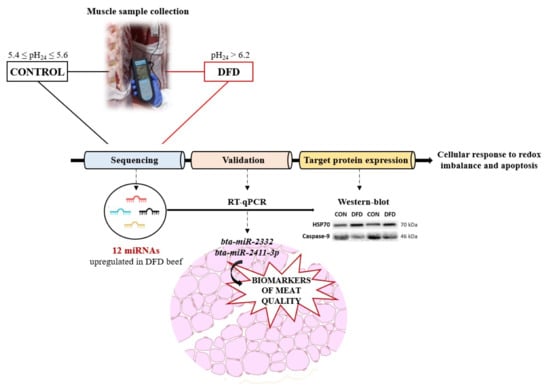
Exploring the miRNAs Profile in Dark-Cutting Beef
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Muscle Sample Collection
2.2. Meat Quality Measurements
2.3. miRNA Deep Sequencing
2.3.1. RNA Sequencing
2.3.2. Identification of Candidate Reference miRNAs for qPCR Normalization
2.3.3. Identification of miRNAs with Different Levels between the CONTROL and DFD Groups
2.4. Validation of Candidate miRNAs via Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis (RT-qPCR)
2.4.1. RT-qPCR
2.4.2. GeNorm Analysis: Selection of Stable Reference miRNA
2.4.3. Normalization of miRNA Levels
2.5. Extraction of Sarcoplasmic Proteins
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Statistical Analysis of Quality Attributes and Western Blot Data
3. Results
3.1. Meat Quality Traits
3.2. miRNA Levels in CONTROL and DFD Beef
3.3. Identification of Differentially Expressed miRNAs via Sequencing
3.4. Validation of Differentially Expressed miRNAs between CONTROL and DFD Meat
3.4.1. Selection of Reference miRNAs
3.4.2. miRNAs Selected for RT-qPCR Validation
3.5. Putative Target Genes and Functional Analysis
3.6. Protein Expression in Control and DFD Beef Based on the Validated miRNA Targets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sierra, V.; Olivan, M. Role of Mitochondria on Muscle Cell Death and Meat Tenderization. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 2013, 7, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Macia, M.; Sierra, V.; Palanca, A.; Vega-Naredo, I.; De Gonzalo-Calvo, D.; Rodríguez-González, S.; Oliván, M.; Coto-Montes, A. Autophagy during Beef Aging. Autophagy 2014, 10, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shange, N.; Gouws, P.; Hoffman, L.C. Changes in PH, Colour and the Microbiology of Black Wildebeest (Connochaetes Gnou) Longissimus Thoracis et Lumborum (LTL) Muscle with Normal and High (DFD) Muscle PH. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdstock, J.; Aalhus, J.L.; Uttaro, B.A.; López-Campos, Ó.; Larsen, I.L.; Bruce, H.L. The Impact of Ultimate PH on Muscle Characteristics and Sensory Attributes of the Longissimus Thoracis within the Dark Cutting (Canada B4) Beef Carcass Grade. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Roy, B.C.; Larsen, I.L.; Aalhus, J.L.; Dixon, W.T.; Bruce, H.L. Understanding the Quality of Typical and Atypical Dark Cutting Beef from Heifers and Steers. Meat Sci. 2017, 133, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, N.; Bach, A.; Velarde, A.; Devant, M. Association between Animal, Transportation, Slaughterhouse Practices, and Meat PH in Beef. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, M.; Martello, G.; Piccolo, S. MicroRNA Control of Signal Transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a Big Role in Gene Regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, J.; Koulmann, N.; Banzet, S. Circulating MyomiRs: A New Class of Biomarkers to Monitor Skeletal Muscle in Physiology and Medicine. J. Cachexia. Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchinovich, A.; Samatov, T.R.; Tonevitsky, A.G.; Burwinkel, B. Circulating MiRNAs: Cell-Cell Communication Function? Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, M.; Novak, J.; Bienertova-Vasku, J. Muscle-Specific MicroRNAs in Skeletal Muscle Development. Dev. Biol. 2016, 410, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Mandel, E.M.; Thomson, J.M.; Wu, Q.; Callis, T.E.; Hammond, S.M.; Conlon, F.L.; Wang, D.Z. The Role of MicroRNA-1 and MicroRNA-133 in Skeletal Muscle Proliferation and Differentiation. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, H. Identification of MicroRNA and Bioinformatics Target Gene Analysis in Beef Cattle Intramuscular Fat and Subcutaneous Fat. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 2154–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yang, J.; Jiang, R.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Lei, C.; Ma, Y.; Qi, X.; et al. MiR-148a-3p Regulates Proliferation and Apoptosis of Bovine Muscle Cells by Targeting KLF6. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 15742–15750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappeler, B.I.G.; Regitano, L.C.A.; Poleti, M.D.; Cesar, A.S.M.; Moreira, G.C.M.; Gasparin, G.; Coutinho, L.L. MiRNAs Differentially Expressed in Skeletal Muscle of Animals with Divergent Estimated Breeding Values for Beef Tenderness. BMC Mol. Biol. 2019, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollins, S.L.; Cairns, M.J. MicroRNA: Small RNA Mediators of the Brains Genomic Response to Environmental Stress. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 143, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggar, K.K.; Storey, K.B. Functional Impact of MicroRNA Regulation in Models of Extreme Stress Adaptation. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar-Malek, I.; Pomiès, L.; de la Foye, A.; Tournayre, J.; Boby, C.; Hocquette, J.F. Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Stress-Responsive Gene Networks in Cattle Muscles. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, P.K.; Therrien, D.A.; Vaughn, R.N.; Rotenberry, M.L.; Davis, B.W.; Herring, A.D.; Riley, D.G.; Cross, H.R. Differential Expression of MicroRNAs in Dark-Cutting Meat from Beef Carcasses. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, A.; Chiti, E.; Maiese, A.; Turillazzi, E.; Spinetti, I.; Area, C.; Chiara, O.S.; Cecilia, V.S. MicroRNAs: An Update of Applications in Forensic Science. Diagnostics 2020, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzitey, F.; Nurul, H. Pale Soft Exudative (PSE) and Dark Firm Dry (DFD) Meats: Causes and Measures to Reduce These Incidences—A Mini Review. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.A.; Hunt, M.C.; Barbut, S.; Claus, J.R.; Cornforth, D.P.; Joseph, P.; Brad Kim, Y.H.; Lindahl, G.; Mancini, R.A.; Nair, M.N.; et al. American Meat Science Association Guidelines for Meat Color Measurement. Meat Muscle Biol. 2022, 6, 12473, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregui, C.A.; Regenstein, J.M.; Baker, R.C. A Simple Centrifugal Method for Measuring Expressible Moisture, A Water-Binding Property of Muscle Foods. J. Food Sci. 1981, 46, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Blanco, L.; Sierra, V.; Diñeiro, Y.; Coto-Montes, A.; Oliván, M. Role of the Endoplasmic Reticulum in the Search for Early Biomarkers of Meat Quality. Meat Sci. 2023, 203, 109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, F.; Díaz-Luis, A.; Sierra, V.; Diñeiro, Y.; González, P.; García-Torres, S.; Tejerina, D.; Romero-Fernández, M.P.; Cabeza de Vaca, M.; Coto-Montes, A.; et al. What Functional Proteomic and Biochemical Analysis Tell Us about Animal Stress in Beef? J. Proteom. 2020, 218, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.L.; Jensen, J.L.; Ørntoft, T.F. Normalization of Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR Data: A Model-Based Variance Estimation Approach to Identify Genes Suited for Normalization, Applied to Bladder and Colon Cancer Data Sets. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5245–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Smyth, G.K. Small-Sample Estimation of Negative Binomial Dispersion, with Applications to SAGE Data. Biostatistics 2008, 9, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor Package for Differential Expression Analysis of Digital Gene Expression Data. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate Normalization of Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR Data by Geometric Averaging of Multiple Internal Control Genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0034.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellemans, J.; Mortier, G.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. QBase Relative Quantification Framework and Software for Management and Automated Analysis of Real-Time Quantitative PCR Data. Genome Biol. 2008, 8, R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, M.A.S.; Marzuca-Nassr, G.N.; Vitzel, K.F.; Da Justa Pinheiro, C.H.; Newsholme, P.; Curi, R. Housekeeping Proteins: How Useful Are They in Skeletal Muscle Diabetes Studies and Muscle Hypertrophy Models? Anal. Biochem. 2016, 504, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunner, S.; Sevane, N.; García, D.; Cortés, O.; Valentini, A.; Williams, J.; Mangin, B.; Cañón, J.; Levéziel, H.; Albertí, P.; et al. Association of Genes Involved in Carcass and Meat Quality Traits in 15 European Bovine Breeds. Livest. Sci. 2013, 154, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, S.; Tong, Y.; Steitz, J.A. Switching from Repression to Activation: MicroRNAs Can up-Regulate Translation. Science 2007, 318, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Ni, W.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Hazi, W.; Wang, D.; Quan, R.; et al. Expression Profiles of MicroRNAs in Skeletal Muscle of Sheep by Deep Sequencing. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Tian, F.; Yu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zan, L.; Updike, M.S.; Song, J. MiRNA-Dysregulation Associated with Tenderness Variation Induced by Acute Stress in Angus Cattle. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sonstegard, T.S.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lan, X.; Zhang, C.; Lei, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H. Altered MicroRNA Expression in Bovine Skeletal Muscle with Age. Anim. Genet. 2015, 46, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitachi, K.; Tsuchida, K. Role of MicroRNAs in Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy. Front. Physiol. 2014, 4, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Clarke, F.; Li, Y.; Purslow, P.; Warner, R. Differences in Light Scattering between Pale and Dark Beef Longissimus Thoracis Muscles Are Primarily Caused by Differences in the Myofilament Lattice, Myofibril and Muscle Fibre Transverse Spacings. Meat Sci. 2019, 149, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mao, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, H.; Wu, J.; Liao, M.; Liang, W.; Zhang, L. 5 MiRNA Expression Analyze in Post-Mortem Interval (PMI) within 48 h. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2013, 4, e190–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouali, A.; Herrera-Mendez, C.H.; Coulis, G.; Becila, S.; Boudjellal, A.; Aubry, L.; Sentandreu, M.A. Revisiting the Conversion of Muscle into Meat and the Underlying Mechanisms. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, G.S.; Deb, R.; Singh, U.; Junghare, V.; Hazra, S.; Raja, T.V.; Alex, R.; Kumar, A.; Alyethodi, R.R.; Kant, R.; et al. Identification of Differentially Expressed MicroRNAs in Sahiwal (Bos Indicus) Breed of Cattle during Thermal Stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 2018, 23, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H.; Wang, P.; Jiang, N.N. The Effect of Transportation of Broilers during Summer on the Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70, Postmortem Metabolism and Meat Quality. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Yadav, B.; Swain, D.K.; Anand, M.; Yadav, S.; Madan, A.K. Differential Expression of MiRNAs and Related MRNAs during Heat Stress in Buffalo Heifers. J. Therm. Biol. 2021, 97, 102904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskov, K.S.; Klokov, D.Y.; Li, J.; Kinsella, T.J.; Boothman, D.A. Synthesis and Functional Analyses of Nuclear Clusterin, a Cell Death Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11590–11600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltai, T. Clusterin: A Key Player in Cancer Chemoresistance and Its Inhibition. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2014, 7, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, J.T.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, W.; Yao, Z.; Chen, B.; Jiang, L.; Feng, J.; Ji, P.; Liu, G.; et al. Genomic Basis of Adaptive Evolution: The Survival of Amur Ide (Leuciscus Waleckii) in an Extremely Alkaline Environment. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Blanco, L.; Diñeiro, Y.; Díaz-Luis, A.; Coto-Montes, A.; Oliván, M.; Sierra, V. Impact of Extraction Method on the Detection of Quality Biomarkers in Normal vs. DFD Meat. Foods 2021, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Chin, E.R. Activation of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response in Skeletal Muscle of G93a*SOD1 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Mice. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delles, R.M.; Xiong, Y.L.; True, A.D.; Ao, T.; Dawson, K.A. Dietary Antioxidant Supplementation Enhances Lipid and Protein Oxidative Stability of Chicken Broiler Meat through Promotion of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würstle, M.L.; Laussmann, M.A.; Rehm, M. The Central Role of Initiator Caspase-9 in Apoptosis Signal Transduction and the Regulation of Its Activation and Activity on the Apoptosome. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Luis, A.; Díaz, F.; Diñeiro, Y.; González-Blanco, L.; Arias, E.; Coto-Montes, A.; Oliván, M.; Sierra-Sánchez, V. Nuevos Indicadores de Carnes DFD: Estrés Oxidativo, Autofagia y Apoptosis. Inf. Tec. Econ. Agrar. 2020, 117, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cai, M.C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.H.; Luo, Z.G.; Zhang, G.W.; Zuo, F.Y. MiR-1246 Is Upregulated and Regulates Lung Cell Apoptosis during Heat Stress in Feedlot Cattle. Cell Stress Chaperones 2018, 23, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Pan, W.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Shao, X.; Tang, Y.; Liang, D.; He, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; et al. The MicroRNA MiR-23b Suppresses IL-17-Associated Autoimmune Inflammation by Targeting TAB2, TAB3 and IKK-α. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Hicks, J.A.; Trakooljul, N.; Zhao, S.H. Current Knowledge of MicroRNA Characterization in Agricultural Animals. Anim. Genet. 2010, 41, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, L.; Ji, C.; Guo, X.; Chi, X. The Role of MicroRNA-23b-5p in Regulating Brown Adipogenesis and Thermogenic Program. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, J.S.; Wen, J.K.; Gao, H.T.; Zheng, B.; Qu, C.B.; Liu, K.L.; Zhang, M.L.; Gu, J.F.; Li, J.D.; et al. Silencing of MiR-193a-5p Increases the Chemosensitivity of Prostate Cancer Cells to Docetaxel. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Ji, J. Functional Study of MiR-27a in Human Hepatic Stellate Cells by Proteomic Analysis: Comprehensive View and a Role in Myogenic Tans-Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Kim, S.; Park, H.T.; Park, H.E.; Choi, J.S.; Yoo, H.S. MicroRNA Profiling in Bovine Serum According to the Stage of Mycobacterium Avium Subsp. Paratuberculosis Infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, X.; Sun, L. Micro-Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Immune-Related Microrna Regulatory Networks of Paralichthys Olivaceus Induced by Vibrio Anguillarum Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandenstein, L.; Schweizer, M.; Sedlacik, J.; Fiehler, J.; Storch, S. Lysosomal Dysfunction and Impaired Autophagy in a Novel Mouse Model Deficient for the Lysosomal Membrane Protein Cln7. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Variable | Time post mortem | CONTROL (5.4 ≤ pH24 ≤ 5.6) | DFD (pH24 ≥ 6.2) | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drip loss (%) | 48 h | 30.98 | 21.84 | 0.79 | 0.000 |
| Meat Color | |||||
| L* | 48 h | 35.74 | 30.50 | 1.93 | 0.004 |
| a* | 48 h | 10.55 | 6.94 | 0.77 | 0.000 |
| b* | 48 h | 10.90 | 6.42 | 1.29 | 0.005 |
| C* | 48 h | 15.25 | 9.74 | 1.21 | 0.000 |
| h° | 48 h | 46.10 | 39.50 | 3.50 | 0.127 |
| Samples | Total Reads | Total Small RNA Reads (%) | Small RNAs (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein Coding RNAs | rRNAs | snRNAs | snoRNAs | miRNAs | lncRNAs | misc-RNAs | scaRNAs | sRNAs | ||||
| CONTROL (5.4 ≤ pH24 ≤ 5.6) | 1B | 14,805,539 | 44 | 33.14 | 3.72 | 1.89 | 14.04 | 20.17 | 10.78 | 16.01 | 0.137 | 0.007 |
| 2B | 7,137,747 | 52 | 41.18 | 3.61 | 2.01 | 12.10 | 18.02 | 8.84 | 14.02 | 0.099 | 0.013 | |
| 3B | 11,939,843 | 45 | 29.02 | 4.96 | 1.53 | 14.79 | 29.92 | 4.69 | 14.88 | 0.108 | 0.000 | |
| 4B | 10,511,703 | 48 | 52.67 | 2.00 | 2.37 | 8.41 | 11.91 | 13.11 | 9.38 | 0.071 | 0.004 | |
| 5B | 10,419,003 | 48 | 37.32 | 4.73 | 1.06 | 12.72 | 26.53 | 4.83 | 12.64 | 0.093 | 0.003 | |
| DFD (pH24 > 6.2) | 1A | 12,854,015 | 52 | 66.83 | 1.47 | 0.57 | 1.54 | 2.14 | 21.73 | 5.65 | 0.018 | 0.001 |
| 2A | 11,807,132 | 44 | 34.61 | 3.72 | 0.87 | 6.93 | 17.08 | 20.81 | 15.81 | 0.056 | 0.004 | |
| 3A | 12,273,319 | 47 | 57.24 | 2.03 | 0.70 | 3.13 | 5.31 | 21.01 | 10.50 | 0.037 | 0.002 | |
| 4A | 16,874,438 | 51 | 81.35 | 1.12 | 0.63 | 1.18 | 0.87 | 11.21 | 3.57 | 0.022 | 0.001 | |
| 5A | 11,361,830 | 50 | 59.33 | 2.59 | 2.40 | 3.80 | 7.39 | 16.14 | 8.21 | 0.049 | 0.001 | |
| Small RNA Class | CONTROL | DFD | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rRNA | 3.81 | 2.19 | 0.695 | 0.049 |
| Protein coding RNA | 38.67 | 59.87 | 8.610 | 0.048 |
| snRNA | 1.78 | 1.04 | 0.411 | 0.118 |
| snoRNA | 12.42 | 3.32 | 1.510 | 0.000 |
| miRNA | 21.31 | 6.56 | 4.281 | 0.009 |
| lncRNA | 8.45 | 18.19 | 2.597 | 0.006 |
| misc-RNA | 13.39 | 8.75 | 2.405 | 0.101 |
| scaRNA | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.013 | 0.001 |
| sRNA | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.168 |
| miRNA | Log2 Fold Change | p-Value | FDR p-Value | Bonferroni |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bta-miR-27a-5p | 3.447 | 4.5 × 10−19 | 1.9 × 10−16 | 3.1 × 10−16 |
| bta-miR-2332 * | 3.735 | 1.6 × 10−9 | 3.5 × 10−7 | 1.1 × 10−6 |
| bta-miR-12034 | 5.117 | 1.9 × 10−8 | 2.8 × 10−6 | 1.3 × 10−5 |
| bta-miR-2411-3p * | 3.718 | 3.92 × 10−8 | 4.3 × 10−6 | 2.7 × 10−5 |
| bta-miR-11980 | 4.035 | 1.3 × 10−7 | 1.1 × 10−5 | 8.6 × 10−5 |
| bta-miR-11987 | 3.535 | 5 × 10−7 | 3.6 × 10−5 | 3.4 × 10−4 |
| bta-miR-1246 * | 2.236 | 1.3 × 10−6 | 8.3 × 10−5 | 9.1 × 10−4 |
| bta-miR-23b-5p * | 1.979 | 2 × 10−6 | 1.1 × 10−4 | 1.4 × 10−3 |
| bta-miR-12030 | 3.339 | 5.2 × 10−6 | 2.5 × 10−4 | 3.6 × 10−3 |
| bta-miR-193a-5p | 1.000 | 7.2 × 10−6 | 2.9 × 10−4 | 4.9 × 10−3 |
| bta-miR-11972 | 4.973 | 7.5 × 10−6 | 2.9 × 10−4 | 5.2 × 10−3 |
| bta-miR-2887 | 2.793 | 2.7 × 10−5 | 9.6 × 10−4 | 1.8 × 10−2 |
| microRNA | Symbol | Gene Name |
|---|---|---|
| miR-2332 | HSPA12B | 70 kDa heat shock protein 12B |
| HSPBAP1 | HSPB (27 kDa heat shock) associated protein 1 | |
| HSPA4 | 70 kDa heat shock protein 4 | |
| HSBP1 | Heat shock factor binding protein 1 | |
| HSPH1 | 105/110 kDa heat shock protein 1 | |
| DNAJA1 | DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily A, member 1 | |
| DNAJB9 | DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 9 | |
| DNAJC10 | DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 10 | |
| miR-2411-3p | GSR | Glutathione reductase |
| GPX5 | Glutathione peroxidase 5 | |
| SERP1 | Stress-associated endoplasmic reticulum protein 1 | |
| CLU | Clusterin | |
| HSPA2 | 70 kDa heat shock protein 2 | |
| TP53AIP1 | Tumor protein p53-regulated apoptosis-inducing protein 1 | |
| CASP2 | Caspase 2 | |
| CASP9 | Caspase 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Blanco, L.; Royo, L.J.; Diñeiro, Y.; García-Torres, S.; Coto-Montes, A.; Sierra, V.; Oliván, M. Exploring the miRNAs Profile in Dark-Cutting Beef. Foods 2024, 13, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060960
González-Blanco L, Royo LJ, Diñeiro Y, García-Torres S, Coto-Montes A, Sierra V, Oliván M. Exploring the miRNAs Profile in Dark-Cutting Beef. Foods. 2024; 13(6):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060960
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Blanco, Laura, Luis J. Royo, Yolanda Diñeiro, Susana García-Torres, Ana Coto-Montes, Verónica Sierra, and Mamen Oliván. 2024. "Exploring the miRNAs Profile in Dark-Cutting Beef" Foods 13, no. 6: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060960
APA StyleGonzález-Blanco, L., Royo, L. J., Diñeiro, Y., García-Torres, S., Coto-Montes, A., Sierra, V., & Oliván, M. (2024). Exploring the miRNAs Profile in Dark-Cutting Beef. Foods, 13(6), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060960