Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Sulfamethizole Using a Reusable Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor
Abstract
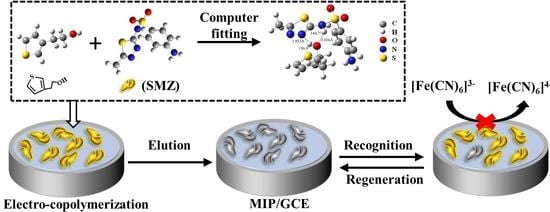
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Apparatus and Measurements
2.3. Preparation of the MIP Film-Modified Electrode (MIP/GCE)
2.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
2.5. Quantitative Determination of SMZ
2.6. Preparation of Spiked Water and Milk Samples
2.7. Quantum Chemical Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Binding between the Template Molecule and Several Monomers
3.2. Monomer Screening
3.3. Characterization of the Imprinting and Recognition Processes for SMZ
3.4. Optimization of Sensor Performance
3.5. Quantitative Determination of SMZ
3.6. Performances of the Sensor
3.7. Real Samples Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, L.; Yang, X.R.; Ji, Y.F.; Wei, J. Sulfate radical-based oxidation of the antibiotics sulfamethoxazole, sulfisoxazole, sul-fathiazole, and sulfamethizole: The role of five-membered heterocyclic rings. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Shen, M.J.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y.C. Rapid and Automated Detection of Six Contaminants in Milk Using a Centrifugal Microfluidic Platform with Two Rotation Axes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7958–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.M.; Zheng, H.; Liu, T.; Xie, Z.Z.; Luo, S.H.; Chen, G.Y.; Tian, Z.Q.; Liu, G.K. Improving SERS Sensitivity toward Trace Sulfonamides: The Key Role of Trade-Off Interfacial Interactions among the Target Molecules, Anions, and Cations on the SERS Active Surface. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 8603–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.L.; Ning, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.P.; Wang, A.J. Determination of sulfonamides in milk and egg samples by HPLC with mesoporous polymelamine-formaldehyde as magnetic solid-phase extraction adsorbent. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 4402–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abafe, O.A.; Gatyeni, P.; Matika, L. A multi-class multi-residue method for the analysis of polyether ionophores, tetracyclines and sulfonamides in multi-matrices of animal and aquaculture fish tissues by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. A 2020, 37, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.K.; Rangasamy, R.; Krishnan, A.A.; Singh, D.P.; Uke, S.P.; Malekadi, P.K.; Sengar, A.S.; Mohamed, D.P.; Gupta, A. Simultaneous determination of multi-residue and multi-class antibiotics in aquaculture shrimps by UPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2018, 260, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Duan, W.Z.; Hu, J.Y.; Zhou, L.; Pu, Q.S. 7-(Diethylamino)coumarin-3-carboxylic acid as derivatization reagent for 405 nm laser-induced fluorescence detection: A case study for the analysis of sulfonamides by capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 2019, 201, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.H.; Huang, H.C.; Jian, D.; Shan, Y.K.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, F. Rapid quantitative detection for multiple antibiotics in honey using a quantum dot microsphere immunochromatographic strip. Food Control 2021, 130, 108256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.C.; Chen, S.C.; Ma, X.C.; Shao, H.; Zhan, J.H. Galvanicdisplacement-induced codeposition of reduced-graphene-oxide/silver on alloy fibers for non-destructive SPME@SERS analysis of antibiotics. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, L.Q.; Shen, Y.J.; Guo, L.; Yin, H.; Fang, X.H.; Yang, Z.J.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.B. Superparamagnetic Nanostructures for Split-Type and Competitive-Mode Photoelectrochemical Aptasensing. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8607–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goines, S.; Dick, J.E. Review-Electrochemistry’s Potential to Reach the Ultimate Sensitivity in Measurement Science. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarchi, F.; Silva, T.R.; Winiarski, J.P.; Santana, E.R.; Vieira, I.C. Polyethylenimine-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Caffeic Acid in Aromatic Herbs. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 357. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, B.T.S.; Auroy, T.; Haupt, K. Fighting Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: Promising Strategies Orchestrated by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202106493. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.M.; Fang, Q.X.; Zhang, L.M.; Yin, H.Q.; Wu, C.C.; Zhang, W.W.; Huang, W.H.; Ni, X.N. Synthesis and characterization of an innovative molecular imprinted polymers based on CdTe QDs fluorescence sensing for selective detection of sulfadimidine. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Ma, X.H.; Pang, C.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Yin, G.H.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.P.; Luo, J.H. Novel chloramphenicol sensor based on aggregation-induced electrochemiluminescence and nanozyme amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112944. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, H.M.; Xu, Y.X.; Pan, H.Z.; Guo, K.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.Q.; Liu, D.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, C.X.; et al. A novel molecularly imprinted polymer composite based on polyaniline nanoparticles as sensitive sensors for parathion detection in the field. Food Control 2022, 133, 108638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Diao, K.S.; Qiu, D.Y.; Zeng, Y.F.; Tang, K.J.; Zhu, Y.F.; Sheng, Y.Y.; Wen, Y.P.; Li, M.F. A highly-sensitive and selective antibody-like sensor based on molecularly imprinted poly(L-arginine) on COOH-MWCNTs for electrochemical recognition and detection of deoxynivalenol. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.M.; Qin, N.; Liu, Z.S.; Han, H.; Tee, S.Y.; Guan, G.J.; Han, M.Y. Functionally Imprinted Orthorhombic WO3 center dot H2O Nanoplates for Ultrasensitive Photoelectrochemical Sensing with Excellent Selectivity. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 2394–2400. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Guo, Q.Y.; Yan, Y.; Yu, C.; Chen, M.N.; Xing, W.D.; Yan, L.; Yan, Y.S.; Wu, Y.L. Templating precise multiple binding sites: Promising molecularly imprinted membrane orchestrated by sequential surface imprinting strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.R.; Kang, T.F.; Lu, L.P.; Cheng, S.Y. Electrochemical magnetic imprinted sensor based on MWCNTs@CS/CTABr surfactant composites for sensitive sensing of diethylstilbestrol. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 818, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Zhang, L.; Dang, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.Q.; Zhang, R.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Ye, B.C. A robust electrochemical sensing of molecularly imprinted polymer prepared by using bifunctional monomer and its application in detection of cypermethrin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 127, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guney, S. Electrosynthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Poly-o-phenylenediamine on MWCNT Modified Electrode for Selective Determination of Meldonium. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.P.; Xia, Y.D.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhao, F.Q.; Zeng, B.Z. Determination of patulin using dual-dummy templates imprinted electrochemical sensor with PtPd decorated N-doped porous carbon for amplification. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, A.R.; Ghaedi, M. Synthesis of chitosan based molecularly imprinted polymer for pipette-tip solid phase extraction of Rhodamine B from chili powder samples. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharif, H.F.; Turner, N.W.; Reddy, S.M.; Sullivan, M.V. Application of thymine-based nucleobase-modified acrylamide as a functional co-monomer in electropolymerised thin-film molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) for selective protein (haemoglobin) binding. Talanta 2022, 240, 123158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.-P.; Sharma, P.S.; Sosnowska, M.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Functionalized polythiophenes: Recognition materials for chemosensors and biosensors of superior sensitivity, selectivity, and detectability. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 47, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Reut, J.; Opik, A.; Syritski, V. Sulfamethizole-imprinted polymer on screen-printed electrodes: Towards the design of a portable environmental sensor. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 320, 128600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, H.; Xu, L.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, X.; Xu, Z. Ultrasensitive determination of sulfathiazole using a molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor with CuS microflowers as an electron transfer probe and Au@COF for signal amplification. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, S.; Pang, C.; Xiong, Y.; Li, J. A Cu(II)-anchored unzipped covalent triazine framework with peroxidase-mimicking properties for molecular imprinting-based electrochemiluminescent detection of sulfaquinoxaline. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.K.; Wang, R.N.; Lu, Y.F.; Jia, M.; Yan, J.; Bian, X.J. Facile Preparation of a Bacteria Imprinted Artificial Receptor for Highly Selective Bacterial Recognition and Label-Free Impedimetric Detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, A.; Corvaglia, S.; Pompa, P.P.; Malitesta, C. An innovative and simple all electrochemical approach to functionalize electrodes with a carbon nanotubes/polypyrrole molecularly imprinted nanocomposite and its application for sulfamethoxazole analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 599, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Liu, Y.; Huang, P.C.; Wu, F.Y.; Ma, L.H. Polydopamine molecularly imprinted polymer coated on a biomimetic iron-based metal-organic framework for highly selective fluorescence detection of metronidazole. Talanta 2021, 232, 122411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, M.; Nia, P.M.; Alias, Y. Morphology and electrical properties of electrochemically synthesized pyrrole-formyl pyrrole copolymer. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraneedharan, P.; Siva, C.; Nehru, K.; Sivakumar, M. Investigations on structural, optical and electrochemical properties of blue luminescence SnO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, J.; Montes, R.; Baeza, M. Trends in electrochemical impedance spectroscopy involving nanocomposite transducers: Characterization, architecture surface and bio-sensing. TrAc-Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, A.; Chhin, D.; Nguyen, D.K.; Sawan, M. A new molecular imprinted PEDOT glassy carbon electrode for carbamazepine detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 180, 113089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, G.Q. Molecularly imprinted sensing platform based on electrochemically modified graphite paper for efficient detection of 3-monochloropropane-1,2-diol. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykstra, G.; Reynolds, B.; Smith, R.; Zhou, K.; Liu, Y.X. Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Synthesis Guided by an Integrated Data-Driven Framework for Cortisol Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 25972–25983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkorucuklu, S.P.; Sahin, Y.; Alsancak, G. Voltammetric Behaviour of Sulfamethoxazole on Electropolymerized-Molecularly Imprinted Overoxidized Polypyrrole. Sensors 2008, 8, 8463–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, J.; Yu, H.; Yan, J.; Luan, D.; Zhao, Y.; Bian, X. Reusable and universal impedimetric sensing platform for the rapid and sensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria based on bacteria-imprinted polythiophene film. Analyst 2022, 147, 4433–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Ren, H.H.; Yu, L.P. Development of molecularly imprinted photonic polymers for sensing of sulfonamides in egg white. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, A.; Corvaglia, S.; Mazzotta, E.; Pomba, P.P.; Malitesta, C. Preparation and characterization of molecularly imprinted mussel inspired film as antifouling and selective layer for electrochemical detection of sulfamethoxazole. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2018, 255, 3374–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, J.H.; Han, Q.Z.; Wei, Q. Ni(OH)2 nanoarrays based molecularly imprinted polymer electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of sulfapyridine. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2019, 287, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, A.K.; Bhand, S. Molecularly Imprinted Polyresorcinol Based Capacitive Sensor for Sulphanilamide Detection. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, S.Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, P.; Zhu, G.T.; Zhu, S.K. Net-like mesoporous carbon nanocomposites for magnetic solid-phase extraction of sulfonamides prior to their quantitation by UPLC-HRMS. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicher, S.; Grimme, S. Robust Atomistic Modeling of Materials, Organometallic, and Biochemical Systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2020, 59, 15665–15673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pracht, P.; Bohle, F.; Grimme, S. Automated exploration of the low-energy chemical space withfast quantum chemical methods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 7169–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S. Exploration of Chemical Compound, Conformer, and Reaction Space with Meta-Dynamics Simulations Based on Tight-Binding Quantum Chemical Calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 2847–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T. Molclus Program, Version 1.9. Available online: http://www.keinsci.com/research/molclus.html (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Neese, F. Software Update: The ORCA Program System, Version 4.0, WIREs ComputationalMolecular Science 8(1) (2017). Available online: https://scirp.org/reference/referencespapers.aspx?referenceid=3028762 (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Sun, Y.; Xu, L.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wang, M.; Qiao, X.; Xu, Z. Novel three-dimensionalelectrochemical sensor with dual signal amplification based on MoS2 nanosheets and high-conductiveNH2-MWCNT@COF for sulfamerazine determination. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2019, 281, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Added | Found | Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| (nM) | (Mean ± SD/nM) | (%) | |
| Water | 0 | 0 | / |
| 1 | 0.93 ± 0.21 | 92.97 | |
| 10 | 9.17 ± 0.18 | 91.69 | |
| 100 | 91.69 ± 0.09 | 98.75 | |
| Milk | 0 | 0 | / |
| 1 | 0.93 ± 0.21 | 92.97 | |
| 10 | 9.17 ± 0.38 | 91.69 | |
| 100 | 108.32 ± 0.22 | 108.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, J.; Xu, X.; Ma, Y.; Miao, J.; Bian, X. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Sulfamethizole Using a Reusable Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor. Foods 2023, 12, 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081693
Kong J, Xu X, Ma Y, Miao J, Bian X. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Sulfamethizole Using a Reusable Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor. Foods. 2023; 12(8):1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081693
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Jie, Xiaoli Xu, Yixin Ma, Junjian Miao, and Xiaojun Bian. 2023. "Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Sulfamethizole Using a Reusable Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor" Foods 12, no. 8: 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081693
APA StyleKong, J., Xu, X., Ma, Y., Miao, J., & Bian, X. (2023). Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Sulfamethizole Using a Reusable Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor. Foods, 12(8), 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081693