Hypertension: Etiology, Risk Factors, Associated Symptoms and Treatment
(Closed)
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Marijana Tadic
Prof. Dr. Marijana Tadic
 Prof. Dr. Marijana Tadic
Prof. Dr. Marijana Tadic
E-Mail
Website1
Website2
Guest Editor
Clinic for Internal Medicine II, University Clinic Ulm, Albert-Einstein Allee 23, 89081 Ulm, Germany
Interests: hypertension; diabetes; obesity; metabolic syndrome; echocardiohgraphy; speckle tracking; 3D echocardiography; cardiac magnetic resonancecardiography; cardiac magnetic resonance
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Prof. Dr. Cesare Cuspidi
Prof. Dr. Cesare Cuspidi
 Prof. Dr. Cesare Cuspidi
Prof. Dr. Cesare Cuspidi
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Department of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca, and Milano Istituto Auxologico Italiano, IRCCS, Milan, Italy
Interests: hypertension; diabetes; metabolic syndrome; obesity; sleep apnea syndrome; echocardiography
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Arterial hypertension is the most frequent cardiovascular disease currently and it is a very important risk factor for development of heart failure, coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, stroke, and so on. The pandemic of hypertension is associated with increasing prevalence of obesity and sedentary lifestyle. Hypertension is usually seen concomitantly with diabetes, dyslipidemia, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and renal dysfunction. Target organ damage in arterial hypertension is of a great importance. Diagnosis of hypertensive heart disease has significantly changed and developed over the last two decades. The new imaging tools that echocardiography provides, speckle tracking at the first side, provide timely diagnosis of the early stages of hypertension-induced cardiac remodeling. The therapeutic approach has also evolved from a single drug to fixed combinations, and some new drugs have appeared. The aim of this issue is to summarize the latest findings about etiology, risk factors, target organ damage and treatment in patients with arterial hypertension.
Prof. Dr. Marijana Tadic
Prof. Cesare Cuspidi
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Journal of Clinical Medicine is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- hypertension
- risk factors
- echocardiography
- therapy
- target organ damage
Published Papers (13 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Relationship of Glycated Hemoglobin A1c with All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality among Patients with Hypertension
by
Ruixiang Zeng, Yuzhuo Zhang, Junpeng Xu, Yongjie Kong, Jiawei Tan, Liheng Guo and Minzhou Zhang
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2971
Abstract
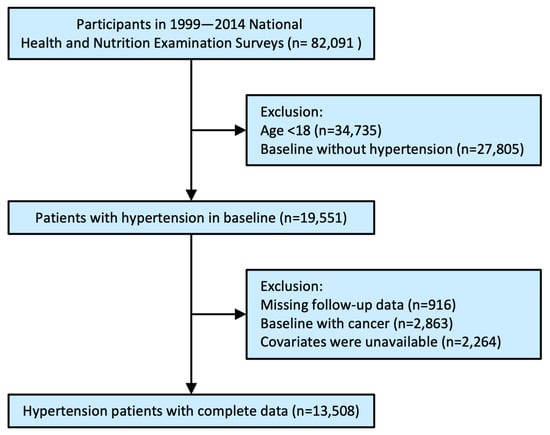
Both low and high glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels are well-established causal risk factors for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the general population and diabetic patients. However, the relationship between HbA1c with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among patients with hypertension is unclear. We
[...] Read more.
Both low and high glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels are well-established causal risk factors for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the general population and diabetic patients. However, the relationship between HbA1c with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among patients with hypertension is unclear. We used NHANES data from 1999 to 2014 as the basis for this population-based cohort study. Based on HbA1c levels (HbA1c > 5, HbA1c > 5.5, HbA1c > 6, HbA1c > 6.5, HbA1c > 7%), hypertensive patients were divided into five groups. An analysis of multivariable Cox proportional hazards was conducted based on hazard ratios (HRs) and respective 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The relationship between HbA1c and mortality was further explored using Kaplan–Meier survival curves, restricted cubic spline curves, and subgroup analyses. In addition, 13,508 patients with hypertension (average age 58.55 ± 15.56 years) were included in the present analysis, with 3760 (27.84%) all-cause deaths during a follow-up of 127.69 ± 57.9 months. A U-shaped relationship was found between HbA1c and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality (all
p for likelihood ratio tests were 0.0001). The threshold value of HbA1c related to the lowest risk for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality was 5.3% and 5.7%, respectively. Below the threshold value, increased HbA1c levels reduced the risk of all-cause mortality (HR 0.68, 95% CI 0.51–0.90,
p = 0.0078) and cardiovascular mortality (HR 0.77, 95% CI 0.57–1.05,
p = 0.0969). Inversely, above the threshold value, increased HbA1c levels accelerated the risk of all-cause mortality (HR 1.14, 95% CI 1.11–1.18,
p < 0.0001) and cardiovascular mortality (HR 1.22, 95% CI 1.16–1.29,
p < 0.0001). In conclusion, A U-shape relationship was observed between HbA1c and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among hypertensive patients.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Factors Associating with Non-Dipping Pattern of Nocturnal Blood Pressure in Patients with Essential Hypertension
by
Tsutomu Koike, Teruhiko Imamura, Fumihiro Tomoda, Maiko Ohara, Hayato Fujioka, Kota Kakeshita, Hidenori Yamazaki and Koichiro Kinugawa
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2808
Abstract
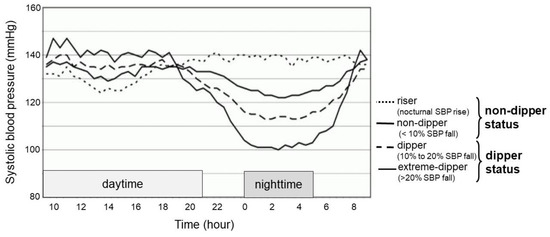
Background: In patients with essential hypertension, a non-dipping blood pressure pattern is a strong risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. However, background factors associating with such a blood pressure pattern remain unknown. Methods: Untreated essential hypertensive patients without chronic kidney diseases who were admitted
[...] Read more.
Background: In patients with essential hypertension, a non-dipping blood pressure pattern is a strong risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. However, background factors associating with such a blood pressure pattern remain unknown. Methods: Untreated essential hypertensive patients without chronic kidney diseases who were admitted to our outpatient clinic were included. Blood sampling and 24 h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring were mandatorily performed. Non-dipper status was defined as a maximum decrease in nocturnal systolic blood pressure within 10%. Clinical factors associating with non-dipper status were investigated. Results: A total of 154 patients (56 ± 12 years old, 86 men) were included. Among baseline characteristics, a higher serum uric acid level was independently associated with non-dipper status (odds ratio 1.03, 95% confidence interval 1.00–1.05,
p < 0.05). Among those with non-dipper status, a higher high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level tended to be associated with incremental nighttime systolic blood pressure levels (
p = 0.065). Conclusions: Hyperuricemia and micro-inflammation might be associated with attenuated nocturnal blood pressure dipping and incremental nighttime systolic blood pressure levels.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Unattended versus Attended Blood Pressure Measurement: Relationship with Retinal Microcirculation
by
Anna Paini, Claudia Agabiti Rosei, Carolina De Ciuceis, Carlo Aggiusti, Fabio Bertacchini, Marco Cacciatore, Sara Capellini, Roberto Gatta, Paolo Malerba, Deborah Stassaldi, Damiano Rizzoni, Massimo Salvetti and Maria Lorenza Muiesan
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1319
Abstract
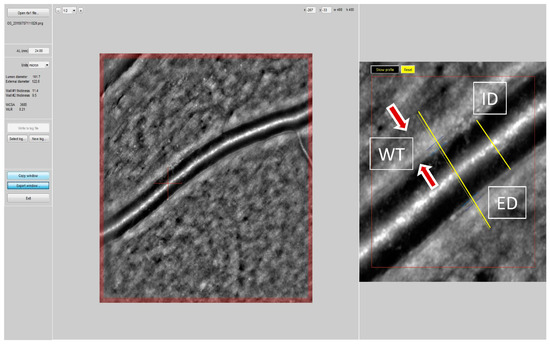
Though the relationship between both “attended” and “unattended” BP and several forms of target organ damage have been evaluated, data on retinal arteriolar alterations are lacking. The aim of our study was to evaluate the relationship between “attended” or “unattended” BP values and
[...] Read more.
Though the relationship between both “attended” and “unattended” BP and several forms of target organ damage have been evaluated, data on retinal arteriolar alterations are lacking. The aim of our study was to evaluate the relationship between “attended” or “unattended” BP values and retinal arteriolar changes in consecutive individuals undergoing a clinical evaluation and assessment of retinal fundus at an ESH Excellence Centre. An oscillometric device programmed to perform 3 BP measurements, at 1 min intervals and after 5 min of rest was used on all individuals to measure BP with the patient alone in the room (“unattended”) or in the presence of the physician (“attended”) in the same day in a random order. The retinal arteriole’s wall thickness (WT) was measured automatically by a localization algorithm as the difference between external (ED) and internal diameter (ID) by adaptive optics (RTX-1, Imagine Eyes, Orsay, Francia). Media-to-lumen ratio (WLR) of the retinal arterioles and cross-sectional area (WCSA) of the vascular wall were calculated. Results: One-hundred-forty-two patients were examined (mean age 57 ± 12 yrs, 48% female, mean BMI 26 ± 4). Among them, 60% had hypertension (84% treated) and 11% had type 2 diabetes mellitus. Unattended systolic BP (SBP) was lower as compared to attended SBP (129 ± 14.8. vs. 122.1 ± 13.6 mmHg,
p < 0.0001). WLR was similarly correlated with unattended and attended SBP (r = 0.281,
p < 0.0001 and r = 0.382,
p < 0.0001) and with unattended and attended diastolic BP (r = 0.34,
p < 0.001 and r = 0.29,
p < 0.0001). The differences between correlations were not statistically significant (Steiger’s
Z test). Conclusion: The measurement of “unattended” or “attended” BP provides different values, and unattended BP is lower as compared to attended BP. In this study a similar correlation was observed between attended and unattended BP values and structural changes of retinal arterioles.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Right Ventricle in Arterial Hypertension: Did We Forget Something?
by
Marijana Tadic and Cesare Cuspidi
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 1575
Abstract
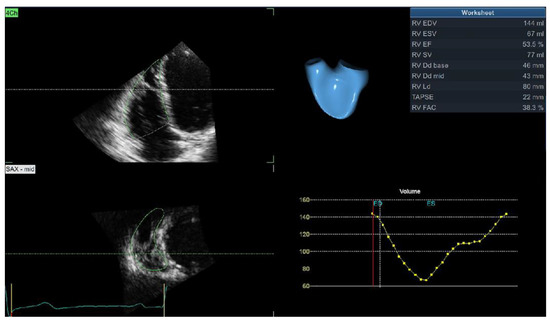
Right ventricular remodeling has been neglected in patients with arterial hypertension as all studies have concentrated on the left ventricle and left atrial-ventricular and ventricular-arterial coupling. The development of novel imaging techniques has revealed significant impairment in the RV structure, systolic and diastolic
[...] Read more.
Right ventricular remodeling has been neglected in patients with arterial hypertension as all studies have concentrated on the left ventricle and left atrial-ventricular and ventricular-arterial coupling. The development of novel imaging techniques has revealed significant impairment in the RV structure, systolic and diastolic function, and, afterwards, RV longitudinal mechanics. However, these changes are subclinical and can be detected only after comprehensive imaging analysis. The latest findings confirm the importance of RV hypertrophy, systolic, and diastolic dysfunction in the prediction of cardiovascular adverse events in the hypertensive population, representing an important clinical implication of these parameters. In clinical practice, 2D echocardiography is widely used for the evaluation of RV remodeling. However, existing techniques are largely underused and limited to a few basic parameters (RV thickness and TAPSE), which are not nearly enough for a detailed assessment of RV remodeling. In addition, 3D echocardiography provides the possibility of accurate evaluation of RV volumes and ejection fraction, which are comparable with results obtained by cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR)—a gold standard for the evaluation of the RV. The use of 3D echocardiography is limited due to its low availability, the lack of adequate software necessary for the calculation of results, and the necessity for a higher level of expertise. CMR provides all information required for a detailed assessment of RV structural, functional, and mechanical remodeling, and it is considered the reference method for this type of evaluation. Furthermore, it is the only technique that may provide tissue characterization and evaluation of the interstitial space, which is essential for hypertensive heart disease. The aim of this review is to provide the current level of evidence regarding RV remodeling in patients with arterial hypertension evaluated with different imaging techniques and various parameters from each method.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
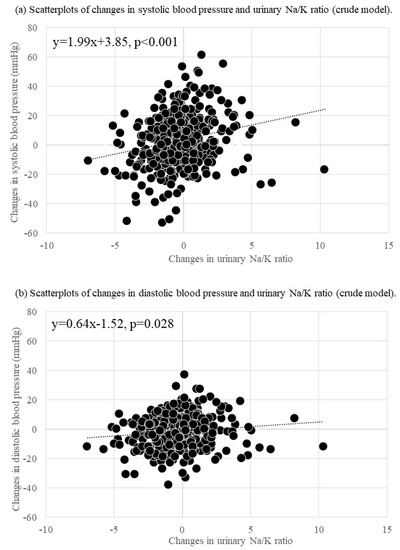
Changes in the Urinary Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio Are Associated with Blood Pressure Change in Older Japanese Adults: A 7-Year Longitudinal Study
by
Takafumi Abe, Takeshi Endo, Tsuyoshi Hamano, Kenta Okuyama and Shozo Yano
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1569
Abstract
Studies on the association between sodium-to-potassium (Na/K) ratio changes and blood pressure (BP) changes among older adults are limited. This 7-year longitudinal study examined the association between Na/K ratio changes (evaluated using spot urine tests) and BP changes among older Japanese adults. Data
[...] Read more.
Studies on the association between sodium-to-potassium (Na/K) ratio changes and blood pressure (BP) changes among older adults are limited. This 7-year longitudinal study examined the association between Na/K ratio changes (evaluated using spot urine tests) and BP changes among older Japanese adults. Data were collected from 432 participants (mean age: 70.3±4.4; range: 65–84 years) in 2012 and 2019. Changes in BP and the Na/K ratio over 7 years were calculated by subtracting baseline values from values noted during a follow-up survey. The median systolic and diastolic BP (SBP) and (DBP) changes after 7 years were 4 (IQR, −7, 14) and −1 (IQR, −9, 5) mmHg, respectively. The median Na/K ratio was changed during the follow-up period by −0.2 (IQR, −1.3, 0.7). A generalized linear model indicated that Na/K ratio changes were positively associated with SBP (B = 2.03,
p < 0.001) and DBP (B = 0.62,
p = 0.021) changes. In the non-antihypertensive medication-using group, urinary Na/K ratio changes were associated with SBP and DBP changes (B = 2.39,
p = 0.001; B = 0.99,
p = 0.033). In the antihypertensive medication user group, urinary Na/K ratio changes were associated with SBP changes (B = 1.62,
p = 0.015). We confirmed the association between changes in the Na/K ratio and changes in BP.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
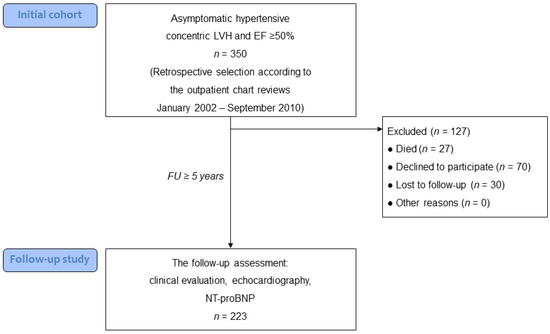
Asymptomatic Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Is a Potent Risk Factor for the Development of HFpEF but Not HFrEF: Results of a Retrospective Cohort Study
by
Artem Ovchinnikov, Evgeny Belyavskiy, Alexandra Potekhina and Fail Ageev
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2598
Abstract
(1) Background: The structural and functional features of the natural history of asymptomatic hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) are not clearly defined. (2) Objective: To determine structural and functional changes in asymptomatic hypertensive LVH, as well as the incidence and predictors of the
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: The structural and functional features of the natural history of asymptomatic hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) are not clearly defined. (2) Objective: To determine structural and functional changes in asymptomatic hypertensive LVH, as well as the incidence and predictors of the transition to different phenotypes of heart failure (HF) after a long-term follow-up. (3) Methods: Based on the assessment of chart reviews, we retrospectively selected 350 asymptomatic patients with hypertensive concentric LVH and LV ejection fraction (EF) ≥ 50%. After a median follow-up of 8.1 years, 223 patients had a re-assessment. The final diagnosis (HF with reduced EF [HFrEF], or HF with preserved EF [HFpEF]) was established according to current recommendations. (4) Results: After a follow-up, only 13% of patients remained asymptomatic, 72% developed HFpEF, and 15% developed HFrEF. The transition to HFpEF was associated with an increase in LV diastolic dysfunction grade in 62% of patients. Multivariable analysis identified age, duration of hypertension, interval changes in LV mass, and a lack of statin treatment as independent predictors of HFpEF. Among 34 patients who developed HFrEF, 16 patients (7% of the whole group) had no interval myocardial infarction, corresponding to an internal mechanism of systolic dysfunction. All these 16 patients had mild systolic dysfunction (LVEF > 40%). Baseline LVEF and LV end-diastolic dimension, and interval atrial fibrillation were identified as predictors of internal HFrEF. (5) Conclusions: The majority of patients with asymptomatic LVH developed HFpEF after long-term follow-up, which was associated with the deterioration of LV diastolic dysfunction and a lack of statin treatment. In contrast, the transition to HFrEF was infrequent and characterized by mild LV systolic dysfunction.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
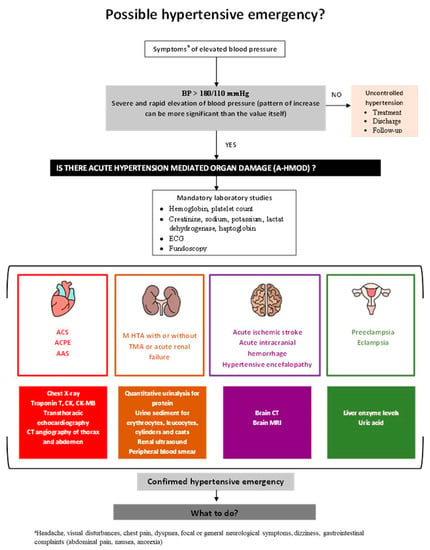
The Management of Hypertensive Emergencies—Is There a “Magical” Prescription for All?
by
Ana-Maria Balahura, Ștefan-Ionuț Moroi, Alexandru Scafa-Udrişte, Emma Weiss, Cristina Japie, Daniela Bartoş and Elisabeta Bădilă
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 64501
Abstract
Hypertensive emergencies (HE) represent high cardiovascular risk situations defined by a severe increase in blood pressure (BP) associated with acute, hypertension mediated organ damage (A-HMOD) to the heart, brain, retina, kidneys, and large arteries. Blood pressure values alone do not accurately predict the
[...] Read more.
Hypertensive emergencies (HE) represent high cardiovascular risk situations defined by a severe increase in blood pressure (BP) associated with acute, hypertension mediated organ damage (A-HMOD) to the heart, brain, retina, kidneys, and large arteries. Blood pressure values alone do not accurately predict the presence of HE; therefore, the search for A-HMOD should be the first step in the management of acute severe hypertension. A rapid therapeutic intervention is mandatory in order to limit and promote regression of end-organ damage, minimize the risk of complications, and improve patient outcomes. Drug therapy for HE, target BP, and the speed of BP decrease are all dictated by the type of A-HMOD, specific drug pharmacokinetics, adverse drug effects, and comorbidities. Therefore, a tailored approach is warranted. However, there is currently a lack of solid evidence for the appropriate treatment strategies for most HE. This article reviews current pharmacological strategies while providing a stepwise, evidence based approach for the management of HE.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditorial
Sacubitril/Valsartan in the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension: Raising Star or Illusion?
by
Marijana Tadic and Cesare Cuspidi
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 1932
Abstract
Sacubitril/valsartan represents the combination that became “
sine qua non” in the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) with significant positive effect on major cardiovascular events [...]
Full article
Open AccessReview
Rethinking Resistant Hypertension
by
Gabrielle Bourque and Swapnil Hiremath
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 5186
Abstract
Resistant hypertension is common and known to be a risk factor for cardiovascular events, including stroke, myocardial infarction, heart failure, and cardiovascular mortality, as well as adverse renal events, including chronic kidney disease and end-stage kidney disease. This review will discuss the definition
[...] Read more.
Resistant hypertension is common and known to be a risk factor for cardiovascular events, including stroke, myocardial infarction, heart failure, and cardiovascular mortality, as well as adverse renal events, including chronic kidney disease and end-stage kidney disease. This review will discuss the definition of resistant hypertension as well as the most recent evidence regarding its diagnosis, evaluation, and management. The issue of medication non-adherence and its association with apparent treatment-resistant hypertension will be addressed. Non-pharmacological interventions for the treatment of resistant hypertension will be reviewed. Particular emphasis will be placed on pharmacological interventions, highlighting the role of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and device therapy, including renal denervation, baroreceptor activation or modulation, and central arteriovenous fistula creation.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
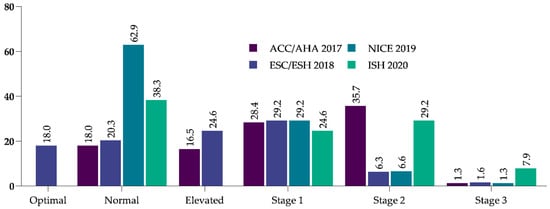
Hypertension Control and Guideline-Recommended Target Blood Pressure Goal Achievement at an Early Stage of Hypertension in the UAE
by
Akshaya Srikanth Bhagavathula, Syed Mahboob Shah, Abubaker Suliman, Abderrahim Oulhaj and Elhadi Husein Aburawi
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 4261
Abstract
(1) Background: The present study aimed to assess the changes in blood pressure (BP) within the first 6 months of treatment initiation in a newly treated hypertensive cohort and to identify the factors that are associated with achieving the target BP recommended by
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: The present study aimed to assess the changes in blood pressure (BP) within the first 6 months of treatment initiation in a newly treated hypertensive cohort and to identify the factors that are associated with achieving the target BP recommended by the American (ACC/AHA, 2017), European (ESC/ESH, 2018), United Kingdom (NICE, 2019), and International Society of Hypertension (ISH, 2020) guidelines. (2) Methods: We analyzed 5308 incident hypertensive outpatients across Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates (UAE), in 2017; each patient was followed up for 6 months. Hypertension was defined as a BP of 130/80 mmHg according to the ACC/AHA guidelines and 140/90 mmHg according to the ESC/ESH, NICE, and ISH guidelines. Multiple logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with achieving the guideline-recommended BP targets. (3) Results: At baseline, the mean BP was 133.9 ± 72.9 mmHg and 132.7 ± 72.5 mmHg at 6 months. The guideline-recommended BP targets were 39.5%, 43%, 65.6%, and 40.8%, according to the ACC/AHA, ESC/ESH, NICE, and ISH guidelines, respectively. A BMI of <25 kg/m
2 was associated with better BP control according to the ACC/AHA (odds ratio (OR) = 1.26; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.07–1.49), ESC/ESH (OR = 1.27; 95% CI = 1.08–1.50), and ISH guidelines (OR = 1.22; 95% CI = 1.03–1.44). Hypertension treated in secondary care settings was more likely to achieve the BP targets recommended by the ACC/AHA (1.31 times), ESC/ESH (1.32 times), NICE (1.41 times), and ISH (1.34 times) guidelines. (4) Conclusions: BP goal achievement was suboptimal. BP control efforts should prioritize improving cardiometabolic goals and lifestyle modifications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Long-Term Impact of Different Triple Combination Antihypertensive Medications on Blood Pressure Control, Metabolic Pattern and Incident Events: Data from the Brisighella Heart Study
by
Arrigo F. G. Cicero, Federica Fogacci, Elisabetta Rizzoli, Sergio D’Addato and Claudio Borghi
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 4270
|
Correction
Abstract
The aim of this study was to comparatively evaluate clinical, laboratory and hemodynamic effects on the long term of different triple combination antihypertensive medications in a well-characterized Italian cohort. We considered the data of a subset of Brisighella Heart Study (BHS) participants who
[...] Read more.
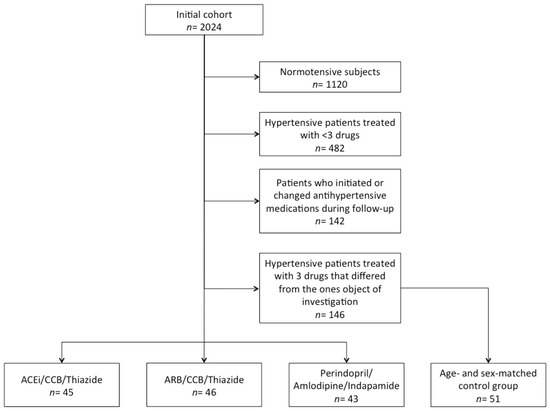
The aim of this study was to comparatively evaluate clinical, laboratory and hemodynamic effects on the long term of different triple combination antihypertensive medications in a well-characterized Italian cohort. We considered the data of a subset of Brisighella Heart Study (BHS) participants who were consecutively evaluated in three epidemiological surveys between 2012 and 2020. For the current analysis, we excluded normotensive subjects, patients treated with <3 or ≥3 antihypertensive drugs without taking angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium-channel blockers (CCB) and/or thiazide/thiazide-like diuretics. The remaining participants were divided into three groups depending on whether they were treated with Perindopril/Amlodipine/Indapamide, ACE-inhibitors (other than perindopril)/CCBs/Thiazide or ARBs/CCBs/Thiazide, either with separate drugs or fixed pill combinations. A further group of age- and sex-matched volunteers was selected as control and included patients receiving other antihypertensive treatments. The long-term (8 years) effects of the different antihypertensive treatments were compared among the pre-defined groups. During the observation period, there was a trend towards increase in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure (BP) in all the investigated subgroups (
p for trend <0.05), but in the subgroup of patients treated with Perindopril/Amlodipine/Indapamide, such increase was significantly lower than in the other groups (
p < 0.05). The combination treatment with renin-angiotensin system (RAS) modulators, CCBs and thiazide/thiazide-like diuretics was associated with significantly lower diastolic BP (
p < 0.05) and more strictly controlled lipid pattern than other triple combination of anti-hypertensive medications. Patients treated with Perindopril/Amlodipine/Indapamide did not experience any age-related increase in serum levels of total cholesterol. Moreover, during the follow up none of them developed type 2 diabetes, nor had a need for a greater number of antihypertensive drugs to improve BP control, mainly because of a more stable BP control. Based on our observations, combination treatment with RAS modulators, amlodipine and thiazides/thiazide-like diuretics is more effective than other triple antihypertensive medications for lowering the diastolic BP and has a better impact on serum lipids. Perindopril/Amlodipine/Indapamide is associated with more protective metabolic profile than any other considered combination antihypertensive medications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Frailty Syndrome and Adherence to Recommendations in Elderly Patients with Hypertension
by
Piotr Pobrotyn, Aleksandra Pasieczna, Dorota Diakowska, Bartosz Uchmanowicz, Grzegorz Mazur, Mirosław Banasik and Aleksandra Kołtuniuk
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2175
Abstract
Frailty syndrome (FS) often coexists with many diseases of the elderly, including arterial hypertension, and may affect the disease course and adherence to therapeutic recommendations. This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between frailty and adherence to therapeutic recommendations in elderly hypertensive patients.
[...] Read more.
Frailty syndrome (FS) often coexists with many diseases of the elderly, including arterial hypertension, and may affect the disease course and adherence to therapeutic recommendations. This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between frailty and adherence to therapeutic recommendations in elderly hypertensive patients. The study included 259 patients hospitalized between January 2019 and November 2020 due to exacerbation of hypertension symptoms. Medical records were used to obtain basic sociodemographic and clinical data. The study was based on the Tilburg Frailty Indicator (TFI) and the Hill–Bone Scale (HBCS). The obtained data were analyzed within a cross-sectional design. The mean frailty score indicated by the TFI questionnaire was 7.09 ± 3.73. The most prominent FS component was associated with the physical domain (4.24 ± 2.54). The mean overall adherence measured with the HBCS was 20.51 ± 3.72. The linear regression model testing the Hill–Bone “reduced sodium intake” score against the TFI domains showed no relationships between the variables. Another regression model for the Hill–Bone “appointment-keeping” subscale indicated significant predictors for physical and social TFI domains (
p = 0.002 and
p < 0.0001, respectively). For the Hill–Bone “taking antihypertensive drugs” variable, the regression model found significant relationships with all TFI domains: physical (
p < 0.0001), psychological (
p = 0.003) and social (
p < 0.0001). Our study suggests that frailty in patients with arterial hypertension can negatively impact their adherence to therapeutic recommendations.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Coronary Artery Disease: More Questions Than Answers
by
Marijana Tadic, Carla Sala, Guido Grassi, Giuseppe Mancia, Stefano Taddei, Wolfgang Rottbauer and Cesare Cuspidi
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3314
Abstract
Studies show that patients with elevated triglycerides and well-controlled LDL levels under statin therapy still have a significant residual risk of cardiovascular (CV) events. Despite many attempts to reduce triglycerides with different hypolipidemic drugs, no therapeutic option has given satisfactory results so far.
[...] Read more.
Studies show that patients with elevated triglycerides and well-controlled LDL levels under statin therapy still have a significant residual risk of cardiovascular (CV) events. Despite many attempts to reduce triglycerides with different hypolipidemic drugs, no therapeutic option has given satisfactory results so far. The initial enthusiasm that omega-3 fatty acids can effectively reduce triglycerides and CV risk was replaced with skepticism when the first large clinical trials failed to show any benefit in primary or secondary prevention. However, the latest studies succeeded in showing a positive effect of omega-3 fatty acids on CV outcome in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. The largest benefit was reported in secondary but not primary prevention. Interestingly, the reduction in triglycerides in some of these studies was disproportionately low to the relatively high CV risk reduction, which could indicate some other effects of omega-3 fatty acids that go well beyond hypotriglyceridemic action. This includes blood pressure reduction, antithrombotic effect, improvement of inflammatory status, endothelial function, and insulin resistance. Investigations also reported a significant and positive influence of omega-3 fatty acids on the composition and stabilization of coronary atherosclerotic plaques in patients with and without previous CV events. In addition to insufficiently known mechanisms of action and conflicting results about the effectiveness of omega-3 fatty acids, the safety problems, which include increased prevalence of atrial fibrillation and hemorrhage, were also reported. The aim of this clinical review was to summarize the current knowledge regarding the use of omega-3 fatty acids in CV patients, particularly those with coronary artery disease, and to present an overview of key clinical trial data.
Full article
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.