Monitoring the Degradation of Collagen Hydrogels by Collagenase Clostridium histolyticum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Gelation of Intact Collagen (C-coll) and Hydrolysed Collagen (D-coll)
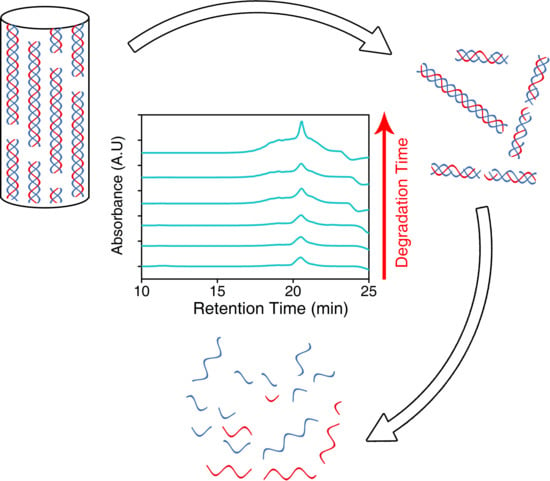
2.2. Degradation of Hydrogels
3. Discussion
3.1. Gelation of Intact Collagen (C-coll) and Hydrolysed Collagen (D-coll)
3.2. Degradation of Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Collagen Extraction
5.2. Hydrogel Preparation
5.3. Swelling Ratio
5.4. Enzymatic Degradation
5.5. Hydroxyproline Assay
5.6. Gel Electrophoresis
5.7. Size Exclusion Chromatography
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C-coll | Intact collagen |
| CB | C-coll in Tris buffer |
| CC | C-coll in collagenase solution in Tris buffer |
| D-coll | Hydrolyzed collagen |
| DB | D-coll in Tris buffer |
| DC | D-coll in collagenase solution in Tris buffer |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| SEC | Size-exclusion column |
| SDS–PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| HHP | High molecular weight hydrolyzed peptides |
| LHP | Low molecular weight hydrolyzed peptides |
References
- Hoffman, A.S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catoira, M.C.; Fusaro, L.; Di Francesco, D.; Ramella, M.; Boccafoschi, F. Overview of natural hydrogels for regenerative medicine applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.H.; Singla, A.; Lee, Y. Biomedical applications of collagen. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 221, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, J.L.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering: Scaffold design variables and applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4337–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, Y.; Miyao, M.; Ozeki, M.; Ikada, Y. Controlled release of vascular endothelial growth factor by use of collagen hydrogels. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2000, 11, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothamel, D.; Schwarz, F.; Sager, M.; Herten, M.; Sculean, A.; Becker, J. Biodegradation of differently crosslinked collagen membranes: An experimental study in the rat. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Ma, S.; Ma, X.; Fan, D.; Zhu, C.; Liu, Y. A novel smart injectable hydrogel prepared by microbial transglutaminase and human-like collagen: Its characterization and biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomihata, K.; Burczak, K.; Shiraki, K.; Ikada, Y. Cross-linking and biodegradation of native and denatured collagen. ACS Symp. Ser. 1993, 540, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ma, X.; Fan, D.; Zhu, C. New suitable for tissue reconstruction injectable chitosan/collagen-based hydrogels. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 3781–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, H.; Jadidi, K.; Pourmotabed, S.; Sharifi, E.; Aghamollaei, H. Preparation and in vitro characterization of cross-linked collagen–gelatin hydrogel using EDC/NHS for corneal tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatiana, N.M.; Cornelia, V.; Tatia, R.; Aurica, C. Hybrid collagen/pNIPAAM hydrogel nanocomposites for tissue engineering application. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 1555–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, H.W. Collagen-apatite nanocomposite membranes for guided bone regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 83, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lian, J.; Agban, Y.; Cheong, S.; Kuchel, R.P.; Raudsepp, A.; Williams, M.A.K.; Rupenthal, I.D.; Henning, A.; Tilley, R.D.; Holmes, G.; et al. ZnO/PVP nanoparticles induce gelation in type I collagen. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulmes, D.J.S.; Miller, A.; Parry, D.A.D.; Piez, K.A.; Woodhead-Galloway, J. Analysis of the primary structure of collagen for the origins of molecular packing. J. Mol. Biol. 1973, 79, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, N.; Leikin, S. Does the triple helical domain of type I collagen encode molecular recognition and fiber assembly while telopeptides serve as catalytic domains? Effect of proteolytic cleavage on fibrillogenesis and on collagen-collagen interaction in fibers. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 36083–36088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hulmes, D.J.S. Collagen diversity, synthesis and assembly. In Collagen: Structure and Mechanics; Fratzl, P., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 15–47. [Google Scholar]
- Fratzl, P. Collagen Structure and Mechanics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Normand, V.; Muller, S.; Ravey, J.C.; Parker, A. Gelation kinetics of gelatin: A master curve and network modeling. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djabourov, M.; Maquet, J.; Theveneau, H.; Leblond, J.; Papon, P. Kinetics of gelation of aqeuous gelatin solutions. Br. Polym. J. 1985, 17, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djabourov, M.; Leblond, J.; Papon, P. Gelation of aqueous gelatin solutions. I. Structural investigation. J. Phys. 1988, 49, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Colby, R.H.; Lusignan, C.P.; Whitesides, T.H. Kinetics of triple helix formation in semidilute gelatin solutions. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 9999–10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.J. The fate of collagen implants in tissue defects. Wound Repair Regen. 2000, 8, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.; Park, J.C. Evaluation of calcification in porcine valves treated by ultraviolet ray and glutaraldehyde. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2000, 13, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, J.W.; Braden, R.L.; Osborn, K.G.; Christman, K.L. Modulating In Vivo Degradation Rate of Injectable Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2794–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallya, S.K.; Mookhtiar, K.A.; Van Wart, H.E. Kinetics of hydrolysis of type I, II, and III collagens by the class I and II Clostridium histolyticum collagenases. J. Protein Chem. 1992, 11, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Ran, L.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Chen, X.L. Diversity, structures, and collagen-degrading mechanisms of bacterial collagenolytic proteases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6098–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mandl, I.; Maclennan, J.D.; Howes, E.L. Isolation and characterization of proteinase and collagenase from Cl. histolyticum. J. Clin. Investig. 1953, 32, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yang, W.; Li, G. Extraction of native collagen from limed bovine split wastes through improved pretreatment methods. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzafriri, A.R.; Bercovier, M.; Parnas, H. Reaction diffusion model of the enzymatic erosion of insoluble fibrillar matrices. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 776–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrington, D.J. Bacterial collagenases and collagen-degrading enzymes and their potential role in human disease. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanzer, M.L. Cross-links in Reconstituted Collagen Fibrils. J. Biol. Chem. 1968, 243, 4045–4054. [Google Scholar]
- Woessner, J.F. The determination of hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportions of this imino acid. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1961, 93, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Type of Collagen Hydrogel | Swelling Ratio |
|---|---|
| Intact Collagen (C-coll) | 724% |
| Hydrolyzed Collagen (D-coll) | 778% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, H.W.; Zhang, Y.; Naffa, R.; Prabakar, S. Monitoring the Degradation of Collagen Hydrogels by Collagenase Clostridium histolyticum. Gels 2020, 6, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6040046
Ng HW, Zhang Y, Naffa R, Prabakar S. Monitoring the Degradation of Collagen Hydrogels by Collagenase Clostridium histolyticum. Gels. 2020; 6(4):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6040046
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Hon Wei, Yi Zhang, Rafea Naffa, and Sujay Prabakar. 2020. "Monitoring the Degradation of Collagen Hydrogels by Collagenase Clostridium histolyticum" Gels 6, no. 4: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6040046
APA StyleNg, H. W., Zhang, Y., Naffa, R., & Prabakar, S. (2020). Monitoring the Degradation of Collagen Hydrogels by Collagenase Clostridium histolyticum. Gels, 6(4), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6040046