A Fast Neutron Radiography System Using a High Yield Portable DT Neutron Source
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
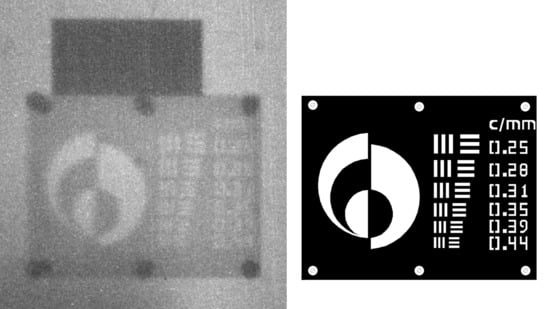
3.1. Analysis of the USAF-1951 Resolution Chart
3.1.1. Visual Inspection
3.1.2. Brightness as a Function of Position across the USAF-1951 Pattern
3.2. Modulation Transfer Function
4. Discussion
- Greater number of neutrons in the image, either higher neutron yield (the generator is capable of 1 × 1010 n/s) or increase the exposure duration (longer than 10 min);
- Careful alignment of the phantom (taking a series of measurements at slightly different angles to optimize for each structure being imaged);
- Use of a different standard that minimizes the geometrical/parallax effects (for example a spoke wheel);
- Acquiring multiple shorter exposures and adding or averaging them with appropriate filtering methods (e.g., median);
- Improving neutron and gamma-ray shielding around the neutron camera’s scintillator to reduce the effects of scattered neutrons and gamma rays produced by neutron interactions within the scene which subsequently scatter onto the detector;
- Use of a scintillator that is more sensitive to fast neutrons and less sensitive to gamma rays could also be explored.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kallmann, H.; Kuhn, E. Photographic Detection of Slowly Moving Neutrons. United States Patent 2,186,757, 9 January 1940. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US2186757A/en (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Lehmann, E.H. Neutron imaging facilities in a global context. J. Imaging 2017, 3, 52. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2313-433X/3/4/52 (accessed on 25 November 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visilik, D.; Murri, R. Neutron Radioraphy with a sealed-tube neutron generator and graphite moderated system. In Report US Government Contract AT(29-1)-1106; Dow Chemical Company: Midland, MI, USA, 1971. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/4019663 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Thewlis, J. Neutron Radiography. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1957, 7, 345. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/0508-3443/7/10/301 (accessed on 20 October 2020). [CrossRef]
- Peter, O. Neutronen-Durchleuchtung. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A 1946, 1, 557–559. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-1946-1002 (accessed on 25 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Andersson, P.; Andersson-Sunden, E.; Sjöstrand, H.; Jacobsson-Svärd, S. Neutron tomography of axially symmetric objects using 14 MeV neutrons from a portable neutron generator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 085109. Available online: http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2:706501 (accessed on 25 November 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y. Development of high intensity D-T fusion neutron generator HINEG. Int. J. Energy Res. 2016, 68–72. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/er.3572 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, Z. Design and Optimization of a Fast Neutron Radiography System Based on a High-Intensity D-T Fusion Neutron Generator. J. Nucl. Technol. 2019, 205, 978–986. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1080/00295450.2019.1575122 (accessed on 25 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, S.; Sarkar, P.S.; Thomas, R.G.; Patel, T.; Gadkari, S.C. Fast Neutron Radiography with DT Neutron Generator Indian National Seminar & Exhibition on Non-Destructive Evaluation 2016, Dec, Thiruvananthapuram (NDE-India 2016). Available online: https://www.ndt.net/article/nde-india2016/papers/A133.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Kam, E.; Reyhancan, A.; Biyak, R. A portable fast neutron radiography system for non-destructive analysis of composite materials. Nukleonika 2019, 64, 97–101. Available online: https://content.sciendo.com/downloadpdf/journals/nuka/64/3/article-p97.xml (accessed on 25 November 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cremer, J.T.; Williams, D.L.; Gary, C.K.; Piestrup, M.A.; Faber, D.A.; Fuller, M.J.; Vainionpaa, J.H.; Apodaca, M.; Pantell, R.H.; Feinstein, J. Large area imaging of hydrogenous materials using fast neutrons from a DD fusion generator. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2012, 675, 51–55. Available online: http://www.academia.edu/download/47825443/Fast_Radiography_-_published_-_1-s2.0-S0168900212001386-main.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2020). [CrossRef]
- Bergaoui, K.; Reguigui, N.; Gary, C.K.; Cremer, J.T.; Vainionpaa, J.H.; Piestrup, M.A. Design, Testing and optimization of a neutron radiography systembased on a Deuterium–Deuterium (D–D) neutron generator. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2014, 299, 41–51. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/download/37816092/2014_JRANC_-_NG_Radiography.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2020). [CrossRef]
- Popova, V.; Degtiarenkoa, P.; Musatov, I. New detector for use in fast neutron radiography. J. Instrum. 2011, 6, 1–11. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-0221/6/01/C01029/pdf (accessed on 25 November 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iaea Radiation Technology Reports No. 1, Neutron Generators for Analytical Purposes, Neutron Generators for Analytical Purposes; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2012; p. 1. ISBN 978-92-0-125110-7. Available online: https://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/P1535_web.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Brenizer, J. A review of significant advances in neutron imaging from conception to the present. The 7th International Topical Meeting on Neutron Radiograpy. Phys. Procedia 2013, 43, 10–20. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1875389213000163/pdf?md5=f69b657703c2adb056198e256989f464&pid=1-s2.0-S1875389213000163-main.pdf&_valck=1 (accessed on 25 November 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rant, J.; Kristof, E.; Balasko, M.; Stade, J. Fast Neutron Radiography Using Photoluminescent Imaging Plates. In Proceedings of the International Conference Nuclear Energy in Central Europe, Portorož, Slovenia, 6–9 September 1999; pp. 717–724. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/etdeweb/servlets/purl/20308920 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- USAF-1951 Resolution Cart, MIL-STD-150A, Further Details. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1951_USAF_resolution_test_chart (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Neutron Optics, Grenoble, 8 Allée des Pampres, 38640 Cliaz, France. Available online: https://www.neutronoptics.com/cameras.html (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- RC Tritec Ltd., Speicherstrasse 60A, CH-9053 Teufen, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.rctritec.com/en/scintillators/introduction.html (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Robert, K.; Swank, R.K. Calculation of Modulation Transfer Functions of X-Ray Fluorescent Screens. Appl. Opt. 1973, 12, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, J.T. Neutron and X-ray Optics (Elsevier Insights), 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN-13: 978-0124071643, ISBN-10: 0124071643; Equation 16.75; Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/books/neutron-and-x-ray-optics/cremer-jr/978-0-12-407164-3. https://www.amazon.com/Neutron-X-ray-Optics-Elsevier-Insights/dp/0124071643; (accessed on 25 November 2020). [Google Scholar]











| Spatial Frequency 1 | Horizontal | Vertical | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 c/mm | Visible | Visible |  |
| 0.28 c/mm | Visible | Visible | |
| 0.31 c/mm | Visible | Visible | |
| 0.35 c/mm | Visible | Visible | |
| 0.39 c/mm | Not visible | Visible | |
| 0.44 c/mm | Not Visible | Not visible |
| Material | Location | Orientation | Spatial Frequency 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Left edge | Vertical | 0.17/mm |
| Plastic | Logo top center | Vertical | 0.18/mm |
| Plastic | Logo bottom, center | Vertical | 0.16/mm |
| Plastic | Bottom edge | Horizontal | 0.42/mm |
| Steel | Left edge | Vertical | 0.2/mm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williams, D.L.; Brown, C.M.; Tong, D.; Sulyman, A.; Gary, C.K. A Fast Neutron Radiography System Using a High Yield Portable DT Neutron Source. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6120128
Williams DL, Brown CM, Tong D, Sulyman A, Gary CK. A Fast Neutron Radiography System Using a High Yield Portable DT Neutron Source. Journal of Imaging. 2020; 6(12):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6120128
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliams, David L., Craig M. Brown, David Tong, Alexander Sulyman, and Charles K. Gary. 2020. "A Fast Neutron Radiography System Using a High Yield Portable DT Neutron Source" Journal of Imaging 6, no. 12: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6120128
APA StyleWilliams, D. L., Brown, C. M., Tong, D., Sulyman, A., & Gary, C. K. (2020). A Fast Neutron Radiography System Using a High Yield Portable DT Neutron Source. Journal of Imaging, 6(12), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6120128