Transition to Industry 4.0 in Emerging Domains: Methodology and Case Studies
A project collection of Electronics (ISSN 2079-9292). This project collection belongs to the section "Computer Science & Engineering".
Papers displayed on this page all arise from the same project. Editorial decisions were made independently of project staff and handled by the Editor-in-Chief or qualified Editorial Board members.
Viewed by 28056Editors
Interests: complex modelling and simulation systems for the environmental, safety, and security fields, including autonomous security, risks, and Industry 4.0
Project Overview
Dear Colleagues,
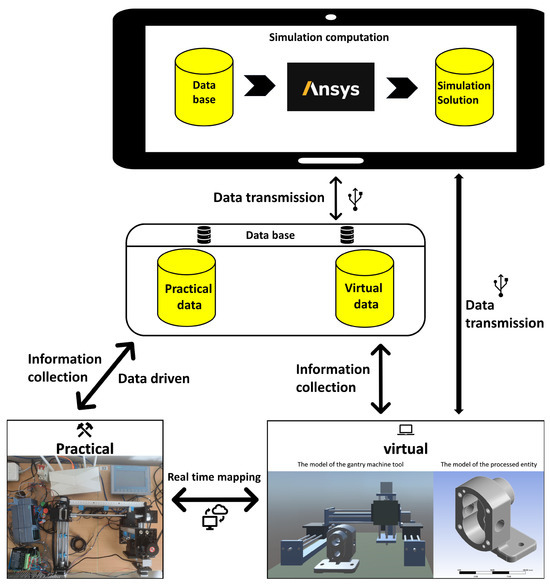
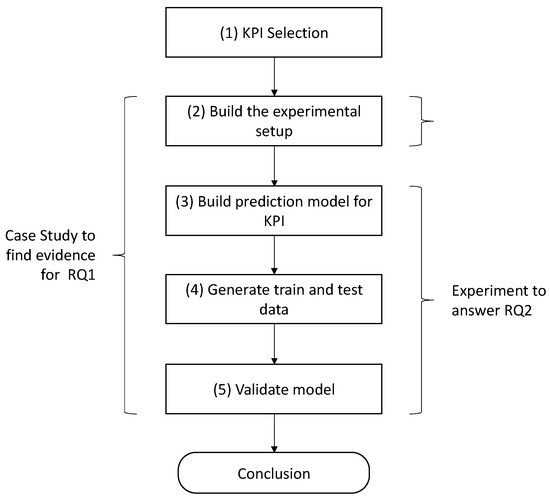
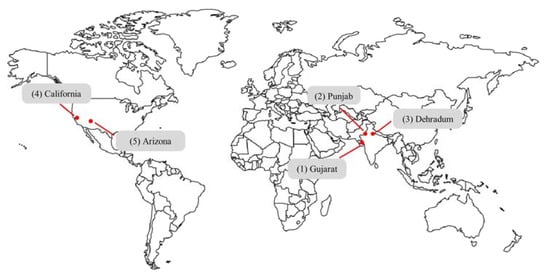
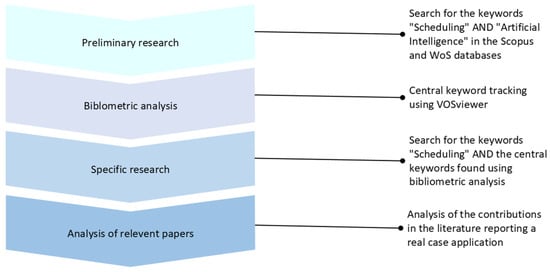
In the last decade, great importance has been given to the digital world and the ramping development of Industry 4.0. The possibility of employing new technologies able to recreate new environments aiming at simplifying and increasing the reliability of the real world has been the driving force for many new inventions and ideas. With augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and the Internet of Thing (IoT) and digital twin paradigms, the view of the world expanded, giving us the possibility of relating ourselves to the real world but with a previous digital simulation or digital enhancement. The possibility of developing technologies, tools and methodologies for the emerging domains of Industry 4.0 is the main reason why the reliability and safety of many systems increased during this period of time.
This Project Collection focuses on the recent advances in the digital technology field, in their implementation, and in their interoperability, with emphasis on the importance of these in the relevant domains, such as: public and private sectors, public administration, healthcare and defense, industrial sector, and the education sector.
Dr. Anastasiia Rozhok
Prof. Dr. Roberto Revetria
Collection Editors
This program intends to provide an opportunity for early career scientists to enhance their editing, networking, and organizational skills and to work closely with our journal to gain more editorial experience. Early career scientists who have novel ideas for new Special Issues of Electronics (ISSN: 2079-9292) will act as Guest Editors under the mentorship of an experienced scientist; this mentor could be a member of the Electronics Editorial Board or may be from other well-established research institutes or laboratories, etc.
Certificates and awards:
When the Special Issue is closed, the Editorial Office will provide official certificates for all of the mentors. The young scholars involved in the program will be prioritized as candidates for Electronics Young Investigator Awards in the future.
If you are interested in this opportunity, please send your Special Issue proposal to the Electronics Editorial Office ([email protected] or [email protected]), and we will discuss the process (mentor collaboration, Special Issue topic feasibility analysis, etc.) in further detail.
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Electronics is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Industry 4.0
- digital technologies
- digitalization
- modeling and simulation
- AR
- VR
- IoT
- digital twins
- business process reengineering
- interoperability
- strategic planning
- supply chain management
- BIM
- PLM