Disinfection Efficacy of Tobamovirus-Contaminated Soil in Greenhouse-Grown Crops
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tested Disinfectants
2.2. Operation of the Experimental Platform
2.3. Monitoring Disinfection Efficacy
3. Results and Discussion
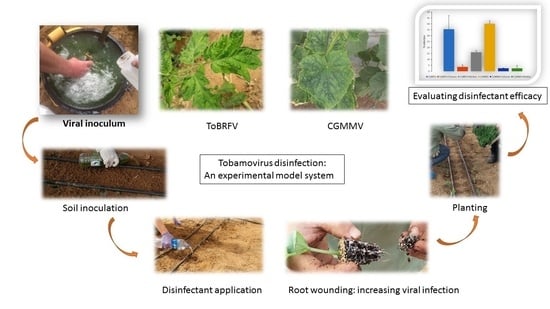
3.1. Establishing an Experimental Platform for Studying Disinfectant Efficacy
- (i)
- Supplementation of viral inoculum. ToBRFV or CGMMV at concentrations of 40 mg/mL infected leaves ground in 0.05 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH = 7.0, were poured into the planting pits prior to the tested disinfectant. A total of ~1.0 µmoles and ~0.5 µmoles of ToBRFV and CGMMV virions, respectively, were in each ~100 mL inoculum.
- (ii)
- Truncated roots. Seedling root edges were cut to increase cellular wounds, thereby ascertaining virus entry via roots.
3.2. Disinfectant Efficacy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broadbent, L. The epidemiology of tomato mosaic VIII. Virus infection through tomato roots. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1965, 55, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanter, J.M.; McGuire, J.M.; Goode, M.J. Persistence of Tomato Mosaic Virus in Tomato Debris and Soil Under Field Conditions. Plant Dis. 1982, 66, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pares, R.D.; Gunn, L.V.; Keskula, E.N. The role of infective plant debris, and its concentration in soil, in the ecology of tomato mosaic tobamovirus—A non-vectored plant virus. J. Phytopathol. 1996, 144, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reingold, V.; Lachman, O.; Belausov, E.; Koren, A.; Mor, N.; Dombrovsky, A. Epidemiological study of Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus in greenhouses enables reduction of disease damage in cucurbit production. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2016, 168, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrovsky, A.; Smith, E. Seed Transmission of Tobamoviruses: Aspects of Global Disease Distribution. In Advances in Seed Biology; InTech: Zagreb, Croatia, 2017; pp. 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.X.; Liu, S.S.; Gu, Q.S. Transmission efficiency of Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus via seeds, soil, pruning and irrigation water. J. Phytopathol. 2016, 164, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Hikichi, Y.; Kawada, Y.; Okuno, T. Detection of tobamoviruses from soils by non-precoated indirect ELISA. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2000, 66, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornai, D.; Mingelgrin, U.; Frenkel, H.; Bar-Joseph, M. Direct quantification of unadsorbed viruses in suspensions of adsorbing colloids with the enzyme-linked-immunosorbent-assay. Appl. Env. Microb. 1993, 59, 3123–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gülser, C.; Yılmaz, N.K.; Candemir, F. Accumulation of Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) at different depths clay and loamy sand textural soils due to tobacco waste application. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 146, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, R. Soil-borne virus diseases. Sci. Hortic. 1959, 14, 90–96. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/45126127 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Smith, E.; Luria, N.; Reingold, V.; Frenkel, O.; Koren, A.; Klein, E.; Bekelman, H.; Lachman, O.; Dombrovsky, A. Aspects in tobamovirus management in modern agriculture: Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus. In Proceedings of the XXX International Horticultural Congress IHC2018: International Symposium on Tropical and Subtropical Vegetable Production, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–17 August 2018; Volume 1257, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ellouze, W.; Mishra, V.; Howard, R.J.; Ling, K.-S.; Zhang, W. Preliminary Study on the Control of Cucumber Green Mottle Mosaic Virus in Commercial Greenhouses Using Agricultural Disinfectants and Resistant Cucumber Varieties. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzi, E.; Lachman, O.; Smith, E.; Koren, A.; Klein, E.; Pass, N.; Frenkel, O.; Dombrovsky, A. Paths of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus disease spread and disinfectant-based management. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2020, 177, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Dombrovsky, A. Aspects in Tobamovirus management in intensive agriculture. In Plant Diseases-Current Threats and Management Trends; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luvisi, A.; Panattoni, A.; Materazzi, A. Heat treatments for sustainable control of soil viruses. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, G.C. Mosaic disease of cucumber. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1935, 22, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrovsky, A.; Tran-Nguyen, L.T.; Jones, R.A. Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus: Rapidly Increasing Global Distribution, Etiology, Epidemiology, and Management. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.; Mansour, A.; Ciuffo, M.; Falk, B.; Turina, M. A new tobamovirus infecting tomato crops in Jordan. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luria, N.; Smith, E.; Reingold, V.; Bekelman, I.; Lapidot, M.; Levin, I.; Elad, N.; Tam, Y.; Sela, N.; Abu-Ras, A.; et al. A New Israeli Tobamovirus Isolate Infects Tomato Plants Harboring Tm-22 Resistance Genes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klap, C.; Luria, N.; Smith, E.; Hadad, L.; Bakelman, E.; Sela, N.; Belausov, E.; Lachman, O.; Leibman, D.; Dombrovsky, A. Tomato Brown Rugose Fruit Virus Contributes to Enhanced Pepino Mosaic Virus Titers in Tomato Plants. Viruses 2020, 12, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molad, O.; Smith, E.; Luria, N.; Sela, N.; Lachman, O.; Bakelman, E.; Leibman, D.; Dombrovsky, A. New early phenotypic markers for cucumber green mottle mosaic virus disease in cucumbers exposed to fluctuating extreme temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molad, O.; Smith, E.; Luria, N.; Sela, N.; Lachman, O.; Bakelman, E.; Leibman, D.; Dombrovsky, A. Plant Disease Symptomatology: Cucumber Green Mottle Mosaic Virus (CGMMV)-Infected Cucumber Plants Exposed to Fluctuating Extreme Temperatures. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2022, 11, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Chanda, B.; Shamimuzzaman, M.; Gilliard, A.; Ling, K.-S. Effectiveness of disinfectants against the spread of tobamoviruses: Tomato brown rugose fruit virus and Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.H.; Grogan, R.G.; Kimble, K.A. Transmission of tobacco mosaic viras in tomato seed. Phytopathology 1961, 51, 837–842. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, L. The epidemiology of tomato mosaic. XI. Seed transmission of TMV. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1965, 56, 177–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowski, R.; De Boer, W.; Van der Wolf, J. Chemical disinfectants can reduce potato blackleg caused by ‘Dickeya solani’. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 136, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Stubbs, G.; Culver, J.N. Coat protein interactions involved in tobacco mosaic tobamovirus cross-protection. Virology 1998, 248, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pryor, A.K.; Brown, R.S. Quaternary ammonium disinfectants: An updated perspective. J. Environ. Health 1975, 37, 326–330. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, R.; Johnston, M. Disinfection kinetics: A new hypothesis and model for the tailing of log-survivor/time curves. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.H.; Li, N.; Tong, D.S.; Zhou, C.H.; Lin, C.X.C.; Xu, C.Y. Adsorption of proteins and nucleic acids on clay minerals and their interactions: A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 80, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andika, I.B.; Kondo, H.; Sun, L. Interplays between soil-borne plant viruses and RNA silencing-mediated antiviral defense in roots. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheol Song, G.; Sim, H.-J.; Kim, S.-G.; Ryu, C.-M. Root-mediated signal transmission of systemic acquired resistance against above-ground and below-ground pathogens. Ann. Bot. 2016, 118, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Treatment | Infection Ratios (%) * | Total Number of Plants | Relative Disinfection Efficiencies ** | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ToBRFV | 38.8 | 7.8 | 17.9 | 29.8 | 250 | 108 | 160 | 47 | ||||
| ToBRFV + Taharan | 13.7 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 10 | 150 | 101 | 156 | 50 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ToBRFV + Chloran | 15.5 | 0.9 | 150 | 107 | 0.98 | 1 | ||||||
| ToBRFV + KlorBack | 27.6 | 0.0 | 6 | 150 | 109 | 50 | 0.84 | 1.13 | 1.2 | |||
| ToBRFV + GreenUp-ABV | 0.0 | 149 | 1 | |||||||||
| ToBRFV + Hydrogen Peroxide | 8.2 | 151 | 0.54 | |||||||||
| Treatment | Infection Ratios (%) * | Total Number of Plants | Relative Disinfection Efficiencies ** | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CGMMV | 20.0 | 15.4 | 22.2 | 15.2 | 12.5 | 30 | 275 | 117 | 109 | 72 | |||||
| CGMMV + Taharan | 6.7 | 7.8 | 11.9 | 0.0 | 0 | 30 | 165 | 91 | 149 | 40 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| CGMMV + Chloran | 13.3 | 11.7 | 24.3 | 30 | 165 | 98 | 0.5 | 0.96 | 0 | ||||||
| CGMMV + KlorBack | 3.3 | 27.3 | 11.9 | 0 | 30 | 165 | 91 | 40 | 1.3 | 0.79 | 1 | 1 | |||
| CGMMV + GreenUp-ABV | 1.4 | 144 | 0.91 | ||||||||||||
| CGMMV + Hydrogen Peroxide | 6.0 | 147 | 0.61 | ||||||||||||
| Treatment | Infection Ratios (%) | Total Number of Plants | Relative Disinfection Efficiencies * |
|---|---|---|---|
| ToBRFV | 29.8 | 47 | |
| ToBRFV + KlorBack 1000 ppm | 14.3 | 42 | 0.78 |
| ToBRFV + KlorBack 2000 ppm | 6 | 50 | 1.2 |
| ToBRFV + Taharan 1000 ppm | 15 | 40 | 0.75 |
| ToBRFV + Taharan 2000 ppm | 10 | 50 | 1 |
| ToBRFV + Cl-TSP 3% | 8 | 50 | 1.1 |
| ToBRFV + Cl-TSP 5% | 2 | 50 | 1.5 |
| SS//ToBRFV | 46 | 41 | |
| SS//ToBRFV + Cl-TSP 5% | 0 | 40 | 1 |
| SS//ToBRFV + TSP 5% | 0 | 39 | 1 |
| SS//ToBRFV + Taharan 2000 ppm | 0 | 37 | 1 |
| CGMMV | 12.5 | 72 | |
| CGMMV + KlorBack 1000 ppm | 5 | 40 | 0.6 |
| CGMMV + KlorBack 2000 ppm | 0 | 40 | 1 |
| CGMMV + Taharan 1000 ppm | 5 | 40 | 0.6 |
| CGMMV + Taharan 2000 ppm | 0 | 40 | 1 |
| CGMMV + Cl-TSP 3% | 7.5 | 40 | 0.4 |
| CGMMV + Cl-TSP 5% | 0 | 40 | 1 |
| SS//CGMMV | 12.6 | 41 | |
| SS//CGMMV + Cl-TSP 5% | 0 | 40 | 1 |
| SS//CGMMV + TSP 5% | 0 | 39 | 1 |
| SS//CGMMV + Taharan 2000 ppm | 0 | 37 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dombrovsky, A.; Mor, N.; Gantz, S.; Lachman, O.; Smith, E. Disinfection Efficacy of Tobamovirus-Contaminated Soil in Greenhouse-Grown Crops. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070563
Dombrovsky A, Mor N, Gantz S, Lachman O, Smith E. Disinfection Efficacy of Tobamovirus-Contaminated Soil in Greenhouse-Grown Crops. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(7):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070563
Chicago/Turabian StyleDombrovsky, Aviv, Netta Mor, Shelly Gantz, Oded Lachman, and Elisheva Smith. 2022. "Disinfection Efficacy of Tobamovirus-Contaminated Soil in Greenhouse-Grown Crops" Horticulturae 8, no. 7: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070563
APA StyleDombrovsky, A., Mor, N., Gantz, S., Lachman, O., & Smith, E. (2022). Disinfection Efficacy of Tobamovirus-Contaminated Soil in Greenhouse-Grown Crops. Horticulturae, 8(7), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070563