Peel of Traditional Apple Varieties as a Great Source of Bioactive Compounds: Extraction by Micro-Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Apples Used for the Experiment
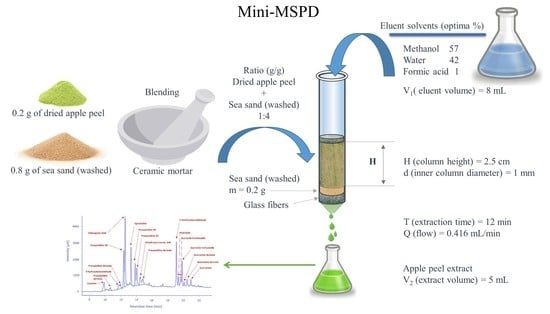
2.3. Micro Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion Extraction (Micro-MSPD)
2.4. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode-Array Detectors (HPLC-PDA)
2.5. Phenolic Identification by LC-MS-MS
2.6. Determination of the Total Polyphenolic Index
2.7. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Experiments
3.2. Optimization of Micro-MSPD
3.3. Total Polyphenolic Index and the Antioxidant Activity of Extracts
3.4. Individual Polyphenolic Profile of Extracts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lo Piccolo, E.; Landi, M.; Massai, R.; Remorini, D.; Conte, G.; Guidi, L. Ancient apple cultivars from Garfagnana (Tuscany, Italy): A potential source for ‘nutrafruit’ production. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobek, L.; Barron, A.R. Ancient apple varieties from Croatia as a source of bioactive polyphenolic compounds. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 45, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, A.; Ross, E.; Walsh, N.; O’Donnell, K.; Williams, A.; Klapp, M.; Fullard, N.; Edelstein, S. Representative literature on the phytonutrients category: Phenolic acids. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 57, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maragò, E.; Michelozzi, M.; Calamai, L.; Camangi, F.; Sebastiani, L. Antioxidant properties, sensory characteristics and volatile compounds profile of apple juices from ancient Tuscany (Italy) apple varieties. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 81, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lončarić, A.; Piližota, V. Effect of variety, growing season and storage on polyphenol profile and antioxidant activity of apple peels. Food Health Dis. 2014, 3, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lončarić, A.; Dugalić, K.; Mihaljević, I.; Jakobek, L.; Piližota, V. Effects of Sugar Addition on Total Polyphenol Content and Antioxidant Activity of Frozen and Freeze-Dried Apple Purée. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1674–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasouli, H.; Farzaei, M.H.; Khodarahmi, R. Polyphenols and their benefits: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2647–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyson, D.A. A Comprehensive Review of Apples and Apple Components and Their Relationship to Human Health. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, J.; Liu, R.H. Apple phytochemicals and their health benefits. Nutr. J. 2004, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sut, S.; Zengin, G.; Maggi, F.; Malagoli, M.; Dall’Acqua, S. Triterpene Acid and Phenolics from Ancient Apples of Friuli Venezia Giulia as Nutraceutical Ingredients: LC-MS Study and In Vitro Activities. Molecules 2019, 24, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kschonsek, J.; Wiegand, C.; Hipler, U.C.; Böhm, V. Influence of polyphenolic content on the in vitro allergenicity of old and new apple cultivars: A pilot study. Nutrition 2019, 58, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kschonsek, J.; Wolfram, T.; Stöckl, A.; Böhm, V. Polyphenolic Compounds Analysis of Old and New Apple Cultivars and Contribution of Polyphenolic Profile to the In Vitro Antioxidant Capacity. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobek, L.; Garcıa-Villalba, R.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. Polyphenolic characterisation of old apple varieties from Southeastern European region. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 31, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donno, D.; Beccaro, G.L.; Mellano, M.G.; Torello Marinoni, D.; Cerutti, A.K.; Canterino, S.; Bounous, G. Application of sensory, nutraceutical and genetic techniques to create a quality profile of ancient apple cultivars. J. Food Qual. 2012, 35, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balík, J.; Rop, O.; Mlček, J.; Híc, P.; Horák, M.; Řezníček, V. Assessment of nutritional parameters of native apple cultivars as new gene sources. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2012, 60, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iacopini, P.; Camangi, F.; Stefani, A.; Sebastiani, L. Antiradical potential of ancient apple varieties of Malus x domestica Borkh. In a peroxynitrite-induced oxidative process. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010, 23, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lončarić, A.; Kopjar, M.; Piližota, V. Improving the quality of apple purée. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3201–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaudanskas, M.; Viškelis, P.; Jakštas, V.; Raudonis, R.; Kviklys, D.; Milašius, A.; Janulis, V. Application of an optimized HPLC method for the detection of various phenolic compounds in apples from Lithuanian cultivars. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 542121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameer, K.; Shahbaz, H.M.; Kwon, J.H. Green extraction methods for polyphenols from plant matrices and their byproducts: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, S.A. Matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD). J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lores, M.; Iglesias-Estévez, M.; Álvarez-Casas, M.; Llompart, M.; García-Jares, C. Extraction of bioactive polyphenols from grape marc by a matrix solid-phase dispersion method. IBADER 2012, 8, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Xijuan, T.; Wenbin, C. A Review on the Recent Progress in Matrix Solid Phase Dispersion. Molecules 2018, 23, 2767. [Google Scholar]
- Guerra, E.; Celeiro, M.; Pablo Lamas, J.; Llompart, M.; Garcia-Jares, C. Determination of dyes in cosmetic products by micro-matrix solid phase dispersion and liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1415, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.J.; Huang, J.P.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, Q.Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Yi, L.; Cao, J.; Peng, L.Q.; Chen, Y.-B.; et al. Carbon molecular sieve based micro-matrix-solid-phase dispersion for the extraction of polyphenols in pomegranate peel by UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2218–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeoni, M.C.; Pellegrini, M.; Sergi, M.; Pittia, P.; Ricci, A.; Compagnone, D. Analysis of Polyphenols in the Lamiaceae Family by Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion Extraction Followed by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Determination. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17610–17616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhita, A.C.; Teixeira, D.M.; da Costa, C.T. Application of sample disruption methods in the extraction of anthocyanins from solid or semi-solid vegetable samples. J. Chromatogr. A. 2006, 1129, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.B.; Krucker, M.; Albert, K.; Liang, X.M. Determination and identification of isoflavonoids in Radix astragali by matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array and mass spectrometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1032, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdešová, A.; Dömötorová, M. MSPD as sample preparation method for determination of selected pesticide residues in apples. Acta Chim. Slovaca 2017, 10, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lončarić, A.; Skendrović Babojelić, M.; Kovač, T.; Šarkanj, B. Pomological properties and polyphenol content of conventional and traditional apple cultivars from Croatia. Food Health Dis. 2019, 8, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A., Jr. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Carres, L.; Mas-Capdevila, A.; Bravo, F.I.; Aragonès, G.; Muguerza, B.; Arola-Arnal, A. Optimization of a polyphenol extraction method for sweet orange pulp (Citrus sinensis L.) to identify phenolic compounds consumed from sweet oranges. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Casas, M.; García-Jares, C.; Llompart, M.; Lores, M. Effect of experimental parameters in the pressurized solvent extraction of polyphenolic compounds from white grape marc. Food Chem. 2014, 15, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assefa, A.D.; Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.S. Extraction of antioxidants and flavonoids from yuzu (Citrus junos Sieb ex Tanaka) peels: A response surface methodology study. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajila, C.M.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Tyagi, R.D.; Godbout, S.; Valéro, J.R. Extraction and analysis of polyphenols: Recent trends. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2011, 31, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovska, A.; Gjamovski, V.; Stefova, M. Comparison of different extraction solvents for assay of the polyphenol content in the peel and pulp of 21 apple cultivars from Macedonia. Maced. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2016, 35, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceymann, M.; Arrigoni, E.; Scharer, H.; Nising, A.B.; Hurrell, R.F. Identification of apples rich in health-promoting flavan-3-ols and phenolic acids by measuring the polyphenol profile. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 26, 128–135. [Google Scholar]
- Vrhovsek, U.; Rigo, A.; Tonon, D.; Mattivi, F. Quantitation of polyphenols in different apple varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6532–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdylo, A.; Oszmiański, J.; Laskowski, P. Polyphenolic compoundsand antioxidant activity of new and old apple varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6520–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobek, L.; Boc, M.; Barron, A.R. Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Apples. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 2612–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, R.K.; McGhie, T.K. Genetic variability in apple fruit polyphenol composition in Malus x domestica and Malus sieversii germplasm grown in New Zealand. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11509–11521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wach, A.; Pyrzynska, K.; Biesaga, M. Quercetin content in some food and herbal samples. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszek, W.; Lee, C.Y.; Jaworski, A.W.; Price, K.R. Identification of some phenolic compounds in apples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkhaleq, L.A.; Assi, M.A.; Noor, M.; Abdullah, R.; Saad, M.Z.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H. Therapeutic uses of epicatechin in diabetes and cancer. Vet. World 2017, 10, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauf, A.; Imran, M.; Abu-Izneid, T.; Iahtisham-Ul-Haq; Patel, S.; Pan, X.; Naz, S.; Sanches Silva, A.; Saeed, F.; Rasul Suleria, H.A. Proanthocyanidins: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 108999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullón, B.; Lú-Chau, T.A.; Moreira, M.T.; Lema, J.M.; Eibes, G. Rutin: A review on extraction, identification and purification methods, biological activities and approaches to enhance its bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Hejazi, V.; Abbas, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Khan, G.J.; Shumzaid, M.; Ahmad, F.; Babazadeh, D.; FangFang, X.; Modarresi-Ghazani, F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Phenolic Compound | Molecular Formula | [M − H]− (m/z) a | MS/MS (m/z) b | Collision Energy | Rt (min) HPLC c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catechin + | C15H14O6 | 289.006 | 245.020 203.115 | 17 22 | 9.53 |
| Epicatechin + | C15H14O6 | 289.006 | 245.020 203.115 | 17 22 | 13.35 |
| Phloridzin | C21H24O10 | 273.100 | 166.800 | 35 | 19.20 |
| Procyanidin A2 + | C30H24O12 | 577.090 | 287.002 136.988 425.081 437.078 | 32 62 13 16 | 13.56 |
| Procyanidin B1 | C30H26O12 | 577.033 | 407.066 288.931 424.977 | 26 25 26 | 14.24 |
| Procyanidin B2 | C30H26O12 | 577.033 | 407.066 288.931 424.977 | 26 25 26 | 12.15 |
| Procyanidin derivative 1 | C30H26O12 | 577.033 | − | − | 10.56 |
| Procyanidin derivative 2 | C30H26O12 | 577.033 | − | − | 11.76 |
| Procyanidin derivative 3+ | C30H26O12 | 577.090 | − | − | 14.94 |
| Quercetin + | C15H10O7 | 303.098 | 229.106 153.046 | 28 33 | 21.89 |
| Quercetin-3-glucoside + | C21H20O12 | 465.103 | 461.500 302.966 | 14 18 | 19.45 |
| Quercetin-3-rutinoside | C27H30O16 | 609.182 | 270.917 178.876 300.013 | 56 44 37 | 19.31 |
| Quercetin derivative 1 + | CnHnOn | 319.000 | − | − | 19.99 |
| Quercetin derivative 2 + | CnHnOn | 285.078 | − | − | 20.46 |
| 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde + | C7H6O2 | 121.016 | 93.056 92.054 | 20 23 | 11.52 |
| 4-Hydroxycinnamic acid + | C9H8O3 | 163.016 | 119.072 163.016 163.016 | 18 37 38 | 14.70 |
| Chlorogenic acid + | C16H18O9 | 353.000 | 191.074 85.090 93.073 | 22 43 45 | 12.38 |
| 4-Methoxybenzaldehyde + | C8H8O2 | 136.977 | 109.058 77.056 94.041 | 12 23 18 | 18.52 |
| Factors | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: Extract Volume | B: % Methanol | C: Mass of Dispersant | ||||
| F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| TPI | 71.98 | 0.00 a | 51.89 | 0.00 a | 3.93 | 0.09 |
| TPC | 89.43 | 0.00 a | 0.00 | 0.95 | 5.12 | 0.06 |
| Flavanols | 104.68 | 0.00 a | 1.85 | 0.22 | 4.41 | 0.07 |
| Flavonols | 159.13 | 0.00 a | 70.48 | 0.00 a | 5.55 | 0.05 |
| Non-flavonoids | 75.96 | 0.00 a | 14.12 | 0.01 a | 1.83 | 0.22 |
| Procyanidins | 46.91 | 0.00 a | 4.20 | 0.08 | 5.03 | 0.06 |
| Dihydrochalcones | 75.61 | 0.00 a | 55.11 | 0.00 a | 0.66 | 0.44 |
| Interactions | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | AB | AC | BB | BC | CC | |||||||
| F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| TPI | 3.27 | 0.11 | 6.56 | 0.04 a | 0.05 | 0.83 | 50.06 | 0.00 a | 0.53 | 0.49 | 2.40 | 0.17 |
| TPC | 1.15 | 0.32 | 0.00 | 0.98 | 0.05 | 0.83 | 175.30 | 0.00 a | 0.28 | 0.61 | 4.70 | 0.07 |
| Flavanols | 3.17 | 0.12 | 3.31 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.61 | 213.01 | 0.00 a | 0.10 | 0.76 | 3.75 | 0.09 |
| Flavonols | 8.09 | 0.03a | 5.98 | 0.04 a | 0.18 | 0.69 | 20.00 | 0.00 a | 3.01 | 0.13 | 2.44 | 0.16 |
| Non-flavonoids | 0.21 | 0.66 | 4.14 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.90 | 111.32 | 0.00 a | 0.47 | 0.52 | 1.93 | 0.21 |
| Procyanidins | 0.18 | 0.69 | 0.00 | 0.97 | 0.05 | 0.84 | 150.26 | 0.00 a | 0.25 | 0.63 | 4.63 | 0.07 |
| Dihydrochalcones | 2.71 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 15.98 | 0.01 a | 5.05 | 0.06 | 3.04 | 0.12 |
| Catechin | Epicatechin | Phloridzin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | ‘Crveni Boskop’ | 74.97 ± 1.67 g,* | 219.52 ± 10.25 m | 77.48 ± 4.50 j |
| ‘Francuska Kožara’ | n.d. | 311.03 ± 4.88 j | 87.52 ± 3.45 i | |
| ‘Ljepocvjetka’ | n.d. | 371.00 ± 22.67 h | 212.86 ± 6.83 e | |
| ‘Šampanjka’ | n.d. | 167.71 ± 10.70 n | 556.20 ± 15.90 b | |
| ‘Apistar’ | 512.36 ± 12.20 a | 1194.72 ± 21.41 b | 447.79 ± 10.08 c | |
| ‘Božicnica’ | 172.39 ± 1.84 d | 504.37 ± 14.17 f | 577.58 ± 8.80 a | |
| ‘Brčko’ | 72.93 ± 3.91 g | 492.17 ± 12.28 f | 111.13 ± 6.95 g | |
| ‘Kanadska Reneta’ | 117.79 ± 2.19 f | 565.03 ± 20.47 e | 69.99 ± 2.14 j | |
| ‘Zlatna Zimska Parmenka’ | 150.46 ± 2.00 e | 278.73 ± 3.07 k | 386.23 ± 16.98 d | |
| ‘Kraljevčica’ | 303.33 ± 17.18 b | 663.72 ± 31.99 c | n.d. | |
| ‘Bobovac’ | 186.46 ± 1.12 c | 1317.78 ± 10.80 a | 442.42 ± 9.35 c | |
| ‘Adamčica’ | 165.86 ± 3.56 d | 627.69 ± 7.80 d | 151.40 ± 4.30 f | |
| Commercial | ‘Golden Delicious’ | n.d. | 260.33 ± 3.71 k,l | 72.88 ± 0.35 j |
| ‘Idared’ | n.d. | 144.96 ± 1.94 o | 44.15 ± 0.66 k | |
| ‘Jonagold’ | n.d. | 320.39 ± 4.90 j | 69.15 ± 1.51 j | |
| ‘Fuji’ | 27.28 ± 2.28 i | 256.25 ± 8.83 l | 38.22 ± 2.39 k | |
| ‘Granny Smith’ | 47.45 ± 1.17 h | 201.72 ± 5.61 m | 98.35 ± 2.87 h | |
| ‘Gala’ | n.d. | 413.49 ± 20.85 g | 73.28 ± 2.77 j | |
| ‘Mutsu’ | n.d. | 344.02 ± 5.12 i | 45.89 ± 0.79 k | |
| ‘Red Delicious’ | n.d. | 612.49 ± 9.26 d | n.d. |
| PA2 | PB1 | PB2 | PD1 | PD2 | PD3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | ‘Crveni Boskop’ | 154.25 ± 5.20 i,j,* | n.d. | 663.59 ± 23.75 h | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| ‘Francuska Kožara’ | 193.61 ± 3.29 f,g | n.d. | 999.41 ± 31.06 e | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| ‘Ljepocvjetka’ | 240.61 ± 11.25 d | 219.36 ± 10.57 f | 871.20 ± 53.26 f | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| ‘Šampanjka’ | 147.81 ± 5.58 j | 212.99 ± 8.18 f | 451.35 ± 22.61 j | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| ‘Apistar’ | 277.02 ± 4.38 b | n.d. | 1402.37± 32.48 b | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| ‘Božicnica’ | 278.92 ± 4.03 b | n.d. | 1201.01± 27.35 c | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| ‘Brčko’ | 187.96 ± 6.45 g | 699.35 ± 22.83 b | 727.55± 30.99 g | 116.37 ± 2.36 a | n.d. | 182.93 ± 5.51 d | |
| ‘Kanadska Reneta’ | 266.02 ± 3.94 c | 328.83 ± 10.05 d | 1235.70± 37.19 c | n.d. | n.d. | 303.33 ± 3.77 b | |
| ‘Zlatna Zimska Parmenka’ | 168.97 ± 1.45 h | n.d. | 618.42 ± 7.59 i | n.d. | n.d. | 240.92 ± 3.65 c | |
| ‘Kraljevčica’ | 211.20 ± 5.61 e | n.d. | 714.86 ± 24.75 g | n.d. | n.d. | 352.99 ± 14.65 a | |
| ‘Bobovac’ | 330.75 ± 26.78 a | n.d. | 1574.71 ± 19.79 a | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| ‘Adamčica’ | 231.90 ± 0.97 d | 248.71 ± 4.93 e | 986.56 ± 20.56 e | 106.29 ± 1.42 b | 177.42 ± 4.42 a | 234.16 ± 2.58c | |
| Commercial | ‘Golden Delicious’ | n.d. | 183.70 ± 3.74 g | n.d. | 101.09 ± 0.30 d | 129.42 ± 0.75 b | 173.47 ± 1.95 e |
| ‘Idared’ | 134.13 ± 3.20 k | 352.11 ± 1.61 c | 292.97 ± 6.09 k | 93.85 ± 3.69 e | 114.84 ± 1.16 d | 143.77 ± 2.06f | |
| ‘Jonagold’ | 160.48 ± 8.37 h,i | 738.95 ± 34.27 a | 452.53 ± 28.03 j | n.d. | 120.42 ± 1.55 c | 173.32 ± 3.75 e | |
| ‘Fuji’ | 166.82 ± 2.17 h | n.d. | 453.70 ± 66.42 j | n.d. | 96.94 ± 4.92 e | 147.34 ± 7.45 f | |
| ‘Granny Smith’ | 136.10 ± 3.12 k | 101.37 ± 12.46 j | 476.52 ± 6.09 j | 103.26 ± 0.76 c | n.d. | 130.18 ± 15.40 g | |
| ‘Gala’ | 183.24 ± 6.22 g | 161.71 ± 3.40 h | 618.62 ± 2.28 i | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| ‘Mutsu’ | 200.87 ± 2.15 e,f | 136.88 ± 2.03 i | 837.11 ± 12.84 f | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| ‘Red Delicious’ | 105.29 ± 0.60 l | n.d. | 1112.70 ± 28.48 d | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |
| Que | Que3glu | Que3rut | QueD1 | QueD2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | ‘Crveni Boskop’ | 49.01 ± 3.45 m | 52.67 ± 3.990 k | n.d. | 96.05 ± 9.01 g | 27.47 ± 0.99 h |
| ‘Francuska Kožara’ | n.d. | 56.00 ± 1.79jk | 63.95 ± 1.41 e,f | 133.05 ± 4.93 f | 47.72 ± 0.93 g | |
| ‘Ljepocvjetka’ | 209.31 ± 7.98 b | 108.88 ± 3.77 f | n.d. | 232.63 ± 20.93 e | n.d. | |
| ‘Šampanjka’ | 115.93 ± 4.80 f,g | 135.31 ± 5.36 d | 991.43 ± 62.49 c | 245.62 ± 10.72 e | n.d. | |
| ‘Apistar’ | 119.73 ± 1.98 e,f | 141.01 ± 2.92 c | 956.56 ± 24.61 c | 341.83 ± 7.49 b | n.d. | |
| ‘Božicnica’ | 121.72 ± 1.08 e | 153.50 ± 2.08 b | 2244.46 ± 71.91 a | 320.13 ± 4.28 c | 508.82 ± 21.81 a | |
| ‘Brčko’ | 65.73 ± 3.14 k | 63.47 ± 0.98 i | 234.66 ± 10.35 d,e,f | 131.51 ± 6.38 f | n.d. | |
| ‘Kanadska Reneta’ | 79.51 ± 1.68 i | 57.69 ± 1.90 j | 858.81 ± 5.77 c | 85.57 ± 3.17 g,h | 225.08 ± 13.04 d | |
| ‘Zlatna Zimska Parmenka’ | 54.31 ± 3.05 l | 75.32 ± 1.50 g | 2383.28 ± 77.13 a | 133.74 ± 9.20 f | n.d. | |
| ‘Kraljevčica’ | 119.97 ± 5.16 e,f | 129.93 ± 6.30 e | 1621.28 ± 57.42 b | 285.03 ± 14.59 d | 459.16 ± 20.80 b | |
| ‘Bobovac’ | 270.48 ± 1.56 a | 178.63 ± 1.73 a | 1632.51 ± 939.02 b | 390.52 ± 40.41 a | 360.78 ± 22.48 c | |
| ‘Adamčica’ | 56.36 ± 1.83 l | 46.41 ± 1.42 l | n.d. | 75.78 ± 2.51 h | n.d. | |
| Commercial | ‘Golden Delicious’ | 111.60 ± 1.77 g | 55.36 ± 1.07 j,k | 296.53 ± 4.90 d,e,f | n.d. | 65.21 ± 0.89 f |
| ‘Idared’ | 46.23 ± 1.48 m | n.d. | 90.09 ± 1.83 e,f | 88.33 ± 0.67 g,h | n.d. | |
| ‘Jonagold’ | 148.15 ± 5.92 d | 70.76 ± 3.23 h | 413.42 ± 12.98 d | 133.05 ± 6.23 f | 89.05 ± 4.12 e | |
| ‘Fuji’ | 173.32 ± 3.69 c | 39.68 ± 3.62 m | 316.20 ± 56.38 d,e | 79.31 ± 9.30 g,h | 70.54 ± 9.18 f | |
| ‘Granny Smith’ | 76.61 ± 0.85 i,j | 57.10 ± 0.34 j | n.d. | 76.51 ± 3.70 h | n.d. | |
| ‘Gala’ | 71.98 ± 3.85 j | 56.04 ± 3.52 j,k | n.d. | 121.98 ± 8.24 f | n.d. | |
| ‘Mutsu’ | 106.12 ± 4.28 h | 46.25 ± 1.30 l | 260.07 ± 5.64 d,e,f | 85.77 ± 2.994 g,h | 72.37 ± 0.71 f | |
| ‘Red Delicious’ | 61.71 ± 0.82 k | 64.64 ± 0.87 i | n.d. | 120.06 ± 1.95 f | 225.16 ± 3.66 d |
| 3-Hba | 4-Hca | CA | 4-Mba | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | ‘Crveni Boskop’ | n.d. | 236.76 ± 18.26 d | 877.22 ± 34.89 g | 69.17 ± 0.94 i |
| ‘Francuska Kožara’ | n.d. | 408.77 ± 11.90 a | 2102.58 ± 57.64 b | 20.05 ± 6.51 n | |
| ‘Ljepocvjetka’ | n.d. | 199.82 ± 11.68 e | 2334.11 ± 33.27 a | 219.67 ± 1.85 d | |
| ‘Šampanjka’ | n.d. | 93.92 ± 6.76 i | 1952.01 ± 71.40 c | 336.19 ± 5.70 b | |
| ‘Apistar’ | 183.06 ± 1.66 c | 241.14 ± 4.82 d | 203.66 ± 4.75 j | 280.08 ± 5.34 c | |
| ‘Božicnica’ | n.d. | 372.73 ± 5.48 b | 1212.62 ± 38.03 e | 218.21 ± 2.38 d | |
| ‘Brčko’ | n.d. | n.d. | 112.79 ± 3.54 l | 145.65 ± 1.89 g | |
| ‘Kanadska Reneta’ | 148.70 ± 3.05 d | 113.10 ± 0.95 h | 903.08 ± 25.67 g | 33.05 ± 1.75 m | |
| ‘Zlatna Zimska Parmenka’ | n.d. | n.d. | 1175.78 ± 10.19 e | 153.34 ± 2.71 f | |
| ‘Kraljevčica’ | 213.46 ± 8.83 b | 282.21 ± 15.41 c | 172.26 ± 11.83 j,k | 182.07 ± 2.21 e | |
| ‘Bobovac’ | 297.01 ± 13.94 a | n.d. | 1646.92 ± 12.47 d | 479.80 ± 2.95 a | |
| ‘Adamčica’ | n.d. | n.d. | 1021.78 ± 47.19 f | 49.11 ± 3.42 l | |
| Commercial | ‘Golden Delicious’ | n.d. | n.d. | 378.55 ± 5.25 h | 66.96 ± 1.99 i,j |
| ‘Idared’ | n.d. | n.d. | 330.06 ± 3.91 i | 31.60 ± 2.29 m | |
| ‘Jonagold’ | n.d. | n.d. | 207.01 ± 3.70 j | 96.16 ± 3.21 h | |
| ‘Fuji’ | n.d. | n.d. | 156.21 ± 30.10 k | 30.55 ± 4.49 m | |
| ‘Granny Smith’ | 114.71 ± 1.72 e | n.d. | n.d. | 57.99 ± 1.63 k | |
| ‘Gala’ | n.d. | 165.14 ± 8.03 g | 308.10 ± 4.52 i | 66.07 ± 0.74 j | |
| ‘Mutsu’ | n.d. | 177.37 ± 6.57 f | 375.92 ± 7.65 h | 22.15 ± 3.10 n | |
| ‘Red Delicious’ | n.d. | 277.63 ± 4.22 c | n.d. | 48.90 ± 3.75 l |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lončarić, A.; Matanović, K.; Ferrer, P.; Kovač, T.; Šarkanj, B.; Skendrović Babojelić, M.; Lores, M. Peel of Traditional Apple Varieties as a Great Source of Bioactive Compounds: Extraction by Micro-Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion. Foods 2020, 9, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010080
Lončarić A, Matanović K, Ferrer P, Kovač T, Šarkanj B, Skendrović Babojelić M, Lores M. Peel of Traditional Apple Varieties as a Great Source of Bioactive Compounds: Extraction by Micro-Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion. Foods. 2020; 9(1):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010080
Chicago/Turabian StyleLončarić, Ante, Katarina Matanović, Perla Ferrer, Tihomir Kovač, Bojan Šarkanj, Martina Skendrović Babojelić, and Marta Lores. 2020. "Peel of Traditional Apple Varieties as a Great Source of Bioactive Compounds: Extraction by Micro-Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion" Foods 9, no. 1: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010080
APA StyleLončarić, A., Matanović, K., Ferrer, P., Kovač, T., Šarkanj, B., Skendrović Babojelić, M., & Lores, M. (2020). Peel of Traditional Apple Varieties as a Great Source of Bioactive Compounds: Extraction by Micro-Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion. Foods, 9(1), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010080