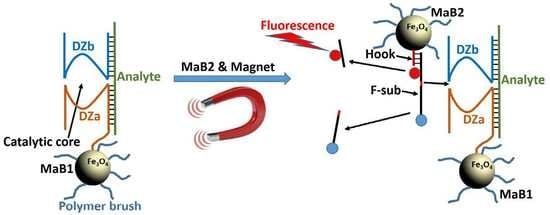
Towards Nanomaterials for Cancer Theranostics: A System of DNA-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles for Detection and Suppression of RNA Marker in Cancer Cells
Abstract
:Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cole, A.J.; Yang, V.C.; David, A.E. Cancer theranostics: The rise of targeted magnetic nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palekar-Shanbhag, P.; Jog, S.V.; Chogale, M.M.; Gaikwad, S.S. Theranostics for cancer therapy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelmann, U.M.; Roeth, A.A.; Eberbeck, D.; Buhl, E.M.; Neumann, U.P.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Slabu, I. Combining bulk temperature and nanoheating enables advanced magnetic fluid hyperthermia efficacy on pancreatic tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avazzadeh, R.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E.; Soleimani, M.; Amanpour, S.; Sadeghi, M. Synthesis and application of magnetite dextran-spermine nanoparticles in breast cancer hyperthermia. Prog. Biomater. 2017, 6, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breaker, R.R.; Joyce, G.F. A DNA enzyme that cleaves RNA. Chem. Biol. 1994, 1, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.W.; Joyce, G.F. A general purpose RNA-cleaving DNA enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4262–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silverman, S.K. Catalytic DNA: Scope, applications, and biochemistry of deoxyribozymes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanovic, M.N.; Stefanovic, D.; Rudchenko, S. Exercises in molecular computing. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerasimova, Y.V.; Kolpashchikov, D.M. Divide and control: Split design of multi-input DNA logic gates. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Zhou, C.; Wu, C.; Zhu, G.; Chen, Z.; Tan, W. Responsive DNA-based hydrogels and their applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGhee, C.E.; Loh, K.Y.; Lu, Y. DNAzyme sensors for detection of metal ions in the environment and imaging them in living cells. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerasimova, Y.V.; Kolpashchikov, D.M. Folding 16S RNA in a signal-producing structure for detection of bacteria. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10586–10588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokina, A.A.; Meschaninova, M.I.; Durfort, T.; Venyaminova, A.G.; Francois, J.-C. Targeting insulin-like growth factor I with 10–23 DNAzymes: 2′-o-methyl modifications in the catalytic core enhance mRNA cleavage. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehl, K.; Joshi, J.P.; Greene, B.L.; Dyer, R.B.; Nahta, R.; Salaita, K. Catalytic deoxyribozyme-modified nanoparticles for RNAi-independent gene regulation. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9150–9157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ding, J.; Liu, J. Theranostic DNAzymes. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1010–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakshi, S.F.; Guz, N.; Zakharchenko, A.; Deng, H.; Tumanov, A.V.; Woodworth, C.D.; Minko, S.; Kolpashchikov, D.M.; Katz, E. Magnetic field-activated sensing of mRNA in living cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12117–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, S.F.; Guz, N.; Zakharchenko, A.; Deng, H.; Tumanov, A.V.; Woodworth, C.D.; Minko, S.; Kolpashchikov, D.M.; Katz, E. Nanoreactors based on DNAzyme-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles activated by magnetic field. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpashchikov, D.M. A binary deoxyribozyme for nucleic acid analysis. ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 2039–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokany, E.; Bone, S.M.; Young, P.E.; Doan, T.B.; Todd, A.V. MNAzymes, a versatile new class of nucleic acid enzymes that can function as biosensors and molecular switches. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Kolpashchikov, D.M. Divide and control: Comparison of split and switch hybridization sensor. Chem. Select. 2017, 2, 5427–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, O.; Sun, S.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Chung, W.-Y.; Lee, M.-S.; Liao, Y.-C.; Kolpashchikov, D.M.; Chuang, M.-C. A mutation-resistant deoxyribozyme OR gate for highly selective detection of viral nucleic acids. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 10592–10595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtson, H.N.; Homolka, S.; Niemann, S.; Reis, A.J.; da Silva, P.E.A.; Gerasimova, Y.V.; Kolpashchikov, D.M.; Rohde, K.H. Multiplex detection of extensively drug resistant tuberculosis using binary deoxyribozyme sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagorovsky, K.; Chan, W.C.W. A plasmonic DNAzyme strategy for point-of-care genetic detection of infectious pathogens. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3168–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halo, T.L.; McMahon, K.M.; Angeloni, N.L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Chinen, A.B.; Malin, D.; Strekalova, E.; Cryns, V.L.; Cheng, C.; et al. NanoFlares for the detection, isolation, and culture of live tumor cells from human blood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17104–17109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dias, N.; Stein, C.A. Antisense oligonucleotides: Basic concepts and mechanisms. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moreno, P.M.D.; Pêgo, A.P. Therapeutic antisense oligonucleotides against cancer: Hurdling to the clinic. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J. CRISPR/Cas9: From genome engineering to cancer drug discovery. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Menezes, M.E.; Bhatia, S.; Wang, X.Y.; Emdad, L.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Gene therapies for cancer: Strategies, challenges and successes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigodich, A.E.; Seferos, D.S.; Massich, M.D.; Giljohann, D.A.; Lane, B.C.; Mirkin, C.A. Nano-flares for mRNA regulation and detection. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, C.; Schillinger, U.; Scherer, F.; Bergemann, C.; Rémy, J.-S.; Krötz, F.; Anton, M.; Lausier, J.; Rosenecker, J. The magnetofection method: Using magnetic force to enhance gene delivery. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, C.; Zelphati, O.; Mykhaylyk, O. Magnetically enhanced nucleic acid delivery. Ten years of magnetofection-progress and prospects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 1300–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.Z.; Chan, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sun, C.D.; Wang, L.-H. Twist transcriptionally up-regulates AKT2 in breast cancer cells leading to increased migration, invasion, and resistance to paclitaxel. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Name a | Sequence |
|---|---|
| DZa | 5′-NH2/AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AAC GAG CGG CTC AGC TAC GCC T AC AAC CGA GAG AGG AAA C |
| DZb | 5′-CCA GGG A GG CTA GCT TCT CGG TCT GGA GGA TGG AG |
| F-Sub | 5′-CGGT ACA TTG TAG AAG TT AAG GTTFAM TCC TCg uCC CTG GGC A-BHQ1 |
| Hook | 5′-NH2/AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AA/iSp9/AAC TTC TAC AAT GTA CCG |
| Forward Twist Primer | 5′-GGAGTCCGCAGTCTTACGAG |
| Reverse Twist Primer | 5′-TCTGGAGGACCTGGTAGAGG |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakshi, S.; Zakharchenko, A.; Minko, S.; Kolpashchikov, D.M.; Katz, E. Towards Nanomaterials for Cancer Theranostics: A System of DNA-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles for Detection and Suppression of RNA Marker in Cancer Cells. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5020024
Bakshi S, Zakharchenko A, Minko S, Kolpashchikov DM, Katz E. Towards Nanomaterials for Cancer Theranostics: A System of DNA-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles for Detection and Suppression of RNA Marker in Cancer Cells. Magnetochemistry. 2019; 5(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5020024
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakshi, Saira, Andrey Zakharchenko, Sergiy Minko, Dmitry M. Kolpashchikov, and Evgeny Katz. 2019. "Towards Nanomaterials for Cancer Theranostics: A System of DNA-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles for Detection and Suppression of RNA Marker in Cancer Cells" Magnetochemistry 5, no. 2: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5020024
APA StyleBakshi, S., Zakharchenko, A., Minko, S., Kolpashchikov, D. M., & Katz, E. (2019). Towards Nanomaterials for Cancer Theranostics: A System of DNA-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles for Detection and Suppression of RNA Marker in Cancer Cells. Magnetochemistry, 5(2), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5020024