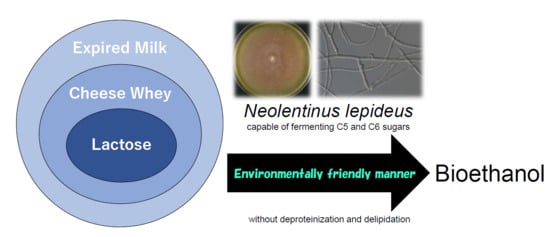
Ethanol Production from Cheese Whey and Expired Milk by the Brown Rot Fungus Neolentinus lepideus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strain and Culture Conditions
2.2. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of the Lactose Concentration on Fermentation
3.2. Effect of Glucose on Lactose Fermentation
3.3. Effect of Calcium on Lactose Fermentation
3.4. Direct Ethanol Production from Cheese Whey
3.5. Direct Ethanol Production from Whole Milk, High-Fat Milk, and Low-Fat Milk
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zabed, H.; Sahu, J.N.; Suely, A.; Boyce, A.N.; Faruq, G. Bioethanol production from renewable sources: Current perspectives and technological progress. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 475–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Qureshi, N.; Chen, M.-H.; Liu, W.; Singh, V. Ethanol production from food waste at high solids content with vacuum recovery technology. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2760–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosikowski, F.V. Whey utilization and whey products. J. Dairy Sci. 1979, 62, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithers, G.W. Whey and whey proteins—from ‘gutter-to-gold’. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, P.M.R.; Teixeira, J.A.; Domingues, L. Fermentation of lactose to bio-ethanol by yeasts as part of integrated solutions for the valorisation of cheese whey. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murani, C.S.; da Silva, D.C.M.N.; Schuina, G.L.; Mosinahti, E.F.; Del Bianchi, V.L. Bioethanol production from dairy industrial coproducts. Bioenergy Res. 2019, 12, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Prazeres, A.R.; Carvalho, F.; Rivas, J. Cheese whey management: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božanić, R.; Barukčić, I.; Jakopović, K.L.; Tratnik, L. Possibilities of whey utilization. Austin J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 2, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Pescuma, M.; de Valdez, G.F.; Mozzi, F. Whey-derived valuable products obtained by microbial fermentation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6183–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Samragy, Y.A.; Khorshid, M.A.; Foda, M.I.; Shehata, A.E. Effect of fermentation conditions on the production of citric acid from cheese whey by Aspergillus niger. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 29, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dantoft, S.H.; Würtz, A.; Jensen, P.R.; Solem, C. A novel cell factory for efficient production of ethanol from dairy waste. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, W.V.; Dudey, G.L.; Ingram, L.O. Fermentation of sweet whey by ethanologenic Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1992, 40, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.R.; Guimaraes, W.V.; de Araujo, E.F.; Silva, D.O. Fermentation of sweet whey by recombinant Escherichia coli KO11. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2000, 31, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasotti, L.; Zucca, S.; Casanova, M.; Micoli, G.; De Angelis, M.G.C.; Magni, P. Fermentation of lactose to ethanol in cheese whey permeate and concentrated permeate by engineered Escherichia coli. BMC Biotechnol. 2017, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamini, N.R.; Gunasekaran, P. Simultaneous ethanol production from lactose by Kluyveromyces fragilis and Zymomonas mobilis. Curr. Microbiol. 1987, 16, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, P.M.R.; François, J.; Parrou, J.L.; Teixeira, J.A.; Domingues, L. Adaptive evolution of a lactose-consuming Saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Teeri, T.T.; Knowles, J.K.C.; Hartley, B.S. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells secreting an Aspergillus niger β-galactosidase grow on whey permeate. Bio/Technology 1992, 10, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; Hartley, B.S. Fermentation of lactose by yeast cells secreting recombinant fungal lactase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 4230–4235. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Domingues, L.; Dantas, M.M.; Lima, N.; Teixeira, J.A. Continuous ethanol fermentation of lactose by a recombinant flocculating Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1999, 64, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, P.M.R.; Teixeira, J.A.; Dominguez, L. Fermentation of high concentrations of lactose to ethanol by engineered flocculent Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 30, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Owais, M. Ethanol production from crude whey by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 27, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmihci, S.; Kargi, F. Ethanol fermentation of cheese whey powder solution by repeated fed-batch operation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 41, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansonetti, S.; Curcio, S.; Calabrò, V.; Iorio, G. Bio-ethanol production by fermentation of ricotta cheese whey as an effective alternative non-vegetable source. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, D. Improved ethanol production by mixed immobilized cells of Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae from cheese whey powder solution fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, A.D.; Kádár, Z.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P.; Thomsen, M.H. Production of bioethanol from organic whey using Kluyveromyces marxianus. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoppellari, F.; Bardi, L. Production of bioethanol from effluents of the dairy industry by Kluyveromyces marxianus. New Biotechnol. 2013, 30, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiboth, B.; Pakdaman, B.S.; Hartl, L.; Kubicek, C.P. Lactose metabolism in filamentous fungi: How to deal with an unknown substrate. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2007, 21, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Imashiro, K.; Akizawa, Y.; Onimura, A.; Yoneda, M.; Nitta, Y.; Maekawa, N.; Yanase, H. Production of ethanol by the white-rot basidiomycetes Peniophora cinerea and Trametes suaveolens. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Nitta, Y.; Maekawa, N.; Yanase, H. Direct ethanol production from starch, wheat bran and rice straw by the white rot fungus Trametes hirsuta. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2011, 48, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Sugita, Y.; Nishikori, N.; Nitta, Y.; Yanase, H. Characterization of two acidic β-glucosidases and ethanol fermentation in the brown rot fungus Fomitopsis palustris. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2011, 48, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Kanawaku, R.; Masumoto, M.; Yanase, H. Efficient xylose fermentation by the brown rot fungus Neolentinus lepideus. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2012, 50, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, K.; Uchii, A.; Kanawaku, R.; Yanase, H. Bioconversion of xylose, hexoses and biomass to ethanol by a new isolate of the white rot basidiomycete Trametes versicolor. Springerplus 2014, 3, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, K.; Yoneda, M.; Fumioka, T. Isolation of a Peniophora strain capable of producing ethanol from starch and kitchen waste. Ferment. Technol. 2017, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, F.; Hou, Z.; Yuan, C.; Zhu, X. High level production of β-galactosidase exhibiting excellent milk-lactose degradation ability from Aspergillus oryzae by codon and fermentation optimization. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 2787–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Németh, Z.; Molnár, Á.P.; Fejes, B.; Novák, L.; Karaffa, L.; Keller, N.P.; Fekete, E. Growth-phase sterigmatocystin formation on lactose is mediated via low specific growth rates in Aspergillus nidulans. Toxins 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, A.L.; Nagem, R.A.P.; Neustroev, K.N.; Arand, M.; Adamska, M.; Eneyskaya, E.V.; Kulminskaya, A.A.; Garratt, R.C.; Golubev, A.M.; Polikarpov, I. Crystal structures of β-galactosidase from Penicillium sp. and its complex with galactose. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jónás, Á.; Fekete, E.; Flipphi, M.; Sándor, E.; Jäger, S.; Molnár, Á.P.; Szentirmai, A.; Karaffa, L. Extra- and intracellular lactose catabolism in Penicillium chrysogenum: Phylogenetic and expression analysis of the putative permease and hydrolase genes. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Texeira, M. Endless versatility in the biotechnological applications of Kluyveromyces LAC genes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovington, J.D. The calcium and magnesium contents of tree species grown in close stand. New Phytol. 1959, 58, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.G.; Gokhale, D.V.; Patil, B.G. Enhancement in ethanol production from cane molasses by skim milk supplementation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1986, 8, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Strain | Maximum Ethanol Concentration (g/L) | Fermentation Time (h) | Ethanol Yield (g/g) | Initial Lactose (g/L) | Ethanol Productivity (g/L/h) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N. lepideus RS1911 | 9 | 48 | 0.38 | 27 | 0.19 | This study |
| 17 | 96 | 0.35 | 54 | 0.18 | ||
| 33 | 192 | 0.32 | 108 | 0.17 | ||
| Recombinant E. coli | 26 | 144 | 0.44 | 60 | 0.18 | Guimaraes et al. [12] |
| Recombinant S. cerevisiae | 55 | 120 | 0.37 | 150 | 0.46 | Guimarães et al. [20] |
| K. marxianus | 30 | 96 | 0.32 | 100 | 0.31 | Guo et al. [24] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okamoto, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Kanawaku, R.; Kawamura, S. Ethanol Production from Cheese Whey and Expired Milk by the Brown Rot Fungus Neolentinus lepideus. Fermentation 2019, 5, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5020049
Okamoto K, Nakagawa S, Kanawaku R, Kawamura S. Ethanol Production from Cheese Whey and Expired Milk by the Brown Rot Fungus Neolentinus lepideus. Fermentation. 2019; 5(2):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5020049
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkamoto, Kenji, Saki Nakagawa, Ryuichi Kanawaku, and Sayo Kawamura. 2019. "Ethanol Production from Cheese Whey and Expired Milk by the Brown Rot Fungus Neolentinus lepideus" Fermentation 5, no. 2: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5020049
APA StyleOkamoto, K., Nakagawa, S., Kanawaku, R., & Kawamura, S. (2019). Ethanol Production from Cheese Whey and Expired Milk by the Brown Rot Fungus Neolentinus lepideus. Fermentation, 5(2), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5020049