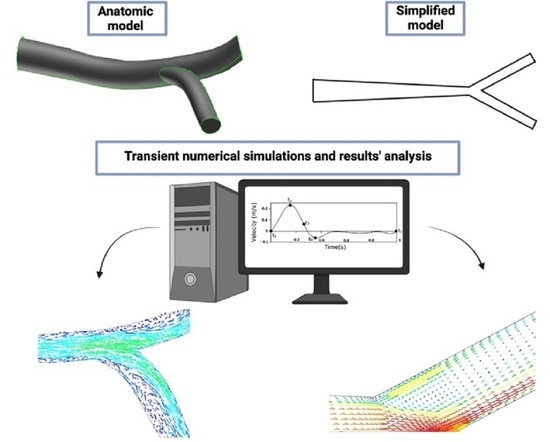
Numerical Study of the Unsteady Flow in Simplified and Realistic Iliac Bifurcation Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Computational Model
2.1. Mathematical Equations
2.2. Boundary Conditions and Fluid Flow Assumptions
2.3. Numerical Solution
3. Geometry and Mesh
3.1. Simplified Model
3.2. Anatomic Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Flow in the Simplified Geometry
4.2. Flow in the Anatomic Geometry
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Libby, P.; Buring, J.E.; Badimon, L.; Hansson, G.K.; Deanfield, J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Tokgözoğlu, L.; Lewis, E.F. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, S.A.; Jou, L. Flows in Stenotic Vessels. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2000, 32, 347–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K. The Cardiovascular System, 1st ed.; Britannica Educational Publishing: Edinburgh, Scotland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Mohammed, S.; Khader, A.; Azriff, A.; Johny, C.; Pai, R.; Zuber, M. Haemodynamics behaviour in normal and stenosed renal artery using computational fluid dynamics Akademia Baru Journal of Advanced Research in Fluid Haemodynamics Behaviour in Normal and Stenosed Renal Artery using Computational Fluid Dynamics. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2018, 51, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, T. Wall shear stress and near-wall flows in the stenosed femoral artery. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 2017, 20, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, V.; Pinho, D.; Lima, R.A.; Teixeira, J.C.; Teixeira, S. Blood Flow Modeling in Coronary Arteries: A Review. Fluids 2021, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, V.; Maia, I.; Souza, A.; Ribeiro, J.; Costa, P.; Puga, H.; Teixeira, S.F.C.F.; Lima, R.A. In vitro stenotic arteries to perform blood analogues flow visualizations and measurements: A Review. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2020, 14, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Saha, V.; Ng, E.Y.K. Skin temperature maps as a measure of carotid artery stenosis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 116, 103548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Liu, W.; Qu, K.; Yin, T.; Qiu, J.; Li, Y. Effects of Different Positions of Intravascular Stent Implantation in Stenosed Vessels on In-stent Restenosis: An Experimental and Numerical Simulation Study. J. Biomech. 2020, 113, 110089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, R.M.; Vergara, C.; Valdettaro, L.; Bose, S.; Quarteroni, A. Large eddy simulations for blood dynamics in realistic stenotic carotids. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wong, K.; Tu, J. Hemodynamics analysis of patient-specific carotid bifurcation: A CFD model of downstream peripheral vascular impedance. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 29, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, V.; Rodrigues, N.; Ribeiro, R.; Costa, P.F.; Lima, R.A.; Teixeira, S.F.C.F. 3D Printed Biomodels for Flow Visualization in Stenotic Vessels: An Experimental and Numerical Study. Micromachines 2020, 11, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, V.; Rodrigues, N.; Lima, R.A.; Teixeira, S.F.C.F. Modeling blood pulsatile turbulent flow in stenotic coronary arteries. Int. J. Biol. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 1998–4510. [Google Scholar]
- Tajeddini, F.; Nikmaneshi, M.R.; Firoozabadi, B.; Pakravan, H.A.; Ahmadi Tafti, S.H.; Afshin, H. High precision invasive FFR, low-cost invasive iFR, or non-invasive CFR?: Optimum assessment of coronary artery stenosis based on the patient-specific computational models. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 36, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Schiavazzi, D.E.; Kahn, A.M.; Marsden, A.L. The effects of clinically-derived parametric data uncertainty in patient-specific coronary simulations with deformable walls. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 36, 3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, F.; Silva, A.E.; Teixeira, S.F.C.F.; Teixeira, J.C.F.; Lobarinhas, P.A.M.; Ribeiro, V.G. The influence of renal branches on the iliac arteries blood flow. In Proceedings of the Annual Frontiers in Biomedical Devices Conference, Irvine, CA, USA, 18–20 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mahé, G.; Kaladji, A.; Le Faucheur, A.; Jaquinandi, V. Internal Iliac Artery Stenosis: Diagnosis and How to Manage it in 2015. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shipkowitz, T.; Rodgers, V.G.J.; Frazin, L.J.; Chandran, K.B. Numerical study on the effect of steady axial flow development in the human aorta on local shear stresses in abdominal aortic branches. J. Biomech. 1998, 31, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Chen, J.Y. Numerical simulation of steady flow fields in a model of abdominal aorta with its peripheral branches. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverich, A.; Boyle, E.C. Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis and Microvascular Dysfunction, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, J.F.; Smits, M.L.J.; van Herwaarden, J.A.; Arntz, M.J.; Vonken, E.J.P.A.; van den Bosch, M.A.A.J.; de Borst, G.J. Endovascular Treatment of Internal Iliac Artery Stenosis in Patients with Buttock Claudication. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griggs, R.; Wing, E.F.G. Cecil Essentials of Medicine, 9th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, A.Y.; Doyle, B.J.; Jansen, S.; Ponosh, S.; Cisonni, J.; Sun, Z. Blood flow velocity prediction in aorto-iliac stent grafts using computational fluid dynamics and Taguchi method. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 84, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huml, E.L.; Davies, R.A.; Kearns, G.A.; Petersen, S.M.; Brismée, J.M. Common iliac artery occlusion presenting with back and leg pain: Case report and differential diagnosis considerations for neurogenic/vascular claudication. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2018, 26, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Tong, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Wang, G. Numerical simulation of haemodynamics of the descending aorta in the non-diabetic and diabetic rabbits. J. Biomech. 2019, 91, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andayesh, M.; Shahidian, A.; Ghassemi, M. Numerical investigation of renal artery hemodynamics based on the physiological response to renal artery stenosis. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 1458–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopalik, S.; Hall Barrientos, P.; Matthews, J.; Radjenovic, A.; Mark, P.; Roditi, G.; Paul, M.C. Image-based computational fluid dynamics for estimating pressure drop and fractional flow reserve across iliac artery stenosis: A comparison with in-vivo measurements. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 15, e3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, V.; Rodrigues, N.; Lima, R.A.; Teixeira, S. Numerical simulation of blood pulsatile flow in stenotic coronary arteries: The effect of turbulence modeling and non-Newtonian assumptions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applied Mathematics & Computer Science, Athens, Greece, 31 May–2 June 2020; pp. 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.X.; Beech-Brandt, J.J.; John, L.R. Numerical analysis of pulsatile blood flow and vessel wall mechanics in different degrees of stenoses. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 3715–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichana, T.; Sun, Z.; Jewkes, J. Computation of hemodynamics in the left coronary artery with variable angulations. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doutel, E.; Viriato, N.; Carneiro, J.; Campos, J.B.L.M.; Miranda, J.M. Geometrical effects in the hemodynamics of stenotic and non-stenotic left coronary arteries—numerical and in vitro approaches. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 35, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queijo, L.; Lima, R. PDMS Anatomical Realistic Models for Hemodynamic Studies Using Rapid Prototyping Technology. In Proceedings of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering (IFMBE), Singapore, 1–6 August 2010; pp. 434–437. [Google Scholar]
- Gijsen, F.J.H.; Schuurbiers, J.C.H.; van de Giessen, A.G.; Schaap, M.; van der Steen, A.F.W.; Wentzel, J.J. 3D reconstruction techniques of human coronary bifurcations for shear stress computations. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.A.; Hughes, T.J.R.; Zarins, C.K. Finite element modeling of three-dimensional pulsatile flow in the abdominal aorta: Relevance to atherosclerosis. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1998, 26, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangha, G.S.; Busch, A.; Acuna, A.; Berman, A.G.; Phillips, E.H.; Trenner, M.; Eckstein, H.; Maegdefessel, L.; Goergen, C.J.; Lafayette, W.; et al. Effects of Iliac Stenosis on Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation in Mice and Humans. J. Vasc. Res. 2019, 56, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys, I. ANSYS® Fluent User ’ s Guide, Release 2020 R2.
- Carneiro, F.; Ribeiro, V.G.; Teixeira, S.F.C.F.; Teixeira, J.C. The effect of outflow distribution on the recirculation properties during the cardiac cycle in the iliac bifurcation. In Proceedings of the IASTED Applied Simulation and Modelling, Corfu, Greece, 23–25 June 2008; pp. 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, F.; Ribeiro, V.G.; Teixeira, S.F.C.F.; Teixeira, J.C. Numerical study of blood fluid rheology in the abdominal aorta bifurcation. In Proceedings of the Design & Nature—WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment, Algarve, Portugal, 24–26 June 2008; Volume 114, pp. 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.A.; Draney, M.T. Experimental and computational methods in cardiovascular fluid mechanics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2004, 36, 197–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, F.; Ribeiro, V.G.; Teixeira, J.C.; Teixeira, S.F.C.F. Numerical Study of the Velocity Profile Effect in the Atherosclerosis Development. In Proceedings of the 4th Engineering Conference “Engenharias’07—Innovation and Development“, Covilhã, Portugal, 21–23 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Versteeg, H.K.; Malalasekera, W. An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Finite Volume Method, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.S.; Liao, W.; Low, H.T. Numerical study of physiological turbulent flows through series arterial stenoses. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 2004, 46, 315–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Axial Positions | Maximum Velocity (m/s) | |
|---|---|---|
 | 1.14 | 1.14 |
 | 0.659 | 0.659 |
 | 0.824 | 0.741 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, V.; Carneiro, F.; Ferreira, A.C.; Gama, V.; Teixeira, J.C.; Teixeira, S. Numerical Study of the Unsteady Flow in Simplified and Realistic Iliac Bifurcation Models. Fluids 2021, 6, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6080284
Carvalho V, Carneiro F, Ferreira AC, Gama V, Teixeira JC, Teixeira S. Numerical Study of the Unsteady Flow in Simplified and Realistic Iliac Bifurcation Models. Fluids. 2021; 6(8):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6080284
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Violeta, Filipa Carneiro, Ana C. Ferreira, Vasco Gama, José C. Teixeira, and Senhorinha Teixeira. 2021. "Numerical Study of the Unsteady Flow in Simplified and Realistic Iliac Bifurcation Models" Fluids 6, no. 8: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6080284
APA StyleCarvalho, V., Carneiro, F., Ferreira, A. C., Gama, V., Teixeira, J. C., & Teixeira, S. (2021). Numerical Study of the Unsteady Flow in Simplified and Realistic Iliac Bifurcation Models. Fluids, 6(8), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6080284