Adaptive Mesh Refinement Strategies for Cost-Effective Eddy-Resolving Transient Simulations of Spray Dryers
Abstract
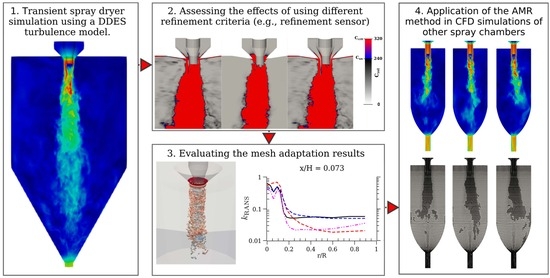
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Methods and Turbulence Modeling
2.1. Governing Equations and Turbulence Modeling
2.2. Adaptive Mesh Refinement
2.3. Numerical Schemes and Methods
3. Computational Configuration
3.1. Flow Configuration and Domain
3.2. Grids
4. Numerical Experiments
4.1. Study Cases
4.2. Simulation Times and Sampling of Data
5. Results
5.1. Computational Costs
5.2. Flow Development and Sampling Times
5.3. Typical Refinement Regions
5.3.1. Pilot-Size Spray Chamber
5.3.2. Semi-Industrial-Size Spray Chamber
5.4. Turbulence Resolution at the Jet Discharge
5.5. Effects of the AMR Approach on the Mean Axial Velocity Profiles and Turbulence Resolution in the Pilot-Size Spray Chamber
5.5.1. Mean Axial Velocity Profiles
5.5.2. Turbulence Statistics
5.6. Effects of the Refinement Threshold and Cell Level
5.6.1. Pilot-Size Spray Chamber
Axial Velocity Profiles
Turbulence Statistics
5.6.2. Semi-Industrial-Size Spray Chamber
Axial Velocity Profiles
Velocity Intervals: Comparison with Experimental Data
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos, D.; Maurício, A.C.; Sencadas, V.; Santos, J.D.; Fernandes, M.H.; Gomes, P.S. Spray drying: An overview. In Biomaterials-Physics and Chemistry-New Edition; IntechOpen: Londone, UK, 2018; pp. 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, M. Modelling Requirements for CFD Calculations of Spray Dryers. Jornada em escoamentos multifásicos 2015. 2015. Available online: https://eventos.abcm.org.br/jem2015/KEYNOTES/K03_PRESENTATION.PDF (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Kieviet, F. Modelling Quality in Spray Drying. Ph.D. Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbicinski, I. Modeling and scaling up of industrial spray dryers: A review. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2017, 50, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieviet, F.; Kerkhof, P. Air flow, temperature and humidity patterns in a co-current spray dryer: Modelling and measurements. Dry. Technol. 1997, 15, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.W.; Huang, L.X.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Daud, W.R.W. CFD Simulation of Spray Dryers; Number 1; National University of Singapore: Singapore, 2010; Chapter 1; pp. 1–36. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/view/32880341/spray-drying-technologypdf-national-university-of-singapore (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Southwell, D.; Langrish, T. Observations of flow patterns in a spray dryer. Dry. Technol. 2000, 18, 661–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwell, D.; Langrish, T. The effect of swirl on flow stability in spray dryers. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2001, 79, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, D.; Guo, B.; Harvie, D.; Langrish, T.; Nijdam, J.; Williams, J. What is important in the simulation of spray dryer performance and how do current CFD models perform? Appl. Math. Model. 2006, 30, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebarbier, C.; Kockel, T.; Fletcher, D.; Langrish, T. Experimental measurement and numerical simulation of the effect of swirl on flow stability in spray dryers. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2001, 79, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langrish, T.; Williams, J.; Fletcher, D. Simulation of the effects of inlet swirl on gas flow patterns in a pilot-scale spray dryer. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2004, 82, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, X.D. A three-dimensional numerical study of the gas/particle interactions in an industrial-scale spray dryer for milk powder production. Dry. Technol. 2009, 27, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongsma, F.; Innings, F.; Olsson, M.; Carlsson, F. Large eddy simulation of unsteady turbulent flow in a semi-industrial size spray dryer. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2013, 93, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, D.; Langrish, T. Scale-adaptive simulation (SAS) modelling of a pilot-scale spray dryer. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2009, 87, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, S.; Jubaer, H.; Chen, B.; Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Woo, M. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of spray dryers: Transient or steady state simulation? In IDS 2018 21st International Drying Symposium Proceedings; Editorial Universitat Politècnica de València: Valencia, Spain, 2018; pp. 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampa, A.; Fritsching, U. Large Eddy Simulation of the spray formation in confinements. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2013, 43, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimbun, J.; Muhammad, N.I.S.; Law, W.P. Unsteady RANS and detached eddy simulation of the multiphase flow in a co-current spray drying. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides-Morán, A.; Cubillos, A.; Gómez, A. Spray drying experiments and CFD simulation of guava juice formulation. Dry. Technol. 2021, 39, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.; Nahi Saleh, S. Transient simulation of air flow in a co-current spray dryer. In Proceedings of the European Drying Conference–EuroDrying, Palma, Spain, 26–28 October 2011; pp. 26–28. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270506995_TRANSIENT_SIMULATION_OF_AIR_FLOW_IN_A_CO-CURRENT_SPRAY_DRYER (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Antepara, O.; Lehmkuhl, O.; Borrell, R.; Chiva, J.; Oliva, A. Parallel adaptive mesh refinement for large-eddy simulations of turbulent flows. Comput. Fluids 2015, 110, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, S.B. Ten questions concerning the large-eddy simulation of turbulent flows. New J. Phys. 2004, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathe, K.J.; Zhang, H. A mesh adaptivity procedure for CFD and fluid-structure interactions. Comput. Struct. 2009, 87, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, B.; Menon, S. Large eddy simulation of turbulent reacting jet in cross flow with adaptive mesh refinement. In Proceedings of the 52nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting, National Harbor, MD, USA, 13–17 January 2014; p. 0825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, S.; Visonneau, M.; Wackers, J. Average-based Adaptive Grid Refinement in Hybrid LES. In Direct and Large Eddy Simulation XII; García-Villalba, M., Kuerten, H., Salvetti, M.V., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 27, pp. 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackers, J.; Visonneau, M.; Ali, Z. Automatic grid adaptation for unstructured finite volumes. Int. J. Eng. Syst. Model. Simul. 2010, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez Suárez, J.A.; Galeano-Urueña, C.H.; Gómez-Mejía, A. Low-Cost Eddy-Resolving Simulation in the Near-Field of an Annular Swirling Jet for Spray Drying Applications. ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez Suárez, J.A. Modelación CFD y validación experimental del proceso de evaporación de agua en un secador por aspersión. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Colombia-Sede Bogotá, Bogota, Colombia, 2015. Available online: https://repositorio.unal.edu.co/handle/unal/56048 (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Davidson, L. Fluid Mechanics, Turbulent Flow and Turbulence Modeling. Lecture Notes; Chalmers University of Technology. 2015. Available online: https://www.tfd.chalmers.se/~lada/postscript_files/solids-and-fluids_turbulent-flow_turbulence-modelling.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Fröhlich, J.; von Terzi, D. Hybrid LES/RANS methods for the simulation of turbulent flows. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2008, 44, 349–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travin, A.K.; Shur, M.L.; Spalart, P.R.; Strelets, M.K. Improvement of delayed detached-eddy simulation for LES with wall modelling. In Proceedings (CDROM) of the European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics ECCOMAS CFD, Egmond aan Zee, The Netherlands, 5–8 September 2006; Available online: https://www.cobaltcfd.com/pdfs/ECCOMAS_2006_improvement_DDESl.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Gritskevich, M.S.; Garbaruk, A.V.; Schütze, J.; Menter, F.R. Development of DDES and IDDES formulations for the k-ω shear stress transport model. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2012, 88, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzmann, T. Mathematics, Numerics, Derivations and OpenFOAM®, 4th ed.; Holzmann CFD: Loeben, Germany, 2017; Available online: https://www.academia.edu/download/56994390/MathematicsNumericsDerivationsAndOpenFOAM.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Moukalled, F.; Mangani, L.; Darwish, M. Temporal Discretization: The Transient Term. In The Finite Volume Method in Computational Fluid Dynamics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 489–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travin, A.; Shur, M.; Strelets, M.; Spalart, P. Physical and numerical upgrades in the detached-eddy simulation of complex turbulent flows. In Advances in LES of Complex Flows; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieviet, F.; Van Raaij, J.; De Moor, P.; Kerkhof, P. Measurement and modelling of the air flow pattern in a pilot-plant spray dryer. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1997, 75, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okiishi, T.H. Fluid Velocity Profile Development for Turbulent Flow in Smooth Annuli; Digital Repository; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubillos Varela, A. Modelación del proceso de deshidratación por espray de jugo de guayaba. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá, Colombia, 2017. Available online: https://repositorio.unal.edu.co/handle/unal/62971 (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Anandharamakrishnan, C.; Gimbun, J.; Stapley, A.G.F.; Rielly, C.D. A study of particle histories during spray drying using computational fluid dynamic simulations. Dry. Technol. 2010, 28, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.N. CFD simulations of a co-current spray dryer. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 62, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Kumar, K.; Mujumdar, A. A comparative study of a spray dryer with rotary disc atomizer and pressure nozzle using computational fluid dynamic simulations. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2006, 45, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.; Jolius, G. Detached eddy simulation (DES) of co-current spray dryer. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2013, 2, 17–22. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/159178374.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Keshani, S.; Montazeri, M.H.; Daud, W.R.W.; Nourouzi, M.M. CFD modeling of air flow on wall deposition in different spray dryer geometries. Dry. Technol. 2015, 33, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culpo, M. Current Bottlenecks in the Scalability of OpenFOAM on Massively Parallel Clusters. PRACE White Paper 2011. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=308b983be3866f527931149b5686335fd8cb99b5 (accessed on 26 September 2023).




















| Schemes | Description |
|---|---|
| Temporal terms | SOUE (Adams Moulton), second-order implicit, described in Moukalled et al. [33]. |
| Gradient— | CDS (central differencing scheme). |
| Gradient— | Limited-CDS. |
| Advective terms—div | Hybrid scheme, described in Gutiérrez Suárez et al. [26], Travin et al. [34]. |
| RANS mode | LUD (linear upwind differencing). |
| LES mode | CDS. |
| Pressure–velocity coupling | PIMPLE algorithm, described in Holzmann [32]. |
| Description | Pilot-Size Spray Drying Chamber | Semi-Industrial Spray Drying Chamber |
|---|---|---|
| Volumetric flow | ||
| RPMs at the discharge | 238 | 0 |
| Swirl number | 0.052 | 0 |
| 0.0355 m | 0.244 m | |
| 0.0260 m | 0.2024 m | |
| 0.0190 m | 0.084 m | |
| Re | 19,600 | 41,200 |
| Reference air density | ||
| Kinematic air viscosity |
| Spray Drying Chamber | Elements | x | r | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pilot-size chamber | 27,505 | 88 | 19 | 16 |
| Semi-industrial-size chamber | 39,540 | 52 | 19 | 28 |
| Drying Chamber | Author | Year | Grid Size | Turbulence | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pilot size | Gutiérrez Suárez [27] | 2015 | 12,672 (2D-axi-symmetric) | steady | |
| Benavides-Morán et al. [18] | 2020 | 2,200,000 | SST and SAS | transient | |
| Present study (level 2 refined base grid) | 2023 | 1,750,000 | SST-DDES | transient | |
| Semi-industrial size | Huang et al. [40] | 2006 | not reported | steady | |
| Anandharamakrishnan et al. [38] | 2010 | 294,237 | steady | ||
| Saleh [39] | 2010 | 840,000 | transient | ||
| Noor and Jolius [41] | 2011 | 503,000 | SA-DES | transient | |
| Saleh and Nahi Saleh [19] | 2011 | 516,000 | RNG | transient | |
| Gimbun et al. [17] | 2015 | 420,000 | SA-DES | transient | |
| Keshani et al. [42] | 2015 | 1,223,675 (Case A) | RNG | transient | |
| Present study (level 2 refined base grid) | 2023 | 736,000 | SST-DDES | transient |
| Pilot-size drying chamber | |||||
| Case | Number of cells | AMR flow variable | Max. refinement level | Turbulence | |
| C (base) | 1,750,000 | fixed grid | - | Level 2 globally refined base grid | DDES |
| C1 | 300,000 | 370 (ref) | 2 | DDES | |
| C2 | 300,000 | 370 | 2 | DDES | |
| C2-1 | 78,000 | 3700 | 2 | DDES | |
| C2-2 | 180,000 | 3700 | 3 | DDES | |
| C2-3 | 380,000 | 370 | 2 using a level 1 globally refined base grid | DDES | |
| C3 | 300,000 | 370 (ref) | 2 | DDES | |
| Semi-industrial-size drying chamber | |||||
| S1 | 170,000 | 12,360 | 2 | DDES | |
| S2 | 220,000 | 4120 | 2 | DDES | |
| S3 | 378,000 | 1236 | 2 | DDES | |
| Reference | rms | k | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 0.0052 | 0.0186 | 0.0789 | 0.097 | 0.191 |
| C1 | 0.0073 | 0.0271 | 0.2443 | 0.271 | 0.100 |
| C2 | 0.0141 | 0.0233 | 0.3289 | 0.352 | 0.066 |
| C3 | 0.0110 | 0.0265 | 0.0950 | 0.122 | 0.218 |
| C2-1 | 0.0146 | 0.0156 | 0.0247 | 0.040 | 0.387 |
| C2-2 | 0.0416 | 0.1239 | 0.0492 | 0.173 | 0.716 |
| C2-3 | 0.0711 | 0.0225 | 0.07508 | 0.095 | 0.237 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez Suárez, J.A.; Galeano Urueña, C.H.; Gómez Mejía, A. Adaptive Mesh Refinement Strategies for Cost-Effective Eddy-Resolving Transient Simulations of Spray Dryers. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7050100
Gutiérrez Suárez JA, Galeano Urueña CH, Gómez Mejía A. Adaptive Mesh Refinement Strategies for Cost-Effective Eddy-Resolving Transient Simulations of Spray Dryers. ChemEngineering. 2023; 7(5):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7050100
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez Suárez, Jairo Andrés, Carlos Humberto Galeano Urueña, and Alexánder Gómez Mejía. 2023. "Adaptive Mesh Refinement Strategies for Cost-Effective Eddy-Resolving Transient Simulations of Spray Dryers" ChemEngineering 7, no. 5: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7050100
APA StyleGutiérrez Suárez, J. A., Galeano Urueña, C. H., & Gómez Mejía, A. (2023). Adaptive Mesh Refinement Strategies for Cost-Effective Eddy-Resolving Transient Simulations of Spray Dryers. ChemEngineering, 7(5), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7050100