Stimuli-Sensitive Pyrenylated Hydrogels as Optical Sensing Platform for Multiple Metal Ions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Gelation Studies
2.3. FT-IR Spectroscopy
2.4. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.5. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.6. Rheological Studies
2.7. Preparation of the Metal Ion Solution
2.8. Preparation of Test Strips
2.9. Analysis of Metal Ions in Different Water Samples
2.10. Stoichiometry Determination using Job Plot
2.11. Binding Constant Calculation
2.12. Detection Limit Determination
3. Results and Discussion
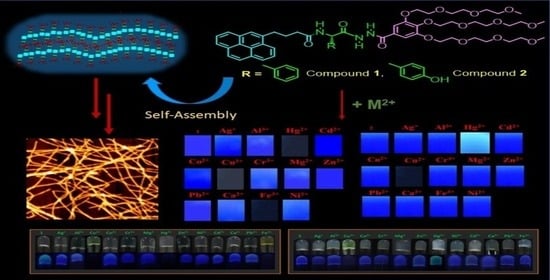
3.1. Design and Synthesis of Hydrogelators 1 and 2
3.2. Interaction of Metal Ions with Compounds 1 and 2
3.3. Mechanistic Investigation of Metal Ions Binding
3.4. Application in Analyzing Real-Life Samples
3.4.1. Detection of Metal Ions in Water Samples
3.4.2. Detection of Metal Ions Using Dye-Coated Paper Strips
3.5. Gelation Ability of Compounds 1 and 2
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, L.; Qiu, L.; Sheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Deng, L.; Li, X.; Bradley, M.; Zhang, R. Biodegradable pH-Responsive Hydrogels for Controlled dual-drug release. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Lu, Z.; Chester, S.A.; Lee, H. Micro 3D Printing of a Temperature-Responsive Hydrogel Using Projection Micro-Stereolithography. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.-W.; Liu, Y.; Xie, M.; Wang, J.; Yan, X.-W.; Li, Z.; Dong, W.-G.; Huang, W.-H. Near-Infrared Light-Responsive Hydrogel for Specific Recognition and Photothermal Site-Release of Circulating Tumor Cells. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6201–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrozc, R.; Plazl, I. Development of an Electrically Responsive Hydrogel for Programmable Insitu Immobilization Within a Microfluidic Device. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 6751–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo-Custódio, S.; Gomez-Florit, M.; Tomás, A.R.; Mendes, B.B.; Babo, P.S.; Mithieux, S.M.; Weiss, A.; Domingues, R.M.A.; Reis, R.L.; Gomes, M.E. Injectable and Magnetic Responsive Hydrogels with Bioinspired Ordered Structures. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswakarma, D.; Dey, N.; Bhattacharya, S. A Biocompatible Aydrogel as a Template for Oxidative Decomposition Reactions: A Chemodosimetric Analysis and In-vitro Imaging of Hypochlorite. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.D.; Mura, C.; Lampe, K.J. Stimuli-Responsive, Pentapeptide, Nanofiber Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4886–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswakarma, D.; Dey, N.; Bhattacharya, S. Thermoresponsive Sustainable Release of Anticancer Drugs using Cyto-compatible Pyrenylated Hydrogel as Vehicle. J. Chem. Sci. 2023, 135, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapiot, F.; Menuel, S.; Monflier, E. Thermoresponsive Hydrogels in Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Han, L.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Pan, L.; Xu, M. Multiple Stimuli-Responsive and Identifiable Zwitterionic Ionic Conductive Hydrogel for Bionic Electronic Skin. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 2000239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswakarma, D.; Dey, N.; Bhattacharya, S. Thermo-responsive Supramolecular Hydrogel that Senses Cholera Toxin via Color-changing Response. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 7789–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemitsu, H.; Hamachi, I. Supramolecular Assemblies Responsive to Biomolecules toward Biological Applications. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 2026–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versluis, F.; van Esch, J.H.; Eelkema, R. Synthetic Self-Assembled Materials in Biological Environments. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4576–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, J.; Xu, B. Supramolecular Hydrogelators and Hydrogels: From Soft Matter to Molecular Biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13165–13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigemitsu, H.; Hamachi, I. Design Strategies of Stimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Hydrogels Relying on Structural Analyses and Cell-Mimicking Approaches. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswakarma, D.; Dey, N.; Bhattacharya, S. A Two-Component Charge Transfer Hydrogel with Excellent Sensitivity Towards the Microenvironment: A Responsive Platform for Biogenic Thiols. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 9882–9889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Morimoto, Y.; Lee, Y.-M.; Nam, W.; Fukuzumi, S. Metal Ion Effect on the Switch of Mechanism from Direct Oxygen Transfer to Metal Ion-Coupled Electron Transfer in the Sulfoxidation of Thioanisoles by a Non-Heme Iron (IV)-Oxo Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5236–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Lee, H.J. Redox-Active Metal Ions and Amyloid-Degrading Enzymes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, Mechanism and Health Effects of Some Heavy Metals. Inter Discip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, K.P.; Young, A.M.; Palmer, A.E. Fluorescent Sensors for Measuring Metal Ions in Living Systems. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4564–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, B.; Peng, X. Fluorescent, MRI, and Colorimetric Chemical Sensors for the First-Row d-Block Metal Ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4337–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.K.; Dey, N.; Kumari, N.; Biswakarma, D.; Bhattacharya, S. Multimodal Ion Sensing by Structurally Simple Pyridine-End Oligo p-Phenylenevinylenes for Sustainable Detection of Toxic Industrial Waste. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12304–12314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.Z.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, C. Fluorescence Array-Based Sensing of Metal Ions Using Conjugated Polyelectrolytes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6882–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.Y.G. Differentiation and Determination of Metal Ions Using Fluorescent Sensor Array Based on Carbon Nanodots. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 246, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswakarma, D.; Dey, N.; Bhattacharya, S. Molecular design of amphiphiles for Microenvironment-Sensitive Kinetically Controlled Gelation and Their Utility in Probing Alcohol Contents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 615, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, N.; Kınal, A.; Yener, N.; Yavas, A.; Güloglu, P. A DFT and TDDFT Investigation of Interactions Between Pyrene and Amino Acids with Cyclic Side Chains. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2016, 1081, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, H.; Williams, R.J.P. The stability of Transition-Metal Complexes. J. Chem. Soc. 1953, 637, 3192–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, N.; Biswakarma, D.; Bhattacharya, S. Metal Complex as an Optical Sensing Platform for Rapid Multimodal Recognition of a Pathogenic Biomarker in Real-Life Samples. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswakarma, D.; Dey, N.; Bhagat, D.; Bhattacharya, S. Switchable Luminescent Probe for Trace-Level Detection of the Spodoptera litura Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus via a Color-Changing Response. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biswakarma, D.; Dey, N.; Bhattacharya, S. Stimuli-Sensitive Pyrenylated Hydrogels as Optical Sensing Platform for Multiple Metal Ions. Organics 2023, 4, 447-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030032
Biswakarma D, Dey N, Bhattacharya S. Stimuli-Sensitive Pyrenylated Hydrogels as Optical Sensing Platform for Multiple Metal Ions. Organics. 2023; 4(3):447-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiswakarma, Dipen, Nilanjan Dey, and Santanu Bhattacharya. 2023. "Stimuli-Sensitive Pyrenylated Hydrogels as Optical Sensing Platform for Multiple Metal Ions" Organics 4, no. 3: 447-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030032
APA StyleBiswakarma, D., Dey, N., & Bhattacharya, S. (2023). Stimuli-Sensitive Pyrenylated Hydrogels as Optical Sensing Platform for Multiple Metal Ions. Organics, 4(3), 447-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/org4030032