Cr(III) Ion-Imprinted Hydrogel Membrane for Chromium Speciation Analysis in Water Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
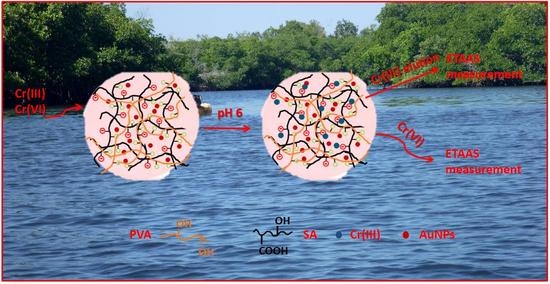
2.1. Cr(III) Ion-Imprinted Hydrogel Membrane Synthesis
2.2. Characterization of SA-AuNPs and Cr(III)-IIM
2.3. Adsorption Behavior of Cr-IIM toward Cr(III) and Cr(VI)—Optimization Studies
2.4. Elution Studies
2.5. Investigations on the Mechanism of Cr(III) Adsorption onto Cr(III)-IIM
2.5.1. Adsorption Isotherm Models
2.5.2. Modeling of Cr(III) Sorption Kinetics
2.6. Analytical Applications
2.7. Analytical Figures of Merit
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials, Reagents, and Instruments
4.2. Synthesis of SA-AuNPs
4.3. Preparation of Cr(III)-IIM and NIIM
4.4. Static Adsorption/Desorption Experiments
4.5. Isotherm and Kinetic Studies
4.6. Interference Studies on the Selective Separation of Cr(III) and Cr(VI)
4.7. Analytical Procedure
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, M.; Klein, C.B. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of chromium compounds in humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ayati, A.; Ghanbari, S.; Orooji, Y.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Rouhi, J.; Fu, L.; Sillanpää, M. Recent advances in removal techniques of Cr(VI) toxic ion from aqueous solution: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.B.; Ali, I.; Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Nanomaterial’s based chromium speciation in environmental samples: A review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 103, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filik, H.; Avan, A.A. Magnetic nanostructures for preconcentration, speciation and determination of chromium ions: A review. Talanta 2019, 203, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Latorre, C.; Barciela-García, J.; García-Martin, S.; Peňa-Crecente, R.M. Graphene and carbon nanotubes as solid phase extraction sorbets for the speciation of chromium: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1002, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhunde, R.; Deshpande, L.; Juneja, H.D. Chemical speciation of chromium in water: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 776–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzonkowska, L.; Leśniewska, B.; Godlewska-Zyłkiewicz, B. Recent advances in on-line methods based on extraction for speciation analysis of chromium in environmental matrices. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 46, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.A.; Grinberg, P.; Bobeda, C.R.; Reyes, M.N.; Campos, R.C. Non-chromatographic atomic spectrometric methods in speciation analysis: A review. Spectrochim. Acta B At. Spectrosc. 2009, 64, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadjova, I.; Yordanova, T.; Dakova, I.; Vasileva, P. Smart Materials in Speciation Analysis. In Handbook of Smart Materials in Analytical Chemistry, 1st ed.; de la Guardia, M., Esteve-Turrillas, F.A., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 757–794. [Google Scholar]
- Birlik, E.; Ersöz, A.; Açıkkalp, E.; Denizli, A.; Say, R. Cr(III)-imprinted polymeric beads: Sorption and preconcentration studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 140, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Chang, X.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, N.; Wang, X. Determination of chromium(III) and total chromium in natural waters using a surface ion imprinted silica gel as selective adsorbent. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2008, 88, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Meng, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Tian, S. Speciation, adsorption and determination of chromium(III) and chromium(VI) on a mesoporous surface imprinted polymer adsorbent by combining inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry and UV spectrophotometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 3949–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniewska, B.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B.; Wilczewska, A.Z. Separation and preconcentration of trace amounts of Cr(III) ions on ion-imprinted polymer for atomic absorption determinations in surface water and sewage samples. Microchem. J. 2012, 105, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniewska, B.; Trzonkowska, L.; Zambrzycka, E.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B. Multi-commutation flow system with on-line solid phase extraction exploiting the ion-imprinted polymer and FAAS detection for chromium speciation analysis in sewage samples. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Suleiman, J.S.; He, M.; Hu, B. Chromium(III)-imprinted silica gel for speciation analysis of chromium in environmental water samples with ICP-MS detection. Talanta 2008, 75, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdi, M.K.; Vatanpour, V.; Taghizadeh, A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Munir, M.T.; Habibzadeh, S.; Saeb, M.R.; Ghaedi, M. Hydrogel membranes: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 111023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Qin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Meng, M.; Yan, Y.; Li, C. Recent Advances in Ion-Imprinted Membranes: Separation and Detection via Ion-Selective Recognition. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1626–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Cartas, S.; Catalá-Icardo, M.; Meseguer-Lloret, S.; Simó-Alfonso, E.F.; Herrero-Martínez, J.M. Recent Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Membranes for Sample Treatment and Separation. Separations 2020, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Li, G.P.; Liu, Q.L.; Ni, J.C.; Wu, W.B.; Lin, J.M. Cr (III) ionic imprinted polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate (PVA/SA) porous composite membranes for selective adsorption of Cr (III) ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Xing, H.T.; Guo, H.X.; Li, G.P.; Weng, W.; Hu, S.R. Preparation, characterization and adsorption properties of a novel 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane functionalized sodium alginate porous membrane adsorbent for Cr(III) ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 248–249, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhao, L.; Hong, Y.; Hu, X.; Zi, F.; Cheng, H. Synthesis and evaluation of ion-imprinted composite membranes of Cr(VI) based on β-diketone functional monomers. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 38915–38924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, S.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, P.; Qin, X.; Cheng, H.; Zi, F. Preparation and Characterization of Chromium(VI) Ion-Imprinted Composite Membranes with a Specifically Designed Functional Monomer. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 1113–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sood, A.; Han, S.S. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-alginate as potential matrix for various applications: A focused review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, F.B.; Robinson, M.; Olson, G.R.; Page, N.P. Toxicity Studies of Epichlorohydrin in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 1996, 19, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Wang, R.-S. Glutaraldehyde Exposure and its Occupational Impact in the Health Care Environment. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2006, 11, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Cui, K.; Mao, Y.; Chai, W.; Wang, N.; Ren, Z. Green preparation of D-tryptophan imprinted selfsupported membrane for ultrahigh enantioseparation of racemic tryptophan. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 109992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, A.; Cao, C.; Cui, D. Toxicity of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs): A review. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 26, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoniyot, P.; Tan, M.J.; Karim, A.A.; Young, D.J.; Loh, X.J. Nanoparticle–hydrogel composites: Concept, design, and applications of these promising, multi-functional materials. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1400010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouardi, Y.E.; Giove, A.; Laatikainen, M.; Branger, C.; Laatikainen, K. Benefit of ion imprinting technique in solid-phase extraction of heavy metals, special focus on the last decade. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borse, S.D.; Joshi, S.S. Optical and Structural Properties of PVA Capped Gold Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Efficacy. Adv. Chem. Lett. 2013, 1, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Zhang, B.; Nie, X.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liao, M.; Li, S. A sodium alginate-based sustained-release IPN hydrogel and its applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 39722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.M.; Takagi, H.D. Degradation Kinetics of Some Coordination Biopolymers of Transition Metal Complexes of Alginates: Influence of Geometrical Structure and Strength of Chelation on the Thermal Stability. Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahakifar, F.; Keshtkar, A.R.; Talebi, M. Synthesis of sodium alginate (SA)/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/polyethylene oxide (PEO)/ZSM-5 zeolite hybrid nanostructure adsorbent by casting method for uranium (VI) adsorption from aqueous solutions. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2021, 134, 103642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-T.; Yan, M.; Xu, W.; Shiu, B.-C.; Lou, C.-W.; Lin, J.-H. Mass-Production and Characterizations of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Sodium Alginate/Graphene Porous Nanofiber Membranes Using Needleless Dynamic Linear Electrospinning. Polymers 2018, 10, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahu, D.; Sarkar, N.; Sahoo, G.; Mohapatra, P.; Swain, S.K. Nano silver imprinted polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite thin films for Hg2+ sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Karim, M.R.; Kim, I.K.; Cheong, I.W.; Kim, J.W.; Bae, D.G.; Cho, J.W.; Yeum, J.H. Electrospinning fabrication and characterization of poly (vinylalcohol)/montmorillonite/silver hybrid nanofibers for antibacterialapplications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.B.; Abdel-Mohsen, A.M.; Emam, H.E. Green-assisted tool for nanogold synthesis based on alginate as a biological macromolecule. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 73974–73985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bello, M.P.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Mele, G.; Scorrano, S.; Mergola, L.; Del Sole, R. A new ion-imprinted chitosan-based membrane with an azo-derivative ligand for the efficient removal of Pd(II). Materials 2017, 10, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertoni, F.A.; Bellú, S.E.; González, J.C.; Sala, L.F. Reduction of hypervalent chromium in acidic media by alginic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almeida, J.C.; Cardoso, C.E.D.; Tavares, D.S.; Freitas, R.; Trindade, T.; Vale, C.; Pereira, E. Chromium removal from contaminated waters using nanomaterials—A review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Guo, C.; Hao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Long, H.; Li, M. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by sodium alginate based adsorbent—A review and new perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4423–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Li, N.; Lu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y. Study on Preparation and Separation and Adsorption Performance of Knitted Tube Composite β-Cyclodextrin/Chitosan Porous Membrane. Polymers 2019, 11, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Liu, H.B.; Tang, Z.S.; Qiu, Z.D.; Zhu, H.X.; Song, Z.X.; Jia, A.L. Synthesis, performance, and application of molecularly imprinted membranes: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, E.; Madaeni, S.S.; Vatanpour, V. Thermodynamic investigation and mathematical modeling of ion-imprinted membrane adsorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 389, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, C.; Zhu, D.; Yang, Y.; Sugiura, N. Preparation and characterization of porous granular ceramic containing dispersed aluminum and iron oxides as adsorbents for fluoride removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, Q.J.; Sun, J.K.; Li, H. Highly enhanced adsorption of congo red onto graphene oxide/chitosan fibers by wet-chemical etching off silica nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 245, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerahov, L.; Vasileva, P.; Karadjova, I. Self-standing chitosan film loaded with silver nanoparticles as a tool for selective determination of Cr(VI) by ICP-MS. Microchem. J. 2016, 129, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Eluent | c, mol/L | DE, % |
|---|---|---|
| HCl (V = 10 mL) | 0.1 | 67.3 ± 3 |
| 0.5 | 80.6 ± 3 | |
| 1.0 | AuNPs dissolution | |
| NH4-EDTA (V = 10 mL) | 0.05 | 68.7 ± 4 |
| 0.1 | >99 | |
| 0.2 | >99 | |
| NH4-EDTA (V = 5 mL) | 0.1 | 75.6 ± 3 |
| NH4-EDTA (V = 10 mL) | 0.1 | >99 |
| NH4-EDTA (V = 20 mL) | 0.1 | >99 |
| Polymer Hydrogel Membrane | Qmax,exp mg/g | Langmuir Isotherm Model | Freundlich Isotherm Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax,calc mg/g | b L/mg | R2 | RL | kF | n | R2 | ||
| Cr(III)-IIM | 1.75 | 1.74 | 3.52 | 0.9997 | 0.01–0.05 | 1.15 | 3.47 | 0.8956 |
| NIIM | 1.23 | 1.25 | 0.32 | 0.9993 | 0.08–0.38 | 11.47 | 2. 38 | 0.9592 |
| Model | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order model | k1 (1/h) | 0.07529 |
| qe,calc * (mg/g) | 0.4496 | |
| R2 | 0.9694 | |
| Pseudo-second-order model | k2 (g/(mg∙h)) | 0.07234 |
| qe,calc * (mg/g) | 0.6974 | |
| R2 | 0.9626 | |
| Elovich equation | α (mg/(g∙h)) | 0.09449 |
| β (g/mg) | 8.1739 | |
| R2 | 0.9331 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion model Region 1 | ki (mg/(g∙h0.5) | 0.1034 |
| Ci (mg/g) | −0.09989 | |
| R2 | 0.9558 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion model Region 2 | ki (mg/(g∙h0.5) | 0.03459 |
| Ci (mg/g) | 0.1892 | |
| R2 | 0.8710 |
| Sample | Cr(III), µg/L Mean ± SD | Cr(VI), µg/L Mean ± SD | Recovery for Cr(VI), % |
|---|---|---|---|
| River water | 2.3 ± 0.2 | <DL | |
| River water + 0.5 µg/L Cr(VI) | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 94 ± 2 |
| Seawater | 0.52 ± 0.04 | <DL | |
| Seawater + 0.2 µg/L Cr(VI) | 0.54 ± 0.04 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 95 ± 4 |
| Groundwater | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 0.25± 0.02 | |
| Groundwater + 0.4 µg/L Cr(VI) | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 0.63 ± 0.03 | 93 ± 4 |
| Species | Detection Limit, µg/L | Determination Limit, µg/L | RSD, % for the Range 0.05–50 µg/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cr(III) | 0.001 | 0.003 | 7–11 |
| Cr(VI) | 0.01 | 0.03 | 4–6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dakova, I.; Vasileva, P.; Karadjova, I. Cr(III) Ion-Imprinted Hydrogel Membrane for Chromium Speciation Analysis in Water Samples. Gels 2022, 8, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110757
Dakova I, Vasileva P, Karadjova I. Cr(III) Ion-Imprinted Hydrogel Membrane for Chromium Speciation Analysis in Water Samples. Gels. 2022; 8(11):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110757
Chicago/Turabian StyleDakova, Ivanka, Penka Vasileva, and Irina Karadjova. 2022. "Cr(III) Ion-Imprinted Hydrogel Membrane for Chromium Speciation Analysis in Water Samples" Gels 8, no. 11: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110757
APA StyleDakova, I., Vasileva, P., & Karadjova, I. (2022). Cr(III) Ion-Imprinted Hydrogel Membrane for Chromium Speciation Analysis in Water Samples. Gels, 8(11), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110757