Scientific Approaches on Extraction, Purification and Stability for the Commercialization of Fucoxanthin Recovered from Brown Algae
Abstract
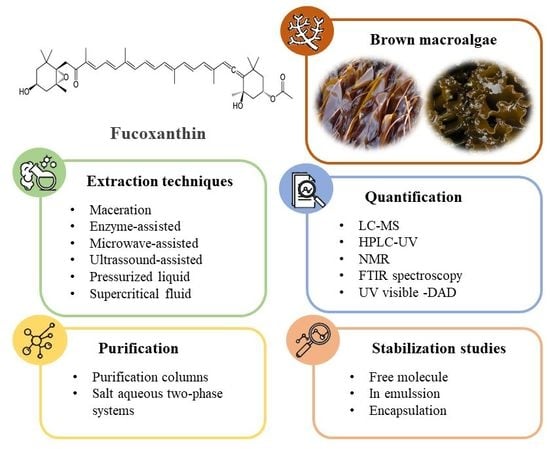
:1. Introduction
2. Extraction Methods
2.1. Conventional Techniques
2.1.1. Maceration Extraction (ME)
2.1.2. Vortex Assisted Extraction (VAE)
2.1.3. Soxhlet Assisted Extraction (SAE)
2.2. Non-Conventional Techniques
2.2.1. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction (EAE)
2.2.2. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
2.2.3. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UEA)
2.2.4. Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE)
2.2.5. Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE)
2.3. Comparison of Extraction Systems
3. Quantification, Identification, and Purification Methods
3.1. Quantification and Identification of Fucoxanthin
3.2. Purification
4. Molecule Stability
4.1. Free Molecule
4.2. In Emulsions
4.3. Encapsulation
5. Developed Products Containing Fucoxanthin and Their Health Benefits
6. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Generic | |
| DW | Dry weight |
| FW | Fresh weight |
| RT | Room temperature |
| Extraction techniques | |
| EAE | Enzyme-assisted extraction |
| MAE | Microwave-assisted extraction |
| ME | Maceration extraction |
| PLE | Pressurized liquid extraction |
| SFE | Supercritical fluid extraction |
| VAE | Vortex assisted extraction |
| Compounds | |
| AcO | Acetone |
| Ch | Chloroform |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| DE | Diethyl ether |
| DME | Dimethyl ether |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| Hp | Heptane |
| Hx | Hexane |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| n-Hx | n-Hexane |
| W | Water |
| Detection and purification techniques | |
| 13C-NMR | Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance |
| 1H-NMR | Proton nuclear magnetic resonance |
| APCI | Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization |
| DAD | Diode-array detector |
| PDA | Photodiode-array detector |
| ESI | Electrospray ionization |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HPTLC | High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography |
| LC | Liquid chromatography |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| QTOF | Quadrupole time of flight |
| Spec | Spectrophotometry |
| TWIMS | Traveling-wave ion mobility MS |
| UPLC | Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Saet, B.L.; Joo, Y.L.; Song, D.G.; Pan, C.H.; Chu, W.N.; Min, C.K.; Eun, H.L.; Sang, H.J.; Kim, H.S.; Yeong, S.K.; et al. Cancer chemopreventive effects of Korean seaweed extracts. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 17, 613–622. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhasankar, P.; Ganesan, P.; Bhaskar, N.; Hirose, A.; Stephen, N.; Gowda, L.R.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Edible Japanese seaweed, wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) as an ingredient in pasta: Chemical, functional and structural evaluation. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Sashima, T.; Takahashi, N.; Kawada, T.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin and its metabolite, fucoxanthinol, suppress adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 18, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maoka, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Akimoto, N. Characterization of fucoxanthin and fucoxanthinol esters in the Chinese surf clam, Mactra chinensis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1563–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willstatter, R.; Page, H. The pigments of the brown algae. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1914, 404, 237–271. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Yuan, J.P.; Wu, C.F.; Wang, J.H. Fucoxanthin, a marine carotenoid present in brown seaweeds and diatoms: Metabolism and bioactivities relevant to human health. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1806–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikami, K.; Hosokawa, M. Biosynthetic pathway and health benefits of fucoxanthin, an algae-specific xanthophyll in brown seaweeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13763–13781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palermo, J.A.; Gros, E.G.; Seldes, A.M. Carotenoids from three red algae of the Corallinaceae. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 2983–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.J.; Ko, S.C.; Kang, S.M.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, J.P.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.W.; Cho, M.G.; Jeon, Y.J. Cytoprotective effect of fucoxanthin isolated from brown algae Sargassum siliquastrum against H2O2 -induced cell damage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 228, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Chuyen, H.; Eun, J.B. Marine carotenoids: Bioactivities and potential benefits to human health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Yamashita, K.; Asai, A.; Nagao, A.; Shiraishi, T.; Imai, I.; Hirata, T. Esterification of xanthophylls by human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 483, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Zavaglia, A.; Prieto, M.A.; Jiménez-López, C.; Mejuto, J.C.; Simal-Gándara, J. The potential of seaweeds as a source of functional ingredients of prebiotic and antioxidant value. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Orazio, N.; Gemello, E.; Gammone, M.A.; De Girolamo, M.; Ficoneri, C.; Riccioni, G. Fucoxantin: A treasure from the sea. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.R.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin: A Marine Carotenoid Exerting Anti-Cancer Effects by Affecting Multiple Mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 5130–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kotake-Nara, E.; Yonekura, L.; Nagao, A. Lysoglyceroglycolipids improve the intestinal absorption of micellar fucoxanthin by Caco-2 cells. J. Oleo Sci. 2015, 64, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, K.; McKinley, K.R. Use of macroalgae for marine biomass production and CO2 remediation: A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 1994, 6, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Research, I.M. Global Fucoxanthin Market Report 2018. 2018. Available online: https://www.businessindustryreports.com/report/102177/global-fucoxanthin-market-report-2018 (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Yamamoto, K.; Ishikawa, C.; Katano, H.; Yasumoto, T.; Mori, N. Fucoxanthin and its deacetylated product, fucoxanthinol, induce apoptosis of primary effusion lymphomas. Cancer Lett. 2011, 300, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, H.; Kamo, Y.; Machmudah, S.; Wahyudiono; Goto, M. Extraction of fucoxanthin from raw macroalgae excluding drying and cell wall disruption by liquefied dimethyl ether. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2383–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguraman, V.; MubarakAli, D.; Narendrakumar, G.; Thirugnanasambandam, R.; Kirubagaran, R.; Thajuddin, N. Unraveling rapid extraction of fucoxanthin from Padina tetrastromatica: Purification, characterization and biomedical application. Process Biochem. 2018, 73, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Ooi, T.; Hiraoka, M.; Oka, N.; Hamada, H.; Tamura, M.; Kusumi, T. Fucoxanthin and Its Metabolites in Edible Brown Algae Cultivated in Deep Seawater. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fung, A.; Hamid, N.; Lu, J. Fucoxanthin content and antioxidant properties of Undaria pinnatifida. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasaki, M.; Kawagoe, C.; Ito, A.; Kumon, H.; Narayan, B.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Spatial and seasonal variations in the biofunctional lipid substances (fucoxanthin and fucosterol) of the laboratory-grown edible Japanese seaweed (Sargassum horneri Turner) cultured in the open sea. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Kamogawa, H.; Susanto, E.; Kawagoe, C.; Yasui, H.; Saga, N.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Seasonal variations of total lipids, fatty acid composition, and fucoxanthin contents of Sargassum horneri (Turner) and Cystoseira hakodatensis (Yendo) from the northern seashore of Japan. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariman, G.A.; Shastan, S.J.; Zahedi, M.M. Seasonal variation of total lipid, fatty acids, fucoxanthin content, and antioxidant properties of two tropical brown algae (Nizamuddinia zanardinii and Cystoseira indica) from Iran. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinela, J.; Prieto, M.A.; Pereira, E.; Jabeur, I.; Barreiro, M.F.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Optimization of heat- and ultrasound-assisted extraction of anthocyanins from Hibiscus sabdariffa calyces for natural food colorants. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heffernan, N.; Smyth, T.J.; FitzGerald, R.J.; Vila-Soler, A.; Mendiola, J.; Ibáñez, E.; Brunton, N.P. Comparison of extraction methods for selected carotenoids from macroalgae and the assessment of their seasonal/spatial variation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 37, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, S.; Wang, K.; Wan, L.; Li, A.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, C. Production, characterization, and antioxidant activity of fucoxanthin from the marine diatom Odontella aurita. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2667–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvani, N.; Hajiaghaee, R.; Zarekarizi, A.R. A review on biosynthesis, health benefits and extraction methods of fucoxanthin, particular marine carotenoids in algae. J. Med. Plants 2018, 17, 6–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, M.W.S.; Tan, K.M.; Chew, L.Y.; Kong, K.W.; Yan, S.W. Application of Two-Level Full Factorial Design for the Extraction of Fucoxanthin and Antioxidant Activities from Sargassum siliquosum and Sargassum polycystum. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2018, 27, 446–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Optimisation of fucoxanthin extraction from Irish seaweeds by response surface methodology. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, N.; Leça, J.M.; Pereira, A.C.; Pereira, V.; Ferraz, S.; Barreto, M.C.; Marques, J.C.; de Carvalho, M.A.A.P. Evaluation of fucoxanthin contents in seaweed biomass by vortex-assisted solid-liquid microextraction using high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection. Algal Res. 2019, 42, 101603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Qiu, Z.D.; Qu, X.Y.; Deng, A.P.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, L.Q.; Lai, C.J.S. Discoursing on Soxhlet extraction of ginseng using association analysis and scanning electron microscopy. J. Pharm. Anal. 2018, 8, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getachew, A.T.; Saravana, P.S.; Cho, Y.J.; Woo, H.C.; Chun, B.S. Concurrent extraction of oil from roasted coffee (Coffea arabica) and fucoxanthin from brown seaweed (Saccharina japonica) using supercritical carbon dioxide. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 25, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Enzymatic extraction of fucoxanthin from brown seaweeds. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Billakanti, J.M.; Catchpole, O.J.; Fenton, T.A.; Mitchell, K.A.; Mackenzie, A.D. Enzyme-assisted extraction of fucoxanthin and lipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids from Undaria pinnatifida using dimethyl ether and ethanol. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Si, X.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, G. Isolation of fucoxanthin from edible brown algae by microwave-assisted extraction coupled with high-speed countercurrent chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 2313–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.F.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, W.J.; Um, B.H. Pressurized liquid method for fucoxanthin extraction from Eisenia bicyclis (Kjellman) Setchell. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Escobedo-Avellaneda, Z.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Welti-Chanes, J. State-of-the-art extraction methodologies for bioactive compounds from algal biome to meet bio-economy challenges and opportunities. Molecules 2018, 23, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roh, M.K.; Uddin, M.S.; Chun, B.S. Extraction of fucoxanthin and polyphenol from Undaria pinnatifida using supercritical carbon dioxide with co-solvent. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2008, 13, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagnanam, S.P.; Yin, S.; Choi, J.H.; Park, Y.B.; Woo, H.C.; Chun, B.S. Biological properties of fucoxanthin in oil recovered from two brown seaweeds using supercritical CO2 extraction. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3422–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gao, X.; Gong, Q. Effects of temperature and salinity on the growth and biochemical composition of the brown alga Sargassum fusiforme (Fucales, Phaeophyceae). J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, K.; Ozaki, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Das, S.K.; Matsushita, S.; Hirano, M.; Okada, T.; Komoto, A.; Mori, N.; Nakatsuka, M. Commercial-scale Preparation of Biofunctional Fucoxanthin from Waste Parts of Brown Sea Algae Laminaria japonica. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2008, 14, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, P.; Kumar, M.; Mishra, G.; Sahoo, D. Multivariate analysis of fatty acid and biochemical constitutes of seaweeds to characterize their potential as bioresource for biofuel and fine chemicals. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 226, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga-Corral, M.; García-Oliveira, P.; Pereira, A.G.; Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Technological application of tannin-based extracts. Molecules 2020, 25, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terasaki, M.; Hirose, A.; Narayan, B.; Baba, Y.; Kawagoe, C.; Yasui, H.; Saga, N.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Evaluation of recoverable functional lipid components of several brown seaweeds (Phaeophyta) from Japan with special reference to fucoxanthin and fucosterol contents. J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mise, T.; Ueda, M.; Yasumoto, T. Production of fucoxanthin-rich powder from Cladosiphon okamuranus. Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 3, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Susanto, E.; Fahmi, A.S.; Abe, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Lipids, Fatty Acids, and Fucoxanthin Content from Temperate and Tropical Brown Seaweeds. Aquat. Procedia 2016, 7, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agatonovic-Kustrin, S.; Morton, D.W. High-performance thin-layer chromatography HPTLC-direct bioautography as a method of choice for alpha-amylase and antioxidant activity evaluation in marine algae. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1530, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.J.; Yoon, W.J.; Kim, K.N.; Ahn, G.N.; Kang, S.M.; Kang, D.H.; Affan, A.; Oh, C.; Jung, W.K.; Jeon, Y.J. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory effect of fucoxanthin isolated from brown algae in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2045–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seely, G.R.; Duncan, M.J.; Vidaver, W.E. Preparative and analytical extraction of pigments from brown algae with dimethyl sulfoxide. Mar. Biol. 1972, 12, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajauria, G.; Foley, B.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Characterization of dietary fucoxanthin from Himanthalia elongata brown seaweed. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.C.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, W.W.; Kang, N.; Kim, E.A.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, D.; Jeon, Y.J. Protective effect of fucoxanthin isolated from Ishige okamurae against high-glucose induced oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and zebrafish model. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 11, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, S.C.; Yusoff, F.M.; Ismail, M.; Basri, M.; Yau, S.K.; Khong, N.M.H.; Chan, K.W.; Ebrahimi, M. Antioxidant capacities of fucoxanthin-producing algae as influenced by their carotenoid and phenolic contents. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 241, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaswir, I.; Noviendri, D.; Salleh, H.M.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin extractions of brown seaweeds and analysis of their lipid fraction in methanol. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 18, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaswir, I.; Noviendri, D.; Salleh, H.M.; Taher, M.; Miyashita, K.; Ramli, N. Analysis of fucoxanthin content and purification of all-trans-fucoxanthin from Turbinaria turbinata and Sargassum plagyophyllum by SiO2 open column chromatography and reversed phase-HPLC. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2013, 36, 1340–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.R.; Lin, D.M.; Chang, C.M.J.; Chou, H.N.; Wu, J.J. Supercritical carbon dioxide anti-solvent crystallization of fucoxanthin chromatographically purified from Hincksia mitchellae P.C. Silva. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 119, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, V.; Loganathan, C.; Sadhasivam, G.; Kandasamy, S.; Poomani, K.; Thayumanavan, P. Purification of fucoxanthin from Sargassum wightii Greville and understanding the inhibition of angiotensin 1-converting enzyme: An in vitro and in silico studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, E.; Moure, A.; Domínguez, H. Supercritical CO2 extraction of fatty acids, phenolics and fucoxanthin from freeze-dried Sargassum muticum. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, D. Chemical cleavage of fucoxanthin from Undaria pinnatifida and formation of apo-fucoxanthinones and apo-fucoxanthinals identified using LC-DAD-APCI-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Shang, Y.F.; Um, B.H. A preparative method for isolation of fucoxanthin from Eisenia bicyclis by centrifugal partition chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. 2011, 22, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, R.K.; Bhaskar, N.; Divakar, S.; Baskaran, V. Bioavailability and metabolism of fucoxanthin in rats: Structural characterization of metabolites by LC-MS (APCI). Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Wong, C.C.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Mao, X.; Wu, T.; Ren, Y.; Chen, F. A novel strategy for isolation and purification of fucoxanthinol and fucoxanthin from the diatom Nitzschia laevis. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajauria, G.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Isolation and partial characterization of bioactive fucoxanthin from Himanthalia elongata brown seaweed: A TLC-based approach. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 2013, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yip, W.H.; Lim, S.J.; Mustapha, W.A.W.; Maskat, M.Y.; Said, M. Characterisation and stability of pigments extracted from Sargassum binderi obtained from Semporna, Sabah. Sains Malays. 2014, 43, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Pardilhó, S.L.; Machado, S.F.; Bessada, S.M.F.; Almeida, M.; Oliveira, M.B.; Dias, J.M. Marine Macroalgae Waste from Northern Portugal: A Potential Source of Natural Pigments? Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohibbullah, M.; Haque, M.N.; Khan, M.N.A.; Park, I.-S.; Moon, I.S.; Hong, Y.-K. Neuroprotective effects of fucoxanthin and its derivative fucoxanthinol from the phaeophyte Undaria pinnatifida attenuate oxidative stress in hippocampal neurons. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 3243–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, A.; Herstad, O.; Liaaen-Jensen, S. Fucoxanthin metabolites in egg yolks of laying hens. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiris, K.; Muylaert, K.; Fraeye, I.; Foubert, I.; De Brabanter, J.; De Cooman, L. Antioxidant potential of microalgae in relation to their phenolic and carotenoid content. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Buschmann, C. Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: Measurement and Characterization by UV-VIS Spectroscopy. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2001, 1, F4.3.1–F4.3.8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.L.; Wang, L.J.; Fan, Y.; Parsons, R.L.; Hu, G.R.; Zhang, P.Y. A rapid method for the determination of fucoxanthin in diatom. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudhakar, M.P.; Ananthalakshmi, J.S.; Nair, B.B. Extraction, purification and study on antioxidant properties of fucoxanthin from brown seaweeds. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2013, 5, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Loredo, A.; González-Valdez, J.; Rito-Palomares, M. Insights on the downstream purification of fucoxanthin, a microalgal carotenoid, from an aqueous two-phase system stream exploiting ultrafiltration. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Zhao, L. Stability, bioactivity, and bioaccessibility of fucoxanthin in zein-caseinate composite nanoparticles fabricated at neutral pH by antisolvent precipitation. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.Y.; Mok, I.-K.; Pan, C.-H.; Kim, S.M. Preparation of Fucoxanthin-Loaded Nanoparticles Composed of Casein and Chitosan with Improved Fucoxanthin Bioavailability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9428–9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yan, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, D. The stability and bioaccessibility of fucoxanthin in spray-dried microcapsules based on various biopolymers. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 35139–35149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, L.; Eitenmiller, R.R. Fat-soluble vitamins. In Handbook of Food Science, Technology, and Engineering—4 Volume Set; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 9781466507876. [Google Scholar]
- López, C.J.; Caleja, C.; Prieto, M.A.; Sokovic, M.; Calhelha, R.C.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Stability of a cyanidin-3-O-glucoside extract obtained from Arbutus unedo L. and incorporation into wafers for colouring purposes. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prieto, M.A.; Murado, M.A.; Rodríguez-Amado, I.; Vázquez, J.A. β-Carotene assay revisited. Application to characterize and quantify antioxidant and prooxidant activities in a microplate. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8983–8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mok, I.K.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, J.H.; Pan, C.H.; Kim, S.M. Fucoxanthin bioavailability from fucoxanthin-fortified milk: In vivo and in vitro study. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Xia, G.; Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Kong, M.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C.; Chen, X.; et al. Isolation of fucoxanthin from Sargassum thunbergii and preparation of microcapsules based on palm stearin solid lipid core. Front. Mater. Sci. 2017, 11, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Khalid, N.; Shu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Kobayashi, I.; Neves, M.A.; Tuwo, A.; Nakajima, M. Fucoxanthin-Loaded Oil-in-Water Emulsion-Based Delivery Systems: Effects of Natural Emulsifiers on the Formulation, Stability, and Bioaccessibility. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 10502–10509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Sun, Q.; Um, B.H.; Park, Y.; McClements, D.J. In Vitro and in vivo study of fucoxanthin bioavailability from nanoemulsion-based delivery systems: Impact of lipid carrier type. J. Funct. Foods 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, D.; Kim, M.; Gu, M.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Pan, C.H.; Kim, G.H.; Chung, D. Effects of temperature, light, and pH on the stability of fucoxanthin in an oil-in-water emulsion. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, H.; Baskaran, V. Biodegradable chitosan-glycolipid hybrid nanogels: A novel approach to encapsulate fucoxanthin for improved stability and bioavailability. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taofiq, O.; Heleno, S.A.; Calhelha, R.C.; Fernandes, I.P.; Alves, M.J.; Barros, L.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barreiro, M.F. Mushroom-based cosmeceutical ingredients: Microencapsulation and in vitro release profile. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 124, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Park, Y.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ryu, B.M. Bioactivities of the edible brown seaweed, Undaria pinnatifida: A review. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, K.; Hosokawa, M. Fucoxanthin in the management of obesity and its related disorders. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Tsukui, T.; Sashima, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Seaweed carotenoid, fucoxanthin, as a multi-functional nutrient. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17, 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Gumus, R.; Urcar Gelen, S.; Koseoglu, S.; Ozkanlar, S.; Ceylan, Z.G.; Imik, H. The effects of fucoxanthin dietary inclusion on the growth performance, antioxidant metabolism and meat quality of broilers. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 2018, 20, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ding, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Fucoxanthin provides neuroprotection in models of traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE and Nrf2-autophagy pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.; Chen, W.; Tian, F.; Yuan, C.; Wang, H.; Yue, H. Neuroprotective role of fucoxanthin against cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Kim, S.M.; Pan, C.H.; Chung, D. Effects of heating, aerial exposure and illumination on stability of fucoxanthin in canola oil. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, R.C.; Gracia Mateo, M.R.; O’Grady, M.N.; Guihéneuf, F.; Stengel, D.B.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Kerry, J.P.; Stanton, C. An assessment of the techno-functional and sensory properties of yoghurt fortified with a lipid extract from the microalga Pavlova lutheri. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 37, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, I.K.; Yoon, J.R.; Pan, C.H.; Kim, S.M. Development, quantification, method validation, and stability study of a novel fucoxanthin-fortified milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6196–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimura, R.; Suda, M.; Sho, A.; Takahashi, T.; Sashima, T.; Abe, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Stability of fucoxanthin in dried Undaria pinnatifida (wakame) and baked products (scones) containing wakame powder. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 18, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, K.; Ishihara, K.; Oyamada, C.; Sato, A.; Fukushi, A.; Arakane, T.; Motoyama, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Mitsumoto, M. Effects of fucoxanthin addition to ground chicken breast meat on lipid and colour stability during chilled storage, before and after cooking. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 21, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Tanaka, K.; Higashiguchi, N.; Okawa, H.; Yamada, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Taira, S.; Aoyama, T.; Takanishi, M.; Natsume, C.; et al. Protective and therapeutic effects of fucoxanthin against sunburn caused by UV irradiation. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 132, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heo, S.J.; Jeon, Y.J. Protective effect of fucoxanthin isolated from Sargassum siliquastrum on UV-B induced cell damage. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2009, 95, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, H.; Tanaka, J.; Shan, S.J.; Maoka, T. Anti-pigmentary activity of fucoxanthin and its influence on skin mRNA expression of melanogenic molecules. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Luna, A.; Ávila-Román, J.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Cózar, M.J.; Rabasco, A.M.; Motilva, V.; Talero, E. Fucoxanthin-containing cream prevents epidermal hyperplasia and UVB-induced skin erythema in mice. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Nam, G.-W. Sunscreen boosting effect by solid lipid nanoparticles-loaded fucoxanthin formulation. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Algae Species | Solvent | Extraction Conditions | Detection Method | Fx (mg/g DW) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ME | |||||
| Alaria crassifolia | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 1.10 | [46] |
| Alaria esculenta | AcO 62.2% | 30 °C, 36.5 min | HPLC-DAD | 0.87 | [31] |
| Analipus japonicas | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 1.40 | [46] |
| Cladosiphon okamuranus | MeOH | RT, 1 h | HPLC-DAD | 0.27 | [47] |
| Cystoseira hakodatensis | Ch, MeOH (1:2) | RT, 2 h | HPLC-DAD | 2.01 | [48] |
| MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 2.40 | [46] | |
| Ch/MeOH (1:2) | RT, 1 h | HPLC-DAD | 3.47 | [24] | |
| Desmarestia viridis | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 0.10 | [46] |
| Dictyopteris australis | AcO | 4 °C, 12 h | Spec | 0.23 | [44] |
| Dictyota dichotoma | EtOH | RT, 15 min × 5 | HPTLC | 0.44 | [49] |
| AcO | 4 °C, 12 h | Spec | 0.18 | [44] | |
| MeOH | RT, 24 h | HPLC-PDA | 6.42 | [50] | |
| Ecklonia kurome | Chl/MeOH (1:2) | RT, 2 h | HPLC-DAD | 1.68 | [48] |
| Fucus distichus | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 0.90 | [46] |
| AcO | RT, 5 min | Spec | 0.16 | [51] | |
| Fucus serratus | Hx/AcO (70:30) | RT, 24 h | HPLC-DAD | 3.57 | [27] |
| Himanthalia elongata | n-Hx, DE, Ch | RT, 15 min | LC-ESI-MS, HPLC, 1H-NMR | 18.60 | [52] |
| Hizikia fusiformis | MeOH | - | HPLC-DAD | 0.02 | [43] |
| Ishige okamurae | MeOH | HPLC-DAD | nd | [53] | |
| Iyengaria stellate | AcO | 4 °C, 12 h | Spec | 0.18 | [44] |
| Kjellmaniella crassifolia | MeOH | RT, 15 min | HPLC-DAD | 0.15 | [54] |
| Laminaria japonica | MeOH | - | HPLC-DAD | 0.19 | [43] |
| Laminaria digitata | AcO 62.2% | 30°, 36.5 min | HPLC-DAD | 0.65 | [31] |
| Laminaria religiosa | MeOH | RT, 96 h | HPLC-DAD, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR | 0.24 | [21] |
| Laminaria saccharina | AcO | RT, 5 min | Spec | 0.24 | [51] |
| Leathesia difformis | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 0.30 | [46] |
| Lobophora variegata | AcO | 4 °C, 12 h | Spec | 0.23 | [44] |
| Melanosiphon intestinalis | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 1.90 | [46] |
| Myagropsis myagroides | MeOH | RT, 24 h | HPLC-PDA | 9.01 | [50] |
| Padina australis | Chl/MeOH (1:2) | RT, 2 h | HPLC-DAD | 1.29 | [48] |
| Padina gymnospora | AcO | 4 °C, 12 h | Spec | 0.43 | [44] |
| Padina minor | EtOH | RT, 15 min × 5 | HPTLC | 0.50 | [49] |
| Padina pavonica | 0.43 | ||||
| Padina tetrastromatica | AcO | 4 °C, 12 h | Spec | 0.41 | [44] |
| Petalonia binghamiae | MeOH | RT, 48 h | HPLC-DAD, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR | 0.58 | [21] |
| Saccharina japonica | MeOH | RT, 15 min | HPLC-DAD | 0.03 | [54] |
| Saccharina sculpera | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 0.70 | [46] |
| Sargassum binderi | MeOH | RT, 12 h × 2 | HPLC-DAD | 0.73 | [55] |
| Sargassum confusum | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 1.60 | [46] |
| Sargassum crassifolium | Chl/MeOH (1:2) | RT, 2 h | HPLC-DAD | 1.64 | [48] |
| Sargassum duplicatum | MeOH | RT, 12 h × 2 | HPLC-DAD | 1.01 | [55] |
| Sargassum fulvellum | MeOH | - | HPLC-DAD | 0.01 * | [43] |
| Sargassum fusiforme | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 1.10 | [46] |
| AcO/EtOH (1:40) | 65 °C, 80 min | Spec | 2.62 | [42] | |
| Sargassum horneri | Chl/MeOH (1:2) | RT, 2 h | HPLC-DAD | 2.12 | [48] |
| MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 3.70 | [46] | |
| Ch/MeOH (1:2) | RT, 1 h | HPLC-DAD | 4.49 | [24] | |
| Sargassum linearifolium | AcO | 4 °C, 12 h | Spec | 0.37 | [44] |
| Sargassum muticum | AcO | RT, 5 min | Spec | 0.29 | [51] |
| Sargassum plagiophyllum | AcO/MeOH (7:3) | ice, 15 min | HPLC | 0.71 | [56] |
| Sargassum polycystum | EtOH | RT, 15 min × 5 | HPTLC | 0.41 | [49] |
| Sargassum siliquastrum | Chl/MeOH (1:2) | RT, 2 h | HPLC-DAD | 1.99 | [48] |
| Sargassum thunbergii | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 1.80 | [46] |
| Scytosiphon lomentaria | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 0.50 | [46] |
| MeOH | RT, 96 h | HPLC-DAD, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR | 0.56 | [21] | |
| Silvetia babingtonii | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 0.70 | [46] |
| Spatoglossum asperum | AcO | 4 °C, 12 h | Spec | 0.58 | [44] |
| Sphaerotrichia divaricata | MeOH | RT, 12 h | HPLC-PDA | 0.20 | [46] |
| Stoechospermum marginatum | AcO | 4 °C, 12 h | Spec | 0.37 | [44] |
| Turbinaria ornate | Chl/MeOH (1:2) | RT, 2 h | HPLC-DAD | 1.27 | [48] |
| Turbinaria spp. | AcO | 4 °C, 12 h | Spec | 0.43 | [44] |
| Turbinaria turbinata | AcO/MeOH (7:3) | ice, 15 min | HPLC | 0.59 | [56] |
| Undaria pinnatifida | MeOH | RT, 96 h | HPLC-DAD, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR | 2.67 | [21] |
| MeOH | RT, 1 h | HPLC-DAD | 2.08 | [22] | |
| MeOH | RT, 1 h | HPLC-DAD | 4.96 * | ||
| EtOH | RT, 1 h | HPLC-DAD | 0.70 | [36] | |
| VAE | |||||
| Ascophylum nodossum | EtOH | RT, 15 min | HPLC-PDA | 0.02 | [32] |
| Dictyota dichotoma | 0.60 | ||||
| Fucus vesiculosus | EtOH | RT, 15 min | HPLC-PDA | 0.02 | [32] |
| AcO | 40 °C, 40 min | HPLC-DAD | 0.70 | [31] | |
| Sargassum vulgare | EtOH | RT, 15 min | HPLC-PDA | 0.40 | [32] |
| Zonaria tournefortii | 0.80 | ||||
| SAE | |||||
| Feldmannia mitchelliae | EA | 80 °C, 16 h | HPLC | 5.50 | [57] |
| Saccharina japonica | n-Hx | 40 °C, 16 h | HPLC | 0.45 | [34] |
| Sargassum swartzii C. Agardh | EA | 80 °C, 6 h | FT-IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR | 0.17 | [58] |
| EAE | |||||
| Fucus vesiculosus | W | Viscozyme, 50 °C, 100 rpm, 10 min | HPLC-UV, LC-MS | 0.66 | [35] |
| MAE | |||||
| Laminaria japonica | Hp, AcO, W | 50 °C, 10 min | LC-ESI-MS, HPLC, 1H-NMR | 0.04 | [37] |
| Sargassum fusiforme | 0.02 | ||||
| Undaria pinnatifida | 0.90 | ||||
| UEA | |||||
| Padina tetrastromatica | EtOH | 50 Hz, 30 min | HPLC-DAD | 0.75 | [20] |
| PLE | |||||
| Eisenia bicyclis | EtOH | 110 °C, 5 min | HPLC-PDA | 0.42 | [38] |
| Undaria pinnatifida | EtOH | 78 °C, 12 h | HPLC-UV | 0.05 | [19] |
| SFE | |||||
| Fucus serratus | EtOH | 50 °C, 304 bars, 1 h | HPLC-DAD | 2.18 | [27] |
| Sargassum horneri | CO2, EtOH | 45 °C, 250 bars | HPLC-DAD | 0.77 | [41] |
| Sargassum japonica | 0.41 | ||||
| Sargassum muticum | CO2, EtOH | 50 °C, 100 bars | HPLC-DAD | 0,55 | [59] |
| Undaria pinnatifida | CO2, EtOH | 50 °C, 200 bars | HPLC-UV | <0.01 | [40] |
| CO2, EtOH | 60 °C, 400 bars | HPLC-UV | 0.99 | [19] | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carpena, M.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Pereira, A.G.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Scientific Approaches on Extraction, Purification and Stability for the Commercialization of Fucoxanthin Recovered from Brown Algae. Foods 2020, 9, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081113
Lourenço-Lopes C, Garcia-Oliveira P, Carpena M, Fraga-Corral M, Jimenez-Lopez C, Pereira AG, Prieto MA, Simal-Gandara J. Scientific Approaches on Extraction, Purification and Stability for the Commercialization of Fucoxanthin Recovered from Brown Algae. Foods. 2020; 9(8):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081113
Chicago/Turabian StyleLourenço-Lopes, Catarina, Paula Garcia-Oliveira, Maria Carpena, Maria Fraga-Corral, Cecilia Jimenez-Lopez, Antia G. Pereira, Miguel A. Prieto, and Jesus Simal-Gandara. 2020. "Scientific Approaches on Extraction, Purification and Stability for the Commercialization of Fucoxanthin Recovered from Brown Algae" Foods 9, no. 8: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081113
APA StyleLourenço-Lopes, C., Garcia-Oliveira, P., Carpena, M., Fraga-Corral, M., Jimenez-Lopez, C., Pereira, A. G., Prieto, M. A., & Simal-Gandara, J. (2020). Scientific Approaches on Extraction, Purification and Stability for the Commercialization of Fucoxanthin Recovered from Brown Algae. Foods, 9(8), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081113