Analysis of Dynamics of Railway Vehicles
(Closed)
A project collection of Applied Sciences (ISSN 2076-3417). This project collection belongs to the section "Transportation and Future Mobility".
Papers displayed on this page all arise from the same project. Editorial decisions were made independently of project staff and handled by the Editor-in-Chief or qualified Editorial Board members.
Viewed by 29667
Share This Project Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Suchao Xie
Prof. Dr. Suchao Xie
 Prof. Dr. Suchao Xie
Prof. Dr. Suchao Xie
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Interests: railway vehicle dynamics; vehicle structure analysis; passive safety; Prognostic and Health Management (PHM); acoustic metamaterials
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Project Overview
Dear Colleagues,
With the developments in the field of rail transportation, rail transportation dynamics is attracting increased attention. In order to help high-speed trains operate with high speed, high load, low noise, and safety, many researchers have conducted research on system dynamics, dynamic performance, longitudinal dynamics, impact dynamics, structural damage, vibration and noise reduction, and many other fields of high-speed trains. In recent decades, researchers have continuously improved the dynamics of high-speed trains by optimizing train bodies, improving traction motors, strengthening vibration damping systems, and applying new materials, but people still want high-speed trains to be faster, more environmentally friendly, more comfortable, and safer. Therefore, many researchers strive to further improve the dynamics of trains by introducing new materials and new technical means. This Special Issue will discuss recent efforts and research advances achieved in high-speed train dynamics. Topics of interest in this Special Issue include but are not limited to:
- Train system dynamics;
- Train aerodynamics;
- Train impact dynamics;
- Train-rail performance matching;
- Structural damage;
- Pantograph network relations;
- Noise control;
- Structural vibration;
- Train longitudinal dynamics.
Prof. Dr. Suchao Xie
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Applied Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- rail vehicle
- system dynamics
- bionic structure
- noise
- vibration
- traction motor
- composites material
- aerodynamics
- passive safety
- pantographs
- wheel–rail relationship
Published Papers (16 papers)
Open AccessEditorial
Special Issue on Dynamics of Railway Vehicles
by
Suchao Xie
Viewed by 235
Abstract
High-speed Railway Vehicle systems have become integral to modern transportation infrastructure, offering a rapid, efficient, and environmentally friendly travel option [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
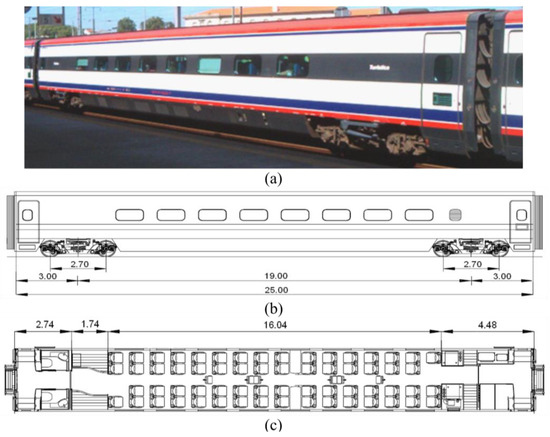
A New Car-Body Structure Design for High-Speed EMUs Based on the Topology Optimization Method
by
Chunyan Liu, Kai Ma, Tao Zhu, Haoxu Ding, Mou Sun and Pingbo Wu
Viewed by 1359
Abstract
In recent years, the research and development of high-speed trains has advanced rapidly. The main development trends of high-speed trains are higher speeds, lower energy consumption, higher safety, and better environmental protection. The realization of a lightweight high-speed car body is one of
[...] Read more.
In recent years, the research and development of high-speed trains has advanced rapidly. The main development trends of high-speed trains are higher speeds, lower energy consumption, higher safety, and better environmental protection. The realization of a lightweight high-speed car body is one of the key features in the development trend of high-speed trains. Firstly, the basic dimensions of the car body’s geometric model are determined according to the external dimensions of the body of a CRH EMU, and the specific topology optimization design domain is selected to establish the finite element analysis model; secondly, the strength and modal analyses of the topology optimization design domain are carried out to check the accuracy of the design domain and provide a comparative analysis for subsequent design. Then, the variables, constraints, and objective functions of the topology optimization design are determined to establish the mathematical model of topology optimization, and the design domain is calculated for topology optimization under single and multiple conditions, respectively. Finally, based on the topology optimization calculation results, truss-type reconstruction modeling is carried out for the car body’s side walls, roof, underframe, end walls, and other parts. Compared with the conventional EMU body structure, the weight of the reconstructed body structure is reduced by about 18%. The results of the finite element analysis of the reconstructed car-body structure prove the reliability and safety of the structure, indicating that the reconstructed car-body scheme meets the corresponding performance indicators.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
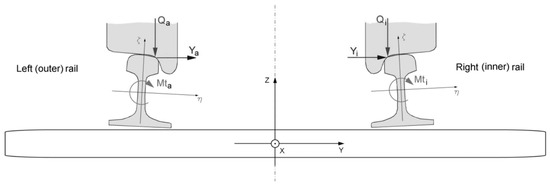
Analysis of Lateral Forces for Assessment of Safety against Derailment of the Specialized Train Composition for the Transportation of Long Rails
by
Valeri Stoilov, Petko Sinapov, Svetoslav Slavchev, Vladislav Maznichki and Sanel Purgic
Viewed by 1055
Abstract
This study proposes a theoretical method for evaluating the “safety against derailment” indicator of a specialized train composition for the transportation of very long rails. A composition of nine wagons, suitable for the transportation of rails with a length of 120 m in
[...] Read more.
This study proposes a theoretical method for evaluating the “safety against derailment” indicator of a specialized train composition for the transportation of very long rails. A composition of nine wagons, suitable for the transportation of rails with a length of 120 m in three layers, is considered. For the remaining recommended rail lengths, the number of wagons is reduced or increased, with the calculation model being modified depending on the required configuration. When the composition is in a curve with the minimum radius (R = 150 m), the rails bend, and some of them come into contact with the vertical stanchions of the wagon and cause additional lateral forces. These forces are then transferred through the wagon body, central pivot, bogie frame, and wheels and act on the wheel–rail contact points. They could potentially lead to derailment of the train composition. The goal of this study is to determine the additional lateral forces that arise because of the bent rails. For the purposes of this study, the finite element method was used. Based on the displacements of the support points of the rails (caused by the geometry of the curve), the bending line of the elastic load is determined and the forces in the supports are calculated. The resulting forces are considered when determining the derailment safety criterion. The analysis of the results shows that the wagon with fixing blocks is the most at risk of derailment. The front and intermediate wagons have criterion values very close to that of the empty wagon. This shows that the emerging horizontal elastic forces do not significantly influence the derailment process. The obtained results show that the transportation of long rails with specialized train composition can be realized on four layers. This will significantly increase the efficiency of delivering new long rails.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Method for Theoretical Assessment of Safety against Derailment of New Freight Wagons
by
Valeri Stoilov, Svetoslav Slavchev, Vladislav Maznichki and Sanel Purgic
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 898
Abstract
The assessment of safety against freight wagons’ derailment is a mandatory element of the documents provided to the EU notifying authorities of the entry into service of new freight wagons. The assessment methodology is presented in EN 14363:2019. It is mainly aimed at
[...] Read more.
The assessment of safety against freight wagons’ derailment is a mandatory element of the documents provided to the EU notifying authorities of the entry into service of new freight wagons. The assessment methodology is presented in EN 14363:2019. It is mainly aimed at the experimental measurement of certain parameters, and the data are used to calculate the safety criterion. The practical implementation of the tests is accompanied by many difficulties: finding a track with a proper radius, ensuring free access to the railway infrastructure for a long period of time, waiting for suitable metrological conditions, preparing the curve and the test wagon, etc. These difficulties are well known to the European legislators, and as a solution, they propose a large set of reference wagons that have undergone real tests. It is sufficient to demonstrate that the parameters of the new wagon relate to some of the reference wagon parameters to avoid such a requirement. Proving the “convergence” of the parameters of the new and the reference wagons is a lengthy, complex, and, in many cases, subjective process. To introduce an objective assessment, the authors set themselves the task of developing a theoretical method to assess safety against derailment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Variable Height of Piers on the Dynamic Characteristics of High-Speed Train–Track–Bridge Coupled Systems in Mountainous Areas
by
Yingying Zeng, Lizhong Jiang, Zhixiong Zhang, Han Zhao, Huifang Hu, Peng Zhang, Fang Tang and Ping Xiang
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 1315
Abstract
With the increase in the occupancy ratio of bridges and the speed of trains, the probability of trains being located on bridges during earthquakes increases, and the risk of derailment increases. To investigate the influence of unequal-height piers on the dynamic response of
[...] Read more.
With the increase in the occupancy ratio of bridges and the speed of trains, the probability of trains being located on bridges during earthquakes increases, and the risk of derailment increases. To investigate the influence of unequal-height piers on the dynamic response of high-speed railway train bridge systems, a seismic action model of high-speed train–track–bridge dynamic systems was established based on the in-house code using the finite element method and multi-body dynamics method. It is found that (1) compared to equal-height piers, the peak lateral dynamic response of unequal-height piers (with gradually increasing pier heights) decreases, while the peak vertical dynamic response increases; (2) the peak lateral dynamic response of unequal-height piers (with a steep increase in pier height) increases sharply, while the peak vertical dynamic response decreases; and (3) the safety indicators of equal-height piers are significantly superior to the two unequal-height pier operating conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
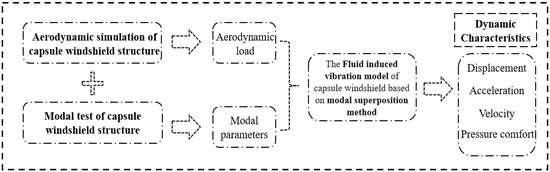
Flow-Induced Vibration Hybrid Modeling Method and Dynamic Characteristics of U-Section Rubber Outer Windshield System of High-Speed Trains
by
Yizheng Yu, Pengxiang Lv, Xiao Liu and Xiang Liu
Viewed by 1777
Abstract
The flow-induced vibration characteristic of the U-section rubber outer windshield structure of high-speed train is the key factor to limit its high-speed movement. Accurate and effective flow-induced vibration analysis of windshield structures is an important topic. In this paper, a hybrid modeling method
[...] Read more.
The flow-induced vibration characteristic of the U-section rubber outer windshield structure of high-speed train is the key factor to limit its high-speed movement. Accurate and effective flow-induced vibration analysis of windshield structures is an important topic. In this paper, a hybrid modeling method for the analysis of flow-induced vibration of windshield structure is innovatively proposed for the U-section rubber windshield system of high-speed train. The method uses the external aerodynamic load obtained by aerodynamic simulation as the input condition of the flow-induced vibration model, and maps the aerodynamic load to the structural dynamics model characterized by the modal test data of the windshield structure. The flow-induced vibration model is established by means of modal superposition method and the time-domain response is effectively integrated by Runge Kutta method with variable step size. The results show that this method can effectively simulate the flow induced vibration of the wind baffle structure, and the real-time relationship between the aerodynamic load and the modal characteristics of the structure and the response of displacement and velocity can be obtained. On this basis, the comprehensive dynamic performance of the windshield system of high-speed trains at 400 km/h under external aerodynamic load is studied, that is, the force, displacement and velocity variation rules of the flexible structure are examined. It is determined that the displacement and velocity response curve of the measuring point near the lower side of the U-section rubber outer windshield is significantly higher than that of other parts. Moreover, the contribution of the first mode to the dynamic response of the structure is very obvious. This method provides an efficient calculation method for analyzing the flow-induced vibration characteristics of complex flexible structures.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
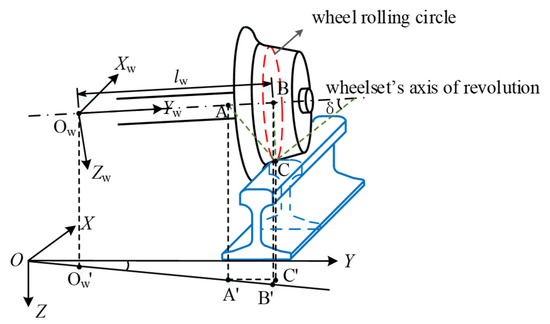
Influence of Wheel-Rail Contact Algorithms on Running Safety Assessment of Trains under Earthquakes
by
Guanmian Cai, Zhihui Zhu, Wei Gong, Gaoyang Zhou, Lizhong Jiang and Bailong Ye
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2063
Abstract
Accurate running safety assessment of trains under earthquakes is crucial to ensuring the safety of line operation. Extreme contact behaviors such as wheel flange contact and wheel jump during earthquakes will directly affect the running safety of trains. To accurately simulate a wheel-rail
[...] Read more.
Accurate running safety assessment of trains under earthquakes is crucial to ensuring the safety of line operation. Extreme contact behaviors such as wheel flange contact and wheel jump during earthquakes will directly affect the running safety of trains. To accurately simulate a wheel-rail extreme contact state, the calculation of the normal compression amount, the normal contact stiffness, and a number of contact points are crucial in wheel-rail space contact modeling. Hence, in order to clarify the applicable algorithms during earthquakes, this paper first introduces different algorithms in three aspects mentioned above. Taking a single CRH2 motor vehicle passing through a ballastless track structure under EI-Centro wave excitation as an example, a comparative analysis of wheel-rail contact dynamics and running safety was conducted. The results showed that adopting the normal compression algorithm based on vertical penetration and the consideration of only single-point contact will result in the maximum calculation error of wheel-rail contact force to reach 339.50% and 35.00%, respectively. This significantly affects the accuracy of train safety assessment, while using the empirical formula for wheel-rail normal contact stiffness has relatively less impact. To ensure the accuracy of running safety assessment of trains during an earthquake, it is recommended to adopt the normal compression algorithm based on normal penetration and consider the multi-point contact in wheel-rail contact modelling.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Review of Fault Diagnosis Methods for Key Systems of the High-Speed Train
by
Suchao Xie, Hongchuang Tan, Chengxing Yang and Hongyu Yan
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2611
Abstract
High-speed train is a large-scale electromechanical coupling equipment with a complex structure, where the coupling is interlaced between various system components, and the excitation sources are complex and diverse. Therefore, reliability has become the top priority for the safe operation of high-speed trains.
[...] Read more.
High-speed train is a large-scale electromechanical coupling equipment with a complex structure, where the coupling is interlaced between various system components, and the excitation sources are complex and diverse. Therefore, reliability has become the top priority for the safe operation of high-speed trains. As the operating mileage of high-speed trains increases, various key systems experience various degrees of performance degradation and damage failures. Moreover, it is accompanied by the influence of external environmental high interference noise and weak early fault information. Thus, those factors are serious challenges for the condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of high-speed trains. Therefore, this paper summarizes the research progress and theoretical results of the fault detection, fault isolation, and fault diagnosis methods of the key systems of high-speed trains. Finally, the paper summarizes the applicability of the main methods, discusses the challenges and opportunities of condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of high-speed trains, and looks forward to improving its diagnosis level.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
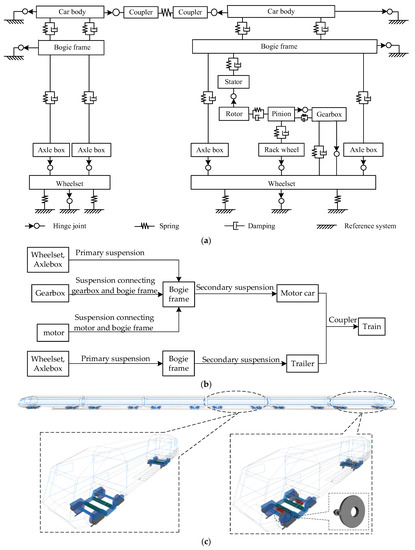
Dynamic Characteristics of Urban Rail Train in Multivehicle Marshaling under Traction Conditions
by
Yichao Zhang, Jianwei Yang, Jinhai Wang and Yue Zhao
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1781
Abstract
In recent years, urban rail transportation has rapidly developed in China and become one of the most important modes of travel. Most existing studies on the dynamic characteristics of urban rail trains have been based on single-section trains, and there have been fewer
[...] Read more.
In recent years, urban rail transportation has rapidly developed in China and become one of the most important modes of travel. Most existing studies on the dynamic characteristics of urban rail trains have been based on single-section trains, and there have been fewer studies on marshaling urban rail trains that incorporate traction transmission systems. The dynamic performance of each carriage directly affects the operational reliability and even the running safety of urban rail trains. For this reason, in this paper, a marshaling urban rail train model with a traction transmission system was established and its accuracy was validated by field tests. This dynamics model enables the consideration of the coupling interactions between the gear transmission motion, the vertical, the lateral and the longitudinal motions of the vehicle. First, the model accuracy was validated by field tests. Then, the relationship between the motor torque and the running time of the urban rail train under traction conditions was calculated. Finally, the dynamic performance of each car of the marshaling train was studied. The research results show that there is a clear difference between the dynamics of the motor car and the trailer, and that the motor car is significantly inferior to the trailer. Among the four motor cars, the dynamic performances of the first and last moving cars were worse than those of the other motor cars. Among the two trailers, the trailer at the back was worse than the trailer at the front. The traction transmission system has a greater impact on the vertical and lateral vibration of the train bogie frame and wheelset, but the impact on the vibration of the car body is negligible. This paper provides theoretical support for the research one train dynamic performance optimization and operation safety.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Strategy for Automatic Mode Pairing on the Model Updating of Railway Systems with Nonproportional Damping
by
Diogo Ribeiro, Cássio Bragança, Maik Brehm, Volkmar Zabel and Rui Calçada
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1647
Abstract
Mode pairing is a crucial step for the stability of any model-updating strategy based on experimental modal parameters. Automatically establishing a stable and assertive correspondence between numerical and experimental modes, in many cases, proves to be a very challenging task, especially in situations
[...] Read more.
Mode pairing is a crucial step for the stability of any model-updating strategy based on experimental modal parameters. Automatically establishing a stable and assertive correspondence between numerical and experimental modes, in many cases, proves to be a very challenging task, especially in situations where complex mode shapes are present. This article presents a novel formulation for the automatic mode pairing between experimental and numerical complex modes based on an Energy-based Modal Assurance Criterion (EMAC). The efficiency of the proposed criterion was demonstrated on the basis of a case study involving the pairing between numerical and experimental modes of a passenger railway vehicle. A highly complex detailed FE numerical model of the vehicle was developed involving the modeling of the carbody, bogies and axles. A numerical damped modal analysis allowed obtaining the main global rigid-body and flexural modes of the vehicle’s carbody, as well as several local modes associated to the vibration of specific components of the carbody. Due to the localized damping provided by the suspensions, these modes presented complex modal ordinates, especially for the rigid-body modes. The comparison between the results obtained from the application of the EMAC and the classical MAC criteria, on the pairing of five global mode shapes, proved that the EMAC criterion is much more assertive, avoiding mismatches between the experimental global modes and some of the local numerical modes with similar configurations, and, consequently, establishing the correct correspondences between experimental and numerical modes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Research on Geometric Parameters Optimization of Fixed Frog Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
by
Rang Zhang, Gang Shen and Xujiang Wang
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1237
Abstract
In this paper, to improve the wheel/rail dynamic performance of the vehicle passing through the fixed frog area and improve the service life of the fixed frog, a geometric parameter optimization design method of the fixed frog area is proposed using particle swarm
[...] Read more.
In this paper, to improve the wheel/rail dynamic performance of the vehicle passing through the fixed frog area and improve the service life of the fixed frog, a geometric parameter optimization design method of the fixed frog area is proposed using particle swarm optimization (PSO). Based on the variable section rail profile interpolation algorithm and wheel/rail contact solution algorithm, the wheel/rail contact characteristics of the fixed frog area are analyzed. Then, the vehicle-fixed frog dynamic model is built using a MATLAB/Simulink platform to complete the dynamic calculation and analysis of the rail vehicle passing through the fixed frog area. Finally, based on the wheel/rail contact characteristics of the fixed frog area, and take wheel/rail forces as the optimization goal, the optimization design method for the wing rail lifting value and the nose rail height of the fixed frog area is proposed. The comparative analysis shows that the wheel/rail dynamic performance in the fixed frog area has been greatly improved after optimization, which verifies the feasibility of the optimization strategy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Limit of the Lateral Fundamental Frequency and Comfort Analysis of a Straddle-Type Monorail Tour Transit System
by
Fengqi Guo, Yanqiang Ji, Qiaoyun Liao, Bo Liu, Chenjia Li, Shiqi Wei and Ping Xiang
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1615
Abstract
The straddle-type monorail tour transit system is a light overhead steel structure, and the lateral stiffness is generally low. However, the limit of the lateral natural vibration frequency is not clear in the current codes of China, and designers may ignore it. Weak
[...] Read more.
The straddle-type monorail tour transit system is a light overhead steel structure, and the lateral stiffness is generally low. However, the limit of the lateral natural vibration frequency is not clear in the current codes of China, and designers may ignore it. Weak lateral stiffness will lead to a violent vibration during vehicle operation and crowds walking, affecting human comfort and structural safety. Based on a practical project, we tested the acceleration of a monorail vehicle under full load conditions, and its running stability and ride comfort were assessed. Then, the impact of pedestrians on lateral vibration under some working conditions was measured and analyzed. Furthermore, the influence of different structural parameters on the lateral fundamental frequency was investigated. The results showed the following: (i) The vehicle’s running stability and riding comfort was good. However, human comfort was poor due to the weak lateral stiffness of the structure, which was affected by human-induced vibration. (ii) The comprehensive response of the structure increased with the increase in walking frequency, increased with the increase in the number of people working or weight, and the growth speed slowed down. (iii) The structural stiffness was most sensitive to the change in steel column diameter. (iv) The recommended value of the lateral fundamental frequency limit for different spans of the straddle-type monorail tour transit system was put forward. The recommended lower limit of fundamental frequency for a 15 m span is 5.0 Hz, for an 18 m span it is 3.5 Hz, and for a 25 m span it is 2.8 Hz.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
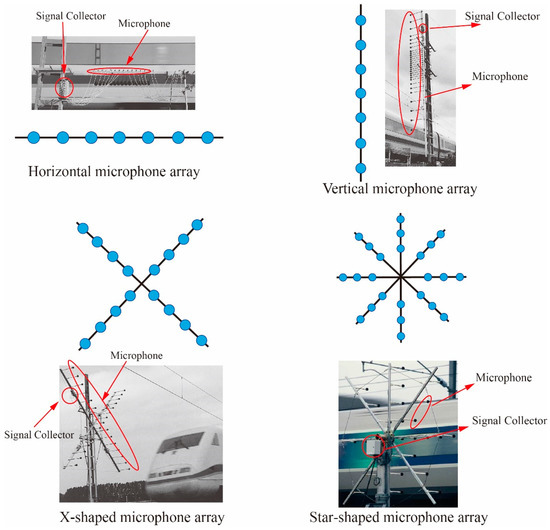
A Review of Recent Research into the Causes and Control of Noise during High-Speed Train Movement
by
Hongyu Yan, Suchao Xie, Kunkun Jing and Zhejun Feng
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 4257
Abstract
Since the invention of the train, the problem of train noise has been a constraint on the development of trains. With increases in train speed, the main noise from high-speed trains has changed from rolling noise to aerodynamic noise, and the noise level
[...] Read more.
Since the invention of the train, the problem of train noise has been a constraint on the development of trains. With increases in train speed, the main noise from high-speed trains has changed from rolling noise to aerodynamic noise, and the noise level and noise frequency range have also changed significantly. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of recent advances in the development of high-speed train noise. Firstly, the train noise composition is summarized; next, the main research methods for train noise, which include real high-speed train noise tests, wind tunnel tests, and numerical simulations, are reviewed and discussed. We also discuss the current methods of noise reduction for trains and summarize the progress in current research and the limitations of train body panels and railroad sound barrier technology. Finally, the article introduces the development and potential future applications of acoustic metamaterials and proposes application scenarios of acoustic metamaterials for the specific needs of railroad sound barriers and train car bodies. This synopsis provides a useful platform for researchers and engineers to cope with problems of future high-speed rail noise in the future.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
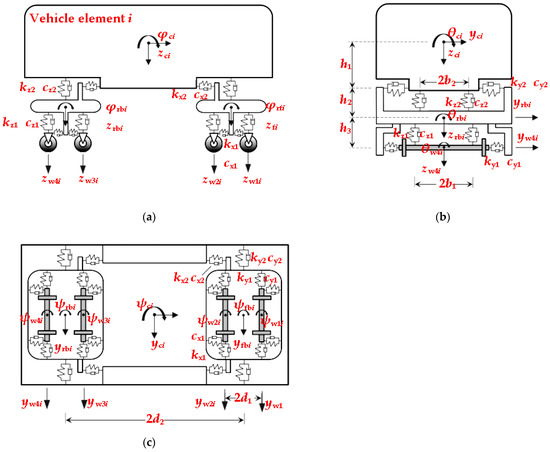
Analysis of Train Car-Body Comfort Zonal Distribution by Random Vibration Method
by
Zhaozhi Wu, Nan Zhang, Jinbao Yao and Vladimir Poliakov
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 1514
Abstract
With the increase in train speeds on high-speed railways, the excitation frequency of track irregularities increases, which has a negative impact on train comfort and opposes the passengers’ desire for high ride comfort. In addition, the uncertainty of train comfort results from the
[...] Read more.
With the increase in train speeds on high-speed railways, the excitation frequency of track irregularities increases, which has a negative impact on train comfort and opposes the passengers’ desire for high ride comfort. In addition, the uncertainty of train comfort results from the stationary randomness of track irregularities and the different zonal distribution in the car body. Therefore, the application of the stationary random vibration method to analyze the zonal distribution of train comfort and the relevant influencing factors is important to guarantee the passengers’ comfortable experience in each ride and to provide a theoretical basis for comfort optimization. First, the train was modeled using eight independent vehicle elements. Second, the pseudo-excitation method was applied to obtain the theoretical zonal distribution of the Sperling index, an indicator of comfort, via the linearity of the power spectrum density of train acceleration. Third, considering various factors affecting train comfort, the results were compared with those calculated using the Monte Carlo method. It was found that the most comfortable area was located slightly in the front of the center of the car body. Improving track irregularities and reasonably controlling the speed of a train will increase the train’s comfort, while it will deteriorate with a loss in car-body mass and damage to the secondary suspension system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Mobile Device-Based Train Ride Comfort Measuring System
by
Yuwei Hu, Lanxin Xu, Shuangbu Wang, Zhen Gu and Zhao Tang
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2169
Abstract
As an important train performance quality, comfort depends on vibration and noise data measured on a running train. Traditional vibration and noise measurement tools are facing challenges in terms of collecting big data, portability, and cost. With the continuous upgrade of mobile terminal
[...] Read more.
As an important train performance quality, comfort depends on vibration and noise data measured on a running train. Traditional vibration and noise measurement tools are facing challenges in terms of collecting big data, portability, and cost. With the continuous upgrade of mobile terminal hardware, the built-in sensors of mobile phones have the ability to undertake relatively complex data measurement and processing tasks. In this study, a new type of train comfort measurement system based on a mobile device is developed by using a built-in sensor to measure the vibration and noise. The functions of the developed system include the real-time display of three-way vibration acceleration, lateral and vertical Sperling indicators, sound pressure level, and train comfort-related data storage and processing. To verify the accuracy of the mobile device-based train ride comfort measuring system (DTRCMS), a comparison of test results from this system and from the traditional measuring system is conducted. The comparison results show that the DTRCMS is in good agreement with the traditional measuring system. The relative error in three-direction acceleration and Sperling values is 2~10%. The fluctuation range of the noise measured by DTRCMS is slightly lower than that of the professional noise meter, and the relative error is mainly between 1.5% and 4.5%. Overall, the study shows that using mobile devices to measure train comfort is feasible and practical and has great potential for big data-based train comfort evaluation in the future.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
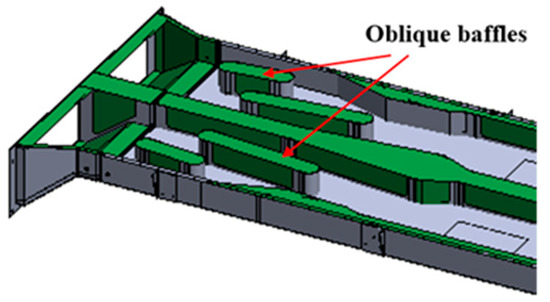
Three-Dimensional Acoustic Analysis of a Rectangular Duct with Gradient Cross-Sections in High-Speed Trains: A Theoretical Derivation
by
Yanhong Sun, Yi Qiu, Lianyun Liu and Xu Zheng
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1658
Abstract
Rectangular ducts used in the air-conditioning system of a high-speed train should be carefully designed to achieve optimal acoustic and flow performance. However, the theoretical analysis of the rectangular ducts with gradient cross-sections (RDGC) at frequencies higher than the one-dimensional cut-off frequency is
[...] Read more.
Rectangular ducts used in the air-conditioning system of a high-speed train should be carefully designed to achieve optimal acoustic and flow performance. However, the theoretical analysis of the rectangular ducts with gradient cross-sections (RDGC) at frequencies higher than the one-dimensional cut-off frequency is rarely published. This paper has developed the three-dimensional analytical solutions to the wave equations of the expanding and shrinking RDGCs. Firstly, a homogeneous second-order variable coefficient differential equation is derived from the wave equations. Two coefficients of the solution to the differential equation are set to zero to ensure convergence. Secondly, the transfer matrices of the duct systems composed of multiple RDGCs are derived from the three-dimensional solutions. The transmission losses of the duct systems are then calculated from the transfer matrices and validated with the measurement. Finally, the acoustic performance and flow efficiency of the RDGCs with different geometries are discussed. The results show that the REC with double baffles distributed transversely has good performance in both acoustic attenuation and flow efficiency. This study shall provide a helpful guide for designing rectangular ducts used in high-speed trains.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures