Influencing the Shape Recovery and Thermomechanical Properties of 3DP PLA Using Smart Textile and Boehmite Alumina and Thermochromic Dye Modifiers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
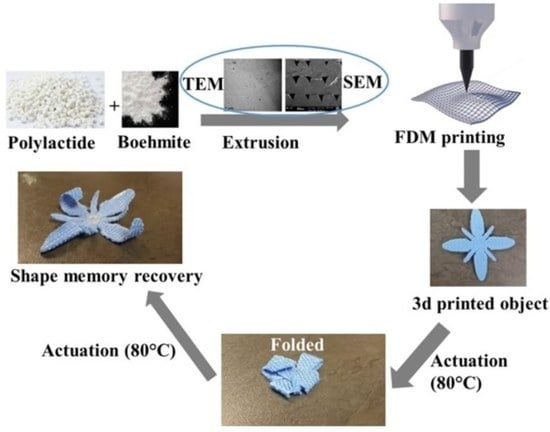
2.2. Preparations of the Samples
2.3. Techniques Used
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Properties of the Produced Filaments
3.2. Shape Memory Properties of Neat and Modified PLA
3.3. The Utility of Smart Textile and PLA Modification in Controlling the Rate and Extent of Shape Recovery of 3DP Objects
3.4. Morphology and Mechanical Properties of the 3D-Printed Components
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leng, J.; Lan, X.; Liu, Y.; Du, S. Shape-memory polymers and their composites: Stimulus methods and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2011, 56, 1077–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Lan, X.; Leng, J.; Du, S. Review of electro-active shape-memory polymer composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 2064–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leist, S.K.; Gao, D.; Chiou, R.; Zhou, J. Investigating the shape memory properties of 4D printed polylactic acid (PLA) and the concept of 4D printing onto nylon fabrics for the creation of smart textiles. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2017, 12, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, B. 3-D printing: The new industrial revolution. Bus. Horiz. 2012, 55, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Liu, P.; Mokasdar, A.; Hou, L. Additive manufacturing and its societal impact: A literature review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 67, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Reddy, S.K.; Usha, C.; Naulakha, N.K.; Adithyakumar, C.R.; Reddy, M.L.K. Advancements in the Research of 4D Printing-A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 376, 012123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Huete, N.; Axpe, E.; Cuevas, J.M.; Mérida, D.; Laza, J.M.; García, J.Á.; Vilas, J.L.; Plazaola, F.; León, L.M. In situ measurements of free volume during recovery process of a shape memory polymer. Polymer 2017, 109, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, H.; Liu, L.; Leng, J. Shape memory polymers and their composites in aerospace applications: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, F.; Hassani, N.S.M.M.; Liu, X.; Ni, J. A review of 4D printing. Mater. Des. 2017, 122, 42–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.C.; Chakraborty, S.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Mohammed, Z. 4D Printing of Shape Memory Materials for Textiles: Mechanism, Mathematical Modeling, and Challenges. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jiménez, A.; Bernal-Ortega, P.; Salamanca, F.M.; Valentin, J.L. Shape-Memory Composites Based on Ionic Elastomers. Polymers 2022, 14, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, P.K.; Yang, J.-M.; Chang, Y.-H. Water-induced shape memory behavior of poly (vinyl alcohol) and p-coumaric acid-modified water-soluble chitosan blended membrane. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.M.; Panda, P.K.; Jie, C.J.; Dash, P.; Chang, Y.H. Poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan/sodium alginate composite blended membrane: Preparation, characterization, and water-induced shape memory phenomenon. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K.; Dash, P.; Biswal, A.K.; Chang, Y.-H.; Misra, P.K.; Yang, J.-M. Synthesis and Characterization of Modified Poly(vinyl alcohol) Membrane and Study of Its Enhanced Water-Induced Shape-Memory Behavior. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 3409–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-C.; Wan, Y.; Nam, R.; Chu, M.; Naguib, H.E. 4D-printed hybrids with localized shape memory behaviour: Implementation in a functionally graded structure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Arya, S.; Gupta, V.; Furukawa, H.; Khosla, A. 4D printing: Fundamentals, materials, applications and challenges. Polymer 2021, 228, 123926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.; Lafont, U.; Hołyńska, M.; Semprimoschnig, C. Additive manufacturing—A review of 4D printing and future applications. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 606–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qin, H.; Mather, P.T. Review of progress in shape-memory polymers. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1543–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrpouya, M.; Azizi, A.; Janbaz, S.; Gisario, A. Investigation on the functionality of thermoresponsive origami structures. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 2000296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, L.; Zeng, C.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. 4D printed anisotropic structures with tailored mechanical behaviors and shape memory effects. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 186, 107935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, D.; Zhang, K.; Hu, G. Pattern transformation of heat-shrinkable polymer by three-dimensional (3D) printing technique. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep08936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Stimulus methods of multi-functional shape memory polymer nanocomposites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 100, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girifalco, L.A.; Hodak, M.; Lee, R.S. Carbon nanotubes, buckyballs, ropes, and a universal graphitic potential. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 13104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, G.I.; Larsen, M.B.; Ganter, M.A.; Storti, D.W.; Boydston, A.J. 3D-printed mechanochromic materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Gou, J.J.; Leng, J.; Du, S. Surface coating of multi-walled carbon nanotube nanopaper on shape-memory polymer for multifunctionalization. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, K.; Lan, X. Study on the activation of styrene-based shape memory polymer by medium-infrared laser light. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 111905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malwela, T.; Khumalo, V.M.; Salehiyan, R.; Ray, S.S. Characterization of polypropylene/polystyrene boehmite alumina nanocomposites: Impact of filler surface modification on the mechanical, thermal, and rheological properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makwakwa, D.; Ojijo, V.; Bandyopadhyay, J.; Ray, S.S. Flow Characteristics, Mechanical, Thermal, and Thermomechanical Properties, and 3D Printability of Biodegradable Polylactide Containing Boehmite at Different Loadings. Polymers 2021, 13, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, C.; Lievenbrück, M.; Ritter, H. Polymers and Dyes: Developments and Applications. Polymers 2015, 7, 717–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Ray, S.S.; Chapple, S.; Wesley-Smith, J. Mechanical, Thermal, and Fire Properties of Biodegradable Polylactide/Boehmite Alumina Composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 6083–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, T.; Kou, J.; Xu, C.; Gao, E. Effect of Na2CO3 and CaCO3 on coreduction roasting of blast furnace dust and high-phosphorus oolitic hematite. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2017, 32, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, K.; Kaseem, M.; Yang, H.; Deri, F.; Ko, Y. Properties and medical applications of polylactic acid: A review. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, M.S.; Rahaman, M.H.; Gafur, M.; Habib, R.; Qadir, M. Preparation and characterization of poly (L-lactic acid)/chitosan/microcrystalline cellulose blends. Chem. Sci. Int. J. 2017, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orasugh, J.T.; Saha, N.R.; Rana, D.; Sarkar, G.; Mollick, M.M.R.; Chattoapadhyay, A.; Mitra, B.C.; Mondal, D.; Ghosh, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, D. Jute cellulose nano-fibrils/hydroxypropylmethylcellulose nanocomposite: A novel material with potential for application in packaging and transdermal drug delivery system. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 112, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, P.; Xia, Y.; Kong, Q. Thermal stability and flame-retardancy mechanism of poly (ethylene terephthalate)/boehmite nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, I.; Ronkay, F.; Lendvai, L. Highly toughened blends of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and natural rubber (NR) for FDM-based 3D printing applications: The effect of composition and infill pattern. Polym. Test. 2021, 99, 107205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlroy, C.; Olmsted, P.D. Deformation of an amorphous polymer during the fused-filament-fabrication method for additive manufacturing. J. Rheol. 2017, 61, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harishanand, K.; Nagabhushana, H.; Nagabhushana, B.; Panda, P.; Gupta, R.; Muruli, M.; Raghavendra, N.; Mahesh, K.V. Comparitive study on mechanical properties of ZnO, ZrO2 and CeO2 nanometal oxides reinforced epoxy composites. Adv. Polym. Sci. Technol. Int. J 2013, 3, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Hingorani, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Ge, Q. Self-healing four-dimensional printing with an ultraviolet curable double-network shape memory polymer system. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10328–10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrpouya, M.; Gisario, A.; Azizi, A.; Barletta, M. Investigation on shape recovery of 3D printed honeycomb sandwich structure. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 3361–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M.; Li, Y. Development and kinetic evaluation of a low-cost temperature-sensitive shape memory polymer for 4-dimensional printing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 4263–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Sample Name | Tcc (°C) | ∆Hcc | Xcc (%) | Tm (°C) | ∆Hm | Xm (%) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat PLA_3dp | 106.7 ± 0.3 | 35.6 ± 1.5 | 36.59 | 167.3 ± 0.4 | 38.0 ± 0.8 | 39.05 | 2.47 |
| BA3_3dp | 106.0 ± 0.7 | 32.3 ± 1.9 | 34.36 | 167.4 ± 0.8 | 37.0 ± 0.6 | 39.68 | 5.32 |
| PLA/Dye_3dp | 107.0 ± 2.2 | 33.6 ± 1.7 | 35.60 | 167.5 ± 0.9 | 36.5 ± 0.3 | 38.67 | 3.07 |
| BA3/Dye_3dp | 109.0 ± 0.5 | 32.7 ± 1.1 | 33.91 | 167.4 ± 0.5 | 40.3 ± 0.9 | 41.79 | 7.88 |
| Sample Name | T0.05 (°C) | Tmax (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Neat PLA | 311.2 | 361.6 |
| Dye | 214.1 | 260.0 |
| BA | 59.0 | 436.0 |
| PLA/dye | 326.3 | 360.0 |
| BA3 | 339.1 | 371.3 |
| BA3/dye | 324.9 | 353.4 |
| PLA_3dp | 330.3 | 360.2 |
| BA3_3dp | 334.0 | 364.4 |
| Sample Name | Modulus (MPa) | Elongation at Break % | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neat PLA | 1470.2 ± 262.79 | 5.70 ± 0.21 | 65.25 ± 20.43 |
| PLA/dye | 1499.0 ± 233.01 | 6.01 ± 0.21 | 69.30 ± 0.91 |
| BA3 | 1652.3 ± 4031 | 7.00 ± 0.07 | 73.05 ± 1.20 |
| Year | Polymers | Conclusions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | PLA | The authors revealed that low temperatures (65 °C) did not result in full shape recovery but did at higher temperatures (75 °C). | [38] |
| 2019 | PCL | The addition of 20 wt.% PCL to the created system, the linear polymer reveals the self-healing capacity to 4D-printed structures, and the improvement of mechanical properties by more than 90%. | [39] |
| 2020 | PLA | PLA revealed a shape recovery ratio of more than 91%, with the existence of water resistance and a shape fixity ratio of more than 99.7% after 20 h at room temperature. | [20] |
| 2020 | PLA | The authors revealed that the optimal recovery ratio can be attained by using higher activations and nozzle temperatures and lower printing speeds. | [40] |
| 2020 | PLA and TPU | When PLA and TPU load is at 80% and 20% weight, the filament revealed the consistent and greatest shape memory characteristics. Maintains good shape fixity and shape recovery ratios, as well as resisting repeated deformation and recovery cycles. PLA has the ability to accelerate and maintain velocity during recovery. | [41] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makwakwa, D.; Motloung, M.P.; Ojijo, V.; Bandyopadhyay, J.; Ray, S.S. Influencing the Shape Recovery and Thermomechanical Properties of 3DP PLA Using Smart Textile and Boehmite Alumina and Thermochromic Dye Modifiers. Macromol 2022, 2, 485-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2030030
Makwakwa D, Motloung MP, Ojijo V, Bandyopadhyay J, Ray SS. Influencing the Shape Recovery and Thermomechanical Properties of 3DP PLA Using Smart Textile and Boehmite Alumina and Thermochromic Dye Modifiers. Macromol. 2022; 2(3):485-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakwakwa, Dimakatso, Mpho Phillip Motloung, Vincent Ojijo, Jayita Bandyopadhyay, and Suprakas Sinha Ray. 2022. "Influencing the Shape Recovery and Thermomechanical Properties of 3DP PLA Using Smart Textile and Boehmite Alumina and Thermochromic Dye Modifiers" Macromol 2, no. 3: 485-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2030030
APA StyleMakwakwa, D., Motloung, M. P., Ojijo, V., Bandyopadhyay, J., & Ray, S. S. (2022). Influencing the Shape Recovery and Thermomechanical Properties of 3DP PLA Using Smart Textile and Boehmite Alumina and Thermochromic Dye Modifiers. Macromol, 2(3), 485-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2030030