Red Blood Cell Agglutination for Blood Typing Within Passive Microfluidic Biochips
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microfluidic Chip
2.2. Embedded Reagents
2.3. Blood Samples
2.4. Operating Protocol for the Blood Typing Experiments
2.5. Observations, Video Recording
2.6. Image Processing and Agglutination Indicator Computation
3. Results
3.1. Microfluidic Biochip Design and Fabrication
3.2. Capillarity Filling of the Channel
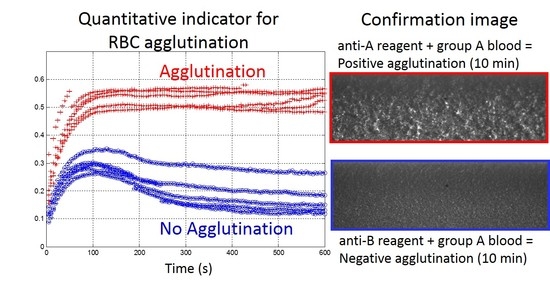
3.3. Image Observation of the Agglutination
3.4. Choice and Optimization of the Agglutination Indicator
4. Discussion
4.1. Ease of Handling
4.2. Cost of Analysis
4.3. Operator Safety
4.4. Results Reading
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitra, R.; Mishra, N.; Rath, G.P. Blood groups systems. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, L. Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2005. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2261/ (accessed on 16 April 2018).
- Kawagishi, N.; Takeda, I.; Miyagi, S.; Satoh, K.; Akamatsu, Y.; Sekiguchi, S.; Satomi, S. Long-term outcome of ABO-incompatible living-donor liver transplantation: A single-center experience. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Surg. 2009, 16, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-J.; Kang, H.-W.; Kim, Y.; Lee, G.-W.; Lim, G.; Cho, D.-W. Development of a micro-blood-typing system using micro-stereolithography technology. Sens. Mater. 2005, 17, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach, F.T.; Dunning, M.B. A Manual of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Baglin, T.; Ouwehand, W.; Voak, D.; Waters, A.H.; Gunson, H.H.; Lloyd, E. Bedside blood compatibility testing. Lancet 1990, 336, 1196–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krombach, J.; Kampe, S.; Gathof, B.S.; Diefenbach, C.; Kasper, S.-M. Human Error: The persisting risk of blood transfusion: A report of five cases. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dujardin, P.-P.; Salmi, L.R.; Ingrand, P. Errors in interpreting the pretransfusion bedside compatibility test. Vox Sang. 2000, 78, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malomgré, W.; Neumeister, B. Recent and future trends in blood group typing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migeot, V.; Ingrand, I.; Salmi, L.R.; Ingrand, P. Reliability of bedside ABO testing before transfusion. Transfusion 2002, 42, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giebel, F.; Picker, S.M.; Gathof, B.S. Evaluation of four bedside test systems for card performance, handling and safety. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2008, 35, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migeot, V.; Tellier, S.; Ingrand, P. Diversity of bedside pretransfusion ABO compatibility devices in France. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2003, 10, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, D.J. Red cell genotyping and the future of pretransfusion testing. Blood 2009, 114, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouse, C.; Vincek, V. Identification of ABO alleles on forensic-type specimens using rapid-ABO genotyping. BioTechniques 1995, 18, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doi, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Inagaki, S.; Shigeta, Y.; Miyaishi, S.; Ishizu, H. A new method for ABO genotyping using a multiplex single-base primer extension reaction and its application to forensic casework samples. Leg. Med. 2004, 6, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugozzoli, L.; Wallace, R.B. Application of an allele-specific polymerase chain reaction to the direct determination of ABO blood group genotypes. Genomics 1992, 12, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazer, M.H.; Hosseini-Maaf, B.; Olsson, M.L. Blood grouping discrepancies between ABO genotype and phenotype caused by O alleles. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2008, 15, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, C.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kwon, T.H. Disposable integrated microfluidic biochip for blood typing by plastic microinjection moulding. Lab. Chip 2006, 6, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llopis, F.; Carbonell-Uberos, F.; Montero, M.C.; Bonanad, S.; Planelles, M.D.; Plasencia, I.; Riol, C.; Planells, T.; Carrillo, C.; De Miguel, A. A new method for phenotyping red blood cells using microplates. Vox Sang. 1999, 77, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langston, M.M.; Procter, J.L.; Cipolone, K.M.; Stroncek, D.F. Evaluation of the gel system for ABO grouping and D typing. Transfusion 1999, 39, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caesar, A.; Meyer, S.; Trost, N.; Neuenschwander, K.; Geisen, C.; Frey, B.M.; Gassner, C.; Schwind, P. A uniform method for the simultaneous blood group phenotyping of Fya, Fyb, Jka, Jkb, S, s̅, P1, k applying lateral flow technique. Vox Sang. 2018, 113, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huet, M.; Cubizolles, M.; Buhot, A. Real time observation and automated measurement of red blood cells agglutination inside a passive microfluidic biochip containing embedded reagents. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makulska, S.; Jakiela, S.; Garstecki, P. A micro-rheological method for determination of blood type. Lab. Chip 2013, 13, 2796–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, J.; Brakke, K.A.; Furlani, E.P.; Karampelas, I.H.; Poher, V.; Gosselin, D.; Cubizolles, M.; Pouteau, P. Whole blood spontaneous capillary flow in narrow V-groove microchannels. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Boynard, M.; Cokelet, G.C.; Connes, P.; Cooke, B.M.; Forconi, S.; Liao, F.; Hardeman, M.R.; Jung, F.; Meiselman, H.J.; et al. New guidelines for hemorheological laboratory techniques. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2009, 42, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachel, J.; Plapp, F. Bedside blood grouping. Med. Lab. Sci. 1990, 47, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tian, J.; Cao, R.; Guan, L.; Shen, W. A low-cost forward and reverse blood typing device—A blood sample is all you need to perform an assay. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballerini, D.R.; Li, X.; Shen, W. An inexpensive thread-based system for simple and rapid blood grouping. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, T.R.; Runyon, M.K.; Pothiawala, M.; Ismagilov, R.F. ABO, D blood typing and subtyping using plug-based microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6190–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Artemiou, A.; Minerick, A.R. Direct current insulator-based dielectrophoretic characterization of erythrocytes: ABO-Rh human blood typing. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2530–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Kim, D.S.; Kwon, T.H. Microinjection molded disposable microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for efficient detection of agglutination. Microsyst. Technol. 2009, 15, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plapp, F.; Rachel, J.; Sinor, L. Dipsticks for determining ABO blood groups. Lancet 1986, 327, 1465–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tamimi, M.; Shen, W.; Zeineddine, R.; Tran, H.; Garnier, G. Validation of paper-based assay for rapid blood typing. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Tian, J.; Cao, R.; Li, M.; Cai, Z.; Shen, W. Barcode-like paper sensor for smartphone diagnostics: An application of blood typing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11362–11367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tian, J.; Al-Tamimi, M.; Shen, W. Paper-based blood typing device that reports patient’s blood type “in writing”. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5497–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noiphung, J.; Talalak, K.; Hongwarittorrn, I.; Pupinyo, N.; Thirabowonkitphithan, P.; Laiwattanapaisal, W. A novel paper-based assay for the simultaneous determination of Rh typing and forward and reverse ABO blood groups. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeow, N.; McLiesh, H.; Garnier, G. Indirect antiglobulin paper test for red blood cell antigen typing by flow-through method. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 4645–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Huang, Y.-T.; Chou, H.-H.; Wang, C.-P.; Chen, C.-F. Rapid and inexpensive blood typing on thermoplastic chips. Lab. Chip 2015, 15, 4533–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Pan, T. Manually operatable on-chip bistable pneumatic microstructures for microfluidic manipulations. Lab. Chip 2014, 14, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneman, E.A.; Cobleigh, R.; Avrunin, G.S.; Clarke, L.A.; Osterweil, L.J.; Henneman, P.L. Designing property specifications to improve the safety of the blood transfusion process. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2008, 22, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhre, B.A.; McRuer, D. Human error—A significant cause of transfusion mortality. Transfusion 2000, 40, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrière, K.; Rouleau, A.; Gaiffe, O.; Fertey, J.; Morel, P.; Bourcier, V.; Pieralli, C.; Boireau, W.; Pazart, L.; Wacogne, B. Biochip technology applied to an automated ABO compatibility test at the patient bedside. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, A.; Carvalho, V.; Soares, F.; Leão, C.P. Characterization of blood samples using image processing techniques. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 172, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupin, O.; Wang, C.; Berini, P. Selective capture of human red blood cells based on blood group using long-range surface plasmon waveguides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Then, W.L.; Aguilar, M.-I.; Garnier, G. Quantitative blood group typing using surface plasmon resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huet, M.; Cubizolles, M.; Pouteau, P.; Poher, V.; Buhot, A. D-dimer quantification from autologous red blood cells agglutination by a lens-free imaging device. Proced. Technol. 2017, 27, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kilpatrick, P.K.; Melvin, E.; Velev, O.D. On-chip latex agglutination immunoassay readout by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Lab. Chip 2012, 12, 4279–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, Y.; Lehnert, T.; Gijs, M.A. On-chip immuno-agglutination assay with analyte capture by dynamic manipulation of superparamagnetic beads. Lab. Chip 2009, 9, 3261–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huet, M.; Cubizolles, M.; Buhot, A. Red Blood Cell Agglutination for Blood Typing Within Passive Microfluidic Biochips. High-Throughput 2018, 7, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht7020010
Huet M, Cubizolles M, Buhot A. Red Blood Cell Agglutination for Blood Typing Within Passive Microfluidic Biochips. High-Throughput. 2018; 7(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht7020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuet, Maxime, Myriam Cubizolles, and Arnaud Buhot. 2018. "Red Blood Cell Agglutination for Blood Typing Within Passive Microfluidic Biochips" High-Throughput 7, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht7020010
APA StyleHuet, M., Cubizolles, M., & Buhot, A. (2018). Red Blood Cell Agglutination for Blood Typing Within Passive Microfluidic Biochips. High-Throughput, 7(2), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht7020010