Enhancing the Gelation Behavior of Transglutaminase-Induced Soy Protein Isolate(SPI) through Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
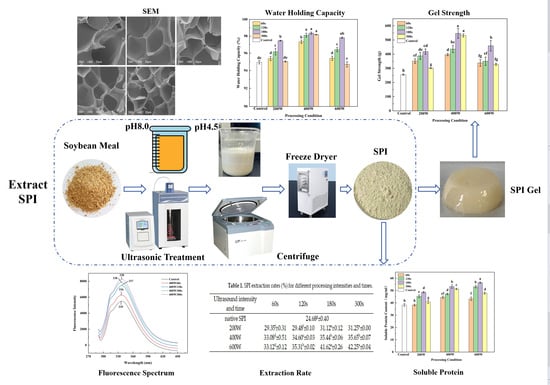
2.2. Preparation of Ultrasonic Modified SPI (UM-SPI) during Extraction Processing
2.3. Preparation of UM-SPI after (UMA-SPI) Protein Extraction
2.4. Physicochemical Properties of Ultrasonic-Modified SPI (UM-SPI)
2.4.1. Extraction Rate of Ultrasonic Modified SPI
2.4.2. Soluble Protein Content
2.4.3. Free Sulfhydryl (SH) Content
2.4.4. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
2.4.5. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.4.6. SDS-PAGE Analysis
2.4.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.5. Preparation of TGase-Catalyzed Soy Protein Isolate Gel (TCSG)
2.6. Gel Properties of UM-SPI or UMA-SPI
2.6.1. Gel Strength Analysis
2.6.2. Water Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.6.3. Rheological Measurements
2.6.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Extraction Rate
3.2. Soluble Protein
3.3. Free SH Content
3.4. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
3.5. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.7. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
3.8. Gel Strength Analysis
3.9. WHC Analysis
3.10. Rheological Measurements
3.11. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.12. Comparison of Gel Properties Modified by Ultrasound before and after SPI Extraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y.; Guo, S.; Phillips, G.O. Soy proteins: A review on composition, aggregation and emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, X.M.; Ding, X.Z.; Dong, H.Z.; Wang, W.T. Effects of High-Intensity Ultrasound Pretreatment on Structure, Properties, and Enzymolysis of Soy Protein Isolate. Molecules 2019, 24, 3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wu, J.H.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Xu, X.Y.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.F.; Huang, X.J.; Pan, S.Y. Effects of ultrasound on structural and physical properties of soy protein isolate (SPI) dispersions. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Balada, E.; Taylor, M.M.; Phillips, J.G.; Marmer, W.N.; Brown, E.M. Properties of biopolymers produced by transglutaminase treatment of whey protein isolate and gelatin. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3638–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.S.; Chen, S.S.; Li, X.J.; Luo, S.Z.; Zhong, X.Y.; Jiang, S.T.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zheng, Z. Gelation Properties of Transglutaminase-Induced Soy Protein Isolate and Wheat Gluten Mixture with Ultrahigh Pressure Pretreatment. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Jia, J.Q.; Kuang, C.; Yang, H.S. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on whey protein hydrolysis by alcalase: Thermodynamic parameters, physicochemical properties and bioactivities. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera-Barraza, O.A.; Del Toro-Sanchez, C.L.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Marquez-Rios, E. Effects of high-energy ultrasound on the functional properties of proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, A.B.; Kaur, A.; Khatkar, S.K. Restructuring of soy protein employing ultrasound: Effect on hydration, gelation, thermal, in-vitro protein digestibility and structural attributes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 132, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, N.A.; Kennedy, D.; Hogan, S.A.; Kelly, P.M.; Thapa, K.; Murphy, K.M.; Fenelon, M.A. Emulsification properties of pea protein isolate using homogenization, microfluidization and ultrasonication. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzeni, C.; Martinez, K.; Zema, P.; Arias, A.; Perez, O.E.; Pilosof, A.M.R. Comparative study of high intensity ultrasound effects on food proteins functionality. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y.; Wan, L.; Tian, M.; Pan, S. The effect of high intensity ultrasonic pre-treatment on the properties of soybean protein isolate gel induced by calcium sulfate. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.P.; Hu, T.; Feng, S.L.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, M.X.; Chu, X.Q.; Huang, X.J.; Lu, X.N.; Pan, S.Y.; et al. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on transglutaminase-catalyzed soy protein isolate cold set gel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 29, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, B.; Lamsal, B.P.; Jung, S.; van Leeuwen, J.; Pometto, A.L.; Grewell, D.; Khanal, S.K. Enhancing protein and sugar release from defatted soy flakes using ultrasound technology. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hayakawa, S.; Izumori, K. Modification of ovalbumin with a rare ketohexose through the Maillard reaction: Effect on protein structure and gel properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boatright, W.L.; Hettiarachchy, N.S. Effect of lipids on soy protein isolate solubility. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1995, 72, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhu, X.R.; Hu, T.; Cheung, I.W.Y.; Pan, S.Y.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Effect of ultrasound pre-treatment on formation of transglutaminase-catalysed soy protein hydrogel as a riboflavin vehicle for functional foods. J. Funct. Food. 2015, 19, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerati-u-rai, M.; Miriani, M.; Iametti, S.; Bonomi, F.; Corredig, M. Structural changes of soy proteins at the oil-water interface studied by fluorescence spectroscopy. Colloids Surf. B 2012, 93, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.L.; Li, L.J.; Wu, C.L.; Huang, Y.Y.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Effects of combined enzymatic and ultrasonic treatments on the structure and gel properties of soybean protein isolate. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 158, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Han, K.; Wang, S.; Muhindo, E.M.; Wei, W.; Li, J.; Wu, T.; Fersht, V.; Zhang, M. Design and structural characterization of edible double network gels based on wheat bran arabinoxylan and pea protein isolate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Bao, Z.Y.; Wang, H.; Tu, Z.C.; Sha, X.M.; Hu, Y.M. Ultrasonic pretreatment improved the physicochemical properties and riboflavin delivery ability of transglutaminase-catalyzed soy protein isolate gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittikijyothin, W.; Sampaio, P.; Goncalves, M.P. Microstructure and rheology of beta-lactoglobulin-galactomannan aqueous mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.W.; Liu, W.; McClements, D.J.; Zou, L.Q. Rheological, structural, and microstructural properties of ethanol induced cold-set whey protein emulsion gels: Effect of oil content. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Wang, Y.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M.; Jiang, H.; He, R.H.; Ma, H.L. Modification of rapeseed protein by ultrasound-assisted pH shift treatment: Ultrasonic mode and frequency screening, changes in protein solubility and structural characteristics. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 69, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.L.; Li, S.Y.; Oladejo, A.O.; Wang, Y.C.; Huang, S.F.; Zhou, C.S.; Ye, X.F.; Ma, H.L.; Duan, Y.Q. Effects of ultrasound-assisted alpha-amylase degradation treatment with multiple modes on the extraction of rice protein. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Sicaire, A.G.; Meullemiestre, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Abert-Vian, M. Ultrasound assisted extraction of food and natural products. Mechanisms, techniques, combinations, protocols and applications. A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civan, M.; Kumcuoglu, S. Green ultrasound-assisted extraction of carotenoid and capsaicinoid from the pulp of hot pepper paste based on the bio-refinery concept. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 113, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzah, C.S.; Duan, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.H.; Wen, C.T.; Zhang, J.X.; Chen, G.Y.; Ma, H.L. The effects of ultrasound assisted extraction on yield, antioxidant, anticancer and antimicrobial activity of polyphenol extracts: A review. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, A.N.; Anon, M.C. Effect of solution pH on solubility and some structural properties of soybean protein isolate films. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yildiz, G.; dos Santos, L.C.; Jiang, S.; Andrade, J.E.; Engeseth, N.J.; Feng, H. Soy protein nano-aggregates with improved functional properties prepared by sequential pH treatment and ultrasonication. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Fan, X.X.; Shao, X.Q.; Cheng, M.; Wang, C.F.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.N.; Yuan, C.Z. Modifying the physicochemical properties, solubility and foaming capacity of milk proteins by ultrasound-assisted alkaline pH-shifting treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 88, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.S.; Luo, S.Z.; Cai, J.; Zhong, X.Y.; Jiang, S.T.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zheng, Z. Transglutaminase-induced gelation properties of soy protein isolate and wheat gluten mixtures with high intensity ultrasonic pretreatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Diaz, M.D.; Barsotti, L.; Dumay, E.; Cheftel, J.C. Effects of pulsed electric fields on ovalbumin solutions and dialyzed egg white. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2332–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, L.B. The basics of thiols and cysteines in redox biology and chemistry. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 80, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Laer, K.; Hamilton, C.J.; Messens, J. Low-Molecular-Weight Thiols in Thiol-Disulfide Exchange. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1642–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.T.; Smith, B. The functional modification of legume proteins by ultrasonication: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, X.B.; Liu, J.N.; Cui, Q.; Wang, X.D.; Chen, S.; Jiang, L.Z. Relationship between Molecular Flexibility and Emulsifying Properties of Soy Protein Isolate-Glucose Conjugates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4089–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Structural and Emulsifying Properties of Soy Protein Isolate Subjected to Acid and Alkaline pH-Shifting Processes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7576–7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Zhao, M.M.; Yuan, B.E.; Zhang, Y.H.; Ren, J.Y. Effect of pH and Pepsin Limited Hydrolysis on the Structure and Functional Properties of Soybean Protein Hydrolysates. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C1871–C1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.N.; Zhao, M.M.; Sun, W.Z.; Ren, J.Y.; Cui, C. Effect of oxidation on the emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.P.H.; Omura, M.H.; Barbosa, É.; Bressan, G.C.; Vieira, É.; Coimbra, J.S.D.; de Oliveira, E.B. Combined adjustment of pH and ultrasound treatments modify techno-functionalities of pea protein concentrates. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 603, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tu, Z.C.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.X.; Liao, Z.W.; Zhang, L. LC-Orbitrap MS analysis of the glycation modification effects of ovalbumin during freeze-drying with three reducing sugar additives. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.M.; Chen, H.Q.; Xiao, L.; Chu, L.L.; Wang, S.; Wang, H. Comparison of ovalbumin glycation by microwave irradiation and conventional heating. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 116, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Q.; Min, C.; Shen, L.L.; Sun, Q.C.; Yang, P.Y.; Rui, G.; Wang, S.J.; Duan, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.H.; Haile, M. Ultrasound Pretreatment Increases the Bioavailability of Dietary Proteins by Dissociating Protein Structure and Composition. Food Biophys. 2020, 15, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafodin, H.; Soltanizadeh, N. Potential application of DBD Plasma Technique for modifying structural and physicochemical properties of Soy Protein Isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellepola, S.W.; Choi, S.M.; Ma, C.Y. Conformational study of globulin from rice (Oryza sativa) seeds by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2005, 37, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.R.; Ding, X.N.; Li, Y.L.; Ma, H.L. The aggregation, structures and emulsifying properties of soybean protein isolate induced by ultrasound and acid. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Ma, H.; Mao, S.; Zhou, H. Effects of sweeping frequency ultrasound treatment on enzymatic preparations of ACE-inhibitory peptides from zein. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 238, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapala, J.; Zisu, B.; Palmer, M.; Kentish, S.; Ashokkumar, M. Effects of ultrasound on the thermal and structural characteristics of proteins in reconstituted whey protein concentrate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Majzoobi, M.; Farahnaky, A. Ultrasound-assisted modification of functional properties and biological activity of biopolymers: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 65, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Z.; Sha, X.M.; Huang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.Y.; Tu, Z.C. Microbial transglutaminase (MTGase) modified fish gelatin-gamma-polyglutamic acid (gamma-PGA): Rheological behavior, gelling properties, and structure. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, X.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Pan, S.; Zhu, L. Acid-induced gelation behavior of soybean protein isolate with high intensity ultrasonic pre-treatments. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.Q.; Zhang, L.T.; Li, R.J.; Zheng, B.D.; Rea, M.C.; Miao, S. Effect of plant protein mixtures on the microstructure and rheological properties of myofibrillar protein gel derived from red sea bream (Pagrosomus major). Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, X.Q.; Li, L. Formation of soluble aggregates from insoluble commercial soy protein isolate by means of ultrasonic treatment and their gelling properties. J. Food Eng. 2009, 92, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; McClements, D.J.; He, M.; Fan, Z.; Li, Y.; Teng, F. Preparation of okara cellulose hydrogels using ionic liquids: Structure, properties, and performance. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 331, 115744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chu, Z.; Miao, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Qi, B.; Yan, J. Ultrasound heat treatment effects on structure and acid-induced cold set gel properties of soybean protein isolate. Food Biosci. 2021, 39, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Qu, W.; Ye, X.; Muatasim, R.; Oladejo, A.O. Enzymolysis kinetics and structural characteristics of rice protein with energy-gathered ultrasound and ultrasound assisted alkali pretreatments. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Ultrasound Intensity and Time | 60 s | 120 s | 180 s | 300 s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Un-sonicated native SPI | 24.68 g ± 0.40 | |||
| 200 W | 29.35 f ± 0.31 | 29.48 f ± 0.10 | 31.12 e ± 0.12 | 31.25 e ± 0.00 |
| 400 W | 33.08 d ± 0.51 | 34.60 c ± 0.03 | 35.44 b ± 0.06 | 35.65 b ± 0.07 |
| 600 W | 33.12 d ± 0.12 | 35.31 b ± 0.02 | 41.62 a ± 0.26 | 42.25 a ± 0.04 |
| Ultrasound Intensity and Time | 60 s | 120 s | 180 s | 300 s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Un-sonicated native SPI | 4.00 h ± 0.01 | |||
| 200 W | 4.03 h ± 0.03 | 4.05 h ± 0.06 | 5.13 g ± 0.00 | 5.47 e ± 0.01 |
| 400 W | 5.31 f ± 0.01 | 5.33 f ± 0.01 | 5.82 d ± 0.01 | 5.42 e ± 0.01 |
| 600 W | 5.84 d ± 0.00 | 6.34 c ± 0.03 | 6.49 b ± 0.00 | 6.83 a ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Tao, R.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Fan, B.; Wang, F. Enhancing the Gelation Behavior of Transglutaminase-Induced Soy Protein Isolate(SPI) through Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction. Foods 2024, 13, 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13050738
Li G, Tao R, Sun Y, Wang L, Li Y, Fan B, Wang F. Enhancing the Gelation Behavior of Transglutaminase-Induced Soy Protein Isolate(SPI) through Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction. Foods. 2024; 13(5):738. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13050738
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Gaolin, Ran Tao, Yufeng Sun, Lili Wang, Yurui Li, Bei Fan, and Fengzhong Wang. 2024. "Enhancing the Gelation Behavior of Transglutaminase-Induced Soy Protein Isolate(SPI) through Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction" Foods 13, no. 5: 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13050738
APA StyleLi, G., Tao, R., Sun, Y., Wang, L., Li, Y., Fan, B., & Wang, F. (2024). Enhancing the Gelation Behavior of Transglutaminase-Induced Soy Protein Isolate(SPI) through Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction. Foods, 13(5), 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13050738