Challenges and Solutions for Commercial Scale Manufacturing of Allogeneic Pluripotent Stem Cell Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
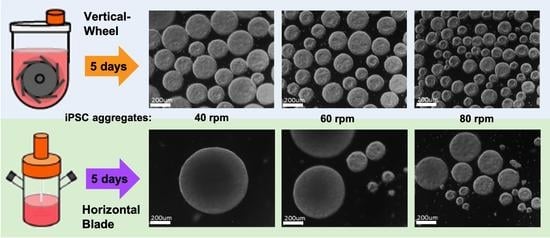
2. Scalable Bioreactor Technology as Manufacturing Solution
3. Independent Biological Performance Data from Collaborators
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induced Puripotent Stem Cells in Medicine and Biology. Development 2013, 140, 2457–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Inoue, H.; Wu, J.C. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Technology: A Decade of Progress. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simaria, A.S.; Hassan, S.; Varadaraju, H.; Rowley, J.; Warren, K.; Vanek, P.; Farid, S.S. Allogeneic Cell Therapy Bioprocess Economics and Optimization: Single-Use Cell Expansion Technologies. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, C.A.V.; Fernandes, T.G.; Diogo, M.M. Stem Cell Cultivation in Bioreactors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.A.V.; Branco, M.; Nogueira, D.E.S.; Silva, T.; Gomes, A.R.; Diogo, M.M.; Cabral, J.M.S. Chapter 2—Bioreactors for Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Expansion and Differentiation. In Bioreactors for Stem Cell Expansion and Differentiation; Cabral, J.M.S., Lobato de Silva, Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.G.; Mallon, B.S.; McKay, R.D.G. Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Culture: Considerations for Maintenance, Expansion, and Therapeutics. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nogueira, D.E.S.; Rodrigues, C.A.V.; Carvalho, M.S.; Miranda, C.C.; Hashimura, Y.; Jung, S.; Lee, B.; Cabral, J.M.S. Strategies for The Expansion of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem cells as Aggregates in Single-Use Vertical-Wheel Bioreactors. J. Biol. Eng. 2019, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauwens, C.L.; Peerani, R.; Niebruegge, S.; Woodhouse, K.A.; Kumacheva, E.; Husain, M.; Zandstra, P.W. Control of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Colony and Aggregate Size Heterogeneity Influences Differentiation Trajectories. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 2300–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.W.; Binder, B.Y.K.; Khalili, A.S.; Schmitt, S.K.; Johnson, H.J.; Zacharias, N.A.; Murphy, W.L. Controlled Self-Assembly of Stem Cell Aggregates Instructs Pluripotency and Lineage Bias. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Winkle, A.P.; Gates, I.D.; Kallos, M.S. Mass transfer limitations in embryoid bodies during human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Cells Tissues Organs 2012, 196, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Rostami, M.R.; Cadavid Olaya, D.P.; Tzanakakis, E.S. Oxygen Transport and Stem Cell Aggregation in Stirred-Suspension Bioreactor Cultures. PLos ONE 2014, 9, e102486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nogueira, D.E.S.; Rodrigues, C.A.V.; Hashimura, Y.; Jung, S.; Lee, B.; Cabral, J.M.S. Suspension Culture of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Single-Use Vertical-Wheel Bioreactors Using Aggregate and Microcarrier Culture Systems. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Amit, M.; Margulets, V.; Laevsky, I.; Shariki, K. Suspension Culture of Undifferentiated Human Embryonic Stem Cells and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2010, 6, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.Y.; Chung, B.G.; Ortmann, D.; Hattori, N.; Moeller, H.C.; Khademhosseini, A. Microwell-Mediated Control of Embryoid Body Size Regulates Embryonic Stem Cell Fate via Differential Expression of WNT5a and WNT11. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16978–16983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miranda, C.; Fernandes, T.G.; Pascoal, J.F.; Haupt, S.; Brüstle, O.; Cabral, J.; Diogo, M.M. Spatial and Temporal Control of Cell Aggregation Efficiently Directs Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Towards Neural Commitment. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 1612–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosough, M.; Omidinia, E.; Kadivar, M.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Pournasr, B.; Aghdami, N.; Baharvand, H. Generation of Functional Hepatocyte-Like Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in a Scalable Suspension Culture. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 2693–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, H.; Andree, B.; Zweigerdt, R. Large-Scale Production of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Cardiomyocytes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 96, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, M.A.; Sargent, C.Y.; McDevitt, T.C. The Multiparametric Effects of Hydrodynamic Environments on Stem Cell Culture. Tissue Eng. Part B 2011, 17, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollet, M.; Ma, N.; Zhao, Y.; Brodkey, R.; Taticek, R.; Chalmers, J.J. Bioprocess Equipment: Characterization of Energy Dissipation Rate and its Potential to Damage Cells. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, S.C.; Löffelholz, C.; Werner, S.; Eibl, D. Chapter 4—CFD for Characterizing Standard and Single-Use Stirred Cell Culture Bioreactors. In Computational Fluid Dynamics Technologies and Applications; Minin, O., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; pp. 97–122. [Google Scholar]
- Croughan, M.S.; Giroux, D.; Fang, D.; Lee, B. Chapter 5—Novel Single-Use Bioreactors for Scale-Up of Anchorage-Dependent Cell Manufacturing for Cell Therapies. In Stem Cell Manufacturing; Cabral, J.M.S., Lobato de Silva, C., Chase, L.G., Diogo, M.M., Eds.; Elsevier, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 105–139. [Google Scholar]
- Borys, B.S.; So, T.; Colter, J.; Dang, T.; Roberts, E.L.; Revay, T.; Larijani, L.; Krawetz, R.; Lewis, I.; Argiropoulos, B. Optimized Serial Expansion of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Using Low Density Inoculation to Generate Clinically Relevant Quantities in Vertical-Wheel Bioreactors. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.P.; Fernandes, T.G.; Nogueira, D.E.S.; Rodrigues, C.A.V.; Bekman, E.P.; Hashimura, Y.; Jung, S.; Lee, B.; Carmo-Fonseca, M.; Cabral, J.M.S. Scalable Generation of Mature Cerebellar Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells and Characterization by Immunostaining. JoVE 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Borys, B.S.; Roberts, E.L.; Le, A.; Kallos, M.S. Scale-Up of Embryonic Stem Cell Aggregate Stirred Suspension Bioreactor Culture Enabled by Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 133, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, B.; Borys, B.S.; Kallos, M.S.; Rodrigues, C.A.V.; Silva, T.P.; Cabral, J.M.S. Challenges and Solutions for Commercial Scale Manufacturing of Allogeneic Pluripotent Stem Cell Products. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7020031
Lee B, Borys BS, Kallos MS, Rodrigues CAV, Silva TP, Cabral JMS. Challenges and Solutions for Commercial Scale Manufacturing of Allogeneic Pluripotent Stem Cell Products. Bioengineering. 2020; 7(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Brian, Breanna S. Borys, Michael S. Kallos, Carlos A. V. Rodrigues, Teresa P. Silva, and Joaquim M. S. Cabral. 2020. "Challenges and Solutions for Commercial Scale Manufacturing of Allogeneic Pluripotent Stem Cell Products" Bioengineering 7, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7020031
APA StyleLee, B., Borys, B. S., Kallos, M. S., Rodrigues, C. A. V., Silva, T. P., & Cabral, J. M. S. (2020). Challenges and Solutions for Commercial Scale Manufacturing of Allogeneic Pluripotent Stem Cell Products. Bioengineering, 7(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7020031