Elucidating the Mechanism of Trypanosoma cruzi Acquisition by Triatomine Insects: Evidence from a Large Field Survey of Triatoma infestans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Stage | Median Quantity of Blood Ingested during this Stage (mg) | Estimated Cumulative Blood Ingested during Lifetime Prior to Capture (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| First instar | 7.1 | 7.1 |
| Second instar | 18.3 | 25.4 |
| Third instar | 62.4 | 87.8 |
| Fourth instar | 215.0 | 302.8 |
| Fifth instar | 770.0 | 1072.8 |
References
- Rassi, A.; Rassi, A.; Marin-Neto, J.A. Chagas disease. Lancet 2010, 375, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, G.A. Direct transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi between vectors of Chagas’ disease. Acta Trop. 1988, 45, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kollien, A.H.; Schaub, G.A. The development of Trypanosoma cruzi (Trypanosomatidae) in the Reduviid bug Triatoma infestans (Insecta): Influence of starvation. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1998, 45, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juarez, E. Comportamento do Triatoma infestans sob várias condições de laboratório. Rev. Saude Publica 1970, 4, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, C.B.; Dotson, E.M.; Pennington, P.M.; Eichler, S.; Cordon-Rosales, C.; Durvasula, R.V. Bacterial symbiosis and paratransgenic control of vector-borne Chagas disease. Int. J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beard, C.B.; Cordon-Rosales, C.; Durvasula, R.V. Bacterial Symbionts of the Triatominae and Their Potential Use in Control of Chagas Disease Transmission. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática INEI. Perú: Perfil Sociodemográfico. Censos nacionales 2017: XI de Población y VI de Vivienda; INEI: Lima, Peru, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, M.Z.; Barbu, C.M.; Castillo-Neyra, R.; Quispe-Machaca, V.R.; Ancca-Juarez, J.; Escalante-Mejia, P.; Borrini-Mayori, K.; Niemierko, M.; Mabud, T.S.; Behrman, J.R.; et al. Urbanization, land tenure security and vector-borne Chagas disease. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20141003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayer, A.M.; Hunter, G.C.; Gilman, R.H.; Cornejo Del Carpio, J.G.; Naquira, C.; Bern, C.; Levy, M.Z. Chagas disease, migration and community settlement patterns in Arequipa, Peru. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, S.; Ernst, K.C.; Pumahuanca, M.L.; Yool, S.R.; Comrie, A.C.; Sterling, C.R.; Gilman, R.H.; Náquira, C.; Levy, M.Z. A country bug in the city: Urban infestation by the Chagas disease vector Triatoma infestans in Arequipa, Peru. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2013, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foley, E.A.; Khatchikian, C.E.; Hwang, J.; Ancca-Juárez, J.; Borrini-Mayori, K.; Quıspe-Machaca, V.R.; Levy, M.Z.; Brisson, D. Population structure of the Chagas disease vector, Triatoma infestans, at the urban-rural interface. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5162–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khatchikian, C.E.; Foley, E.A.; Barbu, C.M.; Hwang, J.; Ancca-Juárez, J.; Borrini-Mayori, K.; Quıspe-Machaca, V.R.; Naquira, C.; Brisson, D.; Levy, M.Z. Population Structure of the Chagas Disease Vector Triatoma infestans in an Urban Environment. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levy, M.Z.; Bowman, N.M.; Kawai, V.; Waller, L.A.; Del Carpio, J.G.C.; Benzaquen, E.C.; Gilman, R.H.; Bern, C. Periurban Trypanosoma cruzi-infected Triatoma infestans, Arequipa, Peru. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delgado, S.; Castillo Neyra, R.; Quispe Machaca, V.R.; Ancca Juárez, J.; Chou Chu, L.; Verastegui, M.R.; Moscoso Apaza, G.M.; Bocángel, C.D.; Tustin, A.W.; Sterling, C.R.; et al. A history of chagas disease transmission, control, and re-emergence in peri-rural La Joya, Peru. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurtler, R.E.; Cohen, J.E.; Cecere, M.C.; Lauricella, M.A.; Chuit, R.; Segura, E.L. Influence of humans and domestic animals on the household prevalence of Trypanosoma cruzi in Triatoma infestans populations in northwest Argentina. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1998, 58, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.Z.; Tustin, A.; Castillo-Neyra, R.; Mabud, T.S.; Levy, K.; Barbu, C.M.; Quispe-Machaca, V.R.; Ancca-Juarez, J.; Borrini-Mayori, K.; Naquira-Velarde, C.; et al. Bottlenecks in domestic animal populations can facilitate the emergence of Trypanosoma cruzi, the aetiological agent of Chagas disease. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20142807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Neyra, R.; Borrini Mayorí, K.; Salazar Sánchez, R.; Ancca Suarez, J.; Xie, S.; Náquira Velarde, C.; Levy, M.Z. Heterogeneous infectiousness in guinea pigs experimentally infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 65, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gürtler, R.E.; Ceballos, L.A.; Ordóñez-Krasnowski, P.; Lanati, L.A.; Stariolo, R.; Kitron, U. Strong host-feeding preferences of the vector Triatoma infestans modified by vector density: Implications for the epidemiology of Chagas disease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catalá, S.S.; Noireau, F.; Dujardin, J.-P. Biology of Triatominae. In American Trypanosomiasis Chagas Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 145–167. [Google Scholar]
- Cecere, M.C.; Castañera, M.B.; Canale, D.M.; Chuit, R.; Gürtler, R.E. Trypanosoma cruzi infection in Triatoma infestans and other triatomines: Long-term effects of a control program in rural northwestern Argentina. Rev. Panam. Salud Pública 1999, 5, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miles, M.A.; Patterson, J.W.; Marsden, P.D.; Minter, D.M. A comparison of Rhodnius prolixus, Triatoma infestans and Panstrongylus megistus in the xenodiagnosis of a chronic Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) cruzi infection in a rhesus monkey (Macaca mullatta). Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1975, 69, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M. Alguns fatos que interessam á epidemiolojia da molestia de Chagas. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1915, 7, 120–138. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, N.R. Experimental Studies on the Quantitative Transmission of Trypanosoma Cruzi: Aspects of the Rearing, Maintenance and Testing of Vector Material, and of the Origin and Course of Infection in the Vector. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1960, 54, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyirady, S.A. The Germfree Culture of Three Species of Triatominae: Triatoma Protracta (Uhler), Triatoma Rubida (Uhler) and Rhodnius Prolixus StÅL1. J. Med. Entomol. 1973, 10, 417–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, A.F.; Lynch, P.A.; Thomas, M.B. How to make evolution-proof insecticides for malaria control. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, 0001–00010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koella, J.C.; Lynch, P.A.; Thomas, M.B.; Read, A.F. Towards evolution-proof malaria control with insecticides. Evol. Appl. 2009, 2, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlani, L.; Pedrini, N.; Girotti, J.R.; Mijailovsky, S.J.; Cardozo, R.M.; Gentile, A.G.; Hernández-Suárez, C.M.; Rabinovich, J.E.; Juárez, M.P. Biological Control of the Chagas Disease Vector Triatoma infestans with the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria bassiana Combined with an Aggregation Cue: Field, Laboratory and Mathematical Modeling Assessment. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, E. Observações sôbre eliminação de dejeções e tempo de sucção em alguns triatomíneos sul-americanos. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1956, 54, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trumper, E.V.; Gorla, D.E. Density-dependent timing of defaecation by Triatoma infestans. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1991, 85, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.K.; Graham, A.L.; Dobson, A.P.; Chávez, O.T. Rhodnius prolixus life history outcomes differ when infected with different trypanosoma cruzi i strains. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




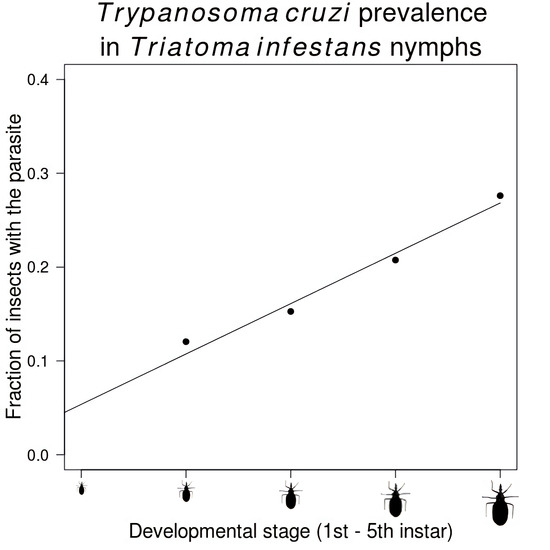
| Stage | Number Infected/Total Insects (%) |
|---|---|
| Second instar | 125/1037 (12.1) |
| Third instar | 512/3352 (15.3) |
| Fourth instar | 687/3310 (20.8) |
| Fifth instar | 1060/3838 (27.6) |
| Adult | 1326/3715 (35.7) |
| Male | 853/2225 (38.3) |
| Female | 473/1490 (31.7) |
| Total | 3710/15,252 (24.3) |
| Model Name | Fitted Parameter | Best-Fit Parameter (95% Confidence Interval) | AIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bites Hypothesis | pbite: probability of parasite acquisition during any given stage | pbite = 0.059 (0.057 to 0.061) | 11,672 |
| Blood Hypothesis | pblood: probability of parasite acquisition with each milligram of blood ingested | pblood = 0.00036 (0.00035 to 0.00038) | 112,302 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tustin, A.W.; Castillo-Neyra, R.; Tamayo, L.D.; Salazar, R.; Borini-Mayorí, K.; Levy, M.Z. Elucidating the Mechanism of Trypanosoma cruzi Acquisition by Triatomine Insects: Evidence from a Large Field Survey of Triatoma infestans. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020087
Tustin AW, Castillo-Neyra R, Tamayo LD, Salazar R, Borini-Mayorí K, Levy MZ. Elucidating the Mechanism of Trypanosoma cruzi Acquisition by Triatomine Insects: Evidence from a Large Field Survey of Triatoma infestans. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2020; 5(2):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020087
Chicago/Turabian StyleTustin, Aaron W., Ricardo Castillo-Neyra, Laura D. Tamayo, Renzo Salazar, Katty Borini-Mayorí, and Michael Z. Levy. 2020. "Elucidating the Mechanism of Trypanosoma cruzi Acquisition by Triatomine Insects: Evidence from a Large Field Survey of Triatoma infestans" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 5, no. 2: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020087
APA StyleTustin, A. W., Castillo-Neyra, R., Tamayo, L. D., Salazar, R., Borini-Mayorí, K., & Levy, M. Z. (2020). Elucidating the Mechanism of Trypanosoma cruzi Acquisition by Triatomine Insects: Evidence from a Large Field Survey of Triatoma infestans. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 5(2), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed5020087