Efficient Stereospecific Hβ2/3 NMR Assignment Strategy for Mid-Size Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
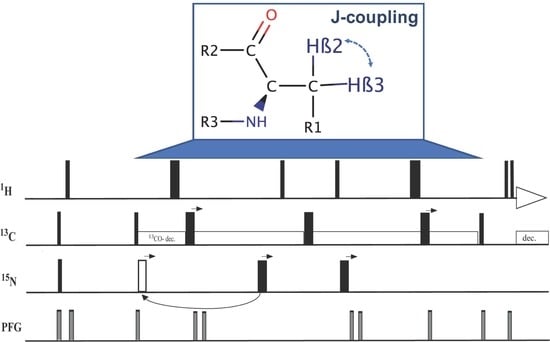
2.1. Description of Pulse Sequence
2.2. Protein Expression and Purification
2.3. NMR Spectroscopy
2.4. J-Coupling Value Determination and Stereospecific Assignment Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparing NUS and Linear Sampling 3JHα–Hβ Values in OBP22
3.2. Comparing NUS and Linear Sampling 3JHα–Hβ Values in Pin1
3.3. Stereospecific Assignment Using CYANA
3.4. Correlation between 3JHα–Hβ Couplings in Pin1’s WW Domain to Isolated WW Domain
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guentert, P.; Braun, W.; Billeter, M.; Wuethrich, K. Automated stereospecific proton NMR assignments and their impact on the precision of protein structure determinations in solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 3997–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuethrich, K. NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991; ISBN 0471828939. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.S.; Bax, A. Determination of φ and χ1 angles in proteins from 13C- 13C three-bond J couplings measured by three-dimensional heteronuclear NMR. How planar is the peptide bond? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 6360–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-S.; Grzesiek, S.; Bax, A. Two-Dimensional NMR Methods for Determining Angles of Aromatic Residues in Proteins from. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 1803–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.S.; Bax, A. Chi 1 angle information from a simple two-dimensional NMR experiment that identifies trans 3JNC gamma couplings in isotopically enriched proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 1997, 9, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, M.P.; Asakura, T. The application of 1H NMR chemical shift calculations to diastereotopic groups in proteins. FEBS Lett. 1992, 302, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, L.P.E. COSY, a simple alternative to E.COSY. J. Magn. Reson. 1987, 72, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggenberger, U.; Karimi-Nejad, Y.; Thüring, H.; Rüterjans, H.; Griesinger, C. Determination of Hα,Hβ and Hβ,C′ coupling constants in 13C-labeled proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 1992, 2, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald Emerson, S.; Montelione, G.T. 2D and 3D HCCH TOCSY experiments for determining 3J(HαHβ) coupling constants of amino acid residues. J. Magn. Reson. 1992, 99, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesiek, S.; Kuboniwa, H.; Hinck, A.P.; Bax, A. Multiple-Quantum Line Narrowing for Measurement of H-Alpha-H-Beta J-Couplings in Isotopically Enriched Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5312–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyberts, S.G.; Milbradt, A.G.; Wagner, A.B.; Arthanari, H.; Wagner, G. Application of iterative soft thresholding for fast reconstruction of NMR data non-uniformly sampled with multidimensional Poisson Gap scheduling. J. Biomol. NMR 2012, 52, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Radtke, A.; Choi, Y.-J.; Mendes, A.M.; Valenzuela, J.G.; Dimopoulos, G. Transcriptomic and functional analysis of the Anopheles gambiae salivary gland in relation to blood feeding. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Dimopoulos, G. Molecular analysis of photic inhibition of blood-feeding in Anopheles gambiae. BMC Physiol. 2008, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.; Ramirez, J.L.; Dimopoulos, G. Dengue Virus Infection of the Aedes aegypti Salivary Gland and Chemosensory Apparatus Induces Genes that Modulate Infection and Blood-Feeding Behavior. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.P.; Hanes, S.D.; Hunter, T. A human peptidyl–prolyl isomerase essential for regulation of mitosis. Nature 1996, 380, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, R.; Lu, K.P.; Hunter, T.; Noel, J.P. Structural and Functional Analysis of the Mitotic Rotamase Pin1 suggest substrate recognition is phosphorylation dependent_Noel 1997.pdf. Cell 1997, 89, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Abdul, H.M.; Opii, W.; Newman, S.F.; Joshi, G.; Ansari, M.A.; Sultana, R. REVIEW: Pin1 in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.W. Investigating dynamic interdomain allostery in Pin1. Biophys. Rev. 2015, 7, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, J. Protein NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Practice; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780121644918. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, M.A.; Mueller, L. Selective shaped pulse decoupling in NMR: homonuclear [carbon-13]carbonyl decoupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 2108–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, D.; Ikura, M.; Tschudin, R.; Bax, A. Rapid recording of 2D NMR spectra without phase cycling. Application to the study of hydrogen exchange in proteins. J. Magn. Reson. 1989, 85, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, E.; Goettsch, S.; Mueller, J.W.; Griewel, B.; Guiberman, E.; Mayr, L.M.; Bayer, P. Structural analysis of the mitotic regulator hPin1 in solution: Insights into domain architecture and substrate binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26183–26193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaglio, F.; Grzesiek, S.; Vuister, G.W.; Zhu, G.; Pfeifer, J.; Bax, A. NMRPipe: A multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J. Biomol. NMR 1995, 6, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranken, W.F.; Boucher, W.; Stevens, T.J.; Fogh, R.H.; Pajon, A.; Llinas, M.; Ulrich, E.L.; Markley, J.L.; Ionides, J.; Laue, E.D. The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: Development of a software pipeline. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005, 59, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orts, J.; Vögeli, B.; Riek, R.; Güntert, P. Stereospecific assignments in proteins using exact NOEs. J. Biomol. NMR 2013, 57, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güntert, P. Automated NMR Structure Calculation With CYANA. In Protein NMR Techniques; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 353–378. ISBN 1064-3745 (Print)r1064-3745 (Linking). [Google Scholar]
- Vuister, G.W.; Bax, A. Quantitative J correlation: A new approach for measuring homonuclear three-bond J(HNH.alpha.) coupling constants in 15N-enriched proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 7772–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuister, G.; Yamazaki, T.; Torchia, D.; Bax, A. Measurement of two- and three-bond 13C?1H J couplings to the Cd carbons of leucine residues in staphylococcal nuclease. J. Biomol. NMR 1993, 3, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, C.; Löhr, F.; Rüterjans, H.; Schmidt, J.M. Self-consistent Karplus parametrization of3J couplings depending on the polypeptide side-chain torsion X1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7081–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, P.; Born, A.; Henen, M.; Strotz, D.; Orts, J.; Olsson, S.; Güntert, P.; Chi, C.; Vögeli, B. The Exact Nuclear Overhauser Enhancement: Recent Advances. Molecules 2017, 22, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strotz, D. eNOE Method Development and Applications to Protein Allostery. Ph.D Thesis, No. 23867, ETH Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, K.A.; Bouchard, J.J.; Peng, J.W. Interdomain interactions support interdomain communication in human pin1. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 6968–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Restraints Used | Number Total Stereospecific Assignments | Number HB2/3 Stereospecific Assignments Only |
|---|---|---|
| OBP22 NOEs alone | 0 | 0 |
| OBP22 NOEs + 3JHα-Hβ couplings | 39 | 39 |
| Pin1 NOEs alone | 0 | 0 |
| Pin1 NOEs + 3JHα-Hβ couplings | 66 | 42 |
| Pin1 eNOEs alone | 103 | 48 |
| Pin1 eNOEs + 3JHα-Hβ couplings | 114 | 54 |
| Restraints Used | RMSD [Å], Backbone | RMSD [Å], Heavy Atom | RMSD to 1pin [Å], Backbone (Heavy Atom) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pin1 eNOEs alone | WW: 2.12 ± 0.54 | WW: 2.93 ± 0.53 | WW: 1.69 (2.31) |
| PPIase: 1.26 ± 0.17 | PPIase: 1.81 ± 0.13 | PPIase: 2.27 (3.16) | |
| Pin1 eNOEs + 3JHα-Hβ couplings, not ass. | WW: 1.95 ± 0.85 | WW: 2.66 ± 0.84 | WW: 1.32 (2.15) |
| PPIase: 1.28 ± 0.21 | PPIase: 1.88 ± 0.24 | PPIase: 2.43 (3.19) | |
| Pin1 eNOEs + 3JHα-Hβ couplings, ass. | WW: 1.47 ± 0.43 | WW: 2.12 ± 0.47 | WW: 1.19 (2.04) |
| PPIase: 1.07 ± 0.14 | PPIase: 1.59 ± 0.16 | PPIase: 1.90 (2.72) | |
| Pin1 NOEs alone | WW: 0.72 ± 0.20 | WW: 1.21 ± 0.24 | WW: 1.44 (2.46) |
| PPIase: 0.84 ± 0.08 | PPIase: 1.37 ± 0.1 | PPIase: 2.26 (2.89) | |
| Pin1 NOEs + 3JHα-Hβ couplings, not ass. | WW: 0.75 ± 0.24 | WW: 1.30 ± 0.27 | WW: 1.55 (2.57) |
| PPIase: 1.03 ± 0.16 | PPIase: 1.52 ± 0.15 | PPIase: 2.27 (2.88) | |
| Pin1 NOEs + 3JHα-Hβ couplings, ass. | WW: 0.59 ± 0.29 | WW: 1.04 ± 0.28 | WW: 1.47 (2.24) |
| PPIase: 0.78 ± 0.11 | PPIase: 1.24 ± 0.11 | PPIase: 2.32 (3.08) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Born, A.; Henen, M.A.; Nichols, P.; Wang, J.; Jones, D.N.; Vögeli, B. Efficient Stereospecific Hβ2/3 NMR Assignment Strategy for Mid-Size Proteins. Magnetochemistry 2018, 4, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry4020025
Born A, Henen MA, Nichols P, Wang J, Jones DN, Vögeli B. Efficient Stereospecific Hβ2/3 NMR Assignment Strategy for Mid-Size Proteins. Magnetochemistry. 2018; 4(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry4020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorn, Alexandra, Morkos A. Henen, Parker Nichols, Jing Wang, David N. Jones, and Beat Vögeli. 2018. "Efficient Stereospecific Hβ2/3 NMR Assignment Strategy for Mid-Size Proteins" Magnetochemistry 4, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry4020025
APA StyleBorn, A., Henen, M. A., Nichols, P., Wang, J., Jones, D. N., & Vögeli, B. (2018). Efficient Stereospecific Hβ2/3 NMR Assignment Strategy for Mid-Size Proteins. Magnetochemistry, 4(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry4020025