Solution-State Spin Crossover in a Family of [Fe(L)2(CH3CN)2](BF4)2 Complexes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
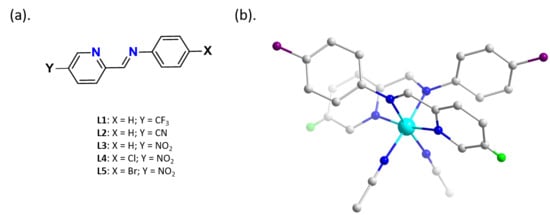
2.1. Single Crystal Structural Analysis
2.2. Variable-Temperature UV-Visible Spectroscopic Studies
3. Discussion
3.1. Single Crystal Structures
3.2. VT-UV-Visible Measurements for Characterisation of SCO
3.3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gütlich, P.; Goodwin, H.A. Spin-crossover in Transition metal compounds. In Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Halcrow, M.A. Spin Crossover Materials. In Properties and Applications; Wiley: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bousseksou, A.; Molnar, G.; Salmon, L.; Nicolazzi, W. Molecular spin crossover phenomenon: Recent achievements and prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3313–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O.; Martinez, C.J. Spin-Transition Polymers: From Molecular Materials Toward Memory Devices. Science 1998, 279, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, D.; Demitri, N.; Schafer, B.; Liscio, F.; Bergenti, I.; Ruani, G.; Ruben, M.; Cavallini, M. Multi-modal sensing in spin crossover compounds. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7836–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, F.; Monrabal-Capilla, M.; Osorio, E.A.; Coronado, E.; van der Zant, H.S.J. Room-Temperature Electrical Addressing of a Bistable Spin-Crossover Molecular System. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gütlich, P.; Garcia, Y.; Goodwin, H.A. Spin crossover phenomena in Fe(II) complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2000, 29, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gütlich, P.; Gaspar, A.B.; Garcia, Y. Spin state switching in iron coordination compounds. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 342–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinkowicz, D.; Rams, M.; Misek, M.; Kamenev, K.V.; Tomkowiak, H.; Katrusiak, A.; Sieklucka, B. Enforcing multifunctionality: A pressure-induced spin-crossover photomagnet. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8795–8802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gütlich, P.; Ksenofontov, V.; Gaspar, A.B. Pressure effect studies on spin crossover systems. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 1811–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkoshi, S.-I.; Imoto, K.; Tsunobuchi, Y.; Takano, S.; Tokoro, H. Light-induced spin-crossover magnet. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halcrow, M.A. Spin-crossover compounds with wide thermal hysteresis. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A. Ligand Field Theoretical Considerations, Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds I. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 233, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.S.; Kepert, C.J. Cooperativity in spin crossover systems: Memory, magnetism and microporosity. In Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 233, pp. 195–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.S.; Ross, T.M.; Phonsri, W.; Moubaraki, B.; Chastanet, G.; Létard, J.-F.; Batten, S.R.; Murray, K.S. Discrete FeII Spin-Crossover Complexes of 2,2′-Dipyridylamino-Substituted s-Triazine Ligands with Phenoxo, Cyanophenoxo and Dibenzylamino Functionalities. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.M.; Moubaraki, B.; Neville, S.M.; Batten, S.R.; Murray, K.S. Polymorphism and spin crossover in mononuclear FeII species containing new dipyridylamino-substituted s-triazine ligands. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 1512–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phonsri, W.; Harding, D.J.; Harding, P.; Murray, K.S.; Moubaraki, B.; Gass, I.A.; Cashion, J.D.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Adams, H. Stepped spin crossover in Fe(III) halogen substituted quinolylsalicylaldimine complexes. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 17509–17518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.S.; Stanilands, R.W.; Kruger, P.E. Spin crossover in homoleptic Fe(II) imidazolylimine complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 362, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Walker, F.A. Solution NMR Studies of Iron(II) Spin-Crossover Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 6794–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, R.J.; Scott, H.S.; Polson, M.I.J.; Williamson, B.E.; Mathonière, C.; Rouzières, M.; Clérac, R.; Kruger, P.E. Varied spin crossover behaviour in a family of dinuclear Fe(II) triple helicate complexes. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 7965–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.-H.; Hsiao, C.-S. Synthesis and Mössbauer Spectroscopy Studies on the Spin States of tris(2-Pyridylimine) Iron(ii) Complexes. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 1981, 28, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, K.; Suemura, N.; Yoneda, K.; Kawata, S.; Kaizaki, S. Substituent effect of the coordinated pyridine in a series of pyrazolato bridged dinuclear diiron(II) complexes on the spin-crossover behaviour. Dalton Trans. 2005, 4, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.J.K.; Kulmaczewski, R.; Mohammed, R.; Dudley, S.; Barrett, S.A.; Little, M.A.; Deeth, R.J.; Halcrow, M.A. A Unified Treatment of the Relationship Between Ligand Substituents and Spin State in a Family of Iron(II) Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4327–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.G.; Jeon, I.-R.; Harris, T.D. Electronic Effects of Ligand Substitution on Spin Crossover in a Series of Diiminoquinonoid-Bridged FeII2 Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Campolo, D.; Dumur, F.; Xiao, P.; Fouassier, J.P.; Gigmes, D.; Lalevee, J. Iron complexes as photoinitiators for radical and cationic polymerization through photoredox catalysis processes. J. Polym. Sci. A 2015, 53, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guionneau, P.; Marchivie, M.; Bravic, G.; Létard, J.-F.; Chasseau, D. Structural Aspects of Spin Crossover. Example of the [FeIILn(NCS)2] Complexes. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 234, 97–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiak, C. A critical account on π–π stacking in metal complexes with aromatic nitrogen-containing ligands. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2000, 3885–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A. Light Induced Spin Crossover and the High Spin to Low Spin Relaxation. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 234, 155–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.; Paula, J.D. Physical Chemistry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Toftlund, H. Spin equilibria in iron(II) complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1989, 94, 67–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvey, J.J.; Lawthers, I.; Heremans, K.; Toftlund, H. Spin-state relaxation dynamics in iron(II) complexes: Solvent on the activation and reaction and volumes for the 1A ⇌ 5T interconversion. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1984, 23, 1575–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ferraté, O.; Britovsek, G.J.P.; Claver, C.; van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M. C–H benzylic oxidation promoted by dinuclear iron DBDOC iminopyridine complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2015, 431, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ferraté, O. Synthesis of Dinuclear Complexes. From Ligand Design to Catalysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Rovira i Virgili, Tarragona, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A.; Taft, R.W. A survey of Hammett substituent constants and resonance and field parameters. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-J.; Siretanu, D.; Dickie, D.A.; Subedi, D.; Scepaniak, J.J.; Mitcov, D.; Clérac, R.; Smith, J.M. Steric and Electronic Control of the Spin State in Three-Fold Symmetric, Four-Coordinate Iron(II) Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13326–13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tweedle, M.F.; Wilson, L.J. Variable spin iron(III) chelates with hexadentate ligands derived from triethylenetetramine and various salicylaldehydes. Synthesis, characterization, and solution state studies of a new 2T. dblarw. 6A spin equilibrium system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 4824–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, I.; Company, A.; Corona, T.; Parella, T.; Ribas, X.; Costas, M. Assessing the Impact of Electronic and Steric Tuning of the Ligand in the Spin State and Catalytic Oxidation Ability of the FeII(Pytacn) Family of Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 9229–9244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, J.; Deeth, R.J. Spin-State Energetics of FeII Complexes—The Continuing Voyage Through the Density Functional Minefield. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2014, 4573–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Sakamoto, R.; Nishikawa, M.; Kume, S.; Nishibori, E.; Nishihara, H. Solid-State Ligand-Driven Light-Induced Spin Change at Ambient Temperatures in Bis(dipyrazolylstyrylpyridine)iron(II) Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 5188–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryliakov, K.P.; Duban, E.A.; Talsi, E.P. The Nature of the Spin-State Variation of [FeII(BPMEN)(CH3CN)2](ClO4)2 in Solution. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXL-97, Programs for X-ray Crystal Structure Refinement; University of Gottingen: Gottingen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space Group | C2/c | C2/c | C2/c | C2/c | C2/c |
| Formula | [Fe(L1)2(CH3CN)2]·2CH3CN | [Fe(L2)2(CH3CN)2]·2CH3CN | [Fe(L3)2(CH3CN)2] | [Fe(L4)2(CH3CN)2] | [Fe(L5)2(CH3CN)2] |
| T/K | 120(2) | 120(2) | 293(2) | 270(2) | 270(2) |
| Crystal Colour | Purple | Purple | Black | Red | Red |
| Av. Fe-N Distance (Å) | 1.95 | 1.96 | 1.98 | 1.96 | 1.96 |
| FeII Spin State | LS | LS | LS | LS | LS |
| Σ (°) a | 54.3 | 48.9 | 45.9 | 50.69 | 47.15 |
| cis Nimine-Fe-Npyridyl (°) | 80.84 | 81.06 | 80.06 | 80.89 | 81.04 |
| Imine-phenyl torsion (°) | 59.88 | 61.0 | 71.2 | 69.69 | 70.83 |
| Magnetic Behaviour | T1/2 (K) | ΔS (J K−1 mol−1) | ΔH (kJ mol−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LS | - | - | - |
| 2 | LS | - | - | - |
| 3 | SCO | 299.5 (±0.4) | 237 (±8) | 71 (±2) |
| 4 | SCO | 290 (±2) | 131 (±7) | 38 (±2) |
| 5 | SCO | 299.0 (±0.4) | 158 (±4) | 47 (±1) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilson, B.H.; Scott, H.S.; Archer, R.J.; Mathonière, C.; Clérac, R.; Kruger, P.E. Solution-State Spin Crossover in a Family of [Fe(L)2(CH3CN)2](BF4)2 Complexes. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5020022
Wilson BH, Scott HS, Archer RJ, Mathonière C, Clérac R, Kruger PE. Solution-State Spin Crossover in a Family of [Fe(L)2(CH3CN)2](BF4)2 Complexes. Magnetochemistry. 2019; 5(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilson, Benjamin H., Hayley S. Scott, Rosanna J. Archer, Corine Mathonière, Rodolphe Clérac, and Paul E. Kruger. 2019. "Solution-State Spin Crossover in a Family of [Fe(L)2(CH3CN)2](BF4)2 Complexes" Magnetochemistry 5, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5020022
APA StyleWilson, B. H., Scott, H. S., Archer, R. J., Mathonière, C., Clérac, R., & Kruger, P. E. (2019). Solution-State Spin Crossover in a Family of [Fe(L)2(CH3CN)2](BF4)2 Complexes. Magnetochemistry, 5(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5020022