Chronometric Quantitation of Analytes in Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices (MicroPADs) via Enzymatic Degradation of a Metastable Biomatrix
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Highlights
3. Methods
4. Quantitative MicroPAD Overview
4.1. Quantitation Mechanism
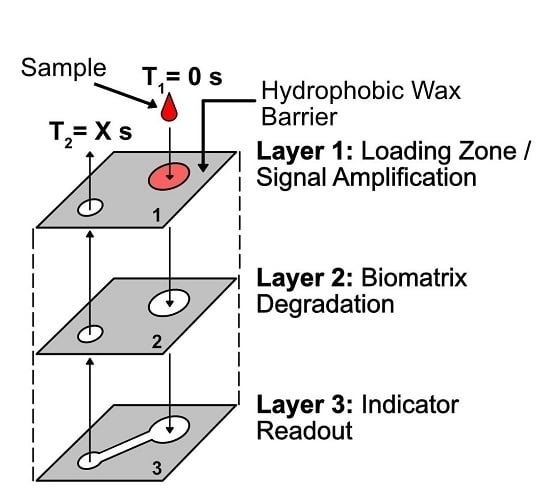
4.2. MicroPAD with Integrated Chronometric Quantitation
4.2.1. Overview of Device Design and Mechanism
4.2.2. Overview of Analyte Selection, Isolation, and Competition
4.2.3. Overview of the Biomatrix Degradation and Chronometric Quantitation
5. Main Patent Claims
5.1. Claim 1
5.2. Claims 2 and 3
5.3. Claims 4 and 5
5.4. Claims 6–8
5.5. Claims 9 and 10
5.6. Claims 11 and 12
5.7. Claims 13 and 14
5.8. Claims 15 and 16
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
8. Patent Information & Disclaimer
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO—World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2017: Monitoring Health for The SDGs; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- WHO—World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2018: Monitoring Health for the SDGs; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yager, P.; Domingo, G.J.; Gerdes, J. Point-of-care diagnostics for global health. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 107–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, S.K.; Linder, V.; Parviz, B.A.; Siegel, A.; Whitesides, G.M. An integrated approach to a portable and low-cost immunoassay for resource-poor settings. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laksanasopin, T.; Chin, C.D.; Moore, H.; Wang, J.; Cheung, Y.K.; Sia, S.K.; Reader, A. Microfluidic point-of-care diagnostics for resource-poor environments. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 1057–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, B.D.; Wasserman, J.; Dahl, C.A. Global health diagnostics. Nature 2006, 444, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosack, C.S.; Page, A.-L.; Klatser, P.R. A guide to aid the selection of diagnostic tests. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; Korf, J.; Van Amerongen, A. Lateral flow (immuno) assay: Its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.; Pugh, C.S.G. Lateral Flow Chromatographic Binding Assay Device. U.S. Patent 4,956,302, 11 September 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Shuler, J.K.; Lovell, S.J.; Fisher, A.S.; Weiss, A.J.; Rosenstein, R.W. Direct Read Lateral Flow Assay for Small Analytes. U.S. Patent 5,798,273, 25 August 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wild, D. The Immunoassay Handbook: Theory and Applications of Ligand Binding, ELISA and Related Techniques, 4th ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 0080970389. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M.; Carrilho, E. Diagnostics for the developing world: Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.M.; Sinton, D. Turning the page: Advancing paper-based microfluidics for broad diagnostic application. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8447–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, E.B.; Schultz, S.A.; Martinez, A.W.; Martinez, N.W. Fabrication of miniaturized paper-based microfluidic devices (MicroPADs). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrilho, E.; Martinez, A.W.; Whitesides, G.M. Understanding wax printing: A simple micropatterning process for paper-based microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7091–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyazi, T.; Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Benito-Lopez, F. Review on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices towards commercialisation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1001, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, E.B.; Knutsen, C.; Wells, J.; Jangid, A.; Mitchell, M.; Martinez, N.; Martinez, A. Wax-printed fluidic time delays for automating multi-step assays in paper-based microfluidic devices (MicroPADs). Inventions 2019, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, K.J. (Ed.) Paper-Based Diagnostics; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9783319968681. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Carrilho, E.; Thomas, S.W.; Sindi, H.; Whitesides, G.M. Simple telemedicine for developing regions: Camera phones and paper-based microfluidic devices for real-time, off-site diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3699–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morbioli, G.G.; Mazzu-Nascimento, T.; Stockton, A.M.; Carrilho, E. Technical aspects and challenges of colorimetric detection with microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs)—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 970, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cate, D.M.; Adkins, J.A.; Mettakoonpitak, J.; Henry, C.S. Recent developments in paper-based micro fluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, M.S.; Tsaloglou, M.-N.; Sisley, T.; Christodouleas, D.; Chen, A.; Milette, J.; Whitesides, G.M. Sliding-strip microfluidic device enables ELISA on paper. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.R.; Hu, J.; Tang, R.; Gong, Y.; Feng, S.; Ren, H.; Wen, T.; Li, X.; Wan Abas, W.A.B.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; et al. An integrated paper-based sample-to-answer biosensor for nucleic acid testing at the point of care. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Ge, L.; Ge, S. A novel chemiluminescence paper microfluidic biosensor based on enzymatic reaction for uric acid determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3284–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ge, L.; Song, X.; Yu, J.; Ge, S. Paper-based chemiluminescence ELISA: Lab-on-paper based on chitosan modified paper device and wax-screen-printing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Takaki, S.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Device for Fluorescence Detection of Lactoferrin in Tear Fluid. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences, MicroTAS 2013, Freiburg, Germany, 27–31 October 2013; Chemical and Biological Microsystems Society, 2013; pp. 895–897. [Google Scholar]
- Adkins, J.; Boehle, K.; Henry, C. Electrochemical paper-based microfluidic. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettakoonpitak, J.; Boehle, K.; Nantaphol, S.; Teengam, P.; Adkins, J.A.; Srisa-Art, M.; Henry, C.S. Electrochemistry on paper-based analytical devices: A review. Electroanalysis 2016, 7, 1420–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Nijhuis, C.A.; Gong, J.; Chen, X.; Kumachev, A.; Martinez, A.W.; Narovlyansky, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Electrochemical sensing in paper-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhiago, M.; Henry, C.S.; Kubota, L.T. Electrochimica acta low cost, simple three dimensional electrochemical paper-based analytical device for determination of p-nitrophenol. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 130, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Liu, X.; Akbulut, O.; Whitesides, G.M. Integration of paper-based microfluidic devices with commercial electrochemical readers †. Lab Chip 2010, 3163–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungchai, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. Electrochemical detection for paper-based microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5821–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossi, N.; Toniolo, R.; Impellizzieri, F.; Bontempelli, G. Doped pencil leads for drawing modified electrodes on paper-based electrochemical devices. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 723, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalhal, R.F.; Sima, M.; Helena, M.; Piazetta, D.O.; Gobbi, A.L.; Kubota, L.T. Electrochemical detection in a paper-based separation device. Electroanal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1162–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboud, J.; Xu, G.; Garrett, A.; Adriko, M.; Yang, Z.; Tukahebwa, E.M.; Rowell, C.; Cooper, J.M. based microfluidics for DNA diagnostics of malaria in low resource underserved rural communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4834–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, D.; Ge, L.; Yan, M.; Song, X.; Yu, J. Electrochemical immunoassay on a 3D microfluidic paper-based device. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4683–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scida, K.; Cunningham, J.C.; Renault, C.; Richards, I.; Crooks, R.M. Simple, sensitive, and quantitative electrochemical detection method for paper analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6501–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Parvez, K.; Li, R.; Dong, R.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Transparent conductive electrodes from graphene/PEDOT:PSS hybrid inks for ultrathin organic photodetectors. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, J.C.; Brenes, N.J.; Crooks, R.M. Paper electrochemical device for detection of DNA and thrombin by target-induced conformational switching. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6166–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, E.J.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper-based electroanalytical devices for accessible diagnostic testing. MRS Bull. 2019, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.G.; DiTucci, M.J.; Phillips, S.T. Quantifying analytes in paper-based microfluidic devices without using external electronic readers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12707–12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Phillips, S.T. Fluidic timers for time-dependent, point-of-care assays on paper. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8071–8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.G.; Robbins, J.S.; Phillips, S.T. Phase-switching depolymerizable poly(carbamate) Oligomers for signal amplification in quantitative time-based assays. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 5177–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.G.; Robbins, J.S.; Phillips, S.T. Point-of-care assay platform for quantifying active enzymes to femtomolar levels using measurements of time as the readout. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10432–10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.G.; Robbins, J.S.; Phillips, S.T. A prototype point-of-use assay for measuring heavy metal contamination in water using time as a quantitative readout. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5352–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toley, B.J.; McKenzie, B.; Liang, T.; Buser, J.R.; Yager, P.; Fu, E. Tunable-delay shunts for paper microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11545–11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, B.; Liang, T.; Fu, E.; Ramachandran, S.; Kauffman, P.; Yager, P. Dissolvable fluidic time delays for programming multi-step assays in instrument-free paper diagnostics. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2840–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jangid, A.R.; Strong, E.B.; Escamilla, E.; Lore, B.A.; Tod, N.J.; Thiel, R.; Martinez, A.W.; Martinez, N.W. Chronometric Quantitation of Analytes in Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices (MicroPADs) via Enzymatic Degradation of a Metastable Biomatrix. Inventions 2019, 4, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions4030048
Jangid AR, Strong EB, Escamilla E, Lore BA, Tod NJ, Thiel R, Martinez AW, Martinez NW. Chronometric Quantitation of Analytes in Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices (MicroPADs) via Enzymatic Degradation of a Metastable Biomatrix. Inventions. 2019; 4(3):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions4030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleJangid, Aditya R., E. Brandon Strong, Emiliano Escamilla, Brittany A. Lore, Nicholas J. Tod, Robert Thiel, Andres W. Martinez, and Nathaniel W. Martinez. 2019. "Chronometric Quantitation of Analytes in Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices (MicroPADs) via Enzymatic Degradation of a Metastable Biomatrix" Inventions 4, no. 3: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions4030048
APA StyleJangid, A. R., Strong, E. B., Escamilla, E., Lore, B. A., Tod, N. J., Thiel, R., Martinez, A. W., & Martinez, N. W. (2019). Chronometric Quantitation of Analytes in Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices (MicroPADs) via Enzymatic Degradation of a Metastable Biomatrix. Inventions, 4(3), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions4030048