Differential Fluorescent Chemosensing of Antibiotics Using a Luminescent Zn(II) Coordination Polymer Based on a 4-Amino-1,8-naphthalimide Tröger’s Base Fluorophore
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentations
2.3. Synthesis and Characterization of Coordination Polymer TB-Zn-CP
2.4. Fluorescence Sensing Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of TB-Zn-CP
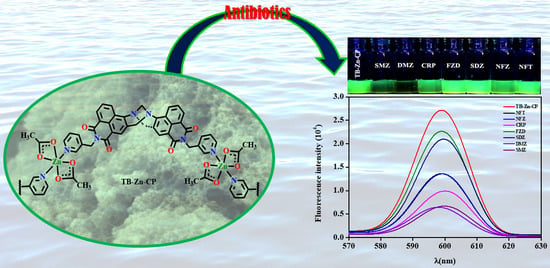
3.2. Fluorescence Sensing of Antibiotics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mesak, L.R.; Miao, V.; Davies, J. Effects of Subinhibitory Concentrations of Antibiotics on SOS and DNA Repair Gene Expression in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3394–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Huang, D.; Qin, L.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Cheng, M.; Ye, S.; Song, B.; Ren, X.; Guo, X. Selective Prepared Carbon Nanomaterials for Advanced Photocatalytic Application in Environmental Pollutant Treatment and Hydrogen Production. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 239, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Shani, V.; Muchtar, E.; Kariv, G.; Robenshtok, E.; Leibovici, L. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Appropriate Empiric Antibiotic Therapy for Sepsis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4851–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, M.; Wang, R.; Hu, Z.; Qin, X. Sorptive Removal of Ionizable Antibiotic Sulfamethazine from Aqueous Solution by Graphene Oxide-Coated Biochar Nanocomposites: Influencing Factors and Mechanism. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J. What Are Antibiotics? Archaic Functions for Modern Activities. Mol. Microbiol. 1990, 4, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, M. Efficacy of Carbonaceous Nanocomposites for Sorbing Ionizable Antibiotic Sulfamethazine from Aqueous Solution. Water Res. 2016, 95, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global Increase and Geographic Convergence in Antibiotic Consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, L.; Zembower, T.R. Antimicrobial Resistance. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. 2020, 30, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, X.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Azam, M.; Al-Resayes, S.I.; Lu, Y.; Sun, W.-Y. Luminescent Cd (II)–Organic Frameworks with Chelating NH 2 Sites for Selective Detection of Fe (III) and Antibiotics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15797–15807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-D.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Long, W.-W.; Sa, R.-J.; Liu, T.-F.; Lv, J. Fluorescent Metal–Organic Framework (MOF) as a Highly Sensitive and Quickly Responsive Chemical Sensor for the Detection of Antibiotics in Simulated Wastewater. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Shi, J.-J.; Ding, B.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-G.; Zhao, X.-J.; Yang, E.-C. A Heterometallic Sodium (i)–Europium (Iii)-Organic Layer Exhibiting Dual-Responsive Luminescent Sensing for Nitrofuran Antibiotics, Cr2O72− and MnO4− Anions. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-G.; Tao, C.-L.; Yu, H.-Q.; Chen, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, G.-P.; Zhao, Z.; Shen, L.; Tang, B.Z. A New Luminescent Metal–Organic Framework Based on Dicarboxyl-Substituted Tetraphenylethene for Efficient Detection of Nitro-Containing Explosives and Antibiotics in Aqueous Media. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 2983–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungroo, N.A.; Neethirajan, S. Biosensors for the Detection of Antibiotics in Poultry Industry—A Review. Biosensors 2014, 4, 472–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-T.; Qu, L.-L.; Li, D.-W.; Song, Q.-X.; Fathi, F.; Long, Y.-T. Rapid and Sensitive In-Situ Detection of Polar Antibiotics in Water Using a Disposable Ag–Graphene Sensor Based on Electrophoretic Preconcentration and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinquina, A.L.; Longo, F.; Anastasi, G.; Giannetti, L.; Cozzani, R. Validation of a High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Oxytetracycline, Tetracycline, Chlortetracycline and Doxycycline in Bovine Milk and Muscle. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 987, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramanayake, P.U.; Tran, T.C.; Hughes, J.G.; Macka, M.; Simpson, N.; Marriott, P.J. Simultaneous Separation of Nitrofuran Antibiotics and Their Metabolites by Using Micellar Electrokinetic Capillary Chromatography. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 4069–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Luiz, M.M.; Vidal, J.L.M.; Romero-Gonzalez, R.; Frenich, A.G. Multi-Residue Determination of Veterinary Drugs in Milk by Ultra-High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1205, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, T.; Miller, P.L.; Strathmann, T.J. Visible-Light-Mediated TiO2 Photocatalysis of Fluoroquinolone Antibacterial Agents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4720–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, O.; Sans, C.; Esplugas, S. Sulfamethoxazole Abatement by Photo-Fenton: Toxicity, Inhibition and Biodegradability Assessment of Intermediates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, H.; Jin, F. Determination of Penicillin G and Its Degradation Products in a Penicillin Production Wastewater Treatment Plant and the Receiving River. Water Res. 2008, 42, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, M.E.; Knapp, M.J. Optical Explosives Detection: From Color Changes to Fluorescence Turn-On. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2543–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. Adsorption of Phenolic Compounds on Low-Cost Adsorbents: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 143, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanderley, M.M.; Wang, C.; Wu, C.-D.; Lin, W. A Chiral Porous Metal–Organic Framework for Highly Sensitive and Enantioselective Fluorescence Sensing of Amino Alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9050–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, S.S.; Desai, A.V.; Ghosh, S.K. A Fluorescent Metal–Organic Framework for Highly Selective Detection of Nitro Explosives in the Aqueous Phase. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8915–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, R.; Wang, C.; Lin, W. Pre-Concentration and Energy Transfer Enable the Efficient Luminescence Sensing of Transition Metal Ions by Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16996–16999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yue, Y.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. Luminescent Functional Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1126–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreno, L.E.; Leong, K.; Farha, O.K.; Allendorf, M.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Hupp, J.T. Metal–Organic Framework Materials as Chemical Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1105–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Voorde, B.; Bueken, B.; Denayer, J.; De Vos, D. Adsorptive Separation on Metal–Organic Frameworks in the Liquid Phase. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5766–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wen, H.-M.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Tyagi, M.; Yildirim, T.; Zhou, W.; Chen, B. A Porous Metal–Organic Framework with Dynamic Pyrimidine Groups Exhibiting Record High Methane Storage Working Capacity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6207–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; Akkaya, E.U.; Yoon, J.; James, T.D. Fluorescent Chemosensors: The Past, Present and Future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7105–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugaraju, S.; Mukherjee, P.S. π-Electron Rich Small Molecule Sensors for the Recognition of Nitroaromatics. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16014–16032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y. Fluorescence Based Explosive Detection: From Mechanisms to Sensory Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8019–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugaraju, S.; Mukherjee, P.S. Self-assembled Discrete Molecules for Sensing Nitroaromatics. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 6656–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbas-Cakmak, S.; Kolemen, S.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; James, T.D.; Yoon, J.; Akkaya, E.U. Molecular Logic Gates: The Past, Present and Future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2228–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, M.P.; Park, H.J.; Prasad, T.K.; Lim, D.-W. Hydrogen Storage in Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 782–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lv, X.-L.; Feng, D.; Xie, L.-H.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.-R.; Zhou, H.-C. Highly Stable Zr (IV)-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Detection and Removal of Antibiotics and Organic Explosives in Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6204–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, W.P.; Mukherjee, S.; Rudd, N.D.; Desai, A.V.; Li, J.; Ghosh, S.K. Metal–Organic Frameworks: Functional Luminescent and Photonic Materials for Sensing Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3242–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, M.; O’Keeffe, M.; Eddaoudi, M. Reticular Chemistry 3.2: Typical Minimal Edge-Transitive Derived and Related Nets for the Design and Synthesis of Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8039–8065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Kosinova, M.; Fedin, V.P.; Gao, E. A Water-stable Lanthanide Coordination Polymer as Multicenter Platform for Ratiometric Luminescent Sensing Antibiotics. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Bai, J.; Huo, Y.; Ning, B.; Peng, Y.; Li, S.; Han, D.; Kang, W.; Gao, Z. A Zirconium-Porphyrin MOF-Based Ratiometric Fluorescent Biosensor for Rapid and Ultrasensitive Detection of Chloramphenicol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 149, 111801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Fan, R.; Zheng, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, W.; Sun, T.; Gai, S.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y. Dual-Emitting Dye-CDs@ MOFs for Selective and Sensitive Identification of Antibiotics and MnO4− in Water. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 15057–15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.-Q.; Zhou, Q.-S.; Zhang, H.-W.; Zhang, W.-W.; Lu, D.-Q.; Guo, M.-T.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, F.; He, H. Design and Construction of a Metal–Organic Framework as an Efficient Luminescent Sensor for Detecting Antibiotics. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, X.-Y.; Cheng, C.; Shao, Z.-S.; Wang, H.-S. Strategies to Fabricate Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Based Luminescent Sensing Platforms. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 10743–10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, C.S.; Máille, G.M.Ó.; Byrne, K.; Schmitt, W.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Tetraarylpyrrolo[3,2-b]Pyrroles as Versatile and Responsive Fluorescent Linkers in Metal–Organic Frameworks. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 10080–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugaraju, S.; Dabadie, C.; Byrne, K.; Savyasachi, A.J.; Umadevi, D.; Schmitt, W.; Kitchen, J.A.; Gunnlaugsson, T. A Supramolecular Tröger’s Base Derived Coordination Zinc Polymer for Fluorescent Sensing of Phenolic-Nitroaromatic Explosives in Water. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, N.D.; Wang, H.; Fuentes-Fernandez, E.M.A.; Teat, S.J.; Chen, F.; Hall, G.; Chabal, Y.J.; Li, J. Highly Efficient Luminescent Metal–Organic Framework for the Simultaneous Detection and Removal of Heavy Metals from Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30294–30303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, W.-J.; Guo, A.; Zhao, F.-Y.; Liu, H.; Ruan, W.-J. Coordination Polymer Nanoarchitecture for Nitroaromatic Sensing by Static Quenching Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 28544–28550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.V.; Inamdar, A.I.; Ghosh, S.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Manna, B. Exploitation of Guest Accessible Aliphatic Amine Functionality of a Metal Organic Framework for Selective Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (TNP) in Water. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 4627–4634. [Google Scholar]
- Joarder, B.; Desai, A.V.; Samanta, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Selective and Sensitive Aqueous-phase Detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP) by an Amine-functionalized Metal–Organic Framework. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivy, M.A.; Gallagher, L.T.; Ellington, A.D.; Anslyn, E. V Exploration of Plasticizer and Plastic Explosive Detection and Differentiation with Serum Albumin Cross-Reactive Arrays. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.-Q.; Qin, C.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Wu, X.-S.; Yang, L.; Shao, K.-Z.; Su, Z.-M. Spontaneous Chiral Resolution of a Rare 3D Self-Penetration Coordination Polymer for Sensitive Aqueous-Phase Detection of Picric Acid. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 18386–18394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, S.S.; Desai, A.V.; Samanta, P.; Ghosh, S.K. Aqueous Phase Selective Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol Using a Fluorescent Metal–Organic Framework with a Pendant Recognition Site. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 15175–15180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bright, S.A.; Smith, J.A.; Burgeat, J.; Martinez-Calvo, M.; Williams, D.C.; Kelly, J.M.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Supramolecular Approach to Enantioselective DNA Recognition Using Enantiomerically Resolved Cationic 4-Amino-1,8-naphthalimide-Based Tröger’s Bases. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 9272–9283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veale, E.B.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Synthesis, Photophysical, and DNA Binding Studies of Fluorescent Troger’s Base Derived 4-Amino-1,8-naphthalimide Supramolecular Clefts. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 5513–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.; Bright, S.A.; Poynton, F.E.; McCabe, T.; Kitchen, J.A.; Veale, E.B.; Williams, D.C.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Synthesis, Photophysical and Cytotoxicity Evaluations of DNA Targeting Agents Based on 3-Amino-1,8-naphthalimide Derived Tröger’s Bases. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 6610–6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Kitchen, J.A.; Bright, S.A.; O’Brien, J.E.; Williams, D.C.; Kelly, J.M.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Synthesis, Spectroscopic and Biological Studies of a Fluorescent Pt (II)(Terpy) Based 1,8-Naphthalimide Conjugate as a DNA Targeting Agent. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8522–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veale, E.B.; Frimannsson, D.O.; Lawler, M.; Gunnlaugsson, T. 4-Amino-1,8-Naphthalimide-Based Troger’s Bases as High Affinity DNA Targeting Fluorescent Supramolecular Scaffolds. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4040–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, B.; Li, W.; Zhao, J.; Sun, S.; Pang, Y. “ICT-Not-Quenching” near Infrared Ratiometric Fluorescent Detection of Picric Acid in Aqueous Media. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4764–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovitt, J.I.; Umadevi, D.; Raja Lakshmi, P.; Twamley, B.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; Shanmugaraju, S. Synthesis, Structural Characterization, Antibiotics Sensing and Coordination Chemistry of a Fluorescent 4-Amino-1,8-Naphthalimide Tröger’s Base Supramolecular Scaffold. Supramol. Chem. 2020, 32, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, P.R.; Nanjan, P.; Kannan, S.; Shanmugaraju, S. Recent Advances in Luminescent Metal–Organic Frameworks (LMOFs) Based Fluorescent Sensors for Antibiotics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 435, 213793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Rana, A.; Biswas, S. Metal–Organic Framework-Based Fluorescent Sensors for the Detection of Pharmaceutically Active Compounds. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 99–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmughan, A.; Lakshmi, P.R.; Umadevi, D.; Shanmugaraju, S. Discriminative Fluorescent Sensing of Nitro-Antibiotics at Ppb Level Using N-Phenyl-Amino-1,8-Naphthalimides Chemosensors. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Antibiotics | KSV (×104 M−1) |
|---|---|
| DMZ | 2.86 |
| SMZ | 2.61 |
| CRP | 2.85 |
| NFT | 0.58 |
| NFZ | 0.14 |
| SDZ | 0.57 |
| FZD | 0.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, P.; Noushija, M.K.; Shanmugaraju, S. Differential Fluorescent Chemosensing of Antibiotics Using a Luminescent Zn(II) Coordination Polymer Based on a 4-Amino-1,8-naphthalimide Tröger’s Base Fluorophore. Chemistry 2024, 6, 237-248. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry6010011
Patel P, Noushija MK, Shanmugaraju S. Differential Fluorescent Chemosensing of Antibiotics Using a Luminescent Zn(II) Coordination Polymer Based on a 4-Amino-1,8-naphthalimide Tröger’s Base Fluorophore. Chemistry. 2024; 6(1):237-248. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry6010011
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Purti, Mannanthara Kunhumon Noushija, and Sankarasekaran Shanmugaraju. 2024. "Differential Fluorescent Chemosensing of Antibiotics Using a Luminescent Zn(II) Coordination Polymer Based on a 4-Amino-1,8-naphthalimide Tröger’s Base Fluorophore" Chemistry 6, no. 1: 237-248. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry6010011
APA StylePatel, P., Noushija, M. K., & Shanmugaraju, S. (2024). Differential Fluorescent Chemosensing of Antibiotics Using a Luminescent Zn(II) Coordination Polymer Based on a 4-Amino-1,8-naphthalimide Tröger’s Base Fluorophore. Chemistry, 6(1), 237-248. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry6010011