Development of Oral In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations of Garcinia Extract for Treating Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization of In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations
2.1.1. pH of Formulations
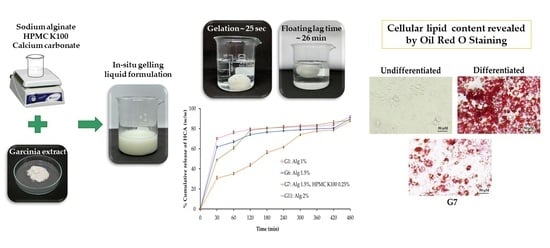
2.1.2. Floating Behavior
2.1.3. Density
2.1.4. Viscosity of In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations
2.1.5. Volume of the Formed Gel
2.1.6. Gel Strength
2.1.7. Entrapment Efficiency
2.2. The Release Behavior of HCA from In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations
2.3. Release Kinetics and Mechanism Release of HCA from In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulation
2.4. Stability Studies of In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulation G7
2.5. Biological Assay of In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations of Garcinia Extract (G7)
2.5.1. Effect on Cell Viability
2.5.2. Assay of Anti-Obesity Activity
2.5.3. Assay of Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations Loaded with Garcinia Extract
4.3. Physicochemical Characterization of In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations
4.3.1. Physical Appearance and Measurement of pH
4.3.2. Floating Behavior
4.3.3. Gel Density
4.3.4. Viscosity of In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations
4.3.5. Gel Strength
4.3.6. Volume of the Formed Gel
4.3.7. Determination of HCA Content of Liquid Formulations
4.3.8. In Vitro Release of HCA from In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations
4.4. Release Kinetics
4.5. Stability Studies
4.6. Biological Assay of In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations of Garcinia Extract
4.6.1. Cell Culture
4.6.2. Cell Differentiation
4.6.3. Cell Viability following Exposure to In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations
4.6.4. Assay of Anti-Obesity Activity
4.6.5. Assay of Anti-Inflammatory Activity
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broskey, N.T.; Martin, C.K.; Burton, J.H.; Church, T.S.; Ravussin, E.; Redman, L.M. Effect of Aerobic Exercise-Induced Weight Loss on the Components of Daily Energy Expenditure. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, D.; Khanna, S.; Khanna, P.; Kahar, P.; Patel, B.M. Obesity: A Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation and Its Markers. Cureus 2022, 14, e22711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, M.; Rao, R.P.; Dorairaj, P.; Koshta, A.; Suresh, S.; Rafiq, M.; Kumawat, R.; Paramesh, R.; Babu, U.V.; Venkatesh, K.V. A Clinical and Computational Study on Anti-Obesity Effects of Hydroxycitric Acid. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 18578–18588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, C.V.; Vijayalakshmi, M.A.; Prakash, K.; Bansal, V.S.; Meenakshi, J.; Amit, A. Review Article: Herbal Approach for Obesity Management. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, T.; Gursel, F.E.; Ateş, A.; Altiner, A. Effect of Garcinia Cambogia Extract on Body Weight Gain, Feed Intake and Feed Conversion Ratio, and Serum Non-Esterified Fatty Acids and C-Reactive Protein Levels in Rats Fed with Atherogenic Diet. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 13, 330–333. [Google Scholar]
- Permana, D.; Lajis, N.H.; Mackeen, M.M.; Ali, A.M.; Aimi, N.; Kitajima, M.; Takayama, H. Isolation and Bioactivities of Constitutents of the Roots of Garcinia Atroviridis. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Law, D.; Azfaralariff, A.; Mackeen, M.M.; Chong, T.F.; Fazry, S. Phytochemicals and Biological Activities of Garcinia Atroviridis: A Critical Review. Toxics 2022, 10, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasha, H.M.; Salha, A.; Thanai, A.; Zahar, A. The Biological Importance of Garcinia Cambogia: A Review. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2012, s5, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, R.B.; Semwal, D.K.; Vermaak, I.; Viljoen, A. A Comprehensive Scientific Overview of Garcinia Cambogia. Fitoterapia 2015, 102, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Rahman, W.N.W.; Lee, K.; Yee, J.W.; Gupta, M.; Ming, L. Evidence of Garcinia Cambogia as a Fat Burning and Appetite Suppressing Agents. Arch. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Peng, M.; Ge, C.; Yu, L.; Ma, H. (−)-Hydroxycitric Acid Reduced Lipid Droplets Accumulation Via Decreasing Acetyl-Coa Supply and Accelerating Energy Metabolism in Cultured Primary Chicken Hepatocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 812–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ma, H. (−)-Hydroxycitric Acid Suppresses Lipid Droplet Accumulation and Accelerates Energy Metabolism via Activation of the Adiponectin-AMPK Signaling Pathway in Broiler Chickens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, V.; Mathieu, A.; Soucy, G.; Giard, J.-M.; Erard-Poinsot, D. Acute Severe Liver Injury Related to Long-Term Garcinia Cambogia Intake. ACG Case Rep. J. 2020, 7, e00429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Li, L.; Yu, L.; Ge, C.; Ma, H. Effects of (−)-Hydroxycitric Acid on Lipid Droplet Accumulation in Chicken Embryos. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golzarand, M.; Omidian, M.; Toolabi, K. Effect of Garcinia Cambogia Supplement on Obesity Indices: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 52, 102451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Nayebi, N.; Larijani, B.; Abdollahi, M. A Systematic Review of the Efficacy and Safety of Herbal Medicines Used in the Treatment of Obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 3073–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, L.O.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, W.Y.; Beh, B.K.; Alitheen, N.B. In Vitro and in Vivo Toxicity of Garcinia or Hydroxycitric Acid: A Review. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 197920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotreka, U.K.; Adeyeye, M.C. Gastroretentive Floating Drug-Delivery Systems: A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2011, 28, 47–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, U.K.; Chatterjee, B.; Senjoti, F.G. Gastro-Retentive Drug Delivery Systems and Their in Vivo Success: A Recent Update. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhi, U.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Nowfiya, F.N.; Mathan, S. Floating Oral In-Situ Gelling System: A Review. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2020, 12, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, R.; Majeed, A.; Ali, T.; Farooq, S.; Khan, N.A. Floating Oral In-Situ Gel: A Review. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, K.; Aggarwal, P.; Dashora, A.; Sahu, D.; Garg, R.; Pareta, L.K.; Menaria, M.; Joshi, B. Formulation, and evaluation of oral floatable in-situ gel of Ranitidine hydrochloride. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2013, 3, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Kawasaki, N.; Kubo, W.; Endo, K.; Attwood, D. Comparison of In Situ Gelling Formulations for the Oral Delivery of Cimetidine. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 220, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Giri, T.K. Hydrogels Based on Gellan Gum in Cell Delivery and Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, W.; Miyazaki, S.; Dairaku, M.; Togashi, M.; Mikami, R.; Attwood, D. Oral Sustained Delivery of Ambroxol from In Situ Gelling Pectin Formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 271, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdsakundee, N.; Mahattanadul, S.; Wiwattanapatapee, R. Development and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Raft Forming Systems Incorporating Curcumin-Eudragit® EPO Solid Dispersions for Gastric Ulcer Treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 94, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, K.; Hossain, M.K.; Khan, T.A. Alginate, and Its Versatile Application in Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 9, 606. [Google Scholar]
- Hampson, F.C.; Farndale, A.; Strugala, V.; Sykes, J.; Jolliffe, I.G.; Dettmar, P.W. Alginate Rafts and Their Characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 294, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.; Abbas, G. PH-Responsive Alginate-Pectin Polymeric Rafts and Their Characterization. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, F.; Ghavami-Lahiji, M.; Kashi, T.J.; Najafi, F. Drug Release Kinetics and Biological Properties of a Novel Local Drug Carrier System. Dent. Res. J. 2021, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.Y.; Bala, S.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; di Cagno, M.P. Interpreting Non-Linear Drug Diffusion Data: Utilizing Korsmeyer-Peppas Model to Study Drug Release from Liposomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 138, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wannasarit, S.; Mahattanadul, S.; Issarachot, O.; Puttarak, P.; Wiwattanapatapee, R. Raft-Forming Gastro-Retentive Formulations Based on Centella Asiatica Extract-Solid Dispersions for Gastric Ulcer Treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 143, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, G.B.; Brooks, M.S.L.; Ghanem, A. Development and Evaluation of a Novel Alginate-Based in Situ Gelling System to Modulate the Release of Anthocyanins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]Hani, U.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Alqahtani, A.; Ghazwani, M.; Rahamathulla, M.; Almordy, S.A.; Alsaleh, H.A. 23 Full Factorial Design for Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Oral In Situ Gelling System of Piroxicam. J. Pharm. Innov. 2021, 16, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators Linking Adipose Tissue, Inflammation, and Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakkawanpitak, C.; Inafuku, M.; Oku, H.; Hutadilok-Towatana, N.; Bunkrongcheap, R.; Sermwittayawong, N.; Aiemchareon, P.; Sermwittayawong, D. Mechanism of the Fungal-like Particles in the Inhibition of Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, N.M.; Prabhu, P.; Charyulu, R.N.; Gulzar, M.A.; Subrahmanyam, E.V.S. Formulation and Evaluation of In Situ Gels Containing Clotrimazole for Oral Candidiasis. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 71, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, V.D.; Jani, G.K.; Khutliwala, T.A.; Zala, B.S. Raft Forming System-An Upcoming Approach of Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System. J. Control. Release 2013, 168, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Zou, A.; Li, W.; Yao, C.; Xie, S. Kinetic Modeling on Drug Release from Controlled Drug Delivery Systems. Acta Pol. Pharm.-Drug Res. 2010, 12, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanti, D.; Hamidon, H.; Taher, M.; Ahmad Rusmili, M.R.; Hamid, S.A.; Zakaria, Z.A. Lipid Accumulation Modulation by Garcinia Atroviridis Fruit Extract in 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Cells. J. Biol. Act. Prod. Nat. 2020, 10, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, C.; Bai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. A Comparison of Methods for Effective Differentiation of the Frozen-Thawed 3T3-L1 Cells. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 568, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewkroek, K.; Tewtrakul, S.; Wiwattanapatapee, R. Development of Expandable, Gastro-Retentive Films for Delivery of Resveratrol and Evaluation of Cytotoxic and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2019, 38, 691–700. [Google Scholar]
- Zebisch, K.; Voigt, V.; Wabitsch, M.; Brandsch, M. Protocol for Effective Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Cells to Adipocytes. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 425, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, C.; Funakoshi-Tago, M.; Aoyagi, R.; Ueda, F.; Kimura, M.; Kobata, K.; Tago, K.; Tamura, H. Coffee Extract Inhibits Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Interrupting Insulin Signaling through the Downregulation of IRS1. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parjapath, R.; Sali, V.K.; Kannan, S.M.; Kurapati, A.; Vasanthi, H.R. Hydroxycitric Acid-Induced Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors in 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Cells. Pharmacogn. Res. 2018, 10, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenon, G.B.; Li, C.G.; Xue, C.C.; Thien, F.C.K.; Story, D.F. Inhibition of Inducible Nitric Oxide Production and INOS Protein Expression in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Rat Aorta and Raw 264.7 Macrophages by Ethanol Extract of a Chinese Herbal Medicine Formula (RCM-101) for Allergic Rhinitis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 116, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Formulation | pH | Density (g/mL) | Gelation Time (sec) | Floating Lag Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 9.58 ± 0.04 | 0.76 ± 0.03 x | 14.2 ± 3.7 x | 9.3 ± 0.8 y |
| G2 | 9.81 ± 0.01 * | 0.76 ± 0.01 | 18.3 ± 2.6 a | 19.6 ± 0.7 * |
| G3 | 9.81 ± 0.02 * | 0.77 ± 0.01 | 19.6 ± 1.9 a | 20.7 ± 0.6 * |
| G4 | 9.86 ± 0.04 * | 0.77 ± 0.01 | 24.6 ± 6.4 a | 22.9 ± 0.4 * |
| G5 | 9.86 ± 0.05 * | 0.77 ± 0.01 | 31.5 ± 5.4 a | 26.6 ± 0.7 * |
| G6 | 9.74 ± 0.04 z | 0.78 ± 0.01 | 15.6 ± 4.7 x | 10.0 ± 1.3 y |
| G7 | 9.41 ± 0.11 ** | 0.77 ± 0.03 | 21.7 ± 2.7 b | 26.1 ± 1.6 ** |
| G8 | 9.26 ± 0.02 ** | 0.77 ± 0.01 | 25.7 ± 5.8 b | 29.2 ± 0.2 ** |
| G9 | 9.30 ± 0.04 ** | 0.77 ± 0.02 | 35.6 ± 7.3 b | 29.7 ± 0.3 ** |
| G10 | 9.29 ± 0.04 ** | 0.78 ± 0.03 | 40.0 ± 7.2 b | 30.0 ± 0.6 ** |
| G11 | 9.73 ± 0.02 z | 0.80 ± 0.04 | 24.9 ± 3.1 | 15.4 ± 0.2 |
| G12 | 9.43 ± 0.02 *** | 0.81 ± 0.03 | 35.3 ± 5.8 c | 31.3 ± 0.2 *** |
| G13 | 9.44 ± 0.01 *** | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 42.2 ± 9.5 c | 31.6 ± 0.4 *** |
| G14 | 9.55 ± 0.02 *** | 0.82 ± 0.10 | 45.0 ± 5.2 c | 31.4 ± 1.1 *** |
| G15 | 9.55 ± 0.03 *** | 0.83 ± 0.02 | 51.1 ± 7.6 c | 31.6 ± 0.4 *** |
| Formulation | Viscosity at 60 rpm (mPas) | Volume of Formed Gel (mL) | Gel Strength (g) | HCA Entrapment Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 716.5 ± 65.8 | 30.17 ± 0.29 | 43.0 ± 1.2 | 92.31 ± 2.66 |
| G2 | 826.5 ± 23.1 * | 30.83 ± 1.04 | 86.6 ± 8.3 | 92.13 ± 2.16 |
| G3 | 959.8 ± 36.1 * | 31.40 ± 1.22 | 120.3 ± 19.1 | 95.78 ± 1.49 |
| G4 | 1256.9 ± 20.6 * | 33.00 ± 0.87 * | 132.5 ± 4.1 | 97.47 ± 0.40 |
| G5 | 1346.4 ± 35.1 * | 38.07 ± 0.12 * | 177.9 ± 17.6 | 94.84 ± 0.14 |
| G6 | 2952.7 ± 23.1 a | 31.67 ± 0.58 a | 63.4 ± 9.7 | 94.38 ± 3.86 |
| G7 | 3995.8 ± 20.8 ** | 40.73 ± 1.10 ** | 158.6 ± 25.1 | 89.79 ± 1.53 |
| G8 | 4599.0 ± 7.1 ** | 41.53 ± 0.81 ** | 219.4 ± 17.2 | 91.06 ± 0.51 |
| G9 | 5032.3 ± 5.8 ** | 41.83 ± 1.26 ** | 318.6 ± 16.3 | 90.63 ± 0.57 |
| G10 | 5505.5 ± 11.5 ** | 42.20 ± 0.35 ** | 344.9 ± 35.8 | 87.92 ± 0.22 |
| G11 | 6688.6 ± 8.0 a | 36.33 ± 1.53 a | 146.1 ± 26.4 | 96.71 ± 0.34 |
| G12 | 8498.2 ± 10.0 *** | 41.50 ± 0.50 *** | 265.6 ± 40.3 | 91.49 ± 0.10 |
| G13 | 9351.3 ± 15.8 *** | 43.17 ± 0.76 *** | 345.8 ± 34.4 | 93.91 ± 0.12 |
| G14 | 10,437.8 ± 129.9 *** | 43.73 ± 1.03 *** | 412.3 ± 46.9 | 89.90 ± 1.27 |
| G15 | 10,916.0 ± 141.4 *** | 45.33 ± 1.15 *** | 513.5 ± 43.2 | 86.21 ± 0.38 |
| Zero-Order (R2) | First-Order (R2) | Higuchi (R2) | Hixson–Crowell (R2) | Korsmeyer–Peppas | Weibull | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | n | R2 | b | |||||
| G7 | 0.6616 | 0.9220 | 0.9812 | 0.8800 | 0.9900 | 0.427 | 0.9770 | 0.672 |
| Test | Freshly Prepared | After 1 Month | After 3 Months | After 6 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 9.4 ± 0.1 | 9.4 ± 0.0 | 9.4 ± 0.1 | 9.2 ± 0.1 |
| Gelation time (sec) | 21.7 ± 2.7 | 22.3 ± 0.9 | 24.3 ± 1.5 | 24.2 ± 2.2 |
| Floating lag time (min) | 26.1 ± 1.6 | 27.0 ± 0.6 | 27.3 ± 0.9 | 26.9 ± 1.7 |
| Duration of floating (h) | >24 | >24 | >24 | >24 |
| Density (g/mL) | 0.77 ± 0.03 | 0.77 ± 0.03 | 0.78 ± 0.05 | 0.81 ± 0.03 |
| Viscosity at 60 rpm (mPa⋅s) | 3995.8 ± 20.9 | 3832.7 ± 15.8 | 3865.0 ± 10.0 | 3835.3 ± 61.6 |
| Gel strength (g) | 158.5 ± 25.1 | 156.5 ± 22.0 | 150.5 ± 17.4 | 148.7 ± 15.0 |
| Samples | % Inhibition of Nitric Oxide Production |
|---|---|
| Indomethacin | 66.93 ± 0.42 |
| Garcinia extract | 33.94 ± 0.74 |
| HCA std. | 29.55 ± 1.70 |
| G7 | 39.44 ± 0.39 |
| G7B | 11.19 ± 0.85 |
| Formulations | Concentration (%w/v) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium Alginate | HPMC K100 | |
| G1 | 1 | - |
| G2 | 1 | 0.25 |
| G3 | 1 | 0.5 |
| G4 | 1 | 0.75 |
| G5 | 1 | 1 |
| G6 | 1.5 | - |
| G7 | 1.5 | 0.25 |
| G8 | 1.5 | 0.5 |
| G9 | 1.5 | 0.75 |
| G10 | 1.5 | 1 |
| G11 | 2 | - |
| G12 | 2 | 0.25 |
| G13 | 2 | 0.5 |
| G14 | 2 | 0.75 |
| G15 | 2 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fungfoung, K.; Praparatana, R.; Issarachot, O.; Wiwattanapatapee, R. Development of Oral In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations of Garcinia Extract for Treating Obesity. Gels 2023, 9, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080660
Fungfoung K, Praparatana R, Issarachot O, Wiwattanapatapee R. Development of Oral In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations of Garcinia Extract for Treating Obesity. Gels. 2023; 9(8):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080660
Chicago/Turabian StyleFungfoung, Kantiya, Rachanida Praparatana, Ousanee Issarachot, and Ruedeekorn Wiwattanapatapee. 2023. "Development of Oral In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations of Garcinia Extract for Treating Obesity" Gels 9, no. 8: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080660
APA StyleFungfoung, K., Praparatana, R., Issarachot, O., & Wiwattanapatapee, R. (2023). Development of Oral In Situ Gelling Liquid Formulations of Garcinia Extract for Treating Obesity. Gels, 9(8), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9080660