Freeze Drying Improves the Shelf-Life of Conductive Polymer Modified Neural Electrodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polymer Modified Implantable Microwires
2.3. Freeze-Drying of Polymer Modified Implantable Microwires
2.4. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV), Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) and Modeling
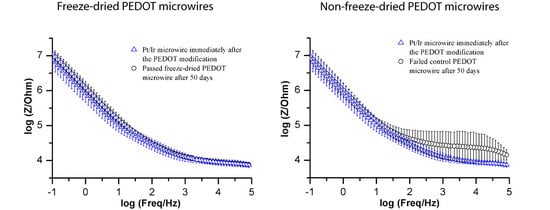
3. Results and Discussion


| Non-Freeze-Dried, Immediately after PEDOT Modification | Non-Freeze-Dried (d41–d50) | Freeze-Dried, Immediately after PEDOT Modification | Freeze-Dried (d1–d50) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs (Ohm-cm2) | 1.21 × 104 (5.22 × 100) | 4.31 × 103 (2.54 × 100) | 9.66 × 103 (2.93 × 100) | 9.39 × 103 (2.30 × 100) |
| Cd (F/cm2) | 2.88 × 10-8 (1.50 × 101) | 1.41 × 10-10 (7.62 × 100) | 2.11 × 10-8 (7.70 × 100) | 2.46 × 10-8 (7.17 × 100) |
| Rpoly (Ohm-cm2) | 3.75 × 104 (2.09 × 101) | 3.71 × 104 (3.15 × 100) | 2.96 × 104 (9.03 × 100) | 2.25 × 104 (8.89 × 100) |
| Qpoly (S-secn/cm2) | 1.24 × 10-7 (9.49 × 100) | 1.44 × 10-7 (2.69 × 100) | 1.28 × 10-7 (4.53 × 100) | 1.27 × 10-7 (3.78 × 100) |
| n (0 < n < 1) | 9.38 × 10-1 (2.88 × 100) | 9.48 × 10-1 (8.34 × 10-1) | 9.38 × 10-1 (1.36 × 100) | 9.29 × 10-1 (1.07 × 100) |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ludwig, K.A.; Langhals, N.B.; Joseph, M.D.; Richardson-Burns, S.M.; Hendricks, J.L.; Kipke, D.R. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) polymer coatings facilitate smaller neural recording electrodes. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, K.A.; Uram, J.D.; Yang, J.; Martin, D.C.; Kipke, D.R. Chronic neural recordings using silicon microelectrode arrays electrochemically deposited with a poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) film. J. Neural Eng. 2006, 3, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.T.; Zhou, D.D. Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) for chronic neural stimulation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.A.; Hassarati, R.T.; Bouchinet, L.; Lee, C.S.; Cheong, G.L.M.; Yu, J.F.; Dodds, C.W.; Suaning, G.J.; Poole-Warren, L.A.; Lovell, N.H. Substrate dependent stability of conducting polymer coatings on medical electrodes. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5875–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwig, R.; Stett, A.; Stelzle, M. PEDOT–CNT composite microelectrodes for recording and electrostimulation applications: Fabrication, morphology, and electrical properties. Front. Neuroeng. 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Weaver, C.L.; Zhou, D.D.; Greenberg, R.; Cui, X.T. Highly stable carbon nanotube doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for chronic neural stimulation. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5551–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, H.S.; Knaack, G.L.; Charkhkar, H.; McHail, D.G.; Kastee, J.S.; Dumas, T.C.; Peixoto, N.; Rubinson, J.F.; Pancrazio, J.J. Improving the performance of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for brain–machine interface applications. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, H.S.; Kastee, J.S.; McHail, D.G.; Rubinson, J.F.; Pancrazio, J.J.; Dumas, T.C. Improved poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) for neural stimulation. Neuromodulation 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispin, X.; Jakobsson, F.L.E.; Crispin, A.; Grim, P.C.M.; Andersson, P.; Volodin, A.; van Haesendonck, C.; Van der Auweraer, M.; Salaneck, W.R.; Berggren, M. The origin of the high conductivity of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)−poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT−PSS) plastic electrodes. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4354–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayinamura, Y.P.; Ovadia, M.; Zavitz, D.; Rubinson, J.F. Investigation of near ohmic behavior for poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): A model consistent with systematic variations in polymerization conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozai, T.D.Y.; Langhals, N.B.; Patel, P.R.; Deng, X.; Zhang, H.; Smith, K.L.; Lahann, J.; Kotov, N.A.; Kipke, D.R. Ultrasmall implantable composite microelectrodes with bioactive surfaces for chronic neural interfaces. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Martin, D.C. Electrochemical deposition and characterization of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) on neural microelectrode arrays. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 89, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collazos-Castro, J.E.; Hernández-Labrado, G.R.; Polo, J.L.; García-Rama, C. N-Cadherin- and L1-functionalised conducting polymers for synergistic stimulation and guidance of neural cell growth. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3603–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamato, H.; Ohwa, M.; Wernet, W. Stability of polypyrrole and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for biosensor application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1995, 397, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrapani, N.; Wei, B.; Carrillo, A.; Ajayan, P.M.; Kane, R.S. Capillarity-driven assembly of two-dimensional cellular carbon nanotube foams. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101, 4009–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Qiu, J. Tailoring of three-dimensional carbon nanotube architectures by coupling capillarity-induced assembly with multiple CVD growth. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 5967–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, S.; Zhai, J.; Li, H.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Self-assembly of large-scale micropatterns on aligned carbon nanotube films. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futaba, D.N.; Hata, K.; Yamada, T.; Hiraoka, T.; Hayamizu, Y.; Kakudate, Y.; Tanaike, O.; Hatori, H.; Yumura, M.; Iijima, S. Shape-engineerable and highly densely packed single-walled carbon nanotubes and their application as super-capacitor electrodes. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshosaz, J.; Eskandari, S.; Tabbakhian, M. Freeze-drying of nanostructure lipid carriers by different carbohydrate polymers used as cryoprotectants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.-W.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.-J.; Wang, W.; Chen, Q.; Chu, L.-Y. Nano-structured smart hydrogels with rapid response and high elasticity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moral-Vico, J.; Carretero, N.M.; Pérez, E.; Suñol, C.; Lichtenstein, M.; Casañ-Pastor, N. Dynamic electrodeposition of aminoacid-polypyrrole on aminoacid-PEDOT substrates: Conducting polymer bilayers as electrodes in neural systems. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 111, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Cheng, X.; Rao, L.; Li, T.; Duan, Y.Y. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/multiwall carbon nanotube composite coatings for improving the stability of microelectrodes in neural prostheses applications. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6439–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Lee, V.A.; Raphael, Y.; Wiler, J.A.; Hetke, J.F.; Anderson, D.J.; Martin, D.C. Surface modification of neural recording electrodes with conducting polymer/biomolecule blends. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 56, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Hetke, J.F.; Wiler, J.A.; Anderson, D.J.; Martin, D.C. Electrochemical deposition and characterization of conducting polymer polypyrrole/PSS on multichannel neural probes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 93, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandal, H.S.; Cliff, R.O.; Pancrazio, J.J. Freeze Drying Improves the Shelf-Life of Conductive Polymer Modified Neural Electrodes. Bioengineering 2015, 2, 176-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering2030176
Mandal HS, Cliff RO, Pancrazio JJ. Freeze Drying Improves the Shelf-Life of Conductive Polymer Modified Neural Electrodes. Bioengineering. 2015; 2(3):176-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering2030176
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandal, Himadri S., Richard O. Cliff, and Joseph J. Pancrazio. 2015. "Freeze Drying Improves the Shelf-Life of Conductive Polymer Modified Neural Electrodes" Bioengineering 2, no. 3: 176-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering2030176
APA StyleMandal, H. S., Cliff, R. O., & Pancrazio, J. J. (2015). Freeze Drying Improves the Shelf-Life of Conductive Polymer Modified Neural Electrodes. Bioengineering, 2(3), 176-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering2030176