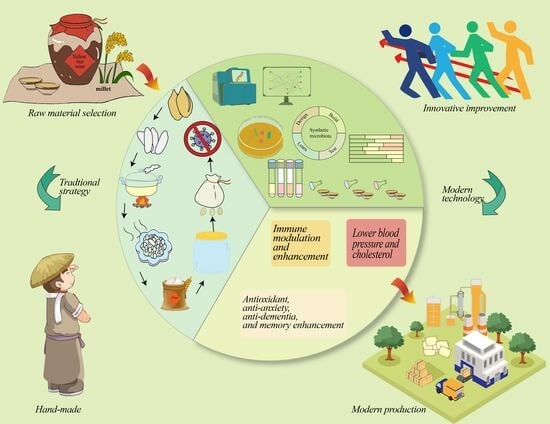
Advancements and Future Directions in Yellow Rice Wine Production Research
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Traditional Brewing Process of Yellow Rice Wine
3. Microbial Improvement of the Composition and Quality of Yellow Rice Wine
| Rice Wine Types | Fermentative Type or Starters | Dominant Microorganisms | Fermentation Products and Flavor Compounds | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hakka rice wine | Semi-dry rice wine | Pediococcus, Bacillus, Acinetobacter, Pantoea, Enterobacter, Lactobacillus, Monascus, Saccharomyces, Rhizopus | Esters, aldehydes, acids, ketones, alcohols, and so on | Qian et al. [67] |
| Traditional sweet rice wine | ||||
| Hong Qu glutinous rice wine | Hong Qu Red koji fermentation | Bacillus ginsengihumi, Pantoea sp., Elizabethkingia sp., Streptococcus sp. Brevundimonas sp., Rickettsia prowazekii, Thermus thermophilus, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus aryabhattai; fungi of Monascus purpureus, Aspergillus niger, Xeromyces bisporus, Aspergillus penicillioides, Aspergillus flavus and Pichia farinose | / | Huang et al. [2] |
| Bai Qu | Lactococcus lactis Lactobacillus brevis, Pediococcus pentosaceus, Weissella paramesenteroides, Lactobacillus fermentum, Gluconobacter thailandicus, Lactobacillus alimentarius, fungi of Rhizopus arrhizus, Saccharomycopsis fibuligera, Aspergillus niger, Issatchenkia orientalis, Saccharomycopsis malanga, Clavispora lusitaniae, Candida tropicalis | |||
| Chinese yellow rice wine | Wine frying | / | Esters, alcohols, heterocyclic compounds, amides, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, acids, alkanes | Bai et al. [68] |
| Chinese rice wine | Jiu Yao (Q1) | Pediococcus, Rhizopus, Lactobacillus, Aspergillus, Enterococcus, Parasitella, Ascoidea, Staphylococcus, Mucor and Vibrio, which accounted for 83.30% (Q1) and 84.85% (Q2) | Ethanol (13.33%), total sugar (22.74 g/L), sweet and umami amino acids | Tian et al. [69] |
| Jiu Yao (Q2) | Ethanol (14.57%), total sugar (30.20 g/L), sweet and umami amino acids | |||
| Shaoxing Huangjiu | Jiu Yao | Pediococcus, Weissella, Pelomonas Saccharomycopsis, Rhizopus, Saccharomyces | / | Peng et al. [27] |
| Black glutinous rice wine | Qu | Lactococcus, Pediococcus, Leuconostoc, Lactobacillus, Cronobacter, Pantoea, Weissella, Enterococcus, Rhizopus, Myceliophthora, Cystofilobasidium, and Aspergillus | Esters, alcohols, acids and 43 volatile flavor compounds | Zhao et al. [70] |
4. The Compounds in Yellow Rice Wine and Their Health Effects
5. Innovation and Development of Yellow Rice Wine Brewing Technology
5.1. The Innovative Technologies for Yellow Wine
5.2. The Application of Microbiome in Modern Yellow Rice Wine Production
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Yuan, C.; Gao, X.; Kang, Y.; Huang, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of key aroma compounds in Huangjiu from northern China by sensory-directed flavor analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Guo, W.; Zhou, W.; Li, L.; Xu, J.; Hong, J.; Liu, H.; Zeng, F.; Bai, W.; Liu, B.; et al. Microbial communities and volatile metabolites in different traditional fermentation starters used for Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, W.; Xia, Y.; Mu, Z.; Tao, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Ni, B.; Ai, L. Flavor formation in Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu): Impacts of the flavor-active microorganisms, raw materials, and fermentation technology. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Zheng, H.; Meng, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, H.; Shen, C.; Fu, J.; Elsheery, N.L.; Xie, G.; et al. The way of Qu-making significantly affected the volatile flavor compounds in Huangjiu (Chinese rice wine) during different brewing stages. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2255–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Li, B.; Mei, J. Research progress in active components and functional properties of Yellow rice wine. Liq.-Mak. Sci. Technol. 2018, 1, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, N.; Rao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Q. Mucor indicus and Rhizopus oryzae co-culture to improve the flavor of Chinese turbid rice wine. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5577–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Jiang, S.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Ma, L.; Xiao, D. Production of low-alcohol Huangjiu with improved acidity and reduced levels of higher alcohols by fermentation with scarless ALD6 overexpression yeast. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Lin, X.; He, Z.; Ren, X.; Li, W.; Molnar, I. Fungal community diversity and fermentation characteristics in regional varieties of traditional fermentation starters for Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Cai, G.; Wu, C.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; Xie, G.; Wu, D.; Lu, J. Profiling the key metabolites produced during the modern brewing process of Chinese rice wine. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ji, Z.; Liu, S.; Han, X.; Zheng, F.; Mao, J. Characterization of the volatile compounds of huangjiu using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to time of flight mass spectrometry (GC × GC-TOFMS). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, Z.; Wu, L.; Wu, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhao, W.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Rao, P.; Lv, X.; et al. Microbial diversity and flavor of Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu): An overview of current research and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zheng, H.; Meng, K.; Yu, H.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Z.; et al. Quantitative study on core bacteria producing flavor substances in Huangjiu (Chinese yellow rice wine). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 168, 113900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Tan, H.; Xie, G.; Xu, Q.; Zou, H.; Yu, W.; Wang, L.; et al. Metagenomic sequencing reveals the relationship between microbiota composition and quality of Chinese Rice Wine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Lee, S.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, B.K.; Park, K.J. Chemical and sensory profiles of makgeolli, Korean commercial rice wine, from descriptive, chemical, and volatile compound analyses. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Xia, Y.; Wang, G.; Ni, L.; Zhang, H.; Ai, L. Effects of different lactic acid bacteria on the characteristic flavor profiles of Chinese rice wine. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2024, 104, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Lin, X.; He, Z.; Su, H.; Li, W.; Ren, X. Amino acid and microbial community dynamics during the fermentation of Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Microbiol. 2020, 90, 103467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, J.; Ni, T.; Lin, N.; Meng, L.; Gao, F.; Luo, H.; Liu, X.; Chi, J.; Guo, H. Yellow wine polyphenolic compounds prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through activation of the Nrf2 signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6034–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Tang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, P.; Han, J. Evaluation of direct sampling method for trace elements analysis in Chinese rice wine by ICP-OES. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 236, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, M.S.; Roullier-Gall, C.; Morge, C.; Sparrow, C.; Gobert, A.; Alexandre, H. Vitamins in wine: Which, what for, and how much? Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2991–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Lee, R.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Henning, S.M.; Hong, X.; Heber, D.; Li, Z. Quantification of bioactive constituents and antioxidant activity of Chinese yellow wine. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 44, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Chi, J.; Tang, W.; Ji, Z.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, C.; Lv, H.; Guo, H. Yellow wine polyphenolic compounds inhibit matrix metalloproteinase-2,-9 expression and improve atherosclerotic plaque in LDL-receptor-knockout mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 125, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.A.; Han, T.; Kim, G.B.; Park, J.E.; Lee, S.Y. Tools and strategies of systems metabolic engineering for the development of microbial cell factories for chemical production. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4615–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.; Venkatraman, S.; Vaidyanathan, V.K. Development of engineered probiotics with tailored functional properties and their application in food science. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Qian, M.; Dong, H.; Liu, X.; Bai, W.; Liu, G.; Lv, X. Effect of Hong Qu on the flavor and quality of Hakka yellow rice wine (Huangjiu) produced in Southern China. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 160, 113264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, X.; Ren, H.; Gong, M.; Ji, Z.; Liu, S.; Hu, Z.; Mao, J. Differentiating Huangjiu with varying sugar contents from different regions based on targeted metabolomics analyses of volatile carbonyl compounds. Foods 2023, 12, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Zou, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, J.; Zhang, S. A metagenomic analysis of the relationship between microorganisms and flavor development in Shaoxing mechanized huangjiu fermentation mashes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 303, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Meng, K.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.; Xie, G.; et al. Analysis on driving factors of microbial community succession in Jiuyao of Shaoxing Huangjiu (Chinese yellow rice wine). Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xu, Y.; Mao, J. Impact of aging microbiome on metabolic profile of natural aging Huangjiu through machine learning. Foods 2023, 12, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Han, J.; Han, X.; Peng, Q.; Fu, J.; Shen, C.; Sun, J.; Sun, J.; Lu, J.; Lu, Y.; et al. Identification of colloidal haze protein in Chinese rice wine (Shaoxing Huangjiu) mainly by matrix-assisted laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4027–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zeng, W.; Zhou, J.; Du, G. Correlation between the microbial community and ethyl carbamate generated during Huzhou rice wine fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 111001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lu, A.; Sun, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, P.; Yang, A.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; et al. Purification and identification of antioxidant and angiotensin converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides from Guangdong glutinous rice wine. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 169, 113953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liang, J.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; Luo, J.; Yu, H.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y. Physicochemical properties of red millet: A novel Chinese rice wine brewing material. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, 15556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, A.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Research progress on the brewing techniques of new-type rice wine. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wu, Y.; Jia, G.; Wang, C.; Xiao, D.; Goff, H.D.; Guo, Q. Structural characterization and immunomodulatory activity of mycelium polysaccharide from liquid fermentation of Monascus purpureus (Hong Qu). Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 262, 117945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Yue, S.; Xu, D.; Fu, R.; Han, J.; Zhou, H.; Tang, Y. Research progress on flavor and quality of Chinese rice wine in the brewing process. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 32311–32330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, M.; Dong, H.; Bai, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, X.; Liu, G. Effect of ageing process on carcinogen ethyl carbamate (EC), its main precursors and aroma compound variation in Hakka Huangjiu produced in southern China. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Mao, J.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Ai-lati, A. Bacterial succession and the dynamics of volatile compounds during the fermentation of Chinese rice wine from Shaoxing region. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, W.; Yang, M.; Zhong, X.; Guo, Z.; Shan, C. High-throughput sequencing-based analysis of microbial diversity in rice wine koji from different areas. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q. Application of bamboo leaves extract to Chinese yellow rice wine brewing for ethyl carbamate regulation and its mitigation mechanism. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Q. Ethyl carbamate regulation and genomic expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during mixed-culture yellow rice wine fermentation with Lactobacillus sp. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Ethyl carbamate formation regulated by Saccharomyces cerevisiae ZJU in the processing of Chinese yellow rice wine. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, B. Mixed starter culture regulates biogenic amines formation via decarboxylation and transamination during Chinese rice wine fermentation. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2018, 66, 6348–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, L.; Luo, J.; Zhu, R.; Mao, J.; Zhao, M.; Cai, C. Phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of Chinese rice wine fermented with different rice materials and starters. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 111, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, B.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y. Effects of fermentation on flavor and antioxidant activity in ginkgo rice wine. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shen, C.; Wang, S.; Marco, M.; Mao, J. Integrated meta-omics approaches reveal Saccharopolyspora as the core functional genus in huangjiu fermentations. npj Biofilms Microbi 2023, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, D.; Tan, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Hou, A.; Zhu, Y.; Lai, L.; Wang, Y. GC-MS coupled with Rate-All-That-Apply (RATA) to analyse the volatile flavor substances of yellow wine during fermentation. Foods 2023, 12, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zheng, D.; Xie, T.; Xie, J.; Tian, H.; Ai, L.; Chen, C. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics to clarify the dynamic variations in the volatile composition of Huangjiu of different ages. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhan, P.; Tian, H.; Liu, J. Characterization of the aroma compounds of Millet Huangjiu at different fermentation stages. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Liu, Z.; Fu, B.; Zhang, X.; Qi, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Xu, N. Metabolites of the soy sauce koji making with Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Deng, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Shen, C.; Lou, K.; et al. Isolation and characterization of yeast for the production of rice wine with low fusel alcohol content. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Haupt, S.; Schulz, K. Defining maximum levels of higher alcohols in alcoholic beverages and surrogate alcohol products. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2008, 50, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, B.; Lou, H.; Huang, G.; Wen, H. Reducing higher alcohols by nitrogen compensation during fermentation of Chinese rice wine. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Hu, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Yao, L.; Sun, M.; Song, S.; Wang, H. Quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR) of aroma compounds in different aged Huangjiu. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3273–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Sun, L.; Xing, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Ren, Q. Microbial succession and exploration of higher alcohols-producing core bacteria in northern Huangjiu fermentation. Amb Express 2022, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Ruan, F.; Zhao, W.; Dong, H.; Bai, W.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Comparison study of the physicochemical properties, amino acids, and volatile metabolites of Guangdong Hakka Huangjiu. Foods 2023, 12, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Han, X.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, J. Combined effects of fermentation temperature and Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains on free amino acids, flavor substances, and undesirable secondary metabolites in Huangjiu fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2022, 108, 104091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ai, L.; Mu, Z.; Liu, H.; Yan, X.; Ni, L.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y. Flavor compounds with high odor activity values (OAV >1) dominate the aroma of aged Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu) by molecular association. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Li, W.; Tong, S.; Qiu, Y.; Han, J.; Lv, X.; Ai, L.; Sun, J.; Sun, B.; Ni, L. Effects of the microbial community on the formation of volatile compounds and biogenic amines during the traditional brewing of Hongqu rice wine. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, S.; Nan, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, G.; Mao, J. Analysis of changes in simulated rancidification process during the storage of Huangjiu. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 3485–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes Ferreira, A.; Mendes-Faia, A. The Role of yeasts and lactic acid bacteria on the metabolism of organic acids during winemaking. Foods 2020, 9, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zheng, H.; Qiu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Peng, Q.; Dula Bealu, G.; Elsheery, N.I.; Lu, Y.; Shen, C.; Fu, J.; et al. Study on relationship between bacterial diversity and quality of Huangjiu (Chinese rice wine) fermentation. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3885–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciosek, A.; Fulara, K.; Hrabia, O.; Satora, P.; Poreda, A. Chemical composition of sour beer resulting from supplementation the fermentation medium with magnesium and zinc ions. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Du, J.; Cao, C.; Cai, G.; Sun, J.; Wu, D.; Lu, J. Development of a novel multi-strain wheat Qu with high enzyme activities for Huangjiu fermentation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4808–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, Q.; Han, X.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with low-yield higher alcohols and high-yield acetate esters improve the quality, drinking comfort and safety of Huangjiu. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Hu, W.; Tao, L.; Ni, L.; Yu, J.; Ai, L. Membrane fluidity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae from Huangjiu (Chinese rice wine) is variably regulated by OLE1 to offset the disruptive effect of ethanol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01620-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Qiu, S. Profiling of fungal diversity and fermentative yeasts in traditional Chinese Xiaoqu. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Ruan, F.; Zhao, W.; Dong, H.; Bai, W.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Li, Y. The dynamics of physicochemical properties, microbial community, and flavor metabolites during the fermentation of semi-dry Hakka rice wine and traditional sweet rice wine. Food Chem. 2023, 416, 135844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Sun, S.; Zhao, W.; Qian, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, W. Determination of ethyl carbamate (EC) by GC-MS and characterization of aroma compounds by HS-SPME-GC-MS during wine frying status in Hakka yellow rice wine. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, G. Effect of two starters (Jiu Yao) on Chinese rice wine microbial community and flavour. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Su, W.; Mu, Y.C. Correlations between microbiota with physicochemical properties and volatile flavor components in black glutinous rice wine fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Ren, C.; Pei, J. A comparative study on the traditional versus modern yellow rice wine processing methods using Taohong Siwu Decoction for pharmaceutical production. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 290, 115114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Guan, H.; Bai, L.; Chen, P.; Gao, W.; Zhuang, G.; Lu, T.; Yan, G. Comparative study on Angelica sinensis after different processing with yellow rice wine in color, aromas, chemical components, and antioxidant activities. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Ren, T.; Niu, C.; Zheng, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Q. Anthocyanins composition and antioxidant activity of purple rice and color degradation under sunlight exposure of purple rice wine. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chi, H.; Ma, S.; Zhao, L.; Cai, S. Identification of novel α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides in rice wine and their antioxidant activities using in silico and in vitro analyses. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 178, 114629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Chung, S.; Choi, W.; Seo, Y.; Jung, S.; Park, J.; Seo, M.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Park, C. Anti-aging effect of rice wine in cultured human fibroblasts and keratinocytes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2009, 107, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.R.; Rendeiro, C.; McGettrick, H.M.; Philp, A.; Lucas, S.J.E. Fine wine or sour grapes? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of red wine polyphenols on vascular health. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Ji, Z.; Chi, J.; Tang, W.; Zhai, X.; Meng, L.; Guo, H. Effects of Chinese yellow wine on nitric oxide synthase and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expressions in rat vascular endothelial cells. Acta Cardiol. 2016, 71, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Meng, L.; Sun, Z.; Sun, S.; Huang, X.; Lin, N.; Zhang, J.; Lu, W.; Yang, Q.; Chi, J.; et al. Yellow wine polyphenolic compound protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by modulating the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Circ.-Heart Fail. 2021, 14, 1136–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, C.; Pan, S.; Zhai, X.; Jiang, C.; Guo, Y.; Ji, Z.; Chi, J.; Peng, F.; et al. Polyphenols and polypeptides in Chinese Rice Wine inhibit homocysteine-induced proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 67, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Mao, Q.; Luan, C.; Han, X.; Xue, J.; Wang, D.; Qin, S.; Hao, F. Effect of yellow rice wine on anti-aging ability in aged mice induced by D-galactose. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2020, 9, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Research progress of peptides in Huangjiu. Modern Food 2021, 02, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, S.; Mao, J. Non-alcoholic components in Huangjiu as potential factors regulating the intestinal barrier and gut microbiota in mouse model of alcoholic liver injury. Foods 2022, 11, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.; Li, C.; Wei, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, S.; Hua, Y.; Yao, W.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Wen, Y. Screening study of blood-supplementing active components in water decoction of Angelica sinensis processed with yellow rice wine based on response surface methodology. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, W.; Chen, S.; Mao, J. Alleviation of loperamide-induced constipation with sticky rice fermented Huangjiu by the regulation of serum neurotransmitters and gut microbiota. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mao, J. The existing recovery approaches of the Huangjiu lees and the future prospects: A mini review. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabaci Karaoglan, S.; Jung, R.; Gauthier, M.; Kincl, T.; Dostalek, P. Maltose-negative yeast in non-alcoholic and low-alcoholic beer production. Fermentation 2022, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zheng, F.; Lin, B.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Preparation and characteristics of sugarcane low alcoholic drink by submerged alcoholic fermentation. Sugar Tech. 2013, 15, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Ren, Y.; Le, Z.; Li, L.; Sun, B. Effects of different brewing technologies on polyphenols and aroma components of black chokeberry wine. Foods 2023, 12, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Meng, K.; Liu, J.; Lin, Z.; Peng, Q.; Xie, G.; Wu, P.; Elsheery, N.I. Identification and expression of bifunctional acid urea-degrading enzyme/urethanase from Enterobacter sp. R-SYB082 and its application in degradation of ethyl carbamate in Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 4599–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Wei, X.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, X.; Mao, J. Sequencing-based screening of functional microorganism to decrease the formation of biogenic amines in Chinese rice wine. Food Control 2016, 64, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Qiu, Y.; Lv, X.; Ai, L.; Ni, L. Insights into microbial communities and metabolic profiles in the traditional production of the two representative Hongqu rice wines fermented with Gutian Qu and Wuyi Qu based on single-molecule real-time sequencing. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Shu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q. Application of mixed-culture with Lactobacillus brevis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae to Chinese yellow rice wine brewing for ethyl carbamate regulation. Food Control 2021, 122, 107821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toy, J.Y.H.; Lu, Y.; Huang, D.; Matsumura, K.; Liu, S. Enzymatic treatment, unfermented and fermented fruit-based products: Current state of knowledge. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2022, 62, 1890–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, T.S.; Kawaguti, H.Y. Cellulases, hemicellulases, and pectinases: Applications in the food and beverage industry. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 1446–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, W.; Gai, J.; Liu, H.; Hou, Q.; Zhao, H.; Shan, C.; Guo, Z. Analysis of the effect of rice wine koji on the fermentation quality of rice wine based on high-depth sequencing. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.; Chang, C.; Hsueh, K.; Liu, F. Optimization of glutinous rice wine brewing conditions by using Taguchi method and semiempirical equation. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Q. Optimization of the brewing conditions of Shanlan rice wine and sterilization by thermal and intense pulse light. Molecules 2023, 28, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brányik, T.; Vicente, A.A.; Dostálek, P.; Teixeira, J.A. Continuous beer fermentation using immobilized yeast cell bioreactor systems. Biotechnol. Prog. 2005, 21, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Z. Yunnan Xiaoqu spirits fermentation control. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 2013, 28, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Ebrahimi, M.; Czermak, P. Anaerobic membrane bioreactor for continuous lactic acid fermentation. Membranes 2017, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, M.; Cui, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Ning, J. Rapid monitoring of black tea fermentation quality based on a solution-phase sensor array combined with UV-visible spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallart-Ayala, H.; Kamleh, M.A.; Hernández-Cassou, S.; Saurina, J.; Checa, A. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry based metabolomics as a strategy for beer characterization. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Yang, X.; Guo, Q.; Li, B.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, L. Microbial communities and flavor compounds during the fermentation of traditional Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Foods 2022, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhao, X.; Shi, J. Correlation of microbial community structure and volatile flavor compounds during corn yellow wine fermentation. Biotechnol. Prog. 2023, e3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ni, L.; Lv, X. Metagenomic insights into the regulatory effects of microbial community on the formation of biogenic amines and volatile flavor components during the brewing of Hongqu rice wine. Foods 2023, 12, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Du, Z.; Ma, L.; Du, L.; Zhang, H.; Tian, X.; Yang, W. Effects of Pichia kluyveri on the flavor characteristics of wine by co-fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 1449–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qu, L.; Mijakovic, I.; Wei, Y. Advances in the human skin microbiota and its roles in cutaneous diseases. Microb. Cell Factories 2022, 21, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Li, H.; He, X.; Zheng, F.; Zhu, H.; Liu, L.; Du, W. Research advance in metabolism of effective ingredients from traditional Chinese medicines by probiotics. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2018, 43, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.; Nielsen, J.B.; Wei, Y. Harnessing synthetic biology for mushroom farming. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Xia, Y.J. Enhancement of the aromatic alcohols and health properties of Chinese rice wine by using a potentially probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae BR14. LWT 2023, 181, 114748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, L.; Qu, L.; Wei, Y. Characterization of novel pectinolytic enzymes derived from the efficient lignocellulose degradation microbiota. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, B.; Wen, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, C.; Qu, L.; Yin, Y.; Wei, Y. Advancements in the biotransformation and biosynthesis of the primary active flavonoids derived from epimedium. Molecules 2023, 28, 7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Qu, L.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Advancing insights into probiotics during vegetable fermentation. Foods 2023, 12, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wei, Y.; Ji, B.; Nielsen, J. Advances in metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for cocoa butter equivalent production. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2020, 8, 594081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Du, R.; Fu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Wei, Y.; Lin, W. Heterologous biosynthesis of medicarpin using engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2023, 8, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, G.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Gong, M.; Shang, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Bao, D. Efficient conversion of spent mushroom substrate into a high value-added anticancer drug pentostatin with engineered Cordyceps militaris. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 10030–10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Ji, B.; Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Chen, T.; Ji, X. Editorial: Engineering yeast to produce plant natural products. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2021, 9, 798097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; De Saja, J.A.; Gonzalez-Anton, R.; Garcia-Hernandez, C.; Medina-Plaza, C.; Garcia-Cabezon, C.; Martin-Pedrosa, F. Electronic noses and tongues in wine industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2016, 4, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Meng, K.; Zheng, H.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Lin, Z.; Xie, G. Metabolites comparison in post-fermentation stage of manual (mechanized) Chinese Huangjiu (yellow rice wine) based on GC-MS metabolomics. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Zou, G.; Wei, Y.; Qu, L. Advancements and Future Directions in Yellow Rice Wine Production Research. Fermentation 2024, 10, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10010040
Zhang J, Li T, Zou G, Wei Y, Qu L. Advancements and Future Directions in Yellow Rice Wine Production Research. Fermentation. 2024; 10(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingxian, Tian Li, Gen Zou, Yongjun Wei, and Lingbo Qu. 2024. "Advancements and Future Directions in Yellow Rice Wine Production Research" Fermentation 10, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10010040
APA StyleZhang, J., Li, T., Zou, G., Wei, Y., & Qu, L. (2024). Advancements and Future Directions in Yellow Rice Wine Production Research. Fermentation, 10(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10010040