Alumina Ceramic Nanofibers: An Overview of the Spinning Gel Preparation, Manufacturing Process, and Application
Abstract
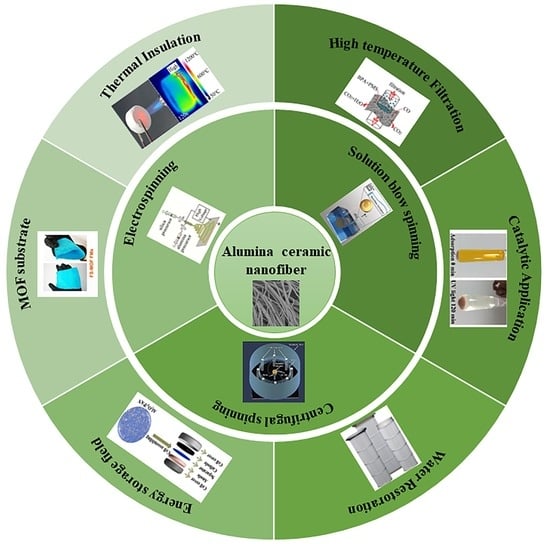
:1. Introduction
2. Preparation of Alumina Spinning Gel
3. Methods for the Preparation of Alumina Nanofibers
3.1. Electrospinning

3.2. Solution Blow Spinning
3.3. Centrifugal Spinning

3.4. Other Preparation Methods
4. Applications of Alumina Nanofibers
4.1. Thermal Insulation
4.2. High-Temperature Filtration
4.3. Catalytic Application
4.4. Water Restoration
4.5. Energy Storage Field
4.6. Other Applications
5. Conclusions and Outlook
- Improved scalability and cost effectiveness: Although various methods such as electrospinning, solution blow spinning, and centrifugal spinning have been used for the fabrication of alumina ceramic nanofibers, there is still a need for scalable and cost-effective manufacturing processes. Developing methods that can produce alumina ceramic nanofibers in large quantities at a reasonable cost will enable their widespread commercial applications.
- Enhanced properties and performance: Further research can focus on improving the properties and performance of alumina ceramic nanofibers. This can involve tuning the composition, morphology, and surface properties of the nanofibers to achieve the desired characteristics such as a higher thermal stability, mechanical strength, and electrical conductivity. This can open up new possibilities for advanced applications in areas such as energy storage, sensors, and electronics.
- Novel applications: While alumina ceramic nanofibers have found applications in various fields such as heat insulation, filtration, catalysis, and energy storage, there may be other untapped areas where they can be utilized. Exploring novel applications of alumina ceramic nanofibers in emerging fields such as flexible electronics, aerospace, and environmental monitoring can provide new opportunities for their utilization.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, S. Current status and prospect of alumina fiber. Mater. Rep. 1990, 02, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Zhao, L.; Tang, H.; Feng, H.; Mao, X.; Zhang, K. Preparation and application status of alumina fiber. Synth. Fiber Ind. 2021, 44, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhong, L.; Gu, L. Preparation and application of alumina fiber. New Chem. Mater. 2002, 04, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Preparation of Alumina Fiber by Electrospinning and Its Application in the Environmental Field. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, X.R.K. Martensite transformation hystereses for CuAINiMnTi shape-memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1992, 11, 1291–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, V.; Kawada, H. Fatigue behaviour of alumina-fibre-reinforced epoxy resin composite pipes under tensile and compressive loading conditions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K. Ceramic nanofibers by electrospinning technique—A review. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2008, 66, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, K.; Kotaki, M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Mo, X.M.; Ramakrishna, S. Recent advances in polymer nanofibers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y.N. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Reinventing the wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.L.; Bates, W.D.; Frisch, H.L.; Wnek, G.E. Role of chain entanglements on fiber formation during electrospinning of polymer solutions: Good solvent, non-specific polymer-polymer interaction limit. Polymer 2005, 46, 3372–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Elkins, C.; Long, T.E.; Wilkes, G.L. Electrospinning of linear homopolymers of poly(methyl methacrylate): Exploring relationships between fiber formation, viscosity, molecular weight and concentration in a good solvent. Polymer 2005, 46, 4799–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.M.; Shintay, S.; Zhang, X.W. Diameter control of electrospun polyacrylonitrile/iron acetylacetonate ultrafine nanofibers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B-Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Woodroof, M.D.; Ji, L.W.; Liang, Y.Z.; Krause, W.; Zhang, X.W. Effect of Platinum Salt Concentration on the Electrospinning of Polyacrylonitrile/Platinum Acetylacetonate Solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrell, H.; Reneker, A.L.Y.; Hao, F.; Koombhongse, S. Bending instability of electrically charged liquid jets of polymer solutions in electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4531–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D.H. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Mujib, S.; Cuccato, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Franchin, G.; Colombo, P.; Singh, G. Electrospun SiOC ceramic fiber mats as freestanding electrodes for electrochemical energy storage applications. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 3565–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinkok, C.; Sagdic, G.; Daglar, O.; Ayra, M.E.; Durmaz, Y.Y.; Durmaz, H.; Acik, G. A new strategy for direct solution electrospinning of phosphorylated poly (vinyl chloride)/polyethyleneimine blend in alcohol media. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 183, 111750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.H.; Yu, Z.C.; Yuan, K.K.; Jin, X.T.; Shi, S.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhu, L.Y.; Zhang, G.H.; Xu, D.; Jiang, H. Improved preparation of electrospun MgO ceramic fibers with mesoporous structure and the adsorption properties for lead and cadmium. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 3743–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Gong, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, D. A novel method for preparing ultra-fine alumina-borate oxide fibres via an electrospinning technique. Nanotechnology 2002, 13, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.M.; Cheng, B.W.; Li, Q.X.; Zhuang, X.P.; Ren, Y.L. A new method for preparing alumina nanofibers by electrospinning technology. Text. Res. J. 2011, 81, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, J.; Zhu, S.Q.; Li, Y.G.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhu, M.F. Preparation of continuous alumina nanofibers via electrospinning of PAN/DMF solution. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.P.; Jiao, X.L.; Chen, D.R. Fabrication of electrospun Al2O3 fibers with CaO-SiO2 additive. Mater. Lett. 2013, 91, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodaev, V.V.; Zhigachev, A.O.; Golovin, Y.I. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun ZrO2/Al2O3 nanofibers. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 16023–16026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, J.S.; Turinske, A.J.; Stojilovic, N.; Lotus, A.F.; Chase, G.G. Temperature-induced changes in morphology and structure of TiO2-Al2O3 fibers. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y.; Yuan, H.H.; Yang, P.F.; Yi, B.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Fabrication of the composite nanofibers of NiO/gamma-Al2O3 for potential application in photocatalysis. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 17405–17409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cheng, X.; Han, G.; Si, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Elastic and compressible Al2O3/ZrO2/La2O3 nanofibrous membranes for firefighting protective clothing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 636, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, B.S.; Yu, W.R. Recent Progress in Coaxial Electrospinning: New Parameters, Various Structures, and Wide Applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1704765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.A.; Greiner, A. Air-Blowing-Assisted Coaxial Electrospinning toward High Productivity of Core/Sheath and Hollow Fibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.F.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. One-Dimensional Composite Nanomaterials: Synthesis by Electrospinning and Their Applications. Small 2009, 5, 2349–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.L.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.L.; Kang, W.M.; Deng, N.P.; Zhuang, X.P.; Zhou, X.H. Research progress of ultrafine alumina fiber prepared by sol-gel method: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 127744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, W.D.; Jiao, X.L.; Chen, D.R. Electrospun flexible self-standing silica/mesoporous alumina core-shell fibrous membranes as adsorbents toward Congo red. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 30790–30797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirtic, J.; Balazic, H.; Zupancic, S.; Kristl, J. Effect of Solution Composition Variables on Electrospun Alginate Nanofibers: Response Surface Analysis. Polymers 2019, 11, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Jun, Y.; Qin, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Electrospinning versus microfluidic spinning of functional fibers for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2017, 114, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhand, C.; Venkatesh, M.; Barathi, V.A.; Harini, S.; Bairagi, S.; Leng, E.G.T.; Muruganandham, N.; Low, K.Z.W.; Fazil, M.; Loh, X.J.; et al. Bio-inspired crosslinking and matrix-drug interactions for advanced wound dressings with long-term antimicrobial activity. Biomaterials 2017, 138, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenry; Lim, C.T. Nanofiber technology: Current status and emerging developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Lu, Y. Centrifugal Spinning: An Alternative Approach to Fabricate Nanofibers at High Speed and Low Cost. Polym. Rev. 2014, 54, 677–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boda, S.K.; Chen, S.X.; Chu, K.; Kim, H.J.; Xie, J.W. Electrospraying Electrospun Nanofiber Segments into Injectable Microspheres for Potential Cell Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 25069–25079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, T.; Wang, X.G. Use of airflow to improve the nanofibrous structure and quality of nanofibers from needleless electrospinning. J. Ind. Text. 2015, 45, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Dong, R.H.; Yan, X.; Yu, G.F.; You, M.H.; Ning, X.; Long, Y.Z. Recent Advances in Needleless Electrospinning of Ultrathin Fibers: From Academia to Industrial Production. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirsak, O.; Petrik, S. Recent advances in nanofibre technology: Needleless electrospinning. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 9, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yu, H.N.; Sun, R.J.; Liu, C.K.; Chen, M.Y.; Liu, H.J.; Xiong, J.; Qin, X.H. Experimental investigation of process parameters for the filtration property of nanofiber membrane fabricated by needleless electrospinning apparatus. J. Ind. Text. 2021, 50, 1528–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Orts, W.J.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Solution Blow Spinning: A New Method to Produce Micro- and Nanofibers from Polymer Solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.X.; Huang, L.P.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.Z. Recent progress and challenges in solution blow spinning. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 426–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daristotle, J.L.; Behrens, A.M.; Sandler, A.D.; Kofinas, P. A Review of the Fundamental Principles and Applications of Solution Blow Spinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34951–34963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.W.; Cui, Z.W.; Zhao, L.H.; Hussain, N.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Yang, C.; Jiang, X.Y.; Li, L.; Song, J.A.; Zhang, B.P.; et al. High-throughput production of kilogram-scale nanofibers by Karman vortex solution blow spinning. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutak, W.; Sarkar, S.; Lin-Gibson, S.; Farooque, T.M.; Jyotsnendu, G.; Wang, D.B.; Kohn, J.; Bolikal, D.; Simon, C.G. The support of bone marrow stromal cell differentiation by airbrushed nanofiber scaffolds. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.L.G.; Braz, A.L.; Porto, I.J.; Menner, A.; Bismarck, A.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Lepry, W.C.; Nazhat, S.N.; Medeiros, E.S.; Blaker, J.J. Porous Bioactive Nanofibers via Cryogenic Solution Blow Spinning and Their Formation into 3D Macroporous Scaffolds. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.F.; Santos, A.M.C.; Farias, R.M.C.; Neves, G.A.; Menezes, R.R. Synthesis and characterization of alumina fibers using solution blow spinning. Cerâmica 2019, 65, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, Y.B.; Li, L.; Song, J.N.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Z.L.; Li, Z.W.; Li, B.; Fang, M.H.; Wu, H. A Foldable All-Ceramic Air Filter Paper with High Efficiency and High-Temperature Resistance. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4993–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, C.S.; Liu, Z.L.; Fang, M.H.; Ou, G.; et al. Ultralight, scalable, and high-temperature-resilient ceramic nanofiber sponges. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1603170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Abrego, M.; Hernandez-Granados, A.; Guerrero-Bermea, C.; de la Cruz, A.M.; Garcia-Gutierrez, D.; Sepulveda-Guzman, S.; Cruz-Silva, R. Mesoporous titania nanofibers by solution blow spinning. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Preparation and Application of Airflow Spinning Oxide Nanofibers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Badrossamay, M.R.; Balachandran, K.; Capulli, A.K.; Golecki, H.M.; Agarwal, A.; Goss, J.A.; Kim, H.; Shin, K.; Parker, K.K. Engineering hybrid polymer-protein super-aligned nanofibers via rotary jet spinning. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.C.; Dulaney, A.R.; Gadley, J.; Maia, J.; Ellison, C.J. A comparative parameter study: Controlling fiber diameter and diameter distribution in centrifugal spinning of photocurable monomers. Polymer 2016, 88, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellison, C.J.; Phatak, A.; Giles, D.W.; Macosko, C.W.; Bates, F.S. Melt blown nanofibers: Fiber diameter distributions and onset of fiber breakup. Polymer 2007, 48, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.G.; Choi, Y.H.; Minus, M.L.; Kumar, S. Carbon nanotube reinforced small diameter polyacrylonitrile based carbon fiber. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Cai, N.; Yang, W.Q.; Chen, W.D.; Liu, H.Q. Sea-Island Polyurethane/Polycarbonate Composite Nanofiber Fabricated Through Electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.X.; Zhang, R. Synthetic nano-scale fibrous extracellular matrix. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 46, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegame, M.; Tajima, K.; Aida, T. Template synthesis of polypyrrole nanofibers insulated within one-dimensional silicate channels: Hexagonal versus lamellar for recombination of polarons into bipolarons. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 2154–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.G.; Bein, T. Conducting polyaniline filaments in a mesoporous channel host. Science 1994, 264, 1757–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, C.R. Nanomaterials: A membrane-based synthetic approach. Science 1994, 266, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-hydrophobic surface of aligned polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2002, 41, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, B. Supramolecular hydrogels based on biofunctional nanofibers of self-assembled small molecules. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, H.W.; Yang, Z.M.; Xu, B. Supramolecular hydrogels respond to ligand-receptor interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13680–13681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.M.; Xu, B. A simple visual assay based on small molecule hydrogels for detecting inhibitors of enzymes. Chem. Commun. 2004, 21, 2424–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.M.; Gu, H.W.; Fu, D.G.; Gao, P.; Lam, J.K.; Xu, B. Enzymatic formation of supramolecular hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akia, M.; Capitanachi, D.; Martinez, M.; Hernandez, C.; de Santiago, H.; Mao, Y.B.; Lozano, K. Development and optimization of alumina fine fibers utilizing a centrifugal spinning process. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 262, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, A.; Taheri-Nassaj, E.; Naghizadeh, R. An alumina mat with a nano microstructure prepared by centrifugal spinning method. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 2818–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xia, L.; Ju, J.G.; Xi, P.; Cheng, B.W.; Liang, Y.X. Preparation and low-temperature gas-sensing properties of SnO2 ultra-fine fibers fabricated by a centrifugal spinning process. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Ju, J.G.; Xu, W.; Ding, C.K.; Cheng, B.W. Preparation and characterization of hollow Fe2O3 ultra-fine fibers by centrifugal spinning. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, B.C.; Xu, F.H.; Salinas, A.; Lozano, K. Mass production of carbon nanotube reinforced poly(methyl methacrylate) nonwoven nanofiber mats. Carbon 2014, 75, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmila Jancic, R.A. Influence of formation conditions and precursor viscosity on mean fiber diameter formed using the rotating disk method. Mater. Lett. 2000, 42, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Fu, S.; Liu, L.; Jia, J.; Gan, X. Effect of process parameter control on the preparation of A80 polycrystalline alumina fiber. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2011, 40, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Mei, S.Q.; Dong, Y.J.; She, F.H.; Kong, L.X. High Efficiency Fabrication of Chitosan Composite Nanofibers with Uniform Morphology via Centrifugal Spinning. Polymers 2019, 11, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, Y.S.; Zhang, Z.M.; Lu, B.B.; Chen, B.Y.; Lai, Z.L. The movement and forces of spinning solution in the nozzle during high-speed centrifugal spinning. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2019, 14, 1558925019828207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J. Preparation of TiO2 Composite Nanofibers by Centrifugal Spinning and Their Photocatalytic Properties. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yanilmaz, M.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.W. SiO2/polyacrylonitrile membranes via centrifugal spinning as a separator for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 273, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.Y.; Ozisik, R.; Kotha, S.P. Rapid and efficient fabrication of multilevel structured silica micro-/nanofibers by centrifugal jet spinning. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 425, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.W.; Mao, K.; Liu, J.; Tao, T.Y.; Zhao, H.Q.; Huang, Z.H.; Liu, Y.G.; Fang, M.H.; Min, X. N–Si doped carbon-embedded TiO2 composite fibers: A new photocatalysts with high yields by centrifugal spinning. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1150h1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.C.; Wang, H.L.; Song, J.A.; Bai, X.P.; Liu, Z.L.; Fang, M.H.; Yuan, Y.S.; Sheng, J.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, N.; et al. Ultralight and resilient Al2O3 nanotube aerogels with low thermal conductivity. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, M.; Xie, S.; Fan, K. A novel sol-gel synthetic route to alumina nanofibers via aluminum nitrate and hexamethylenetetramine. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 5074–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Yang, S.H.; Jun, Y.S.; Hong, W.H.; Kang, J.K. Facile route to synthesize large-mesoporous gamma-alumina by room temperature ionic liquids. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Deng, Y.D.; Hu, W.B. Synthesis of alumina nanofibers by a mercury-mediated method. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yim, H.; Luo, Z.P. Formation of alumina nanofibers in carbon-containing coflow laminar diffusion flames. J. Aerosol Sci. 2009, 40, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, D.; Kikuchi, T.; Natsui, S.; Sakaguchi, N.; Suzuki, R.O. Fabrication of a novel aluminum surface covered by numerous high-aspect-ratio anodic alumina nanofibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.C.; Liu, Y.B.; Wang, Y.J.; Luo, G.S. Preparation of Large-Pore-Volume gamma-Alumina Nanofibers with a Narrow Pore Size Distribution in a Membrane Dispersion Microreactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 8888–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.F.; Liu, H.; Sun, H.J.; Yang, D. PEG-directed hydrothermal synthesis of multilayered alumina microfibers with mesoporous structures. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 123, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, P.A.; Sayegh, S.; Nada, A.A.; Weber, M.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Coy, E.; Abboud, N.; Bechelany, M. Elaboration of porous alumina nanofibers by electrospinning and molecular layer deposition for organic pollutant removal. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Lopez, J.A.; Toledo, J.A.; Escobar, J.; Lopez-Salinas, E. Preparation of alumina-titania nanofibers by a pH-swing method. Catal. Today 2008, 133, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Cui, S.; Xia, Y. Preparation and application of several inorganic fibers. Nonwovens 2010, 18, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Xie, Y.S.; Lv, J.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.Y.; Jia, Z.T.; Tao, X.T. Preparation of ultrafine flexible alumina fiber for heat insulation by the electrospinning method. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 19460–19466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.N.; Zhao, Z.H.; Liu, Y.K.; He, D.X.; Shen, X.Q. Preparation and characterization of Al2O3/SiO2 composite nanofibers by using electrostatic spinning method. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2017, 47, 1275–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Fang, B.; Ding, H.; Song, J.N.; Liu, Y.B.; Xiang, K.J.; Lin, S.; Li, Z.W.; et al. Highly compressible and anisotropic lamellar ceramic sponges with superior thermal insulation and acoustic absorption performances. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Ogami, T.; Kanamura, K. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Hollow Al2O3 Microfibers for Thermal Insulation Materials. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 91, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Dong, X.; Xie, S.T.; Jia, T.; Xue, Y.J.; Liu, J.C.; Jing, W.; Guo, A.R. Ultralight, thermal insulating, and high-temperature-resistant mullite-based nanofibrous aerogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Xia, Y.G.; Jiao, X.L.; Chen, D.R. Electrospun flexible self-standing gamma-alumina fibrous membranes and their potential as high-efficiency fine particulate filtration media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 15124–15131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanishevsky, A.; Brayer, W.A.; Pokorny, P.; Kalous, T.; Lukas, D. Nanofibrous alumina structures fabricated using high-yield alternating current electrospinning. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 17154–17161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.W.; Wang, H.C.; Guan, K.; Wei, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.; Meng, J.L.; Liu, X.J.; Meng, J. La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-delta/CeO2 Heterostructured Composite Nanofibers as a Highly Active and Robust Cathode Catalyst for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 26830–26841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, L.; Wang, Y.F.; Kang, Y.H.; Wang, C.; Yang, S.B. Fabrication of TiO2/ZnO composite nanofibers with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 7834–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Huang, Y.X.; Xiao, A.H.; Liu, H.Q. Preparation and photocatalytic property of mesoporous ZnO/SnO2 composite nanofibers. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 503, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuangchote, S.; Jitputti, J.; Sagawa, T.; Yoshikawa, S. Photocatalytic Activity for Hydrogen Evolution of Electrospun TiO2 Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1140–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, J.Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhao, X. Electrospun flexible self-standing Cu-Al2O3 fibrous membranes as Fenton catalysts for bisphenol A degradation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 19151–19158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.Q.; Zhao, S.Z.; Han, L.H. A novel preparation method for ZnO/gamma-Al2O3 nanofibers with enhanced absorbability and improved photocatalytic water-treatment performance by Ag nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6892–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Koo, W.T.; Jang, J.S.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, I.D. Chitosan-templated Pt nanocatalyst loaded mesoporous SnO2 nanofibers: A superior chemiresistor toward acetone molecules. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13713–13721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.C.; Li, S.X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.J.; Wei, Y. Electrospinning of porous silica nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles for catalytic applications. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.Y.; Wang, G.; Liang, W.H.; Cao, J.H. The electrospun mesoporous Al2O3 and mesoporous Au-Al2O3 nanofiber catalyst. J. Porous Mater. 2016, 23, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhan, S.H.; Di, S.; Zhao, X. Novel Flexible Self-Standing Pt/Al2O3 Nanofibrous Membranes: Synthesis and Multifunctionality for Environmental Remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26396–26404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, B.L.; Rukundo, P.; Wen, S.P.; Wang, Z.J. Synthesis of a highly dispersed Ni/Al2O3 catalyst with enhanced catalytic performance for CO2 reforming of methane by an electrospinning method. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 17361–17369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, S.V.; Rezaei, M.; Meshkani, F.; Daroughegi, R. Synthesis of nanocrystalline mesoporous Ni/Al2O3-SiO2 catalysts for CO2 methanation reaction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 19038–19046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.F.; Zhao, X.L.; Lv, C.X.; Wang, Y.J.; Yang, D.J.; Li, Z.H.; Yao, X.D. Nb2O5-gamma-Al2O3 nanofibers as heterogeneous catalysts for efficient conversion of glucose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, J.; Duan, X.Z.; Qian, G.; Zhou, X.G.; Tong, G.S.; Yuan, W.K. Towards an efficient CoMo/gamma-Al2O3 catalyst using metal amine metallate as an active phase precursor: Enhanced hydrogen production by ammonia decomposition. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 12490–12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.L.; Brame, J.; Li, Q.L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Nanotechnology for a Safe and Sustainable Water Supply: Enabling Integrated Water Treatment and Reuse. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yoo, S.J.; Kwak, D.H.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, T.Y.; Park, K.H.; Lee, J.W. Characterization and application of electrospun alumina nanofibers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahapatra, A.; Mishra, B.G.; Hota, G. Studies on Electrospun Alumina Nanofibers for the Removal of Chromium(VI) and Fluoride Toxic Ions from an Aqueous System. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Mukhlish, M.Z.; Horie, Y.; Nomiyama, T. Flexible Alumina-Silica Nanofibrous Membrane and Its High Adaptability in Reactive Red-120 Dye Removal from Water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Wang, L.Y.; Luo, Y.S.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Cheng, B.W.; Kang, W.M.; Ju, J.G. An Alumina/Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibrous Composite Separator via High-Efficiency Electro-Blown Spinning and Wet-Laid Technologies for Improved Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A4088–A4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Ju, J.G.; Deng, N.P.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Kang, W.M.; Cheng, B.W. Designing inorganic-organic nanofibrous composite membrane for advanced safe Li-ion capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 337, 135821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrell, A.; Torrecillas, R.; Rocha, V.G.; Fernandez, A. Alumina-Carbon Nanofibers Nanocomposites Obtained by Spark Plasma Sintering for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Bipolar Plates. Fuel Cells 2012, 12, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.L.; Guo, Y.D.; Ma, Y.Y.; Zhuang, X.P.; Kang, W.M. Reasonable construction of proton conducting channel via biomimetic caterpillar-like alumina fiber to improve the properties of its composite proton exchange membrane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 29915–29924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Q.; Hou, J.L.; Xiang, J.; Shen, X.Q.; Luan, K.J.; Zhang, Y.J. Effect of Non-Woven Al2O3/C Nanofibers as Functional Interlayer on Electrochemical Performance of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 7824–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, M.; Ivanov, R.; Hussainova, I. 3D Alumina-Graphene Hybrid Nanofibers as a Binder-Free Cathode for Rechargeable Li-S Batteries. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 799, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Xu, Z.; Luo, D.F.; Xiang, H.X.; Zhu, M.F. Flexible Ceramic Fibers: Recent Development in Preparation and Application. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 573–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.X.; Jiao, X.L.; Li, C.; Chen, D.R. Flexible self-supported metal-organic framework mats with exceptionally high porosity for enhanced separation and catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Markhoff, J.; Suter, N.; Rezwan, K.; Bruggemann, D. Effect of Collagen Nanofibers and Silanization on the Interaction of HaCaT Keratinocytes and 3T3 Fibroblasts with Alumina Nanopores. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 1852–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.B.; Huang, Y.M.; Dargaville, T.R.; Fan, Y.Q.; Cui, Z.F.; Zhu, H.Y. Modified alumina nanofiber membranes for protein separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 120, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toloue, E.B.; Karbasi, S.; Salehi, H.; Rafienia, M. Potential of an electrospun composite scaffold of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)-chitosan/alumina nanowires in bone tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 99, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Aluminum Source | Polymers | Solvents | Additives | Aging Time | Calcination Conditions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlCl3·6H2O Al(NO3)3·9H2O Al(O-i-Pr)3 Al | PEO | H2O | HNO3 | / | After the temperature rose to 450 °C at 10 °C/min, the temperature was kept for 12 h and then for 0.5 h at 700 °C, 800 °C, and 900 °C, respectively. | 4 |
| AlCl3 Al | / | H2O | SiO2 | 10 h | After being kept at 200 °C for 4 h, the temperature was heated by 240 °C/h to 1200 °C for 4 h. | 15 |
| H3AlBO2 | PVA | H2O | / | 5 h | The temperature was raised from 1000 °C to 1200 °C by 240 °C/h, and the heat was kept for 2 h. | 44 |
| AlCl3 | PVP | H2O C2H5OH | / | 4 h | It was dried in a vacuum of 100 °C for 24 h and then in air at 450 °C, 900 °C, and 1100 °C for 5 h. | 45 |
| Al(NO3)3·9H2O AlCl3·6H2O Al(O-i-Pr)3 Al | PEO | H2O | HNO3 | 12 h | After drying for 24 h at 80 °C and calcination at different temperatures for 0.5 h, the heating rate was 10 °C min−1, except for 12 h at 450 °C. | 48 |
| Al2(SO4)3·18H2O C6H9AlO6 | PVP | C2H5OH | (CH3COO)2Ba CH3COOH | / | The temperature was heated to 1000 °C at the rate of 5 °C min−1, and the heat was kept for 2 h. | 49 |
| AlCl3·6H2O Al(O-i-Pr)3 | PVP | H2O | C2H5OH C4H6O6 HCl | / | It was dried at 70 °C for 48 h, then the temperature was raised by 2 °C/min to 600 °C for 1.5 h and then by 10 °C/min to 800 °C for 1.5 h. | 50 |
| AlCl3·6H2O Al(NO3)3·9H2O Al(O-i-Pr)3 Al | PVP | H2O | / | / | The temperature rose by 10 °C/min to 800 °C, and the heat was kept for 2 h. | 51 |
| Al(NO3)3·9H2O | PVP | H2O C2H5OH | / | 1 h | It was heated up from 500 °C to 1200 °C and held for 2 h. | 76 |
| AlCl3·6H2O Al | PVA | H2O | mSiO2·nH2O | 12 h | It was dried in air at 70 °C for 12 h; then, it was heated at a heating rate of 4 °C/min and calcined for 2 h. | 77 |
| (Al2(SO4)3·(14–18)H2O | / | H2O | NaOH | / | It was annealed in the air at 600 °C for 1 h or 1200 °C for 5 h. | 85 |
| Al | PEO PVP | H2O | HCOOH CH3COOH CuSO4 | 1 h | The temperature was raised by 1 °C/min to 600 °C, 700 °C, and 800 °C, and the heat was kept at each temperature for 2 h. | 92 |
| AlCl3 | PVP | H2O | C6H12N4 (CH3COO2Zn DMF | / | The temperature was raised by 2.2 °C/min to 700 °C, with heat preservation for 2 h. | 93 |
| Al2O3 | / | H2O | RhCl3·3H2O | / | It was dried overnight at 60 °C. | 96 |
| AlCl3·6H2O | PVP | H2O | CeCl3·7H2O C2H5OH | / | It was kept at 1000 °C for 4 h. | 97 |
| AlCl3 | / | H2O | C18H41NO7S | 1.5 h | The temperature was raised by 1.5 °C/min to 1500 °C, with heat preservation for 2 h. | 100 |
| α-Al2O3 | PAA | H2O | PS 3Al2O3·2SiO2 | 1 h | The temperature was kept at 1550 °C for 2 h, and the residence time was 200 °C (2 h) and 500 °C (1 h). | 101 |
| Al2O3 | Agarose solution | / | / | / | It was kept at 1575 °C for 4 h. | 102 |
| Aluminum salt Al(NO3)3·9H2O | / | H2O | C8H21NO | / | The temperature was raised by 1 °C/min to 500 °C, with heat preservation for 5 h. | 107 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, M.; Ji, S.; Fu, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Liu, R. Alumina Ceramic Nanofibers: An Overview of the Spinning Gel Preparation, Manufacturing Process, and Application. Gels 2023, 9, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080599
Xia M, Ji S, Fu Y, Dai J, Zhang J, Ma X, Liu R. Alumina Ceramic Nanofibers: An Overview of the Spinning Gel Preparation, Manufacturing Process, and Application. Gels. 2023; 9(8):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080599
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Meng, Shuyu Ji, Yijun Fu, Jiamu Dai, Junxiong Zhang, Xiaomin Ma, and Rong Liu. 2023. "Alumina Ceramic Nanofibers: An Overview of the Spinning Gel Preparation, Manufacturing Process, and Application" Gels 9, no. 8: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080599
APA StyleXia, M., Ji, S., Fu, Y., Dai, J., Zhang, J., Ma, X., & Liu, R. (2023). Alumina Ceramic Nanofibers: An Overview of the Spinning Gel Preparation, Manufacturing Process, and Application. Gels, 9(8), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080599