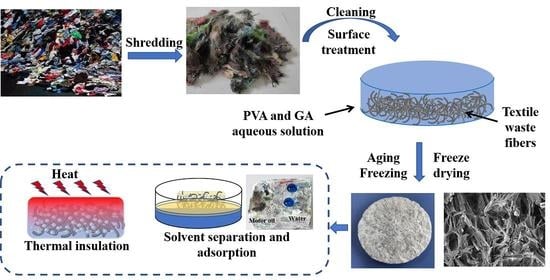
Fabrication of Textile Waste Fibers Aerogels with Excellent Oil/Organic Solvent Adsorption and Thermal Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphologies and Structures of Aerogels
2.2. Hydrophobic Properties
2.3. Thermal Properties of Aerogels
2.3.1. Thermal Conductivity of Aerogels
2.3.2. Thermal Stability of Aerogels
2.4. Mechanical Properties of Aerogels
2.5. Absorption Capabilities of Aerogels
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Fabrication of Textile Waste Fibers Aerogels
4.2.2. Development of the Hydrophobic TWF Aerogels
4.2.3. Characterization
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbas, S.; Chiang Hsieh, L.-H.; Techato, K. Supply chain integrated decision model in order to synergize the energy system of textile industry from its resource waste. Energy 2021, 229, 120754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Määttänen, M.; Gunnarsson, M.; Wedin, H.; Stibing, S.; Olsson, C.; Köhnke, T.; Asikainen, S.; Vehviläinen, M.; Harlin, A. Pre-treatments of pre-consumer cotton-based textile waste for production of textile fibres in the cold NaOH(aq) and cellulose carbamate processes. Cellulose 2021, 28, 3869–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaiškienė, J.; Nagrockienė, D.; Skripkiūnas, G. Possibilities to use textile cord waste from used tires for concrete. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2015, 23, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.; Cicala, G.; Acierno, D. Eco-sustainability of the textile production: Waste recovery and current recycling in the composites world. Polymers 2020, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamble, Z.; Behera, B.K. Fabrication and performance evaluation of waste cotton and polyester fiber-reinforced green composites for building and construction applications. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 3025–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todor, M.P.; Bulei, C.; Heput, T.; Kiss, I. Researches on the development of new composite materials complete / partially biodegradable using natural textile fibers of new vegetable origin and those recovered from textile waste. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 294, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todor, M.P.; Bulei, C.; Kiss, I. Composite materials manufacturing using textile inserts with natural origins fibres. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 39, 012088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanzetto, A.B.; Beltrami, L.V.R.; Zattera, A.J. Textile waste as precursors in nanocrystalline cellulose synthesis. Cellulose 2021, 28, 6967–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrete, I.A.; Quiñonez, P.A.; Bermudez, D.; Roberson, D.A. Incorporating textile-derived cellulose fibers for the strengthening of recycled polyethylene terephthalate for 3D printing feedstock materials. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 29, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todor, M.-P.; Kiss, I.; Cioata, V.G. Development of fabric-reinforced polymer matrix composites using bio-based components from post-consumer textile waste. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 4150–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Du, C.; Lin, C.S.K. Recovery of glucose and polyester from textile waste by enzymatic hydrolysis. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 10, 3763–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, Y.X.; Gan, J.B. Advances in manufacturing composite carbon nanofiber-based aerogels. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhao, J.; Geng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, P. Energy-related GHG emissions of the textile industry in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 119, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.T.; Zhuang, H.K.; Hsieh, L.T.; Lee, W.J.; Tsao, M.C. PAH emission from the incineration of three plastic wastes. Environ. Int. 2001, 27, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamzad, E.; Karimi, K.; Masoomi, M. Effective conversion of waste polyester–cotton textile to ethanol and recovery of polyester by alkaline pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Shi, S.; Hou, W.; Yan, Z. Separation of waste polyester/cotton blended fabrics by phosphotungstic acid and preparation of terephthalic acid. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 161, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Z.Z.; Talib, A.R. Recycled medical cotton industry waste as a source of biogas recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4413–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Bhat, G. Environmentally-friendly thermal and acoustic insulation materials from recycled textiles. J. Env. Manag. 2019, 251, 109536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrolodabaee, P.; Claramunt, J.; Ardanuy, M.; de la Fuente, A. A textile waste fiber-reinforced cement composite: Comparison between short random fiber and textile reinforcement. Materials 2021, 14, 3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, L.; Gan, G.; Pan, G. A comprehensive review on the utilization of recycled waste fibers in cement-based composites. Materials 2021, 14, 3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Teruo, K.; Haruhiro, I. Papermaking from waste silk and its application as reinforcement of green composite. J. Text. Eng. 2010, 56, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mich, A.A.; Leventis, N.; Koebel, M.M. Aerogels Handbook; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gesser, H.D.; Goswami, P.C. Aerogels and Related Porous Materials. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 765–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Yin, Z.; Cao, X.; Xie, X.; Tan, C.; Huang, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Bu, X.; et al. Carbon fiber aerogel made from raw cotton: A novel, efficient and recyclable sorbent for oils and organic solvents. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5916–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Gu, B.; Pennefather, M.P.; Nguyen, T.X.; Phan-Thien, N.; Duong, H.M. Cotton aerogels and cotton-cellulose aerogels from environmental waste for oil spillage cleanup. Mater. Des. 2017, 130, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janqamsari, Y.; Ashjari, M.; Niazi, Z. Carbon nanotube promoted porous nanocomposite based on PVA and recycled PET fibers for efficient oil spills cleanup applications. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 3443–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtauer, S.; Hassan, M.; Elsherbiny, A.; Gabal, S.A.; Mehanny, S.; Abushammala, H. Current status of cellulosic and nanocellulosic materials for oil spill cleanup. Polymers 2021, 13, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Alam, M.K.; He, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Qin, X.; Yu, J. Sustainable cellulose aerogel from waste cotton fabric for high-Performance solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 49860–49867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Robson, M.E.; Phelps, J.L.; Tan, J.S.; Shao, B.; Owens, G.; Xu, H. A flexible photothermal cotton-CuS nanocage-agarose aerogel towards portable solar steam generation. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yang, P.; Yang, L.; Li, N.; Duan, G.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Boosting solar steam generation by photothermal enhanced polydopamine/wood composites. Polymer 2021, 217, 123464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.V.; Fontenot, K.R.; Prevost, N.T.; Pircher, N.; Liebner, F.; Condon, B.D. Preparation, characterization and activity of a peptide-cellulosic aerogel protease sensor from cotton. Sensors 2016, 16, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, W.; Ding, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Duan, G. A review of smart electrospun fibers toward textiles. Compos. Commun. 2020, 22, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mei, C.; Li, Y.; Duan, G.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Ma, C.; Jiang, S. Wood-inspired anisotropic cellulose nanofibril composite sponges for multifunctional applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35513–35522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Liu, L.; Hu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, S.; Chen, A. Raw-cotton-derived N-doped carbon fiber aerogel as an efficient electrode for electrochemical capacitors. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4008–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lu, W.; Han, J.; Zhong, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Robust three-dimensional g-C3N4@cellulose aerogel enhanced by cross-linked polyester fibers for simultaneous removal of hexavalent chromium and antibiotics. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; He, F. Structure characteristics and hygrothermal performance of silica aerogel composites for building thermal insulation in humid areas. Energy Build. 2020, 228, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Cheong, J.Y.; Nam, J.S.; Kim, I.D.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. High density fibrous polyimide sponges with superior mechanical and thermal properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19006–19014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jiang, S.; Hou, H.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Low density, thermally stable, and intrinsic flame retardant poly(bis(benzimidazo)benzophenanthroline-dione) sponge. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1700615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba Thai, Q.; Ee Siang, T.; Khac Le, D.; Shah, W.A.; Phan Thien, N.; Duong, H.M. Advanced fabrication and multi-properties of rubber aerogels from car tire waste. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz, L.G.; Abt, T.; Leon, N.; Wang, L.; Sanchez-Soto, M. Ice-template crosslinked PVA aerogels modified with tannic acid and sodium alginate. Gels 2022, 8, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.W.; Le, D.K.; Ng, G.N.; Zhang, X.; Phan-Thien, N.; Kureemun, U.; Duong, H.M. Advanced recycled polyethylene terephthalate aerogels from plastic waste for acoustic and thermal insulation applications. Gels 2018, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Chaudhary, H.; Gupta, C. Sericin based bioactive coating for polyester fabric. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2015, 40, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.G.; Ihm, S.D.; Kim, B.S.; Mun, S.P.; Rhee, J.M. Recycling of the waste cellulose II. preparation of hydroxyethyl cellulose from knit-cotton-waste. Text. Color. Finish. 1995, 7, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Dave, J.; Kumar, R.; Srivastava, H. Studies on modification of polyester fabrics I: Alkaline hydrolysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1987, 33, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Nguyen, S.T.; Fan, Z.; Duong, H.M. Advanced fabrication and oil absorption properties of super-hydrophobic recycled cellulose aerogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.H.N.; Tran, V.T.; Tran, Q.B.M.; Le, K.A.; Thai, Q.B.; Nguyen, P.T.T.; Duong, H.M.; Le, P.K. Recycling of pineapple leaf and cotton waste fibers into heat-insulating and flexible cellulose aerogel composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuce, E.; Cuce, P.M.; Wood, C.J.; Riffat, S.B. Toward aerogel based thermal superinsulation in buildings: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Noh, Y.J.; Yu, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Youn, J.R. Silica aerogel/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) insulation composites with preserved aerogel pores using interfaces between the superhydrophobic aerogel and hydrophilic PVA solution. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 75, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Song, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y. Multi-functional hydroxyapatite/polyvinyl alcohol composite aerogels with self-cleaning, superior fire resistance and low thermal conductivity. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 158, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Sun, X.; Yao, C.; Mao, L. A new strategy to chemically transform waste PET plastic into aerogel with high fire resistance and mechanical strength. Polymer 2022, 254, 125074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Improving thermal conductivity of cotton fabrics using composite coatings containing graphene, multiwall carbon nanotube or boron nitride fine particles. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Xie, Y.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, T.; Song, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Fan, Z.; et al. Lightweight, flexible, thermally-stable, and thermally-insulating aerogels derived from cotton nanofibrillated cellulose. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9202–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, P.; Wan, K.; Miao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Mechanically strong, low thermal conductivity and improved thermal stability polyvinyl alcohol-graphene-nanocellulose aerogel. Gels 2021, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazhayal, L.; Wilson, P.; Prabhakaran, K. Waste to wealth: Lightweight, mechanically strong and conductive carbon aerogels from waste tissue paper for electromagnetic shielding and CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, C.; Bonet Aracil, M.; Gisbert-Paya, J.; Liuzzi, S.; Stefanizzi, P.; Zamorano Canto, M.; Martellotta, F. Composite eco-friendly sound absorbing materials made of recycled textile waste and biopolymers. Materials 2019, 12, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacoste, C.; El Hage, R.; Bergeret, A.; Corn, S.; Lacroix, P. Sodium alginate adhesives as binders in wood fibers/textile waste fibers biocomposites for building insulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, S.T.; Feng, J.; Le, N.T.; Le, A.; Hoang, N.; Tan, V.; Duong, H.M. Cellulose aerogel from paper waste for crude oil spill cleaning. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 18386–18391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Li, H.; Wang, K.; Wei, J.; Yi, J.; Zhen, L.; Fan, L.; Cao, A.; Zhu, H.; Wu, D. Recyclable carbon nanotube sponges for oil absorption. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 4798–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wan, W.; Qiu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Preparation of hydrophobic polyvinyl alcohol aerogel via the surface modification of boron nitride for environmental remediation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 419, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, J.; Hou, X. Hydrophobic and nanoporous chitosan–silica composite aerogels for oil absorption. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. The preparation of novel polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-based nanoparticle/carbon nanotubes (PNP/CNTs) aerogel for solvents adsorption application. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 569, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ke, Z.; Shen, C.; Sun, R.; Wei, Q.; Yin, Z.; Yang, W. Fabrication of carbon aerogels derived from metal-organic frameworks/carbon nanotubes/cotton composites as an efficient sorbent for sustainable oil–water separation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalapati, R.; Nandi, S.; Gogoi, C.; Shome, A.; Biswas, S. Metal-organic framework (MOF) derived recyclable, superhydrophobic composite of cotton fabrics for the facile removal of oil spills. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 8563–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Gan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Wood sponge reinforced with polyvinyl alcohol for sustainable oil-water separation. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 12866–12876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Cai, Z.; Yan, N.; Liu, M.; Yu, Y. Highly compressible and hydrophobic anisotropic aerogels for selective oil/organic solvent absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wei, Y.H.; Si, J.Y.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Xie, J.S.; Yu, B.; Zhu, S.E.; Lu, H.D.; et al. Robust, lightweight, hydrophobic, and fire-retarded polyimide/MXene aerogels for effective oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 40512–40523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhajed, M.; Verma, C.; Sathawane, M.; Singh, S.; Maji, P.K. Mechanically durable green aerogel composite based on agricultural lignocellulosic residue for organic liquids/oil sorption. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, J.; Hua, L.; Lu, Z. Poly (vinyl alcohol) assisted regulation of aramid nanofibers aerogel structure for thermal insulation and adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 339, 111997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Le, D.; Nguyen, S.T.; Tan Chin Nien, V.; Jewell, D.; Duong, H.M. Silica cellulose hybrid aerogels for thermal and acoustic insulation applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 506, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Sample Name | Composition | Fiber Conc. (wt.%) | Density (g/cm3) | Porosity (%) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWF1a | TWF:PVA = 1 | 2.0 | 0.067 ± 0.003 | 94.8 ± 0.2 | 0.057 ± 0.002 | - |
| TWF1b | TWF:PVA = 3 | 2.0 | 0.045 ± 0.002 | 96.6 ± 0.2 | 0.051 ± 0.001 | - |
| TWF1c | TWF:PVA = 4 | 2.0 | 0.040 ± 0.002 | 96.9 ± 0.3 | 0.049 ± 0.001 | - |
| TW01 | TWF:PVA = 2 | 2.0 | 0.044 ± 0.002 | 96.7 ± 0.2 | 0.052 ± 0.001 | 12.0 |
| TW02 | TWF:PVA = 2 | 3.0 | 0.060 ± 0.003 | 95.4 ± 0.3 | 0.058 ± 0.002 | 10.6 |
| TW03 | TWF:PVA = 2 | 4.0 | 0.068 ± 0.003 | 94.8 ± 0.2 | 0.059 ± 0.002 | 9.0 |
| TW04 | TWF:PVA = 2 | 5.0 | 0.096 ± 0.005 | 94.2 ± 0.4 | 0.061 ± 0.002 | 7.3 |
| Materials | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·k) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| TWF/PVA Aerogel | 0.049–0.062 | This work |
| Air | 0.026 | [47] |
| PVA plastic | 0.200 | [48] |
| Pristine PVA Aerogel | 0.0408 | [49] |
| PET Fiber | 0.15 | [41] |
| PET Plastic | 0.20 | [50] |
| Cotton | 0.047 | [51] |
| Cotton/Cellulose Aerogel | 0.044–0.055 | [52] |
| PVA/TA/SA Aerogel | 0.043–0.060 | [40] |
| PVA/GA/CNF Aerogel | 0.044–0.067 | [53] |
| Waste Tissue Paper/PVA Aerogel | 0.098–0.120 | [54] |
| Wool Waste Fibers Aerogel | 0.049–0.060 | [55] |
| Wood Fibers/Textile Waste Fibers Aerogel | 0.078–0.089 | [56] |
| Sorbent Material | Absorbed Substances | Sorption Capacity (g/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| TWF/PVA Aerogel | oils and organic solvents | 14–27 | This work |
| BN/PVA Aerogel | CCl4 and n-hexane | 12–38 | [59] |
| Chitosan/Silica Composite Aerogel | oils and organic solvents | 13–30 | [60] |
| carbon nanotubes/PVA Aerogels | oils and organic solvents | 17–39 | [61] |
| MOF/Carbon Nanotubes/Cotton Aerogels | oils and organic solvents | 48–84 | [62] |
| MOF-Coated Cotton Fiber Composite | oils and organic solvents | 25–48 | [63] |
| Wood /PVA Sponge | oils and organic solvents | 4–27 | [64] |
| Cellulose-Based Aerogel | oils and organic solvents | 42–99 | [65] |
| Polyimide/MXene Aerogels | oils and organic solvents | 18–58 | [66] |
| PLA/ lignocellulosic Aerogels | oils and organic solvents | 28–70 | [67] |
| Aramid Nanofibers/PVA aerogel | oils and organic solvents | 32–65 | [68] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, X.; Chen, J.; Li, J. Fabrication of Textile Waste Fibers Aerogels with Excellent Oil/Organic Solvent Adsorption and Thermal Properties. Gels 2022, 8, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100684
Dong C, Hu Y, Zhu Y, Wang J, Jia X, Chen J, Li J. Fabrication of Textile Waste Fibers Aerogels with Excellent Oil/Organic Solvent Adsorption and Thermal Properties. Gels. 2022; 8(10):684. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100684
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Chunlei, Yangzhao Hu, Yuxuan Zhu, Jiale Wang, Xuerui Jia, Jianbing Chen, and Jingliang Li. 2022. "Fabrication of Textile Waste Fibers Aerogels with Excellent Oil/Organic Solvent Adsorption and Thermal Properties" Gels 8, no. 10: 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100684
APA StyleDong, C., Hu, Y., Zhu, Y., Wang, J., Jia, X., Chen, J., & Li, J. (2022). Fabrication of Textile Waste Fibers Aerogels with Excellent Oil/Organic Solvent Adsorption and Thermal Properties. Gels, 8(10), 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100684