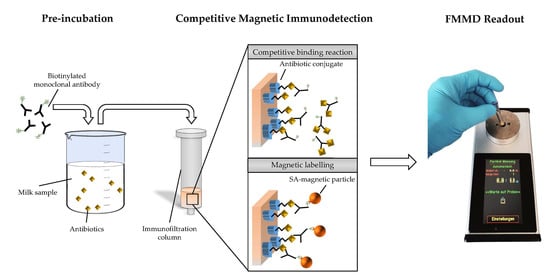
A Novel Method for Antibiotic Detection in Milk Based on Competitive Magnetic Immunodetection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Generation of Antibiotic-BSA Conjugates
2.2.1. Penicillin-BSA
2.2.2. Kanamycin-BSA
2.3. Determination of Protein Concentration
2.4. Determination of Antibody Affinity
2.5. Preparation of Immunofiltration Columns
2.6. cMID Calibration Curve Analysis
2.7. Frequency Mixing Magnetic Detection (FMMD)
2.8. Sample Preparation and cMID in Milk
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Generation of Penicillin-BSA and Kanamycin-BSA Conjugates and Antibody Affinity Determination
3.2. Development of cMID for Detection of Penicllin and Kanamycin in Buffer
3.3. cMID Calibration Measurements in Whole Fat Milk (WFM)
3.4. Spiked Sample Analysis and Determination of Recovery Rate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fleming, A. On the Antibacterial Action of Cultures of a Penicillium, with Special Reference to their Use in the Isolation of B. influenzæ. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1929, 10, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, K.; Kondo, S. Kanamycin and its derivative, arbekacin: Significance and impact. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2018, 71, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fejzic, N.; Begagic, M.; Seric-Haracic, S.; Smajlovic, M. Beta lactam antibiotics residues in cow’s milk: Comparison of efficacy of three screening tests used in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2014, 14, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Eremin, S.A.; Yakup, O.; Yao, G.; Zhang, X. Detection of kanamycin and gentamicin residues in animal-derived food using IgY antibody based ic-ELISA and FPIA. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuong, N.V.; Padungtod, P.; Thwaites, G.; Carrique-Mas, J.J. Antimicrobial Usage in Animal Production: A Review of the Literature with a Focus on Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Antibiotics (Basel) 2018, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sachi, S.; Ferdous, J.; Sikder, M.H.; Azizul Karim Hussani, S.M. Antibiotic residues in milk: Past, present, and future. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 6, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, M.A.; Craigmill, A.; Riviere, J.E.; Webb, A.I. Extralabel use of penicillin in food animals. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 229, 1401–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kummerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment–a review–part II. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farouk, F.; Azzazy, H.M.; Niessen, W.M. Challenges in the determination of aminoglycoside antibiotics, a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 890, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, K.G.; Peter, J.G.; Trubiano, J.A.; Phillips, E.J. Antibiotic allergy. Lancet 2019, 393, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, N.; Scott, H.M.; Norby, B.; Loneragan, G.H.; Vinasco, J.; McGowan, M.; Cottell, J.L.; Chengappa, M.M.; Bai, J.; Boerlin, P. Effects of ceftiofur and chlortetracycline treatment strategies on antimicrobial susceptibility and on tet(A), tet(B), and bla CMY-2 resistance genes among E. coli isolated from the feces of feedlot cattle. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyene, T. Veterinary Drug Residues in Food-animal Products: Its Risk Factors and Potential Effects on Public Health. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EU) No 37/2010 on Pharmacologically Active Substances and Their Classification Regarding Maximum Residue Limits in Foodstuffs of Animal Origin. 2009. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32010R0037&from=EN (accessed on 29 November 2020).
- Shen, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Ma, W.; Wu, X.; Cui, G.; Kuang, H. Rapid detection of praziquantel using monoclonal antibody-based ic-ELISA and immunochromatographic strips. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kloth, K.; Rye-Johnsen, M.; Didier, A.; Dietrich, R.; Martlbauer, E.; Niessner, R.; Seidel, M. A regenerable immunochip for the rapid determination of 13 different antibiotics in raw milk. Analyst 2009, 134, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukunzi, D.; Isanga, J.; Suryoprabowo, S.; Liu, L.; Kuang, H. Rapid and sensitive immunoassays for the detection of lomefloxacin and related drug residues in bovine milk samples. Food Agric. Immunol. 2017, 28, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.A.; Herrero, M.; Cifuentes, A. Determination of quinolone residues in infant and young children powdered milk combining solid-phase extraction and ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 7608–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junza, A.; Amatya, R.; Barrón, D.; Barbosa, J. Comparative study of the LC–MS/MS and UPLC–MS/MS for the multi-residue analysis of quinolones, penicillins and cephalosporins in cow milk, and validation according to the regulation 2002/657/EC. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 2601–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freitas, A.; Barbosa, J.; Ramos, F. Development and validation of a multi-residue and multiclass ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry screening of antibiotics in milk. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 33, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gonzalez, D.; Hamed, A.M.; Gilbert-Lopez, B.; Gamiz-Gracia, L.; Garcia-Campana, A.M. Evaluation of a multiresidue capillary electrophoresis-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry method for the determination of antibiotics in milk samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1510, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Suryoprabowo, S.; Kuang, H.; Liu, L. Detection of aminophylline in serum using an immunochromatographic strip test. Food Agric. Immunol. 2020, 31, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietschmann, J.; Spiegel, H.; Krause, H.J.; Schillberg, S.; Schroper, F. Sensitive Aflatoxin B1 Detection Using Nanoparticle-Based Competitive Magnetic Immunodetection. Toxins 2020, 12, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, M.P.; Althaus, R.L.; Molina, A.; Fernández, N. Antimicrobial agent detection in ewes’ milk by the microbial inhibitor test brilliant black reduction test—BRT AiM®. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, T.; Van Weyenberg, S.; Molina, M.P.; Reybroeck, W. Detection of antibiotics in goats’ milk: Comparison of different commercial microbial inhibitor tests developed for the testing of cows’ milk. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 62, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achtsnicht, S.; Neuendorf, C.; Fassbender, T.; Nolke, G.; Offenhausser, A.; Krause, H.J.; Schroper, F. Sensitive and rapid detection of cholera toxin subunit B using magnetic frequency mixing detection. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.H.; Hartmann, M.; Krause, H.J.; Blankenstein, G.; Mueller-Chorus, B.; Oster, J.; Miethe, P.; Keusgen, M. CRP determination based on a novel magnetic biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 2007, 22, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.H.; Stehr, M.; Bhuju, S.; Krause, H.J.; Hartmann, M.; Miethe, P.; Singh, M.; Keusgen, M. Magnetic biosensor for the detection of Yersinia pestis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 68, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettcher, S.; Jungk, F.; Kuhn, C.; Krause, H.J.; Nolke, G.; Commandeur, U.; Fischer, R.; Schillberg, S.; Schroper, F. Simple and portable magnetic immunoassay for rapid detection and sensitive quantification of plant viruses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achtsnicht, S.; Todter, J.; Niehues, J.; Teloken, M.; Offenhausser, A.; Krause, H.J.; Schroper, F. 3D Printed Modular Immunofiltration Columns for Frequency Mixing-Based Multiplex Magnetic Immunodetection. Sensors 2019, 19, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krause, H.; Wolters, N.; Zhanga, Y.; Offenhäusser, A.; Miethe, P.; Meyer, M.H.F.; Hartmann, M.; Keusgen, M. Magnetic particle detection by frequency mixing for immunoassay applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramana, M.; Rashmi, R.; Uppalapati, S.R.; Chandranayaka, S.; Balakrishna, K.; Radhika, M.; Gupta, V.K.; Batra, H.V. Development of sandwich dot-ELISA for specific detection of Ochratoxin A and its application on to contaminated cereal grains originating from India. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haasnoot, W.; Stouten, P.; Cazemier, G.; Lommen, A.; Nouws, J.F.; Keukens, H.J. Immunochemical detection of aminoglycosides in milk and kidney. Analyst 1999, 124, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tate, J.; Ward, G. Interferences in immunoassay. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2004, 25, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Achtsnicht, S.; Pourshahidi, A.M.; Offenhausser, A.; Krause, H.J. Multiplex Detection of Different Magnetic Beads Using Frequency Scanning in Magnetic Frequency Mixing Technique. Sensors 2019, 19, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Analyte | Concentration Spiked [ng·mL−1] | Concentration Detected [ng·mL−1] | Recovery Rate [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillin G | 2 | 1.83 ± 0.30 | 91.4 ± 14.9 |
| 4 | 3.90 ± 0.56 | 97.4 ± 14.0 | |
| 10 | 10.03 ± 0.67 | 100.3 ± 6.7 | |
| 20 | 22.6 ± 2.61 | 112.9 ± 13.1 | |
| Kanamycin | 1 | 0.88 ± 0.04 | 87.8 ± 4.3 |
| 10 | 9.40 ± 0.01 | 94.1 ± 0.1 | |
| 50 | 26.26 ± 0.36 | 52.5 ± 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietschmann, J.; Dittmann, D.; Spiegel, H.; Krause, H.-J.; Schröper, F. A Novel Method for Antibiotic Detection in Milk Based on Competitive Magnetic Immunodetection. Foods 2020, 9, 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121773
Pietschmann J, Dittmann D, Spiegel H, Krause H-J, Schröper F. A Novel Method for Antibiotic Detection in Milk Based on Competitive Magnetic Immunodetection. Foods. 2020; 9(12):1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121773
Chicago/Turabian StylePietschmann, Jan, Dominik Dittmann, Holger Spiegel, Hans-Joachim Krause, and Florian Schröper. 2020. "A Novel Method for Antibiotic Detection in Milk Based on Competitive Magnetic Immunodetection" Foods 9, no. 12: 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121773
APA StylePietschmann, J., Dittmann, D., Spiegel, H., Krause, H. -J., & Schröper, F. (2020). A Novel Method for Antibiotic Detection in Milk Based on Competitive Magnetic Immunodetection. Foods, 9(12), 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121773