An In Vitro Assay to Quantify Effects of Micro- and Nano-Plastics on Human Gene Transcription
Abstract
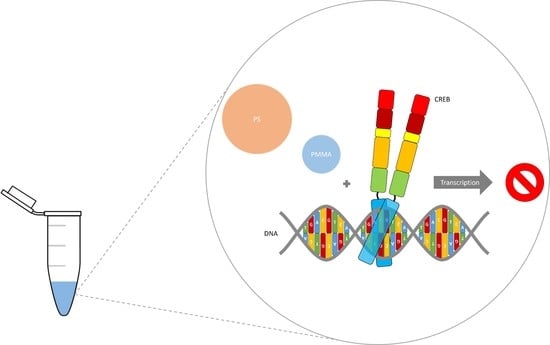
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Purification
2.2. Western Blot
2.3. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
2.4. In Vitro Phosphorylation of CREB with PKA
2.5. In Vitro Transcription Assay
2.6. cDNA Synthesis
2.7. Quantification of Synthezised cDNA
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. CREB Binds Independent of Phosphorylation
3.2. CREB-Mediated Transcription
3.3. Micro- and Nanoplastic In Vitro Transcription
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casillas, G.; Hubbard, B.C.; Telfer, J.; Zarate-Bermudez, M.; Muianga, C.; Zarus, G.M.; Carroll, Y.; Ellis, A.; Hunter, C.M. Microplastics Scoping Review of Environmental and Human Exposure Data. Microplastics 2023, 2, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Huo, Y.; Yang, Y. Microbial Degradation and Valorization of Plastic Wastes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frias, J.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Savino, I.; Locaputo, V.; Uricchio, V.F. A Detailed Review Study on Potential Effects of Microplastics and Additives of Concern on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricciardi, M.; Pironti, C.; Motta, O.; Miele, Y.; Proto, A.; Montano, L. Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment: Occurrence, Persistence, Analysis, and Human Exposure. Water 2021, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdogan, Z.; Guven, B. Microplastics in the environment: A critical review of current understanding and identification of future research needs. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, A.; Ligthart, T.; Boukris, E.; van Harmelen, T. Sources, transport, and accumulation of different types of plastic litter in aquatic environments: A review study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 143, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effect of microplastics in water and aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, S.; Abdull Razis, A.F.; Shaari, K.; Amal, M.N.A.; Saad, M.Z.; Mat Isa, N.; Nazarudin, M.F.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Sutra, J.; Ibrahim, M.A. Microplastics Pollution as an Invisible Potential Threat to Food Safety and Security, Policy Challenges and the Way Forward. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, F.; Cryder, Z.; Huang, D.; Lu, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z.; Brookes, P.C.; Tang, C.; et al. Microplastics in the soil environment: Occurrence, risks, interactions and fate—A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2175–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Cai, H.; Wang, G.; Shi, H. Microplastic Fallout in Different Indoor Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6530–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirt, N.; Body-Malapel, M. Immunotoxicity and intestinal effects of nano- and microplastics: A review of the literature. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandts, I.; Teles, M.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Pereira, M.; Martins, M.; Tort, L.; Oliveira, M. Effects of polymethylmethacrylate nanoplastics on Dicentrarchus labrax. Genomics 2018, 110, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raamsdonk, L.W.D.; van der Zande, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Hoogenboom, R.L.A.P.; Peters, R.J.B.; Groot, M.J.; Peijnenburg, A.A.C.M.; Weesepoel, Y.J.A. Current Insights into Monitoring, Bioaccumulation, and Potential Health Effects of Microplastics Present in the Food Chain. Foods 2020, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heddagaard, F.E.; Møller, P. Hazard assessment of small-size plastic particles: Is the conceptual framework of particle toxicology useful? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, N.H.M.; Kooi, M.; Diepens, N.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Lifetime Accumulation of Microplastic in Children and Adults. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5084–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsperger, A.F.R.M.; Narayana, V.K.B.; Gross, W.; Mohanraj, J.; Thelakkat, M.; Greiner, A.; Schmalz, H.; Kress, H.; Laforsch, C. Environmental exposure enhances the internalization of microplastic particles into cells. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, P.G.; Granner, D.K. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase regulates transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene but not binding of nuclear factors to the cyclic AMP regulatory element. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldave, K. (Ed.) . Progress in Nucleic Acid Research and Molecular Biology, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, G.A.; Montminy, M.R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell 1989, 59, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, G.A.; Menzel, P.; Leonard, J.; Fischer, W.H.; Montminy, M.R. Characterization of motifs which are critical for activity of the cyclic AMP-responsive transcription factor CREB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, S.; Martin, K.J.; Arthur, J.S.C. CREB phosphorylation at Ser133 regulates transcription via distinct mechanisms downstream of cAMP and MAPK signalling. Biochem. J. 2014, 458, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierrat, B.; Correia, J.S.; Mary, J.L.; Tomás-Zuber, M.; Lesslauer, W. RSK-B, a novel ribosomal S6 kinase family member, is a CREB kinase under dominant control of p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38alphaMAPK). J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 29661–29671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, P.; Enslen, H.; Myung, P.S.; Maurer, R.A. Differential activation of CREB by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases type II and type IV involves phosphorylation of a site that negatively regulates activity. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 2527–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chrivia, J.C.; Kwok, R.P.S.; Lamb, N.; Hagiwara, M.; Montminy, M.R.; Goodman, R.H. Phosphorylated CREB binds specifically to the nuclear protein CBP. Nature 1993, 365, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, K.J.; Hendzel, M.J. CBP, a transcriptional coactivator and acetyltransferase. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 79, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonze, B.E.; Ginty, D.D. Function and Regulation of CREB Family Transcription Factors in the Nervous System. Neuron 2002, 35, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramsperger, A.; Jasinski, J.; Völkl, M.; Witzmann, T.; Meinhart, M.; Jérôme, V.; Kretschmer, W.; Freitag, R.; Senker, J.; Fery, A.; et al. Supposedly identical microplastic particles substantially differ in their material properties influencing particle-cell interactions and cellular responses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 425, 127961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.K.; Gonzalez, G.A.; Biggs, W.H.; Montminy, M.R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature 1988, 334, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindle, P.; Linke, S.; Montminy, M. Protein-kinase-A-dependent activator in transcription factor CREB reveals new role for CREM repressors. Nature 1993, 364, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.P.; Bächinger, H.P.; Goodman, R.H.; Brennan, R.G. Analysis of the structural properties of cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) and phosphorylated CREB. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 13716–13723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Gopal, V.K.; Quinn, P.G. cAMP Response Element-binding Protein (CREB) Interacts with Transcription Factors IIB and IID. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 17488–17493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-A.; Lu, J.; Quinn, P.G. Distinct cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) domains stimulate different steps in a concerted mechanism of transcription activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11292–11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruening, W.; Giasson, B.; Mushynski, W.; Durham, H.D. Activation of stress-activated MAP protein kinases up-regulates expression of transgenes driven by the cytomegalovirus immediate/early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.J.; Wu, A.W.; Andrews, J.I.; McGonagill, P.W.; Tibesar, E.E.; Meier, J.L. Reversal of Human Cytomegalovirus Major Immediate-Early Enhancer/Promoter Silencing in Quiescently Infected Cells via the Cyclic AMP Signaling Pathway. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6669–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Everaert, G.; Van Cauwenberghe, L.; De Rijcke, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Mees, J.; Vandegehuchte, M.; Janssen, C.R. Risk assessment of microplastics in the ocean: Modelling approach and first conclusions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.P.d.; Gaylarde, C.; Pompermayer, F.C.; Lima, L.d.S.; Delgado, J.d.F.; Scott, D.; Neves, C.V.; Vieira, K.S.; Baptista Neto, J.A.; Fonseca, E.M. The Complex Dynamics of Microplastic Migration through Different Aquatic Environments: Subsidies for a Better Understanding of Its Environmental Dispersion. Microplastics 2023, 2, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinibilir, M.; Eryalçın, K.M.; Kideys, A.E. Effect of Polystyrene Microplastics in Different Diet Combinations on Survival, Growth and Reproduction Rates of the Water Flea (Daphnia magna). Microplastics 2023, 2, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstein, I.V.; Hensel, F.; Gomiero, A.; Iordachescu, L.; Vianello, A.; Wittgren, H.B.; Vollertsen, J. Drinking plastics?—Quantification and qualification of microplastics in drinking water distribution systems by µFTIR and Py-GCMS. Water Res. 2020, 188, 116519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironti, C.; Ricciardi, M.; Motta, O.; Miele, Y.; Proto, A.; Montano, L. Microplastics in the Environment: Intake through the Food Web, Human Exposure and Toxicological Effects. Toxics 2021, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jensen, U.B.; Jensen, G.V.; Shipovskov, S.; Balakrishnan, V.S.; Otzen, D.; Pedersen, J.S.; Besenbacher, F.; Sutherland, D.S. Soft Interactions at Nanoparticles Alter Protein Function and Conformation in a Size Dependent Manner. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4985–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pellegrino, A.; Danne, D.; Weigel, C.; Seitz, H. An In Vitro Assay to Quantify Effects of Micro- and Nano-Plastics on Human Gene Transcription. Microplastics 2023, 2, 122-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics2010009
Pellegrino A, Danne D, Weigel C, Seitz H. An In Vitro Assay to Quantify Effects of Micro- and Nano-Plastics on Human Gene Transcription. Microplastics. 2023; 2(1):122-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics2010009
Chicago/Turabian StylePellegrino, Antonio, Denise Danne, Christoph Weigel, and Harald Seitz. 2023. "An In Vitro Assay to Quantify Effects of Micro- and Nano-Plastics on Human Gene Transcription" Microplastics 2, no. 1: 122-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics2010009
APA StylePellegrino, A., Danne, D., Weigel, C., & Seitz, H. (2023). An In Vitro Assay to Quantify Effects of Micro- and Nano-Plastics on Human Gene Transcription. Microplastics, 2(1), 122-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics2010009