Impact of Acorn Flour on Gluten-Free Dough Rheology Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Dough Preparation and Sampling
2.3. Rheology Measurements
2.3.1. Pasting Properties
2.3.2. Small Amplitude Oscillatory Measurements (SAOS) Testing
2.3.3. Dough Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.4. Colour Characterisation and pH Values of GF Dough
2.5. Dietary Fibre: Soluble, Insoluble and Total Fibre in GF Bread
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dough Rheology Characterisation
3.1.1. Pasting Properties
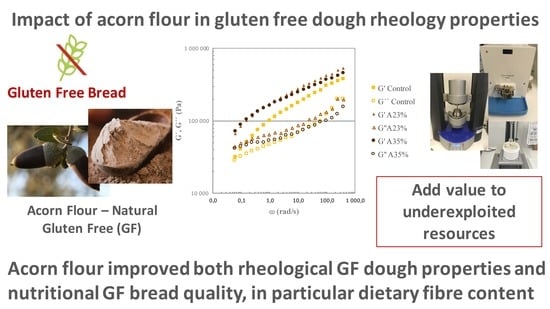
3.1.2. Small Amplitude Oscillatory Measurements (SAOS)
3.1.3. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
3.2. Impact of Acorn Flour Addition in Bread Texture
3.3. Characteristics of GF Dough: Colour and pH
3.4. Dietary Fibre: Soluble, Insoluble and Total Fibre
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schofield, J.D. Wheat proteins: Structure and functionality in milling and breadmaking. In Wheat Production, Properties and Quality, 1st ed.; Bushuk, W., Rasper, V.F., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 73–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.; Gormley, T.R.; Arendt, E.K. Recent advances in the formulation of gluten-free cereal-based products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.E.; Rosell, C.M. Understanding gluten-free dough for reaching breads with physical quality and nutritional balance. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, S.; Kaur, A.; Chopra, C.S. Gluten-Free Products for Celiac Susceptible People. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padalino, L.; Conte, A.; Del Nobile, M. Overview on the General Approaches to Improve Gluten-Free Pasta and Bread. Foods 2016, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deora, N.S.; Deswal, A.; Mishra, H.N. Alternative Approaches Towards Gluten-Free Dough Development: Recent Trends. Food Eng. Rev. 2014, 6, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, C.; Raymundo, A.; Sousa, I. Yogurt as an Alternative Ingredient to Improve the Functional and Nutritional Properties of Gluten-Free Breads. Foods 2020, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, M.C.; Graça, C.; Vlaisavljević, S.; Tenreiro, A.; Sousa, I.; Raymundo, A. Microalgal cell disruption: Effect on the bioactivity and rheology of wheat bread. Algal Res. 2020, 45, 101749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbica, A.; Belovic, M.; Tomic, J. Novel breads of non-wheat flours. Food Chem. 2019, 282, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidaurre-Ruiz, J.; Matheus-Diaz, S.; Salas-Valerio, F.; Barraza-Jauregui, G.; Schoenlechner, R.; Repo-Carrasco-Valencia, R. Influence of tara gum and xanthan gum on rheological and textural properties of starch-based gluten-free dough and bread. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skendi, A.; Mouselemidou, P.; Papageorgiou, M.; Papastergiadis, E. Effect of acorn meal-water combinations on technological properties and fine structure of gluten-free bread. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojceska, V.; Butler, F. Investigation of reported correlation coefficients between rheological properties of the wheat bread doughs and baking performance of the corresponding wheat flours. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 24, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobraszczyk, B.J.; Morgenstern, M.P. Rheology and the breadmaking process. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 38, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masure, H.G.; Fierens, E.; Delcour, J.A. Current and forward looking experimental approaches in gluten-free bread making research. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 67, 92–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Mu, T.; Sun, H. Comparative study of the effect of starches from five different sources on the rheological properties of gluten-free model doughs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 176, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarnicola, B.; Tassielli, G.; Renzulli, P.A.; Monforti, F. Energy flows and greenhouses gases of EU (European Union) national breads using an LCA (Life Cycle Assessment) approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinha, A.F.; Costa, A.S.G.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Pacheco, R.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Chemical and antioxidant profiles of acorn tissues from Quercus spp.: Potential as new industrial raw materials. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 94, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, S.; Costa, E.M.; Borges, A.; Carvalho, A.P.; Monteiro, M.J.; Pintado, M.M.E. Nutritional characterization of acorn flour (a traditional component of the Mediterranean gastronomical folklore). Food Meas. 2016, 10, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švec, I.; Hrušková, M.; Kadlčíková, I. Features of flour composites based on the wheat or wheat-barley flour combined with acorn and chestnut. Croat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 10, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasqualone, A.; Makhlouf, F.Z.; Barkat, M.; Difonzo, G.; Summo, C.; Squeo, G.; Caponio, F. Effect of acorn flour on the physico-chemical and sensory properties of biscuits. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hrusková, M.; Svec, I.; Kadlcíková, I. Effect of chestnut and acorn flour on wheat/wheat-barley flour properties and bread quality. Int. J. Food Stud. 2019, 8, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korus, J.; Witczak, M.; Ziobro, R.; Juszczak, L. The influence of acorn flour on rheological properties of gluten-free dough and physical characteristics of the bread. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cappelli, A.; Oliva, N.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Lorini, C.; Cini, E. Assessment of the rheological properties and bread characteristics obtained by innovative protein sources (Cicer arietinum, Acheta domesticus, Tenebrio molitor): Novel food or potential improvers for wheat flour? LWT 2020, 118, 108867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Walkowiak, K.; Masewicz, Ł.; Bartczak, O.; Lewandowicz, J.; Kubiak, P.; Baranowska, H.M. Gluten-Free Bread with Cricket Powder—Mechanical Properties and Molecular Water Dynamics in Dough and Ready Product. Foods 2019, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacob, H.E. 6000 Anos de Pão, 1st ed.; Antígona: Lisboa, Portugal, 2003; p. 587. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, O. Portugal o Mediterrâneo e o Atlântico, 4th ed.; Livraria Sá da Costa Editora: Lisboa, Portugal, 1986; p. 188. [Google Scholar]
- Veiga de Oliveira, E.; Galhano, F.; Pereira, B. Tecnologia Tradicional Portuguesa-Sistemas de Moagem; INIC, Centro de Estudos de Etnologia: Lisboa, Portugal, 1983; p. 520. [Google Scholar]
- Kiumarsi, M.; Shahbazi, M.; Yeganehzad, S.; Majchrzak, D.; Lieleg, O.; Winkeljann, B. Relation between structural, mechanical and sensory properties of gluten-free bread as affected by modified dietary fibers. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqash, F.; Gani, A.; Gani, A.; Masoodi, F.A. Gluten-free baking: Combating the challenges-A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.C.X. Desenvolvimento de pães sem glúten enriquecidos com Tetraselmis chuii. Dissertação de Mestrado em Engenharia Alimentar; Instituto Superior de Agronomia da Universidade de Lisboa: Lisboa, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, J.M.C.; Bason, M.L. Comparison of Old and New Dough Mixing Methods and their Utility in Predicting Bread Quality. In Proceedings of the 65th Australian Cereal Chemistry Conference, Coogee, NSW, Australia, 16–18 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, R.B.; Nunes, M.C.; Peres, J.A.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A.; Raymundo, A. Acorn Flour as bioactive compounds source in gluten free bread. In Proceedings of the Book of Abstracts of XX EuroFoodChem Congress, Porto, Portugal, 17–19 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, A.; Kim, S.K. Particle size distribution, pasting pattern and texture of gel of acorn, mungbean, and buckwheat starches. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Sciarini, L.S.; Ribotta, P.; León, A.; Pérez, G. Influence of Gluten-free Flours and their Mixtures on Batter Properties and Bread Quality. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2010, 3, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha Parra, A.F.; Ribotta, P.D.; Ferrero, C. Starch–Apple Pomace Mixtures: Pasting Properties and Microstructure. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M. Functionality of Starches and Hydrocolloids in Gluten-Free Foods. In Gluten-Free Food Science and Technology; Gallagher, E., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 200–224. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, M.M.; Gómez, M. Rheological and microstructural evolution of the most common gluten-free flours and starches during bread fermentation and baking. J. Food Eng. 2017, 197, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, A.S.; Wolter, A.; Jacob, F.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K. Nutritional properties and ultra-structure of commercial gluten free flours from different botanical sources compared to wheat flours. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, P.R.; Nunes, M.C.; Beirão-da-Costa, M.L. The effect of starch isolation method on physical and functional properties of Portuguese nut starches. II. Q. rotundifolia Lam. and Q. suber Lam. acorns starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singh, J.; Kaur, L.; Sodhi, N.S.; Gill, B.S. Morphological, thermal and rheological properties of starches from different botanical sources. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debet, M.R.; Gidley, M.J. Three classes of starch granule swelling: Influence of surface proteins and lipids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 64, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbica, A.; Hadnađev, M.; Dapčević, T. Rheological, textural and sensory properties of gluten-free bread formulations based on rice and buckwheat flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappai, M.G.; Alesso, G.A.; Nieddu, G.; Sanna, M.; Pinna, W. Electron microscopy and composition of raw acorn starch in relation to in vivo starch digestibility. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, S.W.; Lynch, K.M.; Arendt, E.K. Starch Characteristics Linked to Gluten-Free Products. Foods 2017, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schirmer, M.; Jekle, M.; Becker, T. Starch gelatinization and its complexity for analysis. Starch-Stärke 2015, 67, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Miravalles, L.; O’Mahony, J.A. Composition, Protein Profile and Rheological Properties of Pseudocereal-Based Protein-Rich Ingredients. Foods 2018, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storck, C.R.; Zavareze, E.R.; Gularte, M.A.; Elias, M.C.; Rosell, C.M.; Dias, A.R.G. Protein enrichment and its effects on gluten-free bread characteristics. LWT 2013, 53, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Jin, Z.; Simsek, S.; Hall, C.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Effect of germination on the chemical composition, thermal, pasting, and moisture sorption properties of flours from chickpea, lentil, and yellow pea. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsaragkou, K.; Yiannopoulos, S.; Kontogiorgi, A.; Poulli, E.; Krokida, M.; Mandala, I. Effect of Carob Flour Addition on the Rheological Properties of Gluten-Free Breads. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2014, 7, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñarro, B.; Albanell, E.; Aguilar, N.; Guamis, B.; Capellas, M. Effect of legume flours on baking characteristics of gluten-free bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha Parra, A.F.; Ribotta, P.D.; Ferrero, C. Apple pomace in gluten-free formulations: Effect on rheology and product quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsaragkou, Κ.; Styliani, P.; Ioanna, M. Structural role of fibre addition to increase knowledge of non-gluten bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 67, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, L.; Cardós, M.; Campaña, L.; Ferrero, C. Effect of glutens of different quality on dough characteristics and breadmaking performance. LWT 2012, 46, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delta E 101. Available online: http://zschuessler.github.io/DeltaE/learn/ (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Fratelli, C.; Muniz, D.G.; Santos, F.G.; Capriles, V.D. Modelling the effects of psyllium and water in gluten-free bread: An approach to improve the bread quality and glycemic response. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devries, J.; Camire, M.; Cho, S.; Craig, S.; Gordon, D.; Jones, J.M.; Li, B.; Lineback, D.; Prosky, L.; Tungland, B. The definition of dietary fiber. Cereal Food World 2001, 46, 112–129. [Google Scholar]
- Melini, V.; Melini, F. Gluten-Free Diet: Gaps and Needs for a Healthier Diet. Nutrients 2019, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vici, G.; Belli, L.; Biondi, M.; Polzonetti, V. Gluten free diet and nutrient deficiencies: A review. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ingredients (%) | Control (C) | Acorn 23% (A23%) | Acorn 35% (A35%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buckwheat flour | 46.0 | 23.0 | 12.0 |
| Rice flour | 31.0 | 31.0 | 31.0 |
| Potato starch | 23.0 | 23.0 | 23.0 |
| Acorn flour | 0.0 | 23.0 | 35.0 |
| Sunflower oil (in relation to flours) | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| HPMC (in relation to flours) | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| Dried yeast (in relation to flours) | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 |
| Sugar (in relation to flours) | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 |
| Salt (in relation to flours) | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Water absorption (14% moisture basis) | 65.0 | 63.0 | 62.0 |
| Control | A23% | A35% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.35 a ± 0.04 | 5.09 b ± 0.05 | 5.05 b ± 0.05 |
| Colour L* | 82.49 a ± 0.42 | 70.90 b ± 0.08 | 66.42 c ± 0.26 |
| Colour a* | 0.56 c ± 0.21 | 6.11 b ± 0.35 | 7.89 a ± 0.31 |
| Colour b* | 15.50 c ± 0.33 | 24.45 b ± 0.83 | 27.31a ± 0.65 |
| Control | A23% | A35% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insoluble Fibre (%) | 8.99 b ± 0.63 | 11.96 a ± 0.53 | 12.46 a ± 0.92 |
| Soluble Fibre (%) | 1.32 a ± 0.38 | 0.31 b ± 0.24 | 0.12 b ± 0.10 |
| Total Fibre (%) | 10.31 b ± 0.65 | 12.27 a ± 0.75 | 12.58 a ± 0.90 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beltrão Martins, R.; Nunes, M.C.; M. Ferreira, L.M.; A. Peres, J.; R. N. A. Barros, A.I.; Raymundo, A. Impact of Acorn Flour on Gluten-Free Dough Rheology Properties. Foods 2020, 9, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050560
Beltrão Martins R, Nunes MC, M. Ferreira LM, A. Peres J, R. N. A. Barros AI, Raymundo A. Impact of Acorn Flour on Gluten-Free Dough Rheology Properties. Foods. 2020; 9(5):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050560
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeltrão Martins, R., M. C. Nunes, L. M. M. Ferreira, J. A. Peres, A. I. R. N. A. Barros, and A. Raymundo. 2020. "Impact of Acorn Flour on Gluten-Free Dough Rheology Properties" Foods 9, no. 5: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050560
APA StyleBeltrão Martins, R., Nunes, M. C., M. Ferreira, L. M., A. Peres, J., R. N. A. Barros, A. I., & Raymundo, A. (2020). Impact of Acorn Flour on Gluten-Free Dough Rheology Properties. Foods, 9(5), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9050560