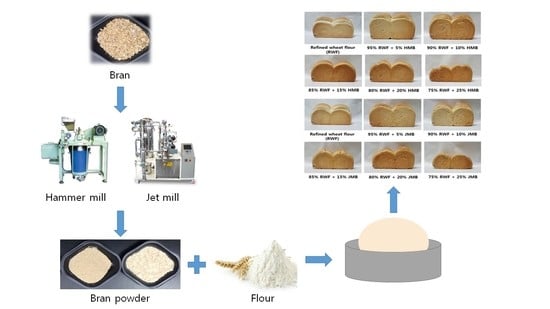
Characteristics of Bread Made of Various Substitution Ratios of Bran Pulverized by Hammer Mill or Jet Mill
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. Microstructure of Bran and Dough with Various Substitution Ratios of Bran by Scanning Electron Micrograph (SEM)
2.4. Evaluation of Dough Characteristics
2.5. Preparation of Bread and Physical Characteristics of Bread
2.6. Free Phenolic Compounds Extraction
2.7. 2,2′-Azino-bis (3-ethylbenz-thiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) Radical Scavenging Activity
2.8. Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composition of Wheat Bran Pulverized by a Hammer Mill or Jet Mill and that of Wheat Flour Substituted with Various Ratios of Bran
3.2. Dough Characteristics by Mixolab®
3.3. Characteristics of Bread
3.4. Antioxidant Activity of Bread
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dewettinck, K.; Van Bockstaele, F.; Kühne, B.; Van de Walle, D.; Courtens, T.; Gellynck, X. Nutritional value of bread: Influence of processing, food interaction and consumer perception. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 48, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Harnly, J.M.; Chen, P. Differentiation of whole grain from refined wheat (T. aestivum) flour using lipid profile of wheat bran, germ, and endosperm with UHPLC-HRAM mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6189–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.W.; Smith, B.M.; Gustafson, N.J. Health benefits and practical aspects of high-fiber diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 59, 1242S–1247S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaoğlu, M.M. Effect of baking procedure and storage on the pasting properties and staling of part-baked and rebaked wheat bran bread. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2006, 41, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hoseney, R.C. Principles of Cereal Science and Technology; American Association of Cereal Chemists (AACC): St Paul, MN, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hemdane, S.; Jacobs, P.J.; Dornez, E.; Verspreet, J.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. Wheat (triticum aestivum l.) bran in bread making: A critical review. Compr 2016, 15, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.H. Whole grain phytochemicals and health. J. Cereal Sci. 2007, 46, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobota, A.; Rzedzicki, Z.; Zarzycki, P.; Kuzawińska, E. Application of common wheat bran for the industrial production of high-fibre pasta. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2015, 50, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccoritti, R.; Terracciano, G.; Cammerata, A.; Sgrulletta, D.; Del Frate, V.; Gazza, L.; Nocente, F. Hydrothermal grain pre-processing and ultra-fine milling for the production of durum wheat flour fractions with high nutritional value. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2018, 24, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccoritti, R.; Nocente, F.; Sgrulletta, D.; Gazza, L. Cooking quality, biochemical and technological characteristics of bran-enriched pasta obtained by a novel pasta-making process. LWT 2019, 101, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhu, W.; Pei, Y.; Ai, Z.; Chen, J. Effects of wheat bran with different colors on the qualities of dry noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 58, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Chun, Y.G.; Cho, A.R.; Park, D.J. Reduction in fat uptake of doughnut by microparticulated wheat bran. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozer, N.; Cicerelli, L.; Heiniö, R.-L.; Poutanen, K. Effect of wheat bran addition on in vitro starch digestibility, physico-mechanical and sensory properties of biscuits. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, J.S.; Al-Hooti, S.N.; Al-Saqer, J.M. Effect of adding wheat bran and germ fractions on the chemical composition of high-fiber toast bread. Food Chem. 1999, 67, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; OSATAKE, H. A new drying method of biological specimens for scanning electron microscopy: The t-butyl alcohol freeze-drying method. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 1988, 51, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banu, I.; Stoenescu, G.; Ionescu, V.S.; Aprodu, I. Effect of the addition of wheat bran stream on dough rheology and bread quality. Ann. Univ. Dunarea Jos Galati. Fascicle VI. Food Technol. 2012, 36, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.S.; Park, S.H.; Ghafoor, K.; Hwang, S.Y.; Park, J. Quality and antioxidant properties of bread containing turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) cultivated in south korea. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, N.N.; Barron, C.; Gaiani, C.; Dufour, C.; Micard, V. Ultra-fine grinding increases the antioxidant capacity of wheat bran. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Hao, Z.G.; Zhou, K.Q.; Luther, M.; Costa, J.; Yu, L.L. Carotenoid, tocopherol, phenolic acid, and antioxidant properties of maryland-grown soft wheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6649–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravacos, G.D.; Kostaropoulos, A.E. Handbook of Food Processing Equipment, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 149–232. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, J.; Al-Jassar, S.; Thomas, L. A comparison in rheological, thermal, and structural properties between indian basmati and egyptian giza rice flour dispersions as influenced by particle size. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 48, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.; Govindan, V. Shadow detection and removal from a single image using lab color space. Cybern. Inf. Technol. 2013, 13, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, I.; Kang, C.S.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, S.L. Classification of 31 korean wheat (triticum aestivum l.) cultivars based on the chemical compositions. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 21, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmiele, M.; Jaekel, L.Z.; Patricio, S.M.C.; Steel, C.J.; Chang, Y.K. Rheological properties of wheat flour and quality characteristics of pan bread as modified by partial additions of wheat bran or whole grain wheat flour. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2012, 47, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Fei, M.J.; Shi, C.L.; Tian, J.C.; Sun, C.L.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Z.; Dong, H.X. Effect of particle size and addition level of wheat bran on quality of dry white chinese noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 53, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozendaal, H.; Abu-Hardan, M.; Frazier, R.A. Thermogravimetric analysis of water release from wheat flour and wheat bran suspensions. J. Food Eng. 2012, 111, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.K.; Yoo, B.H.; Son, D.H.; Kwon, D.J.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, Y.H. Rheological properties of dough added with barley bran. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 37, 751–756. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, M.; Ronda, F.; Blanco, C.A.; Caballero, P.A.; Apesteguia, A. Effect of dietary fibre on dough rheology and bread quality. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 216, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Jiménez, S.; Ruiz, E.; Oliete, B. Effect of extruded wheat bran on dough rheology and bread quality. LWT 2011, 44, 2231–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Rosell, C.M.; de Barber, C.B. Effect of the addition of different fibres on wheat dough performance and bread quality. Food Chem. 2002, 79, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubat, A. A new aacc international approved method to measure rheological properties of a dough sample. Cereal Foods World 2010, 55, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koksel, H.; Kahraman, K.; Sanal, T.; Ozay, D.S.; Dubat, A. Potential utilization of mixolab for quality evaluation of bread wheat genotypes. Cereal Chem. 2009, 86, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noort, M.W.; van Haaster, D.; Hemery, Y.; Schols, H.A.; Hamer, R.J. The effect of particle size of wheat bran fractions on bread quality–evidence for fibre–protein interactions. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 52, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phimolsiripol, Y.; Mukprasirt, A.; Schoenlechner, R. Quality improvement of rice-based gluten-free bread using different dietary fibre fractions of rice bran. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.-K. Effect of barley bran flour addition on the quality of bread. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 37, 746–750. [Google Scholar]
- Hoseney, R.; Finney, K.; Pomeranz, Y. Functional (breadmaking) and biochemical properties of wheat flour components. Vi. Gliadin-lipid-glutenin interaction in wheat gluten. Cereal Chem. 1970, 47, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Helmerich, G.; Koehler, P. Functional properties of individual classes of phospholipids in breadmaking. J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 42, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özboy, Ö.; Köksel, H. Unexpected strengthening effects of a coarse wheat bran on dough rheological properties and baking quality. J. Cereal Sci. 1997, 25, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelles, E.M.; Randall, P.G.; Taylor, J.R. Improvement of brown bread quality by prehydration treatment and cultivar selection of bran. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kock, S.; Taylor, J.; Taylor, J. Effect of heat treatment and particle size of different brans on loaf volume of brown bread. LWT 1999, 32, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyer, M.È.; Gélinas, P. Bran characteristics and wheat performance in whole wheat bread. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2009, 44, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Penella, J.M.; Laparra, J.M.; Sanz, Y.; Haros, M. Influence of added enzymes and bran particle size on bread quality and iron availability. Cereal Chem. 2012, 89, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Hera, E.; Rosell, C.M.; Gomez, M. Effect of water content and flour particle size on gluten-free bread quality and digestibility. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dziki, D.; Rozylo, R.; Gawlik-Dziki, U.; Swieca, M. Current trends in the enhancement of antioxidant activity of wheat bread by the addition of plant materials rich in phenolic compounds. Trends Food Sci Tech 2014, 40, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, K.U.; Rao, U.J.S.P.; Leelavathi, K.; Rao, P.H. Distribution of enzymes in wheat flour mill streams. J. Cereal Sci. 2001, 34, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunenc, A.; Tavakoli, H.; Seetharaman, K.; Mayer, P.M.; Fairbanks, D.; Hosseinian, F. Stability and antioxidant activity of alkyresorcinols in breads enriched with hard and soft wheat brans. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, D.; Kruger, J. Simple phenolic acids in flours prepared from canadian wheat: Relationship to ash content, color, and polyphenol oxidase activity. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Sudheer, A.R.; Menon, V.P. Ferulic acid: Therapeutic potential through its antioxidant property. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2007, 40, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sairam, S.; Krishna, A.G.G.; Urooj, A. Physico-chemical characteristics of defatted rice bran and its utilization in a bakery product. J. Food Sci. Tech. Mys 2011, 48, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Type of Bran | Mean Particle Size *** (µm) | Color | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L *** | a *** | b *** | ||
| Bran | >150 | 64.07 ± 0.31 c | 6.90 ± 0.12 a | 18.36 ± 0.19 b |
| HMB | 119.71 ± 3.13 a | 74.42 ± 0.31 b | 4.64 ± 0.26 b | 19.86 ± 0.61 a |
| JMB | 25.78 ± 0.53 b | 78.37 ± 1.31 a | 2.51 ± 0.03 c | 15.42 ± 0.18 c |
| Type of Bran | Bran (%) | Protein (%, db) *** | TDF (%, db) *** | Wet Gluten (%, 14% mb) *** | Ash (%, db) *** | Color | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L *** | a *** | b *** | ||||||
| RWF | 0 | 10.75 ± 0.04 h | 1.80 ± 0.19 j | 24.70 ± 0.15 a | 0.67 ± 0.10 h | 94.24 ± 0.35 a | 0.27 ± 0.03 g | 8.86 ± 0.05 e |
| HMB | 5 | 11.86 ± 0.10 g | 4.01 ± 0.34 i | 23.05 ± 1.12 ab | 0.74 ± 0.11 gh | 91.97 ± 0.56 b | 0.89 ± 0.10 f | 8.93 ± 0.33 e |
| 10 | 12.25 ± 0.06 e | 7.19 ± 0.37 g | 23.14 ± 1.88 ab | 1.10 ± 0.07 f | 91.55 ± 0.44 bc | 1.23 ± 0.24 de | 9.97 ± 0.22 d | |
| 15 | 12.56 ± 0.06 c | 9.54 ± 0.36 e | 19.80 ± 0.41 cde | 1.36 ± 0.09 de | 90.33 ± 0.25 cd | 1.68 ± 0.24 bc | 11.39 ± 0.32 c | |
| 20 | 12.86 ± 0.02 b | 14.21 ± 0.61 b | 18.26 ± 0.52 de | 1.61 ± 0.04 bc | 88.57 ± 1.19 ef | 1.98 ± 0.36 a | 11.08 ± 0.46 c | |
| 25 | 13.17 ± 0.12 a | 15.61 ± 0.22 a | 18.79 ± 0.27 de | 1.88 ± 0.13 a | 88.44 ± 0.55 ef | 1.79 ± 0.06 ab | 10.96 ± 0.44 c | |
| JMB | 5 | 12.08 ± 0.04 f | 2.42 ± 0.47 j | 21.91 ± 0.82 abc | 0.73 ± 0.08 gh | 89.60 ± 0.16 d | 0.88 ± 0.06 f | 10.35 ± 0.21 d |
| 10 | 12.10 ± 0.05 e | 6.07 ± 0.38 h | 20.55 ± 0.96 bcde | 0.96 ± 0.10 fg | 89.11 ± 0.39 de | 1.16 ± 0.04 e | 11.34 ± 0.03 c | |
| 15 | 12.36 ± 0.05 de | 8.23 ± 0.25 f | 20.64 ± 1.74 bcd | 1.16 ± 0.05 ef | 88.64 ± 0.45 ef | 1.42 ± 0.06 cde | 12.16 ± 0.21 b | |
| 20 | 12.51 ± 0.05 cd | 10.69 ± 0.32 d | 17.67 ± 0.86 e | 1.47 ± 0.03 cd | 88.24 ± 0.18 f | 1.47 ± 0.01 cd | 12.22 ± 0.07 b | |
| 25 | 12.79 ± 0.03 b | 13.12 ± 0.13 c | 13.63 ± 0.67 f | 1.84 ± 0.02 ab | 87.84 ± 0.61 f | 1.65 ± 0.04 bc | 12.87 ± 0.10 a | |
| Type of Bran | Bran (%) | Torque (Nm) | Water Absorption (%) *** | Stability (min) | Dough Development Time (min) ** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 ** | C2 *** | C3 * | C4 *** | C5 ** | |||||
| RWF | 0 | 1.12 bcde | 0.47 d | 1.82 d | 1.32 c | 2.69 de | 58.10 ± 0.42 e | 7.19 ± 0.97 | 1.70 ± 0.49 d |
| HMB | 5 | 1.08 e | 0.50 cd | 1.86 bcd | 1.75 ab | 3.06 ab | 59.00 ± 0.28 e | 8.18 ± 0.21 | 2.73 ± 0.94 bcd |
| 10 | 1.12 bcde | 0.54 bc | 1.91 abc | 1.76 a | 2.95 abc | 61.05 ± 0.64 d | 8.18 ± 0.18 | 3.50 ± 0.18 bcd | |
| 15 | 1.13 bcd | 0.54 bc | 1.91 abc | 1.68 ab | 2.71 cde | 62.55 ± 0.78 c | 8.24 ± 0.08 | 3.51 ± 0.20 bcd | |
| 20 | 1.15 abc | 0.57 ab | 1.93 ab | 1.67 ab | 2.72 cde | 64.15 ± 0.49 b | 8.19 ± 0.09 | 5.06 ± 0.18 ab | |
| 25 | 1.20 a | 0.60 a | 1.96 a | 1.64 b | 2.73 cde | 65.40 ± 0.42 b | 7.43 ± 0.42 | 6.33 ± 0.22 a | |
| JMB | 5 | 1.10 de | 0.50 cd | 1.87 bcd | 1.78 a | 3.09 a | 59.15 ± 0.35 e | 7.95 ± 0.14 | 2.11 ± 0.33 cd |
| 10 | 1.10 cde | 0.47 d | 1.84 cd | 1.75 ab | 3.03 ab | 60.85 ± 0.35 d | 7.82 ± 0.69 | 3.54 ± 0.23 bcd | |
| 15 | 1.16 ab | 0.48 d | 1.85 cd | 1.76 a | 2.93 abcd | 64.25 ± 1.06 b | 7.14 ± 0.40 | 4.23 ± 0.32 abc | |
| 20 | 1.12 bcde | 0.46 d | 1.83 cd | 1.73 ab | 2.83 bcde | 65.10 ± 0.14 b | 7.05 ± 0.53 | 4.14 ± 0.44 abcd | |
| 25 | 1.15 abc | 0.47 d | 1.82 d | 1.69 ab | 2.65 e | 67.60 ± 0.85 a | 7.48 ± 0.88 | 4.56 ± 0.39 abc | |
| Type of Bran | Bran (%) | Bread | Color of Crumb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SV (mL/g) *** | Hardness (N) *** | L *** | a *** | b *** | ||
| RWF | 0 | 3.12 ± 0.07 c | 7.22 ± 0.23 de | 80.93 ± 0.80 a | −0.64 ± 0.11 g | 14.49 ± 0.14 f |
| HMB | 5 | 3.53 ± 0.05 a | 4.36 ± 0.03 e | 74.48 ± 1.25 ab | 1.44 ± 0.36 ef | 18.22 ± 0.73 e |
| 10 | 3.42 ± 0.06 b | 4.81 ± 0.08 e | 73.89 ± 0.40 b | 2.13 ± 0.21 e | 18.94 ± 0.77 e | |
| 15 | 3.01 ± 0.02 d | 8.17 ± 0.14 d | 72.79 ± 0.51 bc | 2.97 ± 0.36 d | 22.15 ± 0.97 cd | |
| 20 | 2.98 ± 0.02 d | 8.23 ± 0.33 d | 69.62 ± 0.75 bc | 4.46 ± 0.17 b | 24.63 ± 0.47 ab | |
| 25 | 2.62 ± 0.02 f | 21.49 ± 0.56 b | 65.92 ± 0.66 c | 5.65 ± 0.19 a | 25.31 ± 0.20 a | |
| JMB | 5 | 3.49 ± 0.01 ab | 5.90 ± 0.25 de | 74.75 ± 0.14 ab | 1.15 ± 0.24 f | 18.85 ± 0.76 e |
| 10 | 3.44 ± 0.02 ab | 6.03 ± 0.20 de | 71.19 ± 6.81 bc | 2.12 ± 0.19 e | 21.47 ± 0.28 d | |
| 15 | 2.67 ± 0.01 ef | 15.12 ± 0.30 c | 71.09 ± 2.27 bc | 3.67 ± 0.29 cd | 23.32 ± 0.72 bc | |
| 20 | 2.77 ± 0.02 e | 14.88 ± 3.52 c | 70.11 ± 0.55 bc | 4.32 ± 0.20 bc | 24.77 ± 0.09 ab | |
| 25 | 2.02 ± 0.01 g | 26.10± 0.49 a | 66.50 ± 0.63 c | 5.85 ± 0.24 a | 25.60 ± 0.44 a | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Kim, M.J.; Kwak, H.S.; Kim, S.S. Characteristics of Bread Made of Various Substitution Ratios of Bran Pulverized by Hammer Mill or Jet Mill. Foods 2020, 9, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010048
Lee D, Kim MJ, Kwak HS, Kim SS. Characteristics of Bread Made of Various Substitution Ratios of Bran Pulverized by Hammer Mill or Jet Mill. Foods. 2020; 9(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dabeen, Mi Jeong Kim, Han Sub Kwak, and Sang Sook Kim. 2020. "Characteristics of Bread Made of Various Substitution Ratios of Bran Pulverized by Hammer Mill or Jet Mill" Foods 9, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010048
APA StyleLee, D., Kim, M. J., Kwak, H. S., & Kim, S. S. (2020). Characteristics of Bread Made of Various Substitution Ratios of Bran Pulverized by Hammer Mill or Jet Mill. Foods, 9(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010048