, T. Japanese Society of Allergology. Japanese guidelines for food allergy 2017. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 248–264. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, E.; Kunie, K.; Matsuo, H. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 47, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kennard, L.; Thomas, I.; Rutkowski, K.; Azzu, V.; Yong, P.F.; Kasternow, B.; Hunter, H.; Cabdi, N.M.; Nakonechna, A.; Wagner, A. A multicenter evaluation of diagnosis and management of omega-5 gliadin allergy (also known as wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis) in 132 adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, H.; Morita, E.; Tatham, A.S.; Morimoto, K.; Horikawa, T.; Osuna, H.; Ikezawa, Z.; Kaneko, S.; Kohno, K.; Dekio, S. Identification of the IgE-binding epitope in ω-5 gliadin, a major allergen in wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12135–12140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, H.; Kohno, K.; Morita, E. Molecular cloning, recombinant expression and IgE-binding epitope of ω-5 gliadin, a major allergen in wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 4431–4438. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, H.; Kohno, K.; Niihara, H.; Morita, E. Specific IgE determination to epitope peptides of ω-5 gliadin and high molecular weight glutenin subunit is a useful tool for diagnosis of wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 8116–8122. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, E.; Matsuo, H.; Mihara, S.; Morimoto, K.; Savage, A.; Tatham, A. Fast ω-gliadin is a major allergen in wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2003, 33, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Palosuo, K.; Alenius, H.; Varjonen, E.; Koivuluhta, M.; Mikkola, J.; Keskinen, H.; Kalkkinen, N.; Reunala, T. A novel wheat gliadin as a cause of exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Al Kindi, M.; Tan, J.A.; Smith, A.; Heddle, R.; Kette, F.; Hissaria, P.; Smith, W. The clinical spectrum of omega-5-gliadin allergy. Intern. Med. J. 2016, 46, 710–716. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, E.; Chinuki, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Nabika, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Shiwaku, K. Prevalence of wheat allergy in Japanese adults. Allergol. Int. 2012, 61, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, M.J.; Eller, E.; Mortz, C.G.; Brockow, K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C. Wheat-dependent cofactor-augmented anaphylaxis: A prospective study of exercise, aspirin, and alcohol efficacy as cofactors. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Feldweg, A.M. Food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis: Diagnosis and management in the outpatient setting. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamada, Y.; Chinuki, Y.; Fukutomi, Y.; Nakatani, E.; Yagami, A.; Matsunaga, K.; Oda, Y.; Fukunaga, A.; Adachi, A.; Hiragun, M. Long-term dynamics of omega-5 gliadin-specific IgE levels in patients with adult-onset wheat allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 1149–1151.E3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Socha, P.; Mickowska, B.; Urminská, D.; Kačmárová, K. The use of different proteases to hydrolyze gliadins. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2015, 4, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- De Zorzi, M.; Curioni, A.; Simonato, B.; Giannattasio, M.; Pasini, G. Effect of pasta drying temperature on gastrointestinal digestibility and allergenicity of durum wheat proteins. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Kohno, K.; Takahashi, H.; Endo, T.R.; Matsuo, H.; Shiwaku, K.; Morita, E. Characterization of a hypoallergenic wheat line lacking ω-5 gliadin. Allergol. Int. 2016, 65, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koopmann, A.-K.; Schuster, C.; Torres-Rodríguez, J.; Kain, S.; Pertl-Obermeyer, H.; Petutschnigg, A.; Hüsing, N. Tannin-based hybrid materials and their applications: A review. Molecules 2020, 25, 4910. [Google Scholar]
- Arbenz, A.; Avérous, L. Chemical modification of tannins to elaborate aromatic biobased macromolecular architectures. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2626–2646. [Google Scholar]
- Schofield, P.; Mbugua, D.; Pell, A. Analysis of condensed tannins: A review. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2001, 91, 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- Tsurunaga, Y.; Onda, M. Effects of soy milk and condensed milk on astringency removal, astringency recurrence, appearance, and syneresis in persimmon paste. Acta Hortic. 2022, 1338, 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- Mateus, N.; Carvalho, E.; Luís, C.; de Freitas, V. Influence of the tannin structure on the disruption effect of carbohydrates on protein–tannin aggregates. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 513, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Tsurunaga, Y.; Takahashi, T. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity, deodorizing effect, and antibacterial activity of ‘Porotan’chestnut by-products and establishment of a compound paper. Foods 2021, 10, 1141. [Google Scholar]
- Tsurunaga, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Kanou, M.; Onda, M.; Ishigaki, M. Removal of astringency from persimmon paste via polysaccharide treatment. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10716. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, G.; Wu, Y.; Ouyang, J. Inhibitory effect of chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume) inner skin extract on the activity of α-amylase, α-glucosidase, dipeptidyl peptidase IV and in vitro digestibility of starches. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Wei, X.; Fan, M. Young astringent persimmon tannin inhibits methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from pork. LWT 2019, 100, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yaqub, S.; Farooq, U.; Shafi, A.; Akram, K.; Murtaza, M.A.; Kausar, T.; Siddique, F. Chemistry and functionality of bioactive compounds present in persimmon. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 3424025. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Ohya, M.-A.; Yokoyama, S.-I. Young persimmon fruits prevent the rise in plasma lipids in a diet-induced murine obesity model. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 2532–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, K.; Yokoyama, S.I.; Gato, N. Bile acid-binding activity of young persimmon (Diospyros kaki) fruit and its hypolipidemic effect in mice. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Dang, M.; Khalifa, I.; Du, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, C. Persimmon tannin changes the properties and the morphology of wheat gluten by altering the cross-linking, and the secondary structure in a dose-dependent manner. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109536. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, H.; Adachi, R. Japanese food allergy-labeling system and comparison with the international experience; detection and thresholds. Food Saf. 2021, 9, 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wheat/Gluten(Gliadin) ELISA Kit II. Available online: https://www.miobs.com/product/tokutei/faspek2/dl/manual_tori04.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- FASTKIT ELISA Ver. III Wheat <<Instruction Manual>>. Available online: https://www.rdc.nipponham.co.jp/kit_eng/images/fk3_elisa_wheat.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Katsube, T.; Tsurunaga, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; Furuno, T.; Yamasaki, Y. Effect of air-drying temperature on antioxidant capacity and stability of polyphenolic compounds in mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 964–969. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, T.; Hillis, W. The phenolic constituents of Prunus domestica. I.—The quantitative analysis of phenolic constituents. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1959, 10, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, Y.; Kitabatake, M.; Ouji-Sageshima, N.; Yasui, S.; Mochida, N.; Nakano, R.; Kasahara, K.; Tomoda, K.; Yano, H.; Kayano, S.I.; et al. Persimmon-derived tannin has bacteriostatic and anti-inflammatory activity in a murine model of Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183489. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanat, F.; Benchaar, C. Assessment of the effect of condensed (acacia and quebracho) and hydrolysable (chestnut and valonea) tannins on rumen fermentation and methane production in vitro. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikegami, A.; Yonemori, K.; Sugiura, A.; Sato, A.; Yamada, M. Segregation of astringency in F1 progenies derived from crosses between pollination-constant, nonastringent persimmon cultivars. HortScience 2004, 39, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, J.; Oki, T.; Takebayashi, J.; Yamasaki, K.; Takano-Ishikawa, Y.; Hino, A.; Yasui, A. Method validation by interlaboratory studies of improved hydrophilic oxygen radical absorbance capacity methods for the determination of antioxidant capacities of antioxidant solutions and food extracts. Anal. Sci. 2012, 28, 159. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, L.A.d.; Lizi, J.M.; Chagas, E.G.L.d.; Carvalho, R.A.d.; Vanin, F.M. From orange juice by-product in the food industry to a functional ingredient: Application in the circular economy. Foods 2020, 9, 593. [Google Scholar]
- Koca, A.F.; Anil, M. Effect of flaxseed and wheat flour blends on dough rheology and bread quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 1172–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S.; Khatkar, B. Cookie texture, spread ratio and sensory acceptability of cookies as a function of soluble dietary fiber, baking time and different water levels. LWT 2017, 80, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, R.; Yoshioka, Y.; Akiyama, H.; Aburatani, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Morishita, N.; Sato, H.; Mishima, T.; Gamo, R. Interlaboratory evaluation of two enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits for the detection of egg, milk, wheat, buckwheat, and peanut in foods. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Girard, A.L.; Bean, S.R.; Tilley, M.; Adrianos, S.L.; Awika, J.M. Interaction mechanisms of condensed tannins (proanthocyanidins) with wheat gluten proteins. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freitas, V.d.; Mateus, N. Nephelometric study of salivary protein–tannin aggregates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, C.; Barathieu, K.; Laguerre, M.; Schmitter, J.-M.; Fouquet, E.; Pianet, I.; Dufourc, E.J. Three-dimensional structure and dynamics of wine tannin− saliva protein complexes. A multitechnique approach. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 10385–10395. [Google Scholar]
- Fermin, B.C.; Hahm, T.; Radinsky, J.A.; Kratochvil, R.J.; Hall, J.E.; Lo, Y.M. Effect of proline and glutamine on the functional properties of wheat dough in winter wheat varieties. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, E273–E278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-T.; Park, D.-S.; Kang, S.-M.; Cho, Y.-C. Effect of fruit-load on the growth, absorption, and partitioning of inorganic nutrients in young ‘Fuyu’persimmon trees. Sci. Hortic.-Amsterdam 2010, 126, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishibori, S.; KAWAKISHI, S. Effects of dough materials on flavor formation in baked cookies. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, F.S.; Damiani, C.; de Melo, A.A.M.; Borges, P.R.S.; de Barros Vilas Boas, E.V. Incorporation of buriti endocarp flour in gluten-free whole cookies as potential source of dietary fiber. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2014, 69, 344–350. [Google Scholar]
- Jurasová, Z.; Kukurová, K. Application of citrus dietary fibre preparations in biscuit production. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 50, 182–190. [Google Scholar]
- Tabacco, E.; Borreani, G.; Crovetto, G.; Galassi, G.; Colombo, D.; Cavallarin, L. Effect of chestnut tannin on fermentation quality, proteolysis, and protein rumen degradability of alfalfa silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4736–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| STC (mg CTN eq/100 g) | L* | a* | b* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIS | 26,454 ± 1262 | 45.9 ± 0.1 | 17.7 ± 0.1 | 16.4 ± 0.1 |
| YPF | 3756 ± 175 | 76.5 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 17.2 ± 0.1 |
| Wheat flour (cake flour type) | 0 | 95.2 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 7.8 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsurunaga, Y.; Arima, S.; Kumagai, S.; Morita, E. Low Allergenicity in Processed Wheat Flour Products Using Tannins from Agri-Food Wastes. Foods 2023, 12, 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142722
Tsurunaga Y, Arima S, Kumagai S, Morita E. Low Allergenicity in Processed Wheat Flour Products Using Tannins from Agri-Food Wastes. Foods. 2023; 12(14):2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142722
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsurunaga, Yoko, Shiori Arima, Sae Kumagai, and Eishin Morita. 2023. "Low Allergenicity in Processed Wheat Flour Products Using Tannins from Agri-Food Wastes" Foods 12, no. 14: 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142722
APA StyleTsurunaga, Y., Arima, S., Kumagai, S., & Morita, E. (2023). Low Allergenicity in Processed Wheat Flour Products Using Tannins from Agri-Food Wastes. Foods, 12(14), 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142722