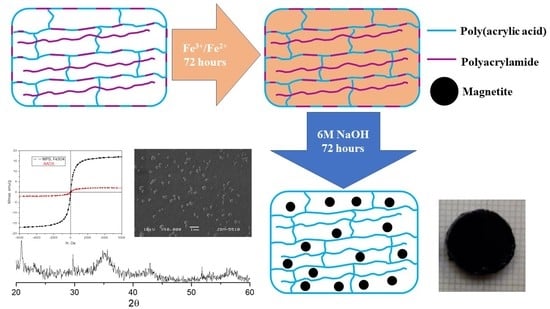
Poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/Polyacrylamide pIPNs/Magnetite Composite Hydrogels: Synthesis and Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Swelling Behavior
Equilibrium Swelling Ratio (ESR)
2.2. Number Average Molecular Mass between Crosslinks and Mesh Size of Neat pIPNs
2.3. Determination of the Iron Content in pIPNs/Magnetite Composites
2.4. X-ray Diffraction of the pIPNs Composites
2.5. pH-Responsive Behavior of pIPNs and the pIPNs/Magnetite Composites
- At pH = 3 (i.e., below pKa of COOH), all –COOH groups are protonated and the pIPNs hydrogels show a swelling ratio ~10 for all pIPNs compositions, i.e., AA content does not influence the ESR.
- At pH = 5 and above (i.e., above pKa of COOH), the polyanionic character of the pIPNs hydrogels makes the hydrogels increase their swelling ratio up to 70–80, i.e., 7 to 8 times, at an alkaline pH when compared to the swelling ratio obtained for pH = 3 (Figure 7A, Figure S10).
2.6. Salt-Concentration Responsiveness of pIPNs and the pIPNs/Magnetite Composites
2.7. Temperature Responsiveness of pIPNs and pIPNs/Magnetite Composites
2.8. Thermal Properties
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.10. Magnetic Properties
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Synthesis of P(AA-co-AAM)/PAAM pIPNs
4.2.2. P(AA-co-AAM) Composition
4.2.3. Preparation of pIPNs/Magnetite Composite Hydrogels
4.2.4. Swelling Behavior
4.2.5. Equilibrium Swelling Ratio (ESR)
4.2.6. pH Responsive Behavior of pIPNs and pIPNs/Magnetite Hydrogels
4.2.7. Temperature Responsive Behavior of pIPNs and the pIPNs/Magnetite Composite Hydrogels
4.2.8. Ionic Strength Responsive Behavior of pIPNs and pIPNs/Magnetite Composite Hydrogels
4.2.9. Attenuated Total Reflectance-FTIR (ATR-FTIR)
4.2.10. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.2.11. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
4.2.12. Iron Content Determination in pIPNs/Magnetite Composites
Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Magnetic Measurements
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dragan, E.S. Design and applications of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 243, 572–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, J.; Tang, Y. Hydrogel Based Sensors for Biomedical Applications: An Updated Review. Polymers 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantha, S.; Pillai, S.; Khayambashi, P.; Upadhyay, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, O.; Pham, H.M.; Tran, S.D. Smart Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Materials 2019, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnaught, A.D.; Wilkinson, A.; Union, I. Compendium of Chemical Terminology: IUPAC Recommendations; Oxford Blackwell Science: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sperling, L.H. Polymeric Multicomponent Materials: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Nashville, TN, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, E.; Pita, M. Biomedical applications of magnetic particles. In Fine Particles in Medicine and Pharmacy; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 147–173. [Google Scholar]
- Sivudu, K.S.; Rhee, K.Y. Preparation and Characterization of PH-Responsive Hydrogel Magnetite Nanocomposite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 349, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.M.; Martin, D.A.; Alvarez, V.A.; Gonzalez, J.S. Polyacrylic Acid-Coated Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles: The Polymer Molecular Weight Influence. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 543, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, G.; Gao, F. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated with different polymers and their MRI contrast effects in the mouse brains. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 326, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Noqta, O.A.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B. Simple rapid stabilization method through citric acid modification for magnetite nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10793. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.T.; Yehya, W.A.; Saad, O.; Simarani, K.; Chowdhury, Z.; Alhadi, A.A.; Al-Ani, L.A. Surface Functionalization of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Gallic Acid as Potential Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Agents. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namdeo, M.; Bajpai, S.K.; Kakkar, S. Preparation of a magnetic-field-sensitive hydrogel and preliminary study of its drug release behavior. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2009, 20, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starodubtsev, S.G.; Saenko, E.V.; Dokukin, M.E.; Aksenov, V.L.; Klechkovskaya, V.V.; Zanaveskina, I.S.; Khokhlov, A.R. Formation of Magnetite Nanoparticles in Poly(Acrylamide) Gels. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakaki, A.; Nakazawa, H.; Nemoto, M.; Mori, T.; Matsunaga, T. Formation of magnetite by bacteria and its application. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 977–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chełminiak, D.; Ziegler-Borowska, M.; Kaczmarek, H. Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles coated with poly(acrylic acid) by photopolymerization. Mater. Lett. 2016, 164, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdov, A.S.; Prilepskii, A.Y.; Koltsova, E.M.; Anastasova, E.I.; Vinogradov, V.V. Magnetic Polyelectrolyte-Based Composites with Dual Anticoagulant and Thrombolytic Properties: Towards Optimal Composition. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, F.-Y.; Lai, J.-Y.; Shih, C.-M.; Tsai, M.-C.; Lue, S.J. In Vitro Biocompatibility of Magnetic Thermo-Responsive Nanohydrogel Particles of Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide-Co-Acrylic Acid) with Fe3O4 Cores: Effect of Particle Size and Chemical Composition. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 104, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, N.M.; Abbass, M.; Ismail, F.; El-Din, H.M.N. Radiation Synthesis and Anticancer Drug Delivery of Poly(Acrylic Acid/Acrylamide) Magnetite Hydrogel. Polym. Bull. 2022, 80, 4573–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.; Benjamin, M.M.; Ryan, J.N. Role of organic acidity in sorption of natural organic matter (NOM) to oxide surfaces. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1996, 107, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todica, M.; Pop, C.V.; Udrescu, L.; Stefan, T. Spectroscopy of a Gamma Irradiated Poly(Acrylic Acid)-Clotrimazole System. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2011, 28, 128201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudeman, L.F.; Peppas, N.A. Preparation and Characterization of PH-Sensitive, Interpenetrating Networks of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Poly(Acrylic Acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1995, 55, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.D.; Tobolsky, A.V.; Hanson, E.E. The Theory of Permanent Set at Elevated Temperatures in Natural and Synthetic Rubber Vulcanizates. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1946, 19, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zahhar, A.A.; Ashraf, I.M.; Idris, A.M.; Zkria, A. Pronounced Effect of PbI2 Nanoparticles Doping on Optoelectronic Properties of PVA Films for Photo-Electronic Applications. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2022, 630, 413604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, C.R.; Cabuil, V.; Lalot, T.; Thouvenot, R. Magnetic Nanoparticles Trapped in PH 7 Hydrogels as a Tool to Characterize the Properties of the Polymeric Network. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, A.S.; Morelos, O. Polyelectrolyte Adsorption by Kaolinite. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1955, 47, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, M.-K.; Cho, C.-S.; Choi, H.-K. Characteristics of Poly(Vinyl Pyrrolidone)/Poly(Acrylic Acid) Interpolymer Complex Prepared by Template Polymerization of Acrylic Acid: Effect of Reaction Solvent and Molecular Weight of Template. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 2390–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, K.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gan, W. Synthesis of Poly(Acrylic Acid) Coated Magnetic Nanospheres via a Multiple Polymerization Route. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolwijk, N.A.; Heddier, C.; Reschke, M.; Wiencierz, M.; Bokeloh, J.; Wilde, G. Salt-Concentration Dependence of the Glass Transition Temperature in PEO–NaI and PEO–LiTFSI Polymer Electrolytes. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 8580–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, L.; Karjalainen, E.; Aseyev, V.; Tenhu, H. Tough Materials through Ionic Interactions. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 721656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namanga, J.; Foba, J.; Ndinteh, D.T.; Yufanyi, D.M.; Krause, R.W.M. Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of a Superparamagnetic Nanocomposite “Pectin-Magnetite Nanocomposite”. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 137275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucheryavy, P.; He, J.; John, V.T.; Maharjan, P.; Spinu, L.; Goloverda, G.Z.; Kolesnichenko, V.L. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Variable Size and an Iron Oxidation State as Prospective Imaging Agents. Langmuir 2013, 29, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rintoul, I.; Wandrey, C. Polymerization of Ionic Monomers in Polar Solvents: Kinetics and Mechanism of the Free Radical Copolymerization of Acrylamide/Acrylic Acid. Polymer 2005, 46, 4525–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Wanchoo, R.K.; Singh, P. Structural Parameters and Swelling Behavior of PH Sensitive Poly(Acrylamide-Co-Acrylic Acid) Hydrogels. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2011, 25, 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Finch, C.A. Polymer Handbook, 3rd ed.; Brandrup, J., Immergut, E.H., Eds.; British Polymer Journal; Wiley-Interscience: Chichester, UK, 1990; Volume 23, p. 277. [Google Scholar]
- Pourjavadı, A.; Mahdavınıa, G.R. Superabsorbency, pH-Sensitivity and Swelling Kinetics of Partially Hydrolyzed Chitosan-g-poly(Acrylamide) Hydrogels. Turk. J. Chem. 2006, 30, 595–608. [Google Scholar]
- Lindén, L.; Rabek, J.F. Structures and Mechanisms of Formation of Poly(Acrylic Acid)-Iron (II and III) Chloride Gels in Water and Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 50, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, E.; Brito, E.; Silva, R.; Streck, L.; Bohn, F.; Fonseca, J. Superparamagnetic Polyacrylamide/Magnetite Composite Gels. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Gayosso, C.A.; Canseco, M.; Estrada, R.; Palacios-Alquisira, J.; Hinojosa, J.; Castano, V. Preparation and Micro-structure of Cobalt(Iii) Poly (Acrylate) Hybrid Materials. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, W.M.; Axelson, D.E.; Van Dyke, J.D. Thermal Degradation of Polyacrylamide and Poly(Acrylamide-Co-Acrylate). J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1987, 25, 25–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonov, M.S.; Apostolov, A.A.; Vassileva, E.D. In Situ Calcium Phosphate Deposition in Hydrogels of Poly(Acrylic Acid)–Polyacrylamide Interpenetrating Polymer Networks. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 16274–16284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, S.; Tang, K.; De Volder, M.; Hwang, Y. Oxidative Degradation of Tetracycline by Magnetite and Persulfate: Performance, Water Matrix Effect, and Reaction Mechanism. Nanomater 2021, 11, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Sample Designation | [Da] | [Da] | ξ [nm] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equation (5) | Equation (6) | Equation (7) | Equation (8) | |
| AA100 | 0.0415 ± 0.0005 | 355,676 ± 11,809 | 1801 | 1144 ± 24 |
| AA80 | 0.0464 ± 0.0037 | 248,403 ± 58,424 | 1797 | 862 ± 125 |
| AA50 | 0.0481 ± 0.0069 | 211,178 ± 60,791 | 1790 | 702 ± 138 |
| AA20 | 0.0484 ± 0.0059 | 182,124 ± 62,749 | 1783 | 561 ± 122 |
| AA0 | 0.0463 ± 0.0028 | 166,366 ± 22,494 | 1777 | 481 ± 42 |
| Sample | Crystallite Size [Å] at 2θ = 35.4 Dhkl (311) | Crystallite Size [Å] at 2θ ~ 43 Dhkl (400) |
|---|---|---|
| AA100X | amorphous | amorphous |
| AA80X | 11 | amorphous |
| AA50X | 46 | 30 |
| AA20X | 73 | 96 |
| AA0X | 72 | 90 |
| MPS | 92 | 98 |
| Sample | H2O | 0.001 M NaCl |
|---|---|---|
| AA80 | 22 ± 2 | 58 ± 5 |
| AA80X | 91 ± 5 | 85 ± 4 |
| AA50 | 26 ± 1 | 57 ± 2 |
| AA50X | 79 ± 2 | 79 ± 4 |
| AA20 | 22 ± 1 | 39 ± 1 |
| AA20X | 61 ± 1 | 67 ± 5 |
| Sample | Initial Polymerization Solution Composition | Reactivity Ratios Values | Copolymer Composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA [mol. %] | AAM [mol. %] | pH | r1 | r2 | AA * [mol. part] | AAM [mol. part] | |
| AA100 | 100 | 0 | 2.7 | PAA homopolymerization | 0.96 | - | |
| AA80 | 80 | 20 | 2.9 | 1.34 | 0.69 | 0.81 | 0.19 |
| AA50 | 50 | 50 | 3.3 | 1.34 | 0.69 | 0.55 | 0.45 |
| AA20 | 20 | 80 | 3.7 | 1.28 | 0.82 | 0.24 | 0.76 |
| AA0 | 0 | 100 | 6.2 | PAAM homopolymerization | 0 | 1 | |
| Sample Designation | AA [mol. %] | AAM [mol. %] | Fe3+ [mol/L] | Fe2+ [mol/L] | 6 M NaOH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA100X | 100 | 0 | 0.30 | 0.15 | yes |
| AA80X | 80 | 20 | 0.30 | 0.15 | yes |
| AA50X | 50 | 50 | 0.30 | 0.15 | yes |
| AA20X | 20 | 80 | 0.30 | 0.15 | yes |
| AA0X | 0 | 100 | 0.003 | 0.0015 | yes |
| 10 times dilution | |||||
| AA80Y | 80 | 20 | 0.03 | 0.015 | yes |
| AA50Y | 50 | 50 | 0.03 | 0.015 | yes |
| AA20Y | 20 | 80 | 0.03 | 0.015 | yes |
| 100 times dilution | |||||
| AA80Z | 80 | 20 | 0.003 | 0.0015 | yes |
| AA50Z | 50 | 50 | 0.003 | 0.0015 | yes |
| AA20Z | 20 | 80 | 0.003 | 0.0015 | yes |
| AA100Fe * | 100 | 0 | 0.30 | 0.15 | no |
| AA0Fe * | 0 | 100 | 0.30 | 0.15 | no |
| AA100N * | 100 | 0 | no | no | yes |
| AA0N * | 0 | 100 | no | no | yes |
| MPS * | - | - | 0.003 | 0.0015 | yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simeonov, M.; Apostolov, A.A.; Georgieva, M.; Tzankov, D.; Vassileva, E. Poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/Polyacrylamide pIPNs/Magnetite Composite Hydrogels: Synthesis and Characterization. Gels 2023, 9, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050365
Simeonov M, Apostolov AA, Georgieva M, Tzankov D, Vassileva E. Poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/Polyacrylamide pIPNs/Magnetite Composite Hydrogels: Synthesis and Characterization. Gels. 2023; 9(5):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050365
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimeonov, Marin, Anton Atanasov Apostolov, Milena Georgieva, Dimitar Tzankov, and Elena Vassileva. 2023. "Poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/Polyacrylamide pIPNs/Magnetite Composite Hydrogels: Synthesis and Characterization" Gels 9, no. 5: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050365
APA StyleSimeonov, M., Apostolov, A. A., Georgieva, M., Tzankov, D., & Vassileva, E. (2023). Poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/Polyacrylamide pIPNs/Magnetite Composite Hydrogels: Synthesis and Characterization. Gels, 9(5), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050365