Experimental Study on Water Electrolysis Using Cellulose Nanofluid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
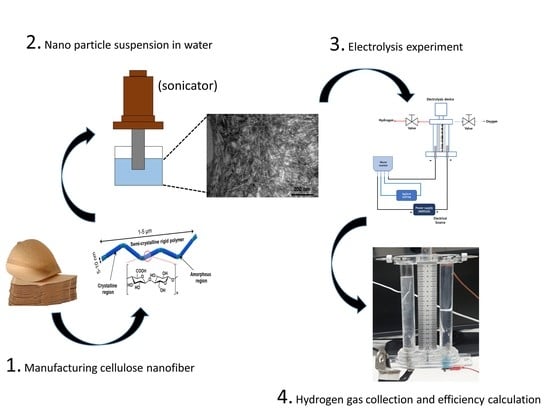
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CNF Production
2.2. Experimental Apparatus and Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experiment According to Electrolyte Concentration
3.2. Comparison of the CNF Solution Sample Replacement
3.3. Experiment According to Anode Material
3.4. Experiment According to Applied Voltage
3.5. Experiment According to Initial Temperature of Electrolyte
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ronneau, C. Energie, Pollution de I’air et Developpement Durable, Louvain-la-Neuve; Presses Universitaires de Louvain: Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, D. Characteristics of Oxygen Evolution Reaction of Ni-Fe Electrodeposition Electrode for Alkaline Water Electrolysis. Master’s Thesis, Chung-Nam University, Yuseong-gu, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolic, V.M.; Tasic, G.S.; Maksic, A.D.; Saponjic, D.P.; Miulovic, S.M.; Kaninski, M.P.M. Raising Efficiency of Hydrogen Generation from Alkaline Water Electrolysis—Energy Saving. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 12369–12373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, S. Hydrogen Futures: Toward a Sustainable Energy System. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2002, 27, 235–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.F.; Padilha, J.C.; Goncalves, R.S.; De Souza, M.O.; Rault-Berthelot, J. Electrochemical Hydrogen Production from Water Electrolysis Using Ionic Liquid as Electrolytes: Towards the Best Device. J. Power Sources 2007, 164, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, A.; Kashiwase, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Hayashida, T.; Kato, A.; Hirao, K.; Shimomura, I.; Nagashima, I. Basic Study of Alkaline Water Electrolysis. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 100, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, M.; Fritz, D.L.; Mergel, J.; Stolten, D. A Comprehensive Review on PEM Water Electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4901–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.F.; Padilha, J.C.; Goncalves, R.S.; Rault-Berthelot, J. Dialkylimidazolium Ionic Liquids as Electrolytes for Hydrogen Production from Water Electrolysis. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Kimura, T.; Oka, T. Existence of Optimum Space Between Electrodes on Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2003, 28, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z. Water Electrolysis Enhanced by Super Gravity Field for Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 3198–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.; Sirkar, A.; De, P.; Kuila, S.B. Studies on the Effect of Electrolyte Concentration on Alkaline Electrolysis and Ion Exchange Membrane Water Splitting for Production of Hydrogen. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kimura, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Isogai, A. Cellulose Nanofibers Prepared by TEMPO—Mediated Oxidation of Native Cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, W.K.; Hyun, M.; Choi, H.; Choy, S.; Hwang, D.S.; Lee, K.Y. An Experimental Investigation on CHF Enhancement of Saturated Water with Coated Surfaces by Cellulose Nanofiber. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants, Fukui/Kyoto, Japan, 26–27 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chakik, F.E.; Kaddami, M.; Mikou, M. Effect of Operating Parameters on Hydrogen Production by Electrolysis of Water. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 25550–25557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstajic, N.; Popovic, M.; Grgur, B.; Vojnovic, M.; Sepa, D. On the Kinetics of the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Nickel in Alkaline Solution: Part II. Effect of Temperature. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 512, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opu, M.S. Effect of Operating Parameters on Performance of Alkaline Water Electrolysis. Int. J. Therm. Environ. Eng. 2015, 9, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, P.; Bourasseau, C.; Bourasseau, P.B. Low-Temperature Electrolysis System Modelling: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 280–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Concentration wt % | Hydrogen Volume mL | Average Temperature [K] | Average Current [mA] | Efficiency [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 5.0 | 295.4 | 11.6 | 76.3 |
| 1.0 | 9.2 | 294.5 | 19.8 | 82.5 |
| 1.5 | 12.8 | 298.4 | 27.0 | 83.1 |
| 1.8 | 15.0 | 293.8 | 30.0 | 89 |
| Sample | Hydrogen Volume [mL] | Average Temperature [K] | Average Current [mA] | Efficiency [%] | Error [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old | 15.0 | 293.8 | 30.0 | 89 | 5.7 |
| New | 5.8 | 298.4 | 12.1 | 83.8 |
| Anode Material | Hydrogen Volume [mL] | Average Temperature [K] | Average Current [mA] | Efficiency [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless | 8.0 | 298.7 | 15.9 | 88.0 |
| Platinum | 5.8 | 298.4 | 12.1 | 83.9 |
| Voltage [V] | Hydrogen Volume [mL] | Average Temperature [K] | Average Current [mA] | Efficiency [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1.1 | 298.1 | 2.5 | 77.1 |
| 6 | 4.0 | 297.0 | 7.9 | 89.1 |
| 10 | 10.8 | 300.1 | 20.3 | 92.6 |
| Initial Electrolyte Temperature [°C] | Hydrogen Volume [mL] | Average Temperature [K] | Average Current [mA] | Efficiency [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 9.3 | 297.6 | 16.7 | 97.8 |
| 26 | 10.8 | 300.1 | 20.3 | 92.6 |
| 52 | 12.7 | 302.1 | 22.1 | 99.4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, D.; Lee, K.-Y. Experimental Study on Water Electrolysis Using Cellulose Nanofluid. Fluids 2020, 5, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5040166
Choi D, Lee K-Y. Experimental Study on Water Electrolysis Using Cellulose Nanofluid. Fluids. 2020; 5(4):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5040166
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Dongnyeok, and Kwon-Yeong Lee. 2020. "Experimental Study on Water Electrolysis Using Cellulose Nanofluid" Fluids 5, no. 4: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5040166
APA StyleChoi, D., & Lee, K. -Y. (2020). Experimental Study on Water Electrolysis Using Cellulose Nanofluid. Fluids, 5(4), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5040166