Microencapsulated and Ready-to-Eat Beetroot Soup: A Stable and Attractive Formulation Enriched in Nitrate, Betalains and Minerals
Abstract
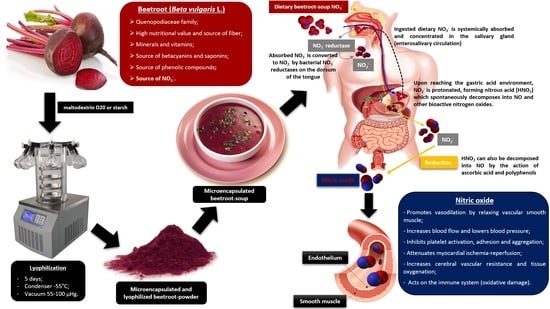
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Beetroot Soup Microparticles
2.3. Beetroot Soup Encapsulation in Starch or Maltodextrin Microparticles
2.4. Morphology and Physicochemical Characterization of Beetroot Soup Microparticles
2.5. Beetroot Soup Microparticle-Bioactive Nutrients and Minerals
2.6. Beetroot Soup Composition Analysis
2.7. Microparticle-Encapsulated Betalain Extraction and Quantification
2.8. Microbial Beetroot Soup Safety throughout 90 Days
2.9. Sensory Analysis and Purchase Intention after Beetroot Soup Production and throughout 90 Days
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Particle Size Distribution
3.2. Morphology
3.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.4. Characterization of Beetroot Soup Microparticles
3.5. Zeta Potential
3.6. Instrumental Color Analyses
3.7. NO3−, NO2−, Saponin and Mineral Contents
3.8. Final Product Characterization
3.9. Centesimal Composition and Sugar Contents
3.10. Total Betalain, Betacyanin and Betaxanthin Encapsulation Efficiencies
3.11. Microbiological Analyses (Shelf Life)
3.12. Sensory Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baião, D.D.S.; da Silva, D.V.; Del Aguila, E.M.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Nutritional, Bioactive and Physicochemical Characteristics of Different Beetroot Formulations. In Food Additives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; Volume 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lara, J.; Ashor, A.; Oggioni, C.; Ahluwalia, A.; Mathers, J.C.; Siervo, M. Effects of inorganic nitrate and beetroot supplementation on endothelial function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, C.S.; da Silva, G.A.; Perrone, D.; Vericimo, M.A.; Baião, D.D.S.; Pereira, P.R.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Del Aguila, E.M. Recovery of Antimicrobials and Bioaccessible Isoflavones and Phenolics from Soybean (Glycine max) Meal by Aqueous Extraction. Molecules 2019, 24, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trindade, L.; da Silva, D.; Baião, D.; Paschoalin, V. Increasing the Power of Polyphenols through Nanoencapsulation for Adjuvant Therapy against Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baião, D.D.S.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Alvares, T.S. Quantitative and Comparative Contents of Nitrate and Nitrite in Beta vulgaris L. by Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva, D.V.T.; Silva, F.D.O.; Perrone, D.; Pierucci, A.P.T.R.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Alvares, T.D.S.; Del Aguila, E.M.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Physicochemical, nutritional, and sensory analyses of a nitrate-enriched beetroot gel and its effects on plasmatic nitric oxide and blood pressure. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 29909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Mejia, E.G.; Zhang, Q.; Penta, K.; Eroğlu, A.; Lila, M.A. The colors of health: Chemistry, bioactivity, and market demand for colorful foods and natural food sources of colorants. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2020, 11, 145–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chazelas, E.; Pierre, F.; Druesne-Pecollo, N.; Esseddik, Y.; de Edelenyi, F.S.; Agaesse, C.; De Sa, A.; Lutchia, R.; Gigandet, S.; Srour, B.; et al. Nitrites and nitrates from food additives and natural sources and cancer risk: Results from the NutriNet-Santé cohort. Leuk. Res. 2022, 51, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.V.T.; Baião, D.D.S.; Ferreira, V.F.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Betanin as a multipath oxidative stress and inflammation modulator: A beetroot pigment with protective effects on cardiovascular disease pathogenesis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 62, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.C.; Baião, D.D.S.; Rodrigues, P.D.A.; Saint’Pierre, T.D.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Leandro, K.C.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; da Costa, M.P.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Macrominerals and Trace Minerals in Commercial Infant Formulas Marketed in Brazil: Compliance with Established Minimum and Maximum Requirements, Label Statements, and Estimated Daily Intake. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 857698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidder, S.; Webb, A.J. Vascular Effects of Dietary Nitrate (as Found in Green Leafy Vegetables and Beetroot) via the Nitrate-Nitrite-Nitric Oxide Pathway. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 677–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baião, D.D.S.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Alvares, T.S. Beetroot juice increase nitric oxide metabolites in both men and women regardless of body mass. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baião, D.D.S.; D’El-Rei, J.; Alves, G.; Neves, M.F.; Perrone, D.; Del Aguila, E.M.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Chronic effects of nitrate supplementation with a newly designed beetroot formulation on biochemical and hemodynamic parameters of individuals presenting risk factors for cardiovascular diseases: A pilot study. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 58, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baião, D.D.S.; da Silva, V.; Paschoalin, M. Beetroot, a Remarkable Vegetable: Its Nitrate and Phytochemical Contents Can be Adjusted in Novel Formulations to Benefit Health and Support Cardiovascular Disease Therapies. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baião, D.D.S.; da Silva, D.V.T.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. A Narrative Review on Dietary Strategies to Provide Nitric Oxide as a Non-Drug Cardiovascular Disease Therapy: Beetroot Formulations—A Smart Nutritional Intervention. Foods 2021, 10, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, S.; Cunha, M.R.; Marques, B.C.; D´el-Rei, J.; Baião, D.D.S.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Oigman, W.; Neves, M.F.; Medeiros, F. Acute effects of dietary nitrate on central pressure and endothelial function in hypertensive patients: A randomized, place-bo-controlled crossover study. Arq. Bras. De Cardiol. 2023, 120, e20220209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baião, D.D.S.; De Freitas, C.S.; Gomes, L.P.; Da Silva, D.; Correa, A.C.N.T.F.; Pereira, P.R.; Del Aguila, E.M.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Polyphenols from Root, Tubercles and Grains Cropped in Brazil: Chemical and Nutritional Characterization and Their Effects on Human Health and Diseases. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baião, D.D.S.; Conte, C.A., Jr.; Silva, J.T.; Paschoalin, V.; Alvares, T.S. L-Arginine Supplementation and Nitric Oxide Production:No Additional Effect When Associated to Exercise. Food Nutr. Sci. 2013, 04, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woessner, M.N.; McIlvenna, L.; De Zevallos, J.O.; Neil, C.J.; Allen, J.D. Dietary nitrate supplementation in cardiovascular health: An ergogenic aid or exercise therapeutic? Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H195–H212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, S.T.J.; Wylie, L.; Thompson, C.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Potential benefits of dietary nitrate ingestion in healthy and clinical populations: A brief review. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 19, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, R.P. Produção de Sopa Instantânea com Resíduos de Tambaqui (Colossoma Macropomum). Dissertação apresentada ao Programa de Pós-Graduação em Ciência de Alimentos da Universidade Federal do Amazonas (10 July 2015). Available online: https://tede.ufam.edu.br/handle/tede/4734 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Gharsallaoui, A.; Roudaut, G.; Chambin, O.; Voilley, A.; Saurel, R. Applications of spray-drying in microencapsulation of food ingredients: An overview. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.; Machado, F.; Moreno, M.; Nunes, C.; Coimbra, M.; Coreta-Gomes, F. Polysaccharide Structures and Their Hypocholesterolemic Potential. Molecules 2021, 26, 4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Polo, J.; Silva-Weiss, A.; Giménez, B.; Cantero-Lopez, P.; Vega, R.; Osorio, F.A. Effect of lyophilization on the physicochemical and rheological properties of food grade liposomes that encapsulate rutin. Food Res. Int. 2019, 130, 108967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosapio, V.; Lopez-Quiroga, E. Freeze-Drying Technology in Foods. Foods 2020, 9, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazuco, R.A.; Cardoso, P.M.M.; Bindaco, É.S.; Scherer, R.; Castilho, R.O.; Faraco, A.A.G.; Ruas, F.G.; Oliveira, J.P.; Guimarães, M.C.C.; De Andrade, T.U.; et al. Maltodextrin and Gum Arabic-Based Microencapsulation Methods for Anthocyanin Preservation in Juçara Palm (Euterpe edulis Martius) Fruit Pulp. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2018, 73, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, P.D.D.S.; dos Santos Baião, D.; da Silva, V.P.F.; Lemos Miguel, M.A.; Quirino Lacerda, E.C.; de Araújo Calado, V.M.; da Silva Carneiro, C.; Finotelli, P.V.; Pierucci, A.P.T.R. Microencapsulation of a craft beer, nutritional composition, antioxidant stability, and drink acceptance. LWT 2020, 133, 110104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, P.D.D.S.; Baião, D.D.S.; da Silva, V.P.F.; Calado, V.M.D.A.; Queiroz, C.; Pedrosa, C.; Valente-Mesquita, V.L.; Pierucci, A.P.T.R. Highly Stable Microparticles of Cashew Apple (Anacardium occidentale L.) Juice with Maltodextrin and Chemically Modified Starch. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 2107–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Nunes, J.; Lima, B.; Pedrosa, C.; Calado, V.; Torres, A.; Pierucci, A. Effective stabilization of CLA by microencapsulation in pea protein. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Favilla, A.L.C.; Junior, E.R.d.S.; Rodrigues, M.C.N.L.; Baião, D.D.S.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Miguel, M.A.L.; Carneiro, C.D.S.; Pierucci, A.P.T.R. Microbial and physicochemical properties of spray dried kefir microcapsules during storage. LWT 2022, 154, 112710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosulski, F.W. The centrifuge method for determining flour absorption in hard red spring wheats. Cereal Chem. 1962, 39, 344–350. [Google Scholar]
- Chandran, J.; Nisha, P.; Singhal, R.S.; Pandit, A.B. Degradation of colour in beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.): A kinetics study. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2678–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Almeida, C.C.; Baião, D.D.S.; Rodrigues, P.D.A.; Saint’Pierre, T.D.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Leandro, K.C.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; da Costa, M.P.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Toxic Metals and Metalloids in Infant Formulas Marketed in Brazil, and Child Health Risks According to the Target Hazard Quotients and Target Cancer Risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Baião, D.D.S.; Silva, F.D.O.; D’El-Rei, J.; Neves, M.F.; Perrone, D.; Del Aguila, E.M.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. A new functional beetroot formulation enhances adherence to nitrate supplementation and health outcomes in clinical practice. SDRP J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 3, 384–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonon, R.V.; Brabet, C.; Hubinger, M.D. Influência da temperatura do ar de secagem e da concentração de agente carreador sobre as propriedades físico-químicas do suco de açaí em pó. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 29, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusznierewicz, B.; Mróz, M.; Koss-Mikołajczyk, I.; Namieśnik, J. Comparative evaluation of different methods for determining phytochemicals and antioxidant activity in products containing betalains—Verification of beetroot samples. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzing, F.C.; Schieber, A.; Carle, R. Evaluation of colour properties and chemical quality parameters of cactus juices. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 216, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamee, B.F.; O’Riorda, E.D.; O’Sullivan, M. Effect of Partial Replacement of Gum Arabic with Carbohydrates on Its Microencapsulation Properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3385–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). American Water Works Association (AWWA) & Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Available online: https://www.mwa.co.th/download/file_upload/SMWW_1000-3000.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Meilgaard, M.C.; Carr, T.; Civille, G.V. Sensory Evaluation Techniques, 5th ed.; Taylor & Francis Group, an Informal Group Co., Ltd.: Boca Raton, Fl, USA, 2015; p. 464. [Google Scholar]
- Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA). Padrões Microbiológicos de Alimentos e sua Aplicação (Resolução n° 331, de 23 de Dezembro de 2019). Available online: http://antigo.anvisa.gov.br/documents/10181/4660474/RDC_331_2019_COMP.pdf/c9282210-371f-4fb6-b343-7622ca9ec493 (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Rezende, Y.R.R.S.; Nogueira, J.P.; Narain, N. Microencapsulation of extracts of bioactive compounds obtained from acerola (Malpighia emarginata DC) pulp and residue by spray and freeze drying: Chemical, morphological and chemometric characterization. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.; Kar, A.; Mohapatra, D.; Kalia, P. Encapsulation of black carrot juice using spray and freeze drying. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2015, 21, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Wang, S.; Tung, Y.-S.; Morrison, B.; Konofagou, E.E. Molecules of Various Pharmacologically-Relevant Sizes Can Cross the Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening in vivo. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhandari, B.; Bansal, N.; Zhang, M.; Schuck, P. Processes and Properties. In Handbook of Food Powder Processes and Properties; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.C.P. Caracterização e Estabilidade de Micropartículas de Antocianinas Extraídas do Bagaço da Produção do suco de Jabuticaba. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul. Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, P.D.D.S.; Baião, D.D.S.; Nanini, H.F.; da Silva, V.P.F.; Frambach, L.B.; Cabral, I.M.; Pêgo, B.; Ribeiro, B.E.; Pavão, M.S.G.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; et al. Bioactive Compounds from Pale Ale Beer Powder Attenuate Experimental Colitis in BALB/c Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashazadeh, H.; Zannou, O.; Ghellam, M.; Koca, I.; Galanakis, C.M.; Aldawoud, T.M.S. Optimization and Encapsulation of Phenolic Compounds Extracted from Maize Waste by Freeze-Drying, Spray-Drying, and Microwave-Drying Using Maltodextrin. Foods 2021, 10, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devadiga, D.; Ahipa, T. Betanin: A Red-Violet Pigment—Chemistry and Applications. Chem. Technol. Nat. Synth. Dye. Pigment. 2020, 5772, 88939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, D.; Mondal, B.; Mukherjee, K. Visible light absorption and photo-sensitizing properties of spinach leaves and beetroot extracted natural dyes. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 148, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.X.; Ong, H.C.; Andriyana, A.; Lim, S.; Pang, Y.L.; Kusumo, F.; Ngoh, G.C. Characterization and Parametric Study on Mechanical Properties Enhancement in Biodegradable Chitosan-Reinforced Starch-Based Bioplastic Film. Polymers 2022, 14, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.H.D.; Chalimah, S.; Primadona, I.; Hanantyo, M.H.G. Physical and chemical properties of corn, cassava, and potato starchs. IOP Conf. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 160, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sritham, E.; Gunasekaran, S. FTIR spectroscopic evaluation of sucrose-maltodextrin-sodium citrate bioglass. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, D.P.V.; Kurozawa, L.E. Influence of combined hydrolyzed collagen and maltodextrin as carrier agents in spray drying of cocona pulp. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2020, 23, e2019254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, R.S.; Mendonça, N.B.; Almeida, M.D.C. Hygroscopic behavior of açaí powder. Braz. Mag. Agroind. Prod. 2010, 12, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Teoh, A.; Massarotto, C.; Wibisono, R.; Wadhwa, S. Comparative analysis of fruit-based functional snack bars. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA). RDC n. 711, de 1° de Julho de 2022. Dispõe Sobre os Requisitos Sanitários dos Amidos, Biscoitos, Cereais Integrais, Cereais Processados, Farelos, Farinhas, Farinhas Integrais, Massas Alimentícias e pães. Available online: http://antigo.anvisa.gov.br/documents/10181/6482578/RDC_711_2022_.pdf/c739c4a9-6d94-424d-b27b-5ffed15474cf (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Cano-Chauca, M.; Stringheta, P.; Ramos, A.; Cal-Vidal, J. Effect of the carriers on the microstructure of mango powder obtained by spray drying and its functional characterization. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2005, 6, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.J.; Almeida, A.; Castro, A.; Domingues, L.; Besir, H. The novel Fh8 and H fusion partners for soluble protein expression in Escherichia coli: A comparison with the traditional gene fusion technology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 6779–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campelo-Felix, P.H.; Souza, H.J.B.; Figueiredo, J.D.A.; Fernandes, R.V.D.B.; Botrel, D.A.; de Oliveira, C.R.; Yoshida, M.I.; Borges, S.V. Prebiotic Carbohydrates: Effect on Reconstitution, Storage, Release, and Antioxidant Properties of Lime Essential Oil Microparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, B.; Hecht, M.; Harting, J.; Nirschl, H. Agglomeration and filtration of colloidal suspensions with DVLO interactions in simulation and experiment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estevinho, B.N.; Damas, A.M.; Martins, P.; Rocha, F. Microencapsulation of β-galactosidase with different biopolymers by a spray-drying process. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albert, K.; Tóth, C.; Verasztó, B.; Vatai, G.; Koris, A. Microencapsulation Analysis Based on Membrane Technology: Basic Research of Spherical, Solid Precursor Microcapsule Production. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2016, 60, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, M.; Mudgil, P.; Gani, A.; Hamed, F.; Masoodi, F.A.; Maqsood, S. Nano-encapsulation of catechin in starch nanoparticles: Characterization, release behavior and bioactivity retention during simulated in-vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, F.H.; e Silveira, B.M.P.; de Souza, L.L.; Duarte, A.K.C.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Pereira, K.C.; da Costa, J.M.G. Influence of wall materials on the microencapsulation of pequi oil by spray drying. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2020, 23, e2019132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khazaei, K.M.; Jafari, S.; Ghorbani, M.; Kakhki, A.H. Application of maltodextrin and gum Arabic in microencapsulation of saffron petal’s anthocyanins and evaluating their storage stability and color. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 105, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blekkenhorst, L.C.; Bondonno, N.P.; Liu, A.H.; Ward, N.C.; Prince, R.L.; Lewis, J.R.; Devine, A.; Croft, K.D.; Hodgson, J.M.; Bondonno, C.P. Nitrate, the oral microbiome, and cardiovascular health: A systematic literature review of human and animal studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 504–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapil, V.; Khambata, R.; Robertson, A.; Caulfield, M.; Ahluwalia, A. Dietary Nitrate Provides Sustained Blood Pressure Lowering in Hypertensive Patients: A randomized, phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Hypertension 2015, 65, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahadoran, Z.; Mirmiran, P.; Kabir, A.; Azizi, F.; Ghasemi, A. The Nitrate-Independent Blood Pressure–Lowering Effect of Beetroot Juice: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2017, 8, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasconcellos, J.; Silvestre, D.H.; Baião, D.D.S.; Werneck-De-Castro, J.P.; Alvares, T.S.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. A Single Dose of Beetroot Gel Rich in Nitrate Does Not Improve Performance but Lowers Blood Glucose in Physically Active Individuals. J. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 2017, 7853034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chhikara, N.; Kushwaha, K.; Sharma, P.; Gat, Y.; Panghal, A. Bioactive compounds of beetroot and utilization in food processing industry: A critical review. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroczek, A.; Kapusta, I.; Janda, B.; Janiszowska, W. Triterpene Saponin Content in the Roots of Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12397–12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Hathan, B.S. Chemical composition, functional properties and processing of beetroot—A review. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 679–684. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Beets, Raw. Vegetables and Vegetable Products, 2019. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169145/nutrients (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Mirmiran, P.; Houshialsadat, Z.; Gaeini, Z.; Bahadoran, Z.; Azizi, F. Functional properties of beetroot (Beta vulgaris) in management of cardio-metabolic diseases. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flores-Mancha, M.A.; Ruíz-Gutiérrez, M.G.; Sánchez-Vega, R.; Santellano-Estrada, E.; Chávez-Martínez, A. Characterization of Betabel Extract (Beta vulgaris) Encapsulated with Maltodextrin and Inulin. Molecules 2020, 25, 5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA). Dispõe sobre o Regulamento Técnico sobre informação nutricional complementar. Ministério da Saúde. RDC n. 54, 12 de novembro de 2012. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/anvisa/2012/rdc0054_12_11_2012.html (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Jones, J.M.; Engleson, J. Whole Grains: Benefits and Challenges. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, T.; Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R.; Bitsch, I.; Quaas, D.; Straß, G.; Bitsch, R.; Netzel, M. Urinary pharmacokinetics of betalains following consumption of red beet juice in healthy humans. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 52, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, T.; Constantinou, C.M.; Keane, K.M.; West, D.J.; Howatson, G.; Stevenson, E.J. The plasma bioavailability of nitrate and betanin from Beta vulgaris rubra in humans. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zabot, G.L.; Rodrigues, F.S.; Ody, L.P.; Tres, M.V.; Herrera, E.; Palacin, H.; Córdova-Ramos, J.S.; Best, I.; Olivera-Montenegro, L. Encapsulation of Bioactive Compounds for Food and Agricultural Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, F.; Rezende, J.D.P.; Dias, M.M.D.S.; Pinto, V.R.A.; Stringheta, P.C.; Pires, A.C.D.S.; Vidigal, M.C.T.R. Complexation of anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids with biopolymers: An approach to complexation techniques and evaluation of binding parameters. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Espinoza, M.A.; Ayed, C.; Foster, T.; Camacho, M.D.M.; Martínez-Navarrete, N. The Impact of Freeze-Drying Conditions on the Physico-Chemical Properties and Bioactive Compounds of a Freeze-Dried Orange Puree. Foods 2019, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otálora, M.C.; Carriazo, J.G.; Iturriaga, L.; Nazareno, M.A.; Osorio, C. Microencapsulation of betalains obtained from cactus fruit (Opuntia ficus-indica) by spray drying using cactus cladode mucilage and maltodextrin as encapsulating agents. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Qiao, J.; Qu, W.; Wang, M.-S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, C.; Brennan, C.S.; Qi, X. Improvement of betalains stability extracted from red dragon fruit peel by ultrasound-assisted microencapsulation with maltodextrin. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 82, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewska, E. Microencapsulated beetroot juice as a potential source of betalain. Powder Technol. 2014, 264, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, C.; Saavedra, J.; Sáenz, C.; García, P.; Robert, P. Microencapsulation of pulp and ultrafiltered cactus pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) extracts and betanin stability during storage. Food Chem. 2014, 157, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesoriere, L.; Butera, D.; Pintaudi, A.M.; Allegra, M.; A Livrea, M. Supplementation with cactus pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) fruit decreases oxidative stress in healthy humans: A comparative study with vitamin C. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahimi, P.; Mesbah-Namin, S.A.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Abedimanesh, S.; Separham, A.; Jafarabadi, M.A. Effects of betalains on atherogenic risk factors in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 8286–8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.V.T.; Pereira, A.D.; Boaventura, G.T.; Ribeiro, R.S.D.A.; Verícimo, M.A.; de Carvalho-Pinto, C.E.; Baião, D.D.S.; Del Aguila, E.M.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Short-Term Betanin Intake Reduces Oxidative Stress in Wistar Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA). Estabelece as Listas de Padrões Microbiológicos Para Alimentos (Instrução Normativa n° 60, de 23 de Dezembro de 2019). Available online: https://cvs.saude.sp.gov.br/zip/U_IN-MS-ANVISA-60_231219.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Microbiological Criteria for Foods: SUMMARY of Recommendations of FAO/OMS; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1983; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/66410/VPH_83.54.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Stone, H.; Sidel, J.L. Sensory Evaluation Practices, 2nd ed.; Tragon: Redwood City, CA, USA, 2004; p. 230. [Google Scholar]
- Battistella, N.; Colombo, J.R.; Abreu, K.C.K. A Importância da Cor nas Embalagens como Fator Influenciador no Momento da Compra; Biblioteca on-line de Ciências da Comunicação: Porto, Portugal, 2010; pp. 1–20. Available online: http://bocc.ufp.pt/pag/bocc-kraemer-embalagens.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2023).




| Diameter Tests (μm) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beetroot Soup (g) | Starch (g) | Maltodextrin (g) | Encapsulating Matrix/Nucleus Ratio (w/w) | d (0.1) | d (0.5) | d (0.9) | Span |
| 25 | 25 | - | 1:1 | 8.57 ± 1.83 e | 28.19 ± 2.19 e | 245.66 ± 2.31 d | 6.21 ± 0.31 a |
| 25 | 50 | - | 1:2 | 8.47 ± 1.29 e | 20.88 ± 2.92 f | 58.64 ± 2.22 f | 2.41 ± 0.22 c |
| 25 | 75 | - | 1:3 | 7.94 ± 1.74 e | 25.52 ± 2.55 e | 128.66 ± 2.14 e | 4.73 ± 0.48 b |
| 25 | - | 25 | 1:1 | 45.88 ± 2.08 a | 222.69 ± 2.39 a | 636.34 ± 2.04 a | 2.65 ± 0.86 c |
| 25 | - | 50 | 1:2 | 38.55 ± 2.44 b | 181.62 ± 2.11 b | 453.94 ± 2.03 b | 2.28 ± 0.49 c |
| 25 | - | 75 | 1:3 | 30.56 ± 1.66 c | 160.99 ± 2.75 c | 365.66 ± 2.01 c | 2.08 ± 0.81 c |
| 25 | - | - | 1:0 | 21.59 ± 2.11 d | 150.12 ± 2.66 d | 369.93 ± 2.16 c | 2.32 ± 0.61 c |
| Beetroot Soup (g) | Starch (g) | Maltodextrin (g) | Total Solids (%) | Beetroot Soup/Encapsulating Agent Ratio (w/w) | Yield (g/%) | Moisture (%) | aw | Solubility Index | Water Absorption Index | ZP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 25 | - | 50 | 1:1 | 38.14 ± 1.40 g/77.68% e | 3.11 ± 0.63 b | 0.05 ± 0.01c | 34.88 ± 1.55 b | 220.53 ± 1.79 b | −14.51 ± 1.14 d |
| 25 | 50 | - | 75 | 1:2 | 65.87 ± 1.62 g/88.91% a | 3.15 ± 0.54 b | 0.07 ± 0.03 c | 33.18 ± 1.31 b | 221.98 ± 1.37 b | −20.28 ± 1.04 a,b |
| 25 | 75 | - | 100 | 1:3 | 80.62 ± 1.51 g/82.13% b | 3.19 ± 0.55 b | 0.13 ± 0.07 c | 31.77 ± 2.39 b | 222.17 ± 1.85 b | −21.29 ± 0.14 a |
| 25 | - | 25 | 50 | 1:1 | 38.33 ± 1.34 g/78.1% d | 4.61 ± 0.95 a,b | 0.41 ± 0.13 b | 52.35 ± 2.38 a | 508.04 ± 1.91 a | −18.09 ± 1.06 b,c |
| 25 | - | 50 | 75 | 1:2 | 59.28 ± 1.82 g/80.25% c | 4.65 ± 0.84 a | 0.47 ± 0.11 b | 50.21 ± 1.88 a | 509.58 ± 1.88 a | −19.16 ± 0.51 b,c |
| 25 | - | 75 | 100 | 1:3 | 74.41 ± 1.19 g/75.01% f | 4.77 ± 0.75 a | 0.69 ± 0.09 a | 48.29 ± 2.72 a | 509.83 ± 1.61 a | −18.71 ± 0.15 c |
| 25 | - | - | 25 | 1:0 | 18.17 ± 0.90 g/73.6% g | 4.50 ± 0.71 a | 0.50 ± 0.15 a,b | 14.69 ± 1.83 c | 155.22 ± 1.57 c | −8.36 ± 0.01 e |
| Pure Beetroot Soup | Beetroot Soup in Starch Ratio (w/w) | Beetroot Soup in Maltodextrin Ratio (w/w) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:0 | 1:1 | 1:2 | 1:3 | 1:1 | 1:2 | 1:3 | |
| Color parameters | |||||||
| L* | 10.11 ± 2.31 | 28.95 ± 3.72 c,*,# | 35.38 ± 2.23 b,*,# | 39.37 ± 1.13 a,*,# | 14.46 ± 2.15 c | 18.27 ± 1.71 b,# | 23.06 ± 1.44 a,# |
| a* | 9.88 ± 0.29 | 4.84 ± 1.07 a,*,# | 3.97 ± 0.41 a,*,# | 2.38 ± 0.34 b,*,# | 8.84 ± 0.67 a,# | 8.07 ± 0.32 a,# | 6.91 ± 0.49 b,# |
| b* | 0.66 ± 0.17 | 1.07 ± 0.15 a,# | 1.18 ± 0.18 a,# | 1.31 ± 0.22 a,# | 0.87 ± 0.45 a | 1.03 ± 0.22 a | 1.13 ± 0.26 a,# |
| Bioactive compounds (100 g−1 fresh weight basis) | |||||||
| NO3− (mmol) | 25.10 ± 0.08 | 16.67 ± 0.19 a,*,# | 10.46 ± 0.22 b,*,# | 4.55 ± 0.16 c,# | 15.98 ± 0.33 a,# | 8.43 ± 0.09 b,# | 4.23 ± 0.17 c,# |
| NO2− (mmol) | 0.76 ± 0.11 | 0.39 ± 0.07 a,# | 0.14 ± 0.04 b,# | 0.07 ± 0.01 c,# | 0.34 ± 0.08 a,# | 0.17 ± 0.03 b,# | 0.05 ± 0.01 c,# |
| Saponins (mg) | 9922 ± 25.14 | 6544 ± 36.35 a,# | 3577 ± 45.60 b,# | 2071 ± 45.65 c,# | 6461 ± 69.72 a,# | 3480 ± 40.55 b,# | 2116 ± 40.35 c,# |
| Minerals (mg·100 g−1 fresh weight basis) | |||||||
| Na | 477 ± 10.41 | 201 ± 9.56 a,*,# | 99.59 ± 13.23 b,*,# | 78.11 ± 5.11 c,*,# | 42.14 ± 7.39 a,# | 29.83 ± 5.31 b,# | 18.35 ± 2.53 b,# |
| K | 1220 ± 18.03 | 610 ± 6.62 a,*,# | 350 ± 7.64 b,*,# | 180 ± 5.06 c,*,# | 247 ± 8.51 a,# | 180 ± 10.13 b,# | 107 ± 11.23 c,# |
| Mg | 60.72 ± 5.18 | 32.45 ± 3.75 a,*,# | 19.76 ± 2.47 b,*,# | 10.27 ± 1.35 c,*,# | 10.01 ± 0.54 a,# | 7.03 ± 0.87 b,# | 4.86 ± 1.27 b,# |
| Mn | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.05 a,*,# | 0.09 ± 0.01 b,*,# | 0.03 ± 0.03 c,*,# | 0.07 ± 0.01 a,# | 0.05 ± 0.01 b,# | 0.02 ± 0.03 c,# |
| Zn | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 0.28 ± 0.03 a,*,# | 0.15 ± 0.01 b,*,# | 0.07 ± 0.03 c,*,# | 0.07 ± 0.02 a,# | 0.03 ± 0.01 b,# | 0.02 ± 0.07 c,# |
| P | 20.64 ± 1.32 | 13.57 ± 0.98 a,*,# | 9.83 ± 0.08 b,*,# | 5.85 ± 0.04 c,*,# | 5.43 ± 2.29 a,# | 3.68 ± 1.19 a,# | 2.11 ± 1.06 a,# |
| Total | 1779 ± 7.18 | 858 ± 3.92 a,*,# | 493 ± 5.44 b,*,# | 274 ± 2.49 c,*,# | 304 ± 3.84 a,# | 221 ± 4.05 b,# | 132 ± 4.28 c,# |
| Formulation | Betacyanin (mg·g−1) | Betaxanthin (mg·g−1) | Total Betalain (mg·g−1) | Encapsulation Efficiency | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure beetroot soup | 258.1 ± 0.45 a | 142.2 ± 2.63 a | 400.2 ± 2.17 a | Betacyanin | Betaxanthin | Betalain |
| Beetroot soup in starch at 1:2 (w/w) ratio | 139.8 ± 3.21 b | 79.9 ± 4.31 b | 219.7 ± 4.92 b | 54.7 ± 0.85% a | 57.8 ± 1.50% a | 55.11 ± 0.66% a |
| Beetroot soup in maltodextrin at 1:2 (w/w) ratio | 141.5 ± 4.73 b | 82.4 ± 3.57 b | 223.9 ± 4.21 b | 55.5 ± 0.93% a | 58.4 ± 1.37% a | 56.2 ± 0.64% a |
| Sensory Attributes | Powdered Beetroot Soup | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Beetroot Soup | Beetroot Soup in Starch (Ratio 1:2 w/w) | Beetroot Soup in Maltodextrin (Ratio 1:2 w/w) | |
| 0 days | |||
| Color | 6.92 ± 0.25 b,*,# | 7.83 ± 0.33 a | 7.78 ± 0.22 a |
| Aroma | 6.51 ± 0.13 b*,# | 7.17 ± 0.18 a | 7.11 ± 0.14 a |
| Texture | 6.77 ± 0.86 a,* | 7.89 ± 0.72 a | 7.36 ± 0.50 a |
| Overall acceptability | 6.95 ± 0.72 a,*,# | 7.97 ± 0.53 a | 7.71 ± 0.46 a |
| Purchase intention | 3.91 ± 0.14 a,*,# | 4.35 ± 0.28 a | 4.20 ± 0.31 a |
| 30 days | |||
| Color | 6.77 ± 0.33 b,* | 7.87 ± 0.21 a | 7.88 ± 0.49 a |
| Aroma | 6.63 ± 0.15 b,*,# | 7.10 ± 0.11 a | 7.38 ± 0.27 a |
| Texture | 6.96 ± 0.42 a,*,# | 7.99 ± 0.64 a | 7.22 ± 0.44 a |
| Overall acceptability | 6.34 ± 0.13 b,*,# | 7.91 ± 0.72 a | 7.37 ± 0.27 a |
| Purchase intention | 4.01 ± 0.36 a,*,# | 4.19 ± 0.23 a | 4.17 ± 0.13 a |
| 60 days | |||
| Color | 6.11 ± 0.22 b | 7.37 ± 0.31 a | 7.22 ± 0.26 a |
| Aroma | 5.89 ± 0.17 b | 7.19 ± 0.52 a | 7.29 ± 0.76 a |
| Texture | 5.73 ± 0.14 b | 7.55 ± 0.88 a | 7.41 ± 0.44 a |
| Overall acceptability | 5.81 ± 0.15 b,# | 7.79 ± 0.61 a | 7.56 ± 0.23 a |
| Purchase intention | 3.21 ± 0.16 b | 4.31 ± 0.48 a | 4.19 ± 0.27 a |
| 90 days | |||
| Color | 5.80 ± 0.74 b | 7.31 ± 0.33 a | 7.14 ± 0.36 a |
| Aroma | 5.77 ± 0.46 b | 7.24 ± 0.39 a | 7.20 ± 0.33 a |
| Texture | 5.81 ± 0.13 b | 7.33 ± 0.42 a | 7.25 ± 0.31 a |
| Overall acceptability | 5.15 ± 0.41 b | 7.81 ± 0.31 a | 7.44 ± 0.28 a |
| Purchase intention | 3.24 ± 0.17 b | 4.15 ± 0.16 a | 4.05 ± 0.11 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trindade, L.R.d.; Baião, D.d.S.; da Silva, D.V.T.; Almeida, C.C.; Pauli, F.P.; Ferreira, V.F.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Paschoalin, V.M.F. Microencapsulated and Ready-to-Eat Beetroot Soup: A Stable and Attractive Formulation Enriched in Nitrate, Betalains and Minerals. Foods 2023, 12, 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071497
Trindade LRd, Baião DdS, da Silva DVT, Almeida CC, Pauli FP, Ferreira VF, Conte-Junior CA, Paschoalin VMF. Microencapsulated and Ready-to-Eat Beetroot Soup: A Stable and Attractive Formulation Enriched in Nitrate, Betalains and Minerals. Foods. 2023; 12(7):1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071497
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrindade, Lucileno Rodrigues da, Diego dos Santos Baião, Davi Vieira Teixeira da Silva, Cristine Couto Almeida, Fernanda Petzold Pauli, Vitor Francisco Ferreira, Carlos Adam Conte-Junior, and Vania Margaret Flosi Paschoalin. 2023. "Microencapsulated and Ready-to-Eat Beetroot Soup: A Stable and Attractive Formulation Enriched in Nitrate, Betalains and Minerals" Foods 12, no. 7: 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071497
APA StyleTrindade, L. R. d., Baião, D. d. S., da Silva, D. V. T., Almeida, C. C., Pauli, F. P., Ferreira, V. F., Conte-Junior, C. A., & Paschoalin, V. M. F. (2023). Microencapsulated and Ready-to-Eat Beetroot Soup: A Stable and Attractive Formulation Enriched in Nitrate, Betalains and Minerals. Foods, 12(7), 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12071497