Exceptionally Fast Temperature-Responsive, Mechanically Strong and Extensible Monolithic Non-Porous Hydrogels: Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Intercalated with Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis
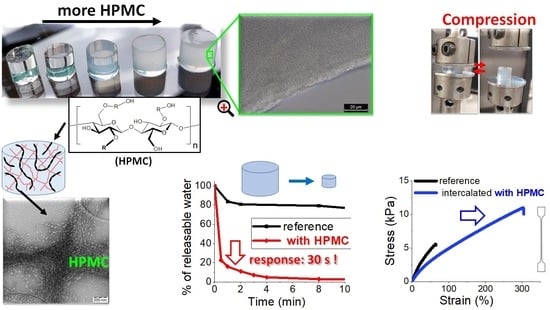
2.2. Morphology of the Prepared Hydrogels
2.2.1. Light Microscopy (LM)
2.2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3. Moduli of the Hydrogels
2.4. Tensile Properties
2.5. Temperature Response
Kinetics of T-Response
2.6. Drug-Release Kinetics
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
Synthesis
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Micron-Scale Morphology
4.2.2. Nano-Morphology Studied by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.2.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
4.2.4. Shear Moduli of the Hydrogels
4.2.5. Tensile Tests
4.2.6. Temperature Dependence of the Swelling Degree in Water
4.2.7. Deswelling ‘Kinetics’ Triggered by T
4.2.8. Drug Release Kinetics
4.2.9. UV/Vis Spectroscopy
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bashir, S.; Hina, M.; Iqbal, J.; Rajpar, A.H.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Alghamdi, N.A.; Wageh, S.; Ramesh, K.; Ramesh, S. Fundamental Concepts of Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties, and Their Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Husseiny, H.M.; Mady, E.A.; Hamabe, L.; Abugomaa, A.; Shimada, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yokoi, A.; Elbadawy, M.; Tanaka, R. Smart/stimuli-responsive hydrogels: Cutting-edge platforms for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 13, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebara, M.; Kotsuchibashi, Y.; Uto, K.; Aoyagi, T.; Kim, Y.J.; Narain, R.; Idota, N.; Hoffman, J.M. Smart Hydrogels. In Smart Biomaterials; NIMS Monographs; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; pp. 9–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, H. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Experiment, theory and application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1992, 17, 163–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heskins, M.; Guillet, J.E. Solution Properties of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Chem. 1968, 2, 1441–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.A.; Su, Y.; Wang, D. Mechanical properties of PNIPAM based hydrogels: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ito, C.; Yoshida, R.; Suzuki, S.; Sasaki, N.; Shibayama, M.; Chung, U.-I. Design and Fabrication of a High-Strength Hydrogel with Ideally Homogeneous Network Structure from Tetrahedron-like Macromonomers. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 5379–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Illeperuma, W.R.K.; Chaudhuri, O.; Oh, K.H.; Mooney, D.J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature 2012, 489, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Imran, A.; Esaki, K.; Gotoh, H.; Seki, T.; Ito, K.; Sakai, Y.; Takeoka, Y. Extremely stretchable thermosensitive hydrogels by introducing slide-ring polyrotaxane cross-linkers and ionic groups into the polymer network. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkan, B.; Orakdogen, N. Anionically modified N-(alkyl)acrylamide-based semi-IPN hybrid gels reinforced with SiO2 for enhanced on–off switching and responsive properties. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 4582–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.P.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Osada, Y. Double-Network Hydrogels with Extremely High Mechanical Strength. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Zhu, W.; Li, X.; Yu, Z. A novel mechanical robust, self-healing and shape memory hydrogel based on PVA reinforced by cellulose nanocrystal. Mater. Lett. 2020, 260, 126884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachotová, B.; Strachota, A.; Uchman, M.; Šlouf, M.; Brus, J.; Pleštil, J.; Matějka, L. Super porous organic–inorganic poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based hydrogel with a very fast temperature response. Polymer 2007, 48, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depa, K.; Strachota, A.; Šlouf, M.; Hromádková, J. Fast temperature-responsive nanocomposite PNIPAM hydrogels with controlled pore wall thickness: Force and rate of T-response. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachota, B.; Šlouf, M.; Matějka, L. Tremendous reinforcing, pore-stabilizing and response-accelerating effect of in situ generated nanosilica in thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) cryogels. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1510–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Angeles, G.; Hishchak, K.; Strachota, A.; Strachota, B.; Šlouf, M.; Matějka, L. Super-porous nanocomposite PNIPAm hydrogels reinforced with titania nanoparticles, displaying a very fast temperature response as well as pH-sensitivity. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 59, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachota, B.; Matějka, L.; Zhigunov, A.; Konefał, R.; Spěváček, J.; Dybal, J.; Puffr, R. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)–clay based hydrogels controlled by the initiating conditions: Evolution of structure and gel formation. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 9291–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachota, B.; Hodan, J.; Matějka, L. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)–clay hydrogels: Control of mechanical properties and structure by the initiating conditions of polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 77, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachota, B.; Šlouf, M.; Hodan, J.; Matějka, L. Advanced two-step cryopolymerization to form superporous thermosensitive PNIPA/clay gels with unique mechanical properties and ultrafast swelling-deswelling kinetics. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Takehisa, T. Nanocomposite Hydrogels: A Unique Organic–Inorganic Network Structure with Extraordinary Mechanical, Optical, and Swelling/De-swelling Properties. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachota, B.; Matějka, L.; Sikora, A.; Spěváček, J.; Konefał, R.; Zhigunov, A.; Šlouf, M. Insight into the cryopolymerization to form a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/clay macroporous gel: Structure and phase evolution. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Sakai, K.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Surface-modulated skin layers of thermal responsive hydrogels as on-off switches: II. Drug permeation. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1992, 3, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-T.; Huang, S.-W.; Zhuo, R.-X. Temperature-Sensitive Polyamidoamine Dendrimer/Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogels with Improved Responsive Properties. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Qing, A.; Lan, Y.; Lu, M. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels with improved shrinking kinetics by RAFT polymerization. Polymer 2006, 47, 2330–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depa, K.; Strachota, A.; Šlouf, M.; Brus, J. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-SiO2 nanocomposites interpenetrated by starch: Stimuli-responsive hydrogels with attractive tensile properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 349–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachota, B.; Strachota, A.; Šlouf, M.; Brus, J.; Cimrová, V. Monolithic intercalated PNIPAm/starch hydrogels with very fast and extensive one-way volume and swelling responses to temperature and pH: Prospective actuators and drug release systems. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 752–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strachota, B.; Strachota, A.; Horodecka, S.; Šlouf, M.; Dybal, J. Monolithic nanocomposite hydrogels with fast dual T- and pH- stimuli responsiveness combined with high mechanical properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 6079–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-M. Cellulosic associative thickeners. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, E.; Siepmann, F.; Flament, M.; Benzine, Y.; Penz, F.; Siepmann, J.; Karrout, Y. Controlled release tablets based on HPMC:lactose blends. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hong, Y. Combination of the Silver–Ethylene Interaction and 3D Printing To Develop Antibacterial Superporous Hydrogels for Wound Management. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 33734–33747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Gehrke, S.H. Microporous, fast response cellulose ether hydrogel prepared by freeze-drying. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2004, 38, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsano, E.; Bianchi, E.; Viscardi, A. Stimuli responsive gels based on interpenetrating network of hydroxy propylcellulose and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Polymer 2004, 45, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Gao, C.; Meng, X.; Wang, S.; Kong, F. Temperature/pH-Responsive Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide) Interpenetrating Polymer Network Aerogels for Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2022, 14, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, B.; Wang, S.; Kong, F. Temperature-responsive hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-N-isopropylacrylamide aerogels for drug delivery systems. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9493–9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, H. Structure and properties of cellulose/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels prepared by SIPN strategy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Hu, X.; Qi, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, W. A novel thermo-responsive hydrogel based on salecan and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Synthesis and characterization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 125, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, J.-P.; Park, S.; Shin, Y.; Hong, I.K.; Kim, M.S.; Jung, S. Novel temperature/pH-responsive hydrogels based on succinoglycan/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) with improved mechanical and swelling properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 174, 111308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, T.; Huang, R.; Zhao, Q.; Xiong, L.; Qin, L.; Tan, X.; Cai, G. Synthesis of wheat straw composite superabsorbent. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3404–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzakhanian, Z.; Faghihi, K.; Barati, A.; Momeni, H.R. Synthesis and characterization of fast-swelling porous superabsorbent hydrogel based on starch as a hemostatic agent. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2015, 26, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.; Huang, Y.; Xiong, F.; Liao, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, X. Preparation and swelling behaviors of rapid responsive semi-IPN NaCMC/PNIPAm hydrogels. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2011, 26, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A.; Dubovik, A.S.; Grinberg, N.V.; Burova, T.V.; Grinberg, V.Y. Temperature-sensitive chitosan-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) interpenetrated networks with enhanced loading capacity and controlled release properties. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-Q.; Zha, L.-S.; Zhou, M.-H.; Ma, J.-H.; Liang, B.-R. Rapid deswelling of sodium alginate/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels in response to temperature and pH changes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2004, 283, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilavský, M. Effect of phase transition on swelling and mechanical behavior of synthetic hydrogels. In Responsive Gels: Volume Transitions I.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 173–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Sakai, K.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Drug release profiles in the shrinking process of thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-alkyl methacrylate) gels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1992, 31, 2339–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Sample | Qap | Qsw | Gap | cEACap * | Gsw | cEACsw * | r1 = Qsw/Qap | r2 = Gap/Gsw = cEACap/cEACsw | r1/r2 Ratio of Change in the Amount of Elastically Active Chains (Crosslinks) ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-) | (-) | (kPa) | (mol/m3) | (kPa) | (mol/m3) | (-) | (-) | (-) | |
| 1B | 11.8 | 25.9 | 5.7 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 1.3 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 1.3 |
| 1B-1H | 10.7 | 25.9 | 5.7 | 2.3 | 2.9 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 2.0 | 1.2 |
| 1B-2H | 9.7 | 27.5 | 5.6 | 2.3 | 2.8 | 1.2 | 2.8 | 2.0 | 1.4 |
| 1B-3H | 8.9 | 30.3 | 4.8 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 1.7 |
| 1B-5H | 7.7 | 31.6 | 4.6 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 4.1 | 2.2 | 1.9 |
| 2B | 11.8 | 18.7 | 6.9 | 2.8 | 5.4 | 2.2 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 1.2 |
| 2B-1H | 10.7 | 19.6 | 6.5 | 2.6 | 5.5 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
| 2B-2H | 9.7 | 20.1 | 6.2 | 2.5 | 5.5 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 1.1 | 1.8 |
| 2B-3H | 8.9 | 22.0 | 5.1 | 2.1 | 4.4 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 2.1 |
| 2B-5H | 7.7 | 27.3 | 3.1 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 1.0 | 3.6 | 1.3 | 2.7 |
| 4B | 11.9 | 15.7 | 11.7 | 4.8 | 7.1 | 2.9 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 0.8 |
| 4B-1H | 10.7 | 15.6 | 14.2 | 5.8 | 9.0 | 3.7 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 0.9 |
| 4B-2H | 9.8 | 15.4 | 10.8 | 4.4 | 7.7 | 3.1 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.1 |
| 4B-3H | 9.0 | 16.5 | 7.4 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 1.5 |
| 4B-5H | 7.7 | 19.6 | 2.9 | 1.2 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 1.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strachota, B.; Strachota, A.; Vratović, L.; Pavlova, E.; Šlouf, M.; Kamel, S.; Cimrová, V. Exceptionally Fast Temperature-Responsive, Mechanically Strong and Extensible Monolithic Non-Porous Hydrogels: Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Intercalated with Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose. Gels 2023, 9, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9120926
Strachota B, Strachota A, Vratović L, Pavlova E, Šlouf M, Kamel S, Cimrová V. Exceptionally Fast Temperature-Responsive, Mechanically Strong and Extensible Monolithic Non-Porous Hydrogels: Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Intercalated with Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose. Gels. 2023; 9(12):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9120926
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrachota, Beata, Adam Strachota, Leana Vratović, Ewa Pavlova, Miroslav Šlouf, Samir Kamel, and Věra Cimrová. 2023. "Exceptionally Fast Temperature-Responsive, Mechanically Strong and Extensible Monolithic Non-Porous Hydrogels: Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Intercalated with Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose" Gels 9, no. 12: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9120926
APA StyleStrachota, B., Strachota, A., Vratović, L., Pavlova, E., Šlouf, M., Kamel, S., & Cimrová, V. (2023). Exceptionally Fast Temperature-Responsive, Mechanically Strong and Extensible Monolithic Non-Porous Hydrogels: Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Intercalated with Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose. Gels, 9(12), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9120926