Effect of Oral Physiology Parameters on In-Mouth Aroma Compound Release Using Lipoprotein Matrices: An In Vitro Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Chemicals
2.1.2. Lipoprotein Matrix
2.2. In Vivo Mastication
2.2.1. Salivary Flow Rate
2.2.2. Electromyography Recording
2.2.3. Motion Capture
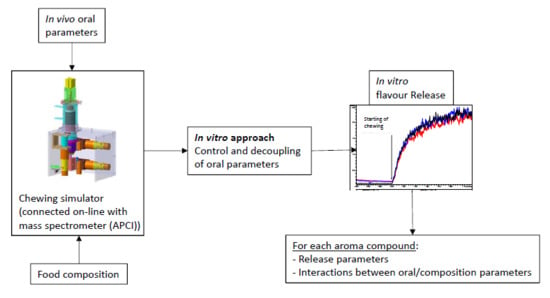
2.3. In Vitro Mastication
2.3.1. Chewing Simulator
2.3.2. Volatile Compound Release Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. In Vivo Aroma Compound Release
3.2. In Vitro Chewing Process
4. Discussion
4.1. Texture of the Lipoprotein Matrices
4.2. Effect of Bite and Shear Forces on In Vitro Aroma Compound Release
4.3. Effect of Salivary Flow Rate on In Vitro Aroma Compound Release
4.4. Effect of Oral Functions and Food Composition Interactions on In Vitro Aroma Compound Release
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salles, C.; Chagnon, M.C.; Feron, G.; Guichard, E.; Laboure, H.; Morzel, M.; Semon, E.; Tarrega, A.; Yven, C. In-mouth mechanisms leading to flavor release and perception. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. Food oral processing—A review. Food Hydrocolloid. 2009, 23, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleris, I.; Saint-Eve, A.; Semon, E.; Guillemin, H.; Guichard, E.; Souchon, I.; Le Quere, J.-L. Comparison of direct mass spectrometry methods for the on-line analysis of volatile compounds in foods. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 48, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisard, L.; Tournier, C.; Sémon, E.; Noirot, E.; Guichard, E.; Salles, C. Salt and fat contents influence the microstructure of model cheeses, chewing/swallowing and in vivo aroma release. Flav. Fragr. J. 2014, 29, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrega, A.; Yven, C.; Sémon, E.; Salles, C. In-mouth aroma compound release during cheese consumption: Relationship with food bolus formation. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Appelqvist, I.; Piyasiri, U.; Delahunty, C. In vitro measurement of volatile release in model lipid emulsions using proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2264–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, E. Interactions between flavor compounds and food ingredients and their influence on flavor perception. Food Rev. Int. 2002, 18, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paravisini, L.; Guichard, E. Interactions between aroma compounds and food matrix. In Flavour: From Food to Perception; Guichard, E., Salles, C., Morzel, M., Le Bon, A.-M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 208–234. [Google Scholar]
- Rekker, R.F. The Hydrophobic Fragmental Constant. Its Derivation and Application; Nauta, W., Rekker, R.F., Eds.; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977; pp. 1–389. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, D.; Eyres, G.T.; Piyasiri, U.; Cochet-Broch, M.; Delahunty, C.M.; Lundin, L.; Appelqvist, I.M. Effects of agar gel strength and fat on oral breakdown, volatile release, and sensory perception using in vivo and in vitro systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9093–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.C.; Eyres, G.T.; Piyasiri, U.; Delahunty, C.M. Effect of food matrix structure and composition on aroma release during oral processing using in vivo monitoring. Flav. Fragr. J. 2012, 27, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ployon, S.; Morzel, M.; Canon, F. The role of saliva in aroma release and perception. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirtz, C.; Chevalier, F.; Centeno, D.; Rofidal, V.; Egea, J.C.; Rossignol, M.; Sommerer, N.; de Periee, D.D. MS characterization of multiple forms of alpha-amylase in human saliva. Proteomics 2005, 5, 4597–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, G.H.; Dominy, N.J.; Claw, K.G.; Lee, A.S.; Fiegler, H.; Redon, R.; Werner, J.; Villanea, F.A.; Mountain, J.L.; Misra, R.; et al. Diet and the evolution of human amylase gene copy number variation. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, P.C.; Denny, P.A.; Klauser, D.K.; Hong, S.H.; Navazesh, M.; Tabak, L.A. Age-related-changes in mucins from human whole saliva. J. Dent. Res. 1991, 70, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feron, G. Unstimulated saliva: Background noise in taste molecules. J. Texture Stud. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejean, C.; Morzel, M.; Neyraud, E.; Issanchou, S.; Martin, C.; Bozonnet, S.; Urbano, C.; Schlich, P.; Hercberg, S.; Peneau, S.; et al. Salivary Composition Is Associated with Liking and Usual Nutrient Intake. PloS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyraud, E.; Palicki, O.; Schwartz, C.; Nicklaus, S.; Feron, G. Variability of human saliva composition: Possible relationships with fat perception and liking. Arch. Oral Biol. 2012, 57, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, E.; Salles, C.; Morzel, M.; Le Bon, A.-M. Flavour: From Food to Perception; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Chichester, UK; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–400. [Google Scholar]
- Gierczynski, I.; Laboure, H.; Guichard, E. In vivo aroma release of milk gels of different hardnesses: Inter-individual differences and their consequences on aroma perception. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboure, H.; Repoux, M.; Courcoux, P.; Feron, G.; Guichard, E. Inter-individual retronasal aroma release variability during cheese consumption: Role of food oral processing. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinot, P.; Arvisenet, G.; Grua-Priol, J.; Fillonneau, C.; Prost, C. Use of an artificial mouth to study bread aroma. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, C.; Benjamin, O. Models of the oral cavity for the investigation of olfaction. In Handbook of Odour; Buettner, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 303–318. [Google Scholar]
- Salles, C.; Tarrega, A.; Mielle, P.; Maratray, J.; Gorria, P.; Liaboeuf, J.; Liodenot, J.J. Development of a chewing simulator for food breakdown and the analysis of in vitro flavor compound release in a mouth environment. J. Food Eng. 2007, 82, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piggott, J.R.; Schaschke, C.J. Release cells, breath analysis and in-mouth analysis in favour research. Biomol. Eng. 2001, 17, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.J.; Henson, L.S.; Reineccius, G.A. Use of a chewing device to perform a mass balance on chewing gum components. Flav. Fragr. J. 2011, 26, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, O.; Silcock, P.; Kieser, J.A.; Waddell, J.N.; Swain, M.V.; Everett, D.W. Development of a model mouth containing an artificial tongue to measure the release of volatile compounds. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 15, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielle, P.; Tarrega, A.; Sémon, E.; Maratray, J.; Gorria, P.; Liodenot, J.J.; Liaboeuf, J.; Andrejewski, J.L.; Salles, C. From human to artificial mouth, from basics to results. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2010, 146, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floury, J.; Camier, B.; Rousseau, F.; Lopez, C.; Tissier, J.-P.; Famelart, M.-H. Reducing salt level in food: Part 1. Factors affecting the manufacture of model cheese systems and their structure-texture relationships. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, G.; Buchin, S.; Achilleos, C.; Berodier, F.; Septier, C.; Courcoux, P.; Salles, C. In vivo sodium release and saltiness perception in solid lipoproteic matrices. 1. Effect of composition and texture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5287–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, Y.; Zannoni, M.; Hunter, E.A. Texture of Parmigiano Reggiano cheese: Statistical relationships between rheological and sensory variates. Lait 1996, 76, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrega, A.; Yven, C.; Semon, E.; Salles, C. Aroma release and chewing activity during different model cheeses. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mioche, L.; Bourdiol, P.; Martin, J.F.; Noël, Y. Variations in human masseter and temporalis muscle activity related to food texture during free and side-imposed mastication. Arch. Oral Biol. 1999, 44, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odake, S.; Roozen, J.P.; Burger, J.J. Flavor release of diacetyl and 2-heptanone from cream style dressings in three mouth model systems. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 2523–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sémon, E.; Gierczynski, I.; Langlois, D.; Le Quéré, J.-L. Analysis of aroma compounds by atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation—Ion trap mass spectrometry. Construction and validation of an interface for in vivo analysis of human breath volatile content. In Proceedings of the 16th International Mass Spectrometry Conference, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK, 31 August–5 September 2003. CD-ROM Supplement, abstract 324. [Google Scholar]
- Repoux, M.; Semon, E.; Feron, G.; Guichard, E.; Laboure, H. Inter-individual variability in aroma release during sweet mint consumption. Flav. Fragr. J. 2012, 27, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijschop, R.M.A.J.; Burgering, M.J.M.; Jacobs, M.A.; Boelrijk, A.E.M. Retro-Nasal Aroma Release Depends on Both Subject and Product Differences: A Link to Food Intake Regulation? Chem. Senses 2009, 34, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pionnier, E.; Chabanet, C.; Mioche, L.; Le Quere, J.L.; Salles, C. 1. In vivo aroma release during eating of a model cheese: Relationships with oral parameters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, H.; Kohyama, K. Interactive relationship between the mechanical properties of food and the human response during the first bite. Arch. Oral Biol. 2007, 52, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Bilt, A. Assessment of mastication with implications for oral rehabilitation: A review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2011, 38, 754–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.; Throckmorton, G.S.; Buschang, P.H.; Hayasaki, H. The effects of bolus hardness on masticatory kinematics. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Food oral processing: Mechanisms and implications of food oral destruction. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ruth, S.M.; Buhr, K. Influence of mastication rate on dynamic flavour release analysed by combined model mouth/proton transfer reaction-mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 239, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ruth, S.M.; Roozen, J.P. Influence of mastication and saliva on aroma release in a model mouth system. Food Chem. 2000, 71, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, K.R.; Lucas, P.W.; Bruce, I.C. The effects of food fragmentation index on mandibular closing angle in human mastication. Arch. Oral Biol. 2000, 45, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipic, S.; Keros, J. Dynamic influence of food consistency on the masticatory motion. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghose, A.K.; Viswanadhan, V.N.; Wendoloski, J.J. Prediction of hydrophobic (lipophilic) properties of small organic molecules using fragmental methods: An analysis of ALOGP and CLOGP methods. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 3762–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromelin, A.; Andriot, I.; Kopjar, M.; Guichard, E. Thermodynamic and Structure Property Study of Liquid-Vapor Equilibrium for Aroma Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4372–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayed, C.; Lubbers, S.; Andriot, I.; Merabtine, Y.; Guichard, E.; Tromelin, A. Impact of structural features of odorant molecules on their retention/release behaviours in dairy and pectin gels. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 846–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, A.; Caporaso, N.; Civitella, A.; Sacchi, R. Effect of human saliva and sip volume of coffee brews on the release of key volatile compounds by a retronasal aroma simulator. Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisard, L.; Andriot, I.; Martin, C.; Septier, C.; Boissard, V.; Salles, C.; Guichard, E. The salt and lipid composition of model cheeses modifies in-mouth flavour release and perception related to the free sodium ion content. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blissett, A.; Hort, J.; Taylor, A.J. Influence of chewing and swallowing behavior on volatile release in two confectionery systems. J. Texture Stud. 2006, 37, 476–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| LPM 1 | LPM 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Composition for 500 g | ||
| Water (g) | 310 (62) | 275 (55) |
| Anhydrous milk fat (g) | 61.5 (12.3) | 110 (22) |
| Milk powder (g) | 123.5 (24.7) | 110 (22) |
| NaCl (g) | 5 (1) | 5 (1) |
| Aromatic solution a (mL) | 0.5 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.1) |
| Rennet b (mL) | 4.8 (0.96) | 4.8 (0.96) |
| Fat/Milk Protein powder | 0.5 | 1 |
| Rheological characteristics | ||
| MD (kPa) | 32.78 * | 44.38 * |
| Df (-) | 0.42 | 0.40 |
| Cf (kPa) | 23.36 | 23.88 |
| Wf (kJ/m3) | 4.14 | 4.34 |
| Subject | Product | Salivary Flow Rate (mL/s) | Chewing Duration (s) | Total Work of Muscle (mV s) | Number of Chewing Cycles | Mandible Force (daN) | Shearing Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | LPM1 | 13.5 ± 2.9 | 1.01 ± 0.31 | 25.0 ± 8.5 | 13.3 ± 1.1 | 2.6 ± 0.4 | |
| LPM2 | 4.0 ± 0.4 | 15.1 ± 4.9 | 1.06 ± 0.13 | 21.3 ± 4.0 | 11.5 ± 0.5 | 2.7 ± 0.6 | |
| B | LPM1 | 23.1 ± 6.7 | 3.48 ± 0.25 | 33.7 ± 7.0 | 21.6 ± 1,5 | 5.0 ± 0.5 | |
| LPM2 | 2.8 ± 0.2 | 24.9 ± 0.7 | 3.75 ± 0.23 | 38.0 ± 0 | 20.4 ± 0.5 | 4.7 ± 0.5 | |
| C | LPM1 | 28.0 ± 2.4 | 2.92 ± 0.19 | 39.0 ± 3.6 | 16.4 ± 0.4 | 3.1 ± 1.5 | |
| LPM2 | 3.5 ± 0.2 | 23.7 ± 0.8 | 2.60 ± 0.16 | 33.7 ± 3.1 | 16.9 ± 0.8 | 3.0 ± 0.3 |
| Ions (m/z) | Release Parameters | F | p | Subject Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 89 | Cmax | 5.66 | 0.018 | B > (C = A) |
| RR | 7.44 | 0.007 | B > (C = A) | |
| 115 | Cmax | 7.71 | 0.007 | (B = C) > A |
| RR | 9.36 | <0.001 | B > (C = A) | |
| 117 | Cmax | 5.47 | 0.021 | B ≥ C ≥ A (B > A) |
| RR | 5.44 | 0.021 | B ≥ A ≥ C (B > C) | |
| 129 | Cmax | 5.98 | 0.015 | C ≥ B ≥ A (C > A) |
| RR | 7.98 | 0.006 | (B = A) > C | |
| 143 | Cmax | 5.88 | 0.016 | (B = C)> A |
| RR | 7.34 | 0.008 | B ≥ A ≥ C (B > C) | |
| RR | 9.31 | 0.003 | Subject*LPM: B-LPM2 > B-LMP1 | |
| 145 | RR | 4.58 | 0.033 | B ≥ A ≥ C (B > C) |
| Compound (Log P) | Butanoic Acid (0.918) | Ethyl Butanoate (1.492) | 2-Heptanone (1.931) | Ethyl Hexanoate (2.405) | 3-Octanone (2.598) | 2-Nonanone (2.843) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/z | 89 | 115 | 117 | 145 | 129 | 143 | |||||||
| Cmax | RR | Cmax | RR | Cmax | RR | Cmax | RR | Cmax | RR | Cmax | RR | ||
| BF | F | 15.77 | 7.09 | 5.02 | 26.56 | ||||||||
| p-value | 0.0005 | 0.0139 | 0.0356 | <0.0001 | |||||||||
| SA | F | 23.10 | 12.51 | 8.92 | 9.17 | 5.22 | |||||||
| p-value | <0.0001 | 0.0017 | 0.0064 | 0.0058 | 0.0315 | ||||||||
| SF | F | 13.89 | 7.24 | 13.30 | 6.30 | ||||||||
| p-value | <0.0001 | 0.0035 | 0.0001 | 0.0063 | |||||||||
| LPM*SA | F | 6.04 | |||||||||||
| p-value | 0.0216 | ||||||||||||
| LPM*SF | F | 6.11 | 7.19 | 6.20 | 6.95 | ||||||||
| p-value | 0.0213 | 0.031 | 0.0201 | 0.0145 | |||||||||
| SF*SA | F | 5.59 | 5.55 | 5.62 | 5.97 | ||||||||
| p-value | 0.0101 | 0.0105 | 0.0099 | 0.0078 | |||||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarrega, A.; Yven, C.; Semon, E.; Mielle, P.; Salles, C. Effect of Oral Physiology Parameters on In-Mouth Aroma Compound Release Using Lipoprotein Matrices: An In Vitro Approach. Foods 2019, 8, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8030106
Tarrega A, Yven C, Semon E, Mielle P, Salles C. Effect of Oral Physiology Parameters on In-Mouth Aroma Compound Release Using Lipoprotein Matrices: An In Vitro Approach. Foods. 2019; 8(3):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8030106
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarrega, Amparo, Claude Yven, Etienne Semon, Patrick Mielle, and Christian Salles. 2019. "Effect of Oral Physiology Parameters on In-Mouth Aroma Compound Release Using Lipoprotein Matrices: An In Vitro Approach" Foods 8, no. 3: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8030106
APA StyleTarrega, A., Yven, C., Semon, E., Mielle, P., & Salles, C. (2019). Effect of Oral Physiology Parameters on In-Mouth Aroma Compound Release Using Lipoprotein Matrices: An In Vitro Approach. Foods, 8(3), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8030106