Polyaniline Functionalized Peptide Self-Assembled Conductive Hydrogel for 3D Cell Culture
Abstract
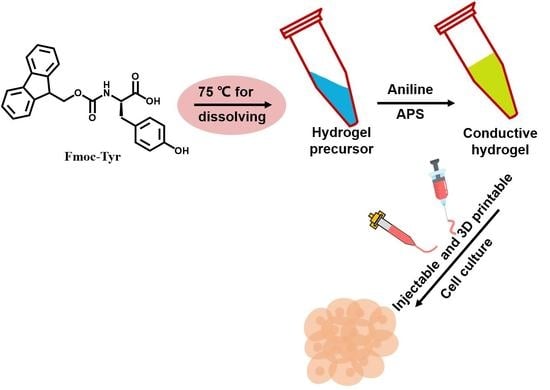
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Morphology Characterization of the Hydrogel
2.1.2. Mechanical Property and Conductivity Characterization of the Hydrogel
2.1.3. Stability and Injectability Characterization of the Hydrogel
2.1.4. Three-Dimensional Culture of C2C12 Cells in the Hydrogel
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Hydrogel Preparation
4.2.2. Morphology Characterization of the Hydrogel
4.2.3. Mechanical Property
4.2.4. Electrical Properties
4.2.5. Stability of the Hydrogel
4.2.6. Injectability and Printability of the Hydrogel
4.2.7. Cell Proliferation in the Hydrogel Scaffold
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoddart, J.F. From supramolecular to systems chemistry: Complexity emerging out of simplicity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12902–12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, S.; Praveen, V.K.; Philip, R.; Ajayaghosh, A. Bioinspired superhydrophobic coatings of carbon nanotubes and linear π systems based on the “bottom-up” self-assembly approach. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5750–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.J.; Smith, A.M.; Collins, R.; Hodson, N.; Das, A.K.; Ulijn, R.V. Enzyme-assisted self-assembly under thermodynamic control. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, J.; Xu, B. Supramolecular hydrogelators and hydrogels: From soft matter to molecular biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13165–13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, O.O.; Mata, A. Multicomponent self-assembly as a tool to harness new properties from peptides and proteins in material design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 3721–3736. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C.J.; Bommarius, A.S.; Champion, J.A.; Chernoff, Y.O.; Lynn, D.G.; Paravastu, A.K.; Liang, C.; Hsieh, M.C.; Heemstra, J.M. Biomolecular assemblies: Moving from observation to predictive design. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11519–11574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.F.; Wang, A.H.; Li, J.L.; Li, Q.; Han, Q.Q.; Zeng, X.F.; Cao, H.Y.; Bai, S. Preparation of conductive and transparent dipeptide hydrogels for wearable biosensor. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2022, 5, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.Q.; Chen, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, M.L.; Wang, S.T.; Ren, P.; Hao, L.N.; Wang, A.H.; Bai, S.; Yin, J. Fabrication of agarose hydrogel with patterned silver nanowires for motion sensor. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2019, 2, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.Q.; Wang, M.Y.; Wang, A.H.; Yu, C.J.; Bai, S.; Yin, J.; You, Q.J. Self-assembly of Fmoc-amino acids in capillary confined space forming a parallel ordered fiber network for application in vascularization. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 1470–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.B.; Gao, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Self-assembled peptide-based nanomaterials for biomedical imaging and therapy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, S.; Ulijn, R.V. Design of nanostructures based on aromatic peptide amphiphiles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8150–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S. Fabrication of novel biomaterials through molecular self-assembly. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Fei, J.B.; Yan, X.H.; Wang, A.H.; Li, J.B. Enzyme responsive release of doxorubicin from monodisperse dipeptide based nanocarriers for highly efficient cancer treatment in vitro. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.J.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, A.H.; Jian, H.L.; Li, Q.; Bai, S. Bioinspired self-assembled nanoparticles with stable fluorescent properties in wide visible light region. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramovich, L.A.; Aronov, D.; Beker, P.; Yevnin, M.; Stempler, S.; Buzhansky, L.; Rosenman, G.; Gazit, E. Self-assembled arrays of peptide nanotubes by vapour deposition. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yan, L.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, A.; Bai, S.; Yan, X. Solvothermally mediated self-assembly of ultralong peptide nanobelts capable of optical waveguiding. Small 2016, 12, 2575–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartgerink, J.D.; Beniash, E.; Stupp, S.I. Self-assembly and mineralization of peptide-amphiphile nanofibers. Science 2001, 294, 1684–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Fu, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Deng, X.; Dhinakar, A.; Huang, W.L.; Qian, H.; Ge, L. pH-sensitive peptide hydrogel for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Javid, N.; Sefcik, J.; Halling, P.J.; Ulijn, R.V. Salt-induced control of supramolecular order in biocatalytic hydrogelation. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16664–16670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Zhang, Q.S.; Jian, H.L.; Liu, S.J.; Li, J.L.; Wang, A.H.; Dong, Q.Q.; Ren, P.; Li, X.; Bai, S. Role of thermolysin in catalytic-controlled self-assembly of Fmoc-dipeptides. CCS Chem. 2020, 2, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.Y.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, A.H.; Zhao, L.Y.; Dong, Q.Q.; Yan, X.H.; Bai, S. Regulating morphologies and near-infrared photothermal conversion of perylene bisimide via sequence-dependent peptide self-assembly. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2208–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.L.; Wang, A.H.; Zhao, L.Y.; Dong, Q.Q.; Wang, M.Y.; Xu, H.L.; Yan, X.H.; Bai, S. Self-assembly of monomeric hydrophobic photosensitizers with short peptides forming photodynamic nanoparticles with real-time tracking property and without the need of release in vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 28420–28427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.L.; Wang, A.H.; Ren, P.; Yan, X.; Bai, S. One-step co-assembly method to fabricate photosensitive peptide nanoparticles for two-photon photodynamic therapy. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 3191–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.L.; Abbas, M.; Zhao, L.Y.; Li, S.K.; Shen, G.Z.; Yan, X.H. Biological photothermal nanodots based on self-assembly of peptide porphyrin conjugates for antitumor therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.L.; Wang, M.Y.; Dong, Q.Q.; Li, J.L.; Wang, A.H.; Li, X.; Ren, P.; Bai, S. Dipeptide self-assembled hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties and degradability for 3D bioprinting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 46419–46426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Li, J.T.; Zhao, L.Y.; Wang, A.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Li, J.L.; Jian, H.L.; Li, X.O.; Yan, X.H.; Bai, S. Dipeptide self-assembled hydrogels with shear-thinning and instantaneous self-healing properties determined by peptide sequences. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21433–21440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, W.J. The mechanobiology of brain function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, A.K.S.; Ohta, S.; Taniguchi, M.; Yoshida, H.; Tanaka, D.; Omichi, K.; Shimizu, A.; Isaji, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Ito, T. Balance of antiperitoneal adhesion, hemostasis, and operability of compressed bilayer ultrapure alginate sponges. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 137, 212825. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.M.; Zhang, T.R.; Tian, Y.Q.; You, L.J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.Y. Novel self-assembling peptide hydrogel with pH-tunable assembly microstructure, gel mechanics and the entrapment of curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.Y.; Park, J.; Kim, W.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Koh, W.G. A novel conductive and micropatterned peg-based hydrogel enabling the topographical and electrical stimulation of myoblasts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 47695–47706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Du, W.; Cai, Z.; Ji, S.; Dwivedi, M.; Chen, J.; Zhao, G.; Chu, J. Uniaxial stretching of cell-laden microfibers for promoting C2C12 myoblasts alignment and myofibers formation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Liao, X.; Fan, X.L.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhan, J.; Liao, X.; Fan, X.L.; Zhang, J.W.; Li, H.K.; Cai, Y.B.; et al. An injectable and conductive TEMPOL/polypyrrole integrated peptide co-assembly hydrogel promotes functional maturation of cardiomyocytes for myocardial infarction repair. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 236, 109794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Xue, Y.; Wang, A.; Tian, S.; Li, Q.; Bai, S. Polyaniline Functionalized Peptide Self-Assembled Conductive Hydrogel for 3D Cell Culture. Gels 2022, 8, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060372
Li J, Xue Y, Wang A, Tian S, Li Q, Bai S. Polyaniline Functionalized Peptide Self-Assembled Conductive Hydrogel for 3D Cell Culture. Gels. 2022; 8(6):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060372
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jieling, Yan Xue, Anhe Wang, Shaonan Tian, Qi Li, and Shuo Bai. 2022. "Polyaniline Functionalized Peptide Self-Assembled Conductive Hydrogel for 3D Cell Culture" Gels 8, no. 6: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060372
APA StyleLi, J., Xue, Y., Wang, A., Tian, S., Li, Q., & Bai, S. (2022). Polyaniline Functionalized Peptide Self-Assembled Conductive Hydrogel for 3D Cell Culture. Gels, 8(6), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060372