miRNAtools: Advanced Training Using the miRNA Web of Knowledge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
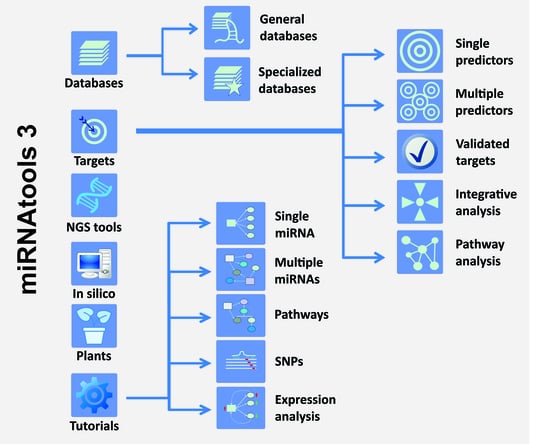
2.1. Structure of the miRNAtools3 Website
2.2. Tutorials within miRNAtools3
2.2.1. Scenario 1: Single miRNA
2.2.2. Scenario 2: Multiple miRNAs
2.2.3. Scenario 3: Pathway Analysis
2.2.4. Scenario 4: Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and miRNA Binding Sites
2.2.5. Scenario 5: miRNA–mRNA Expression Correlation Analysis
3. Conclusions and Further Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, B.; Ha, I.; Ruvkun, G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 1993, 75, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, A.J.; John, B.; Gaul, U.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol. 2003, 5, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahlgren, N.; Carrington, J.C. miRNA target prediction in plants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 592, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, T.; Yada, T. miRNA-target prediction based on transcriptional regulation. BMC Genom. 2013, 14 (Suppl. 2), S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grun, D.; Wang, Y.L.; Langenberger, D.; Gunsalus, K.C.; Rajewsky, N. MicroRNA target predictions across seven Drosophila species and comparison to mammalian targets. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2005, 1, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J.; Bramsen, J.B. Enhancing miRNA annotation confidence in miRBase by continuous cross dataset analysis. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, J. Ensemble methods for miRNA target prediction from expression data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.H.; Chang, N.W.; Shrestha, S.; Hsu, S.D.; Lin, Y.L.; Lee, W.H.; Yang, C.D.; Hong, H.C.; Wei, T.Y.; Tu, S.J.; et al. MiRtarbase 2016: Updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D239–D247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dweep, H.; Gretz, N.; Sticht, C. MiRWalk database for miRNA-target interactions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1182, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Siklenka, K.; Arora, S.K.; Ribeiro, P.; Kimmins, S.; Xia, J. miRNet—Dissecting miRNA-target interactions and functional associations through network-based visual analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W135–W141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Peer, G.; De Paepe, A.; Stock, M.; Anckaert, J.; Volders, P.J.; Vandesompele, J.; De Baets, B.; Waegeman, W. MiSTAR: miRNA target prediction through modeling quantitative and qualitative miRNA binding site information in a stacked model structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Guo, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X. MiRtdl: A deep learning approach for miRNA target prediction. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Yi, S.; Jung, D.; Oh, M.; Kim, B.; Freishtat, R.J.; Giri, M.; Hoffman, E.; Seo, J. MiRTarVis+: Web-based interactive visual analytics tool for microRNA target predictions. Methods 2017, 124, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panwar, B.; Omenn, G.S.; Guan, Y. miRmine: A database of human miRNA expression profiles. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. Diana-miRPath v3.0: deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W460–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohler, U.; Yekta, S.; Lim, L.P.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B. Patterns of flanking sequence conservation and a characteristic upstream motif for microRNA gene identification. RNA 2004, 10, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulas, A.; Boutla, A.; Gkirtzou, K.; Reczko, M.; Kalantidis, K.; Poirazi, P. Prediction of novel microRNA genes in cancer-associated genomic regions—A combined computational and experimental approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 3276–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukasik, A.; Wojcikowski, M.; Zielenkiewicz, P. Tools4miRs—One place to gather all the tools for miRNA analysis. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2722–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghaee-Bakhtiari, S.H.; Arefian, E.; Lau, P. miRandb: A resource of online services for miRNA research. Brief. Bioinform. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asangani, I.A.; Rasheed, S.A.; Nikolova, D.A.; Leupold, J.H.; Colburn, N.H.; Post, S.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA0-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Grocock, R.J.; van Dongen, S.; Bateman, A.; Enright, A.J. Mirbase: MicroRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D140–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnal, R.J.; Rossi, R.L.; Carpi, D.; Ranzani, V.; Abrignani, S.; Pagani, M. Miriadne: A web tool for consistent integration of miRNA nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W487–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihailovich, M.; Bremang, M.; Spadotto, V.; Musiani, D.; Vitale, E.; Varano, G.; Zambelli, F.; Mancuso, F.M.; Cairns, D.A.; Pavesi, G.; et al. miR-17-92 fine-tunes MYC expression and function to ensure optimal B cell lymphoma growth. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitão, A.L.; Costa, M.C.; Enguita, F.J. A guide for miRNA target prediction and analysis using web-based applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1182, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Kranzler, H.R.; Luo, X.; Yang, B.Z.; Weiss, R.; Brady, K.; Poling, J.; Farrer, L.; Gelernter, J. Interaction between two independent CNR1 variants increases risk for cocaine dependence in European Americans: A replication study in family-based sample and population-based sample. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, A.E.; Li, L.; Kalabus, J.L.; Pan, Y.; Yu, A.; Hu, Z. miRdSNP: A database of disease-associated SNPs and microRNA target sites on 3′UTRs of human genes. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Liu, C.J.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.L.; Ma, Z.W.; Chen, H.; Guo, A.Y. An update of miRNASNP database for better SNP selection by GWAS data, miRNA expression and online tools. Database (Oxford) 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxman, N.; Rubin, C.J.; Mallmin, H.; Nilsson, O.; Pastinen, T.; Grundberg, E.; Kindmark, A. Global miRNA expression and correlation with mRNA levels in primary human bone cells. RNA 2015, 21, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.; Wang, R.; Wang, J. Correlation analysis of the mRNA and miRNA expression profiles in the nascent synthetic allotetraploid Raphanobrassica. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Du, M.; Wang, J.; Xing, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Lu, X. miRNA-200a expression is inverse correlation with hepatocyte growth factor expression in stromal fibroblasts and its high expression predicts a good prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 48432–48442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, D.; Kim, B.; Freishtat, R.J.; Giri, M.; Hoffman, E.; Seo, J. MiRTarVis: An interactive visual analysis tool for microRNA-mRNA expression profile data. BMC Proc. 2015, 9, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stępień, E.Ł.; Costa, M.C.; Enguita, F.J. miRNAtools: Advanced Training Using the miRNA Web of Knowledge. Non-Coding RNA 2018, 4, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna4010005
Stępień EŁ, Costa MC, Enguita FJ. miRNAtools: Advanced Training Using the miRNA Web of Knowledge. Non-Coding RNA. 2018; 4(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna4010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleStępień, Ewa Ł., Marina C. Costa, and Francisco J. Enguita. 2018. "miRNAtools: Advanced Training Using the miRNA Web of Knowledge" Non-Coding RNA 4, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna4010005
APA StyleStępień, E. Ł., Costa, M. C., & Enguita, F. J. (2018). miRNAtools: Advanced Training Using the miRNA Web of Knowledge. Non-Coding RNA, 4(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna4010005