1H NMR Spectroscopy and Multivariate Analysis of Monovarietal EVOOs as a Tool for Modulating Coratina-Based Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sample Collection
| Cultivar (cv.) | Number of samples | Geographical origin |
|---|---|---|
| Coratina | 10 | Bari (Apulia, Italy) |
| Ogliarola Garganica | 10 | Gargano, Foggia (Apulia, Italy) |
| Ogliarola Barese | 10 | Bari (Apulia, Italy) |
| Cima di Mola | 10 | Bari (Apulia, Italy) |
| Picholine | 10 | Bari (Apulia, Italy) |
| Peranzana | 3 | San Severo, Foggia (Apulia, Italy) |
| Carolea | 8 | Calabria |
| Rossanese | 3 | Calabria |
| Picual | 3 | Spain |
| Kalamata | 3 | Greece |
| Koroneiki | 3 | Greece |
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. NMR Spectroscopy
2.4. NMR Data Reduction and Preprocessing
2.5. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
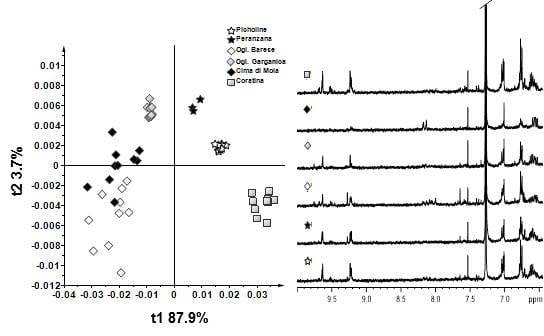
3. Results and Discussion—NMR Spectroscopy and Multivariate Statistical Analyses



4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willett, W.C.; Sacks, F.; Trichopoulou, A.; Drescher, G.; Ferro-Luzi, A.; Helsing, E.; Trichopoulos, D. Mediterranean diet pyramid a cultural model for healthy eating. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 1402S–1406S. [Google Scholar]
- Lipworth, L.; Martinez, M.E.; Angell, J.; Hsien, C.C.; Trichopoulos, D. Olive oil and human cancer, an assessment of the evidence. Prev. Med. 1997, 26, 81–190. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, R.W.; Giacosa, A.; Hull, W.E.; Haubner, R.; Wurtele, G.; Spiegelhalder, B.; Bartsch, H. Olive-oil consumption and health: The possible role of antioxidants. Lancet Oncol. 2000, 1, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimidou, M. Polyphenols and quality of virgin olive oil in retrospect. Ital. J. Food Sci. 1998, 10, 99–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bendini, A.; Cerretani, L.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Lercker, G. Phenolic molecules in virgin olive oils: A survey of their sensory properties, health effects, antioxidant activity and analytical methods. an overview of the last decade. Molecules 2007, 12, 1679–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favati, F.; Condelli, N.; Galgano, F.; Caruso, M.C. Extra virgin olive oil bitterness evaluation by sensory and chemical analyses. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.T.; Tsimidou, M. The role of volatile compounds and polyphenols in olive oil sensory quality. In Handbook of Olive Oil: Analysis and Properties; Aparicio, R., Harwood, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Chapter 12; pp. 393–455. [Google Scholar]
- Vlahov, G. Application of NMR to the study of olive oils. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 1999, 35, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coco, L.; de Pascali, S.A.; Fanizzi, F.P. NMR-metabolomic study on monocultivar and blend salento EVOOs including some from secular olive trees. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oms-Oliu, G.; Odriozola-Serrano, I.; Martín-Belloso, O. Metabolomics for assessing safety and quality of plant-derived food. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghemo, C.; Albertino, A.; Gobetto, R.; Lussiana, C.; de Maria, A.; Isocrono, D. Piedmont olive oils: Compositional characterization and discrimination from oils from other regions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Tech. 2012, 114, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coco, L.; Schena, F.P.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H Nuclear magnetic resonance study of olive oils commercially available as italian products in the United States of America. Nutrients 2012, 4, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coco, L.; Perri, E.; Cesari, G.; Muzzalupo, I.; Zelasco, S.; Simeone, V.; Schena, F.P.; Fanizzi, F.P. NMR-based metabolomic approach for EVOO from secular olive trees of Apulia region. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2013, 115, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate analysis in metabolomics. Curr. Metab. 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar]
- REGOLAMENTO (CE) N. 207/2009 DEL CONSIGLIO. Available online: http://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2009:078:0001:0042:it:PDF (accessed on 31 January 2014).
- The Commission of the European Communities. COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No 182/2009 of 6 March 2009 Amending Regulation (EC) No 1019/2002 on Marketing Standard for Olive Oil. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2009, L63, pp. 6–8. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2009:063:0006:0008:EN:PDF (accessed on 31 January 2014).
- McEwan, J. Consumer attitudes and olive oil acceptance: The potential consumer. Grasas Aceites 1994, 45, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauri, I.; Pagano, B.; Malmendal, A.; Sacchi, R.; Novellino, E.; Randazzo, A. Application of “magnetic tongue” to the sensory evaluation of extra virgin olive oil. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophoridou, S.; Dais, P.; Tseng, L.H.; Spraul, M. Separation and identification of phenolic compounds in olive oil by coupling high-performance liquid chromatography with postcolumn solid-phase extraction to nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (LC-SPE-NMR). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4667–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, R.; Luna, G. Characterisation of monovarietal virgin olive oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2002, 104, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, L.; Patumi, M.; Proietti, N.; Bassi, D.; Segre, A.L. Geographical characterization of Italian extra virgin olive oils using high-field 1H NMR spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 9, 2687–2696. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, M.T.; Alonso, M.V.; Rios, J.J.; Aparicio, R. Virgin olive oil roma: Relationship between volatile compounds and sensory attributesby chemometrics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 2925–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophoridou, S.; Dais, P. Detection and quantification of phenol compounds in olive oils by high resolution 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 633, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Production Specification. Available online: http://www.extra-virgin-olive-oil.it/dop-terra-di-bari.asp (accessed on 31 January 2014).
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Coco, L.; De Pascali, S.A.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR Spectroscopy and Multivariate Analysis of Monovarietal EVOOs as a Tool for Modulating Coratina-Based Blends. Foods 2014, 3, 238-249. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods3020238
Del Coco L, De Pascali SA, Fanizzi FP. 1H NMR Spectroscopy and Multivariate Analysis of Monovarietal EVOOs as a Tool for Modulating Coratina-Based Blends. Foods. 2014; 3(2):238-249. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods3020238
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Coco, Laura, Sandra Angelica De Pascali, and Francesco Paolo Fanizzi. 2014. "1H NMR Spectroscopy and Multivariate Analysis of Monovarietal EVOOs as a Tool for Modulating Coratina-Based Blends" Foods 3, no. 2: 238-249. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods3020238
APA StyleDel Coco, L., De Pascali, S. A., & Fanizzi, F. P. (2014). 1H NMR Spectroscopy and Multivariate Analysis of Monovarietal EVOOs as a Tool for Modulating Coratina-Based Blends. Foods, 3(2), 238-249. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods3020238